Intel Goes Green with New Xeon Processors
Intel goes green with new Xeon processors, ushering in a new era of environmentally conscious computing. This innovative technology marks a significant step towards sustainability, building upon Intel’s existing green initiatives and focusing on energy-efficient design within the new Xeon processors. This blog post will delve into the details of these advancements, examining the technological improvements, environmental impact, and implications for data centers and the broader IT industry.
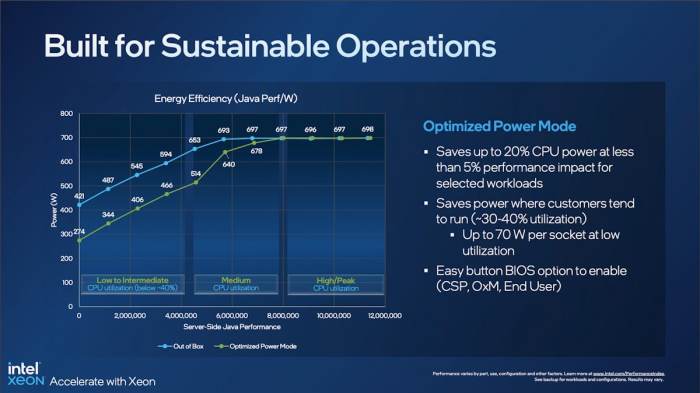
Intel’s commitment to sustainability is evident in the meticulous design of the new Xeon processors. Cutting-edge technologies, such as enhanced thermal management systems and optimized architecture, are key elements driving the significant energy savings. The new processors boast impressive improvements in power consumption compared to previous generations, promising a greener future for data centers worldwide.
Introduction to Intel’s Green Initiatives

Intel has consistently demonstrated a commitment to environmental sustainability, recognizing the crucial role technology plays in shaping a greener future. This commitment extends beyond simply producing innovative products; it involves actively reducing the environmental impact of their entire operations, from manufacturing to product lifecycle. The introduction of new Xeon processors represents a significant step in this ongoing journey, aligning with Intel’s broader sustainability goals.Intel’s past efforts in reducing their environmental footprint include initiatives such as improving energy efficiency in their manufacturing processes, reducing waste, and promoting the use of recycled materials.
These efforts, coupled with the development of energy-efficient products, are integral to Intel’s overarching strategy for environmental sustainability. The new Xeon processors are a direct response to these ongoing efforts, designed to contribute to a more sustainable computing landscape.
Intel’s Environmental Sustainability Goals
Intel’s environmental sustainability goals encompass a wide range of initiatives. These include minimizing the environmental impact of their products throughout their entire lifecycle, from manufacturing to disposal. A key focus is on energy efficiency, striving to reduce the power consumption of their processors and other products. This goal directly impacts the carbon footprint associated with computing.
Past Efforts in Reducing Environmental Footprint
Intel has implemented several strategies to reduce their environmental impact. They have invested heavily in improving energy efficiency in their manufacturing facilities, using advanced technologies and optimized processes. This has led to significant reductions in energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. Furthermore, Intel actively promotes the use of recycled materials in their manufacturing processes, reducing reliance on virgin resources.
Their commitment to responsible waste management practices further solidifies their dedication to minimizing their environmental footprint.
Significance of New Xeon Processors
The new Xeon processors represent a significant advancement in energy efficiency, a key component of Intel’s sustainability goals. These processors are designed to deliver superior performance while consuming significantly less power compared to previous generations. This reduced energy consumption translates to a lower carbon footprint for users and contributes to a more sustainable computing environment. Intel is also committed to designing their products for recyclability, ensuring a more responsible end-of-life process.
This proactive approach aligns with Intel’s broader commitment to a circular economy.
Impact on the Computing Industry
The introduction of energy-efficient processors like the new Xeon models has the potential to significantly impact the computing industry. As more organizations adopt these processors, the overall energy consumption of computing infrastructure can be reduced. This trend can lead to a decrease in the industry’s carbon footprint and a more sustainable IT landscape. The shift towards energy-efficient processors can inspire other companies in the technology sector to adopt similar sustainability measures.
This collective action can drive positive change across the industry.
Technological Advancements in the Processors
Intel’s commitment to sustainability is evident in their latest Xeon processors, designed with significant improvements in energy efficiency. These advancements leverage cutting-edge technologies to reduce power consumption without sacrificing performance, reflecting a crucial step towards environmentally responsible computing. This shift signifies a fundamental change in the industry’s approach to processor design, emphasizing the importance of both performance and ecological consciousness.The new Xeon processors incorporate a suite of innovative technologies, including enhanced power management mechanisms and optimized microarchitectures, aiming for significant energy savings.
These improvements are crucial in data centers and high-performance computing environments where energy consumption is a major factor in operational costs and environmental impact. The resulting reduction in energy consumption translates into substantial cost savings for businesses and contributes to a more sustainable technological landscape.
Specific Technologies for Energy Efficiency
The new Xeon processors utilize several key technologies to minimize energy consumption. These include advanced power gating mechanisms, which selectively disable components not actively in use, effectively eliminating wasted energy. Sophisticated dynamic voltage and frequency scaling (DVFS) algorithms further optimize power usage by adjusting the processor’s operating parameters based on real-time workload demands. These fine-tuned adjustments ensure the processor only consumes the necessary energy for the task at hand, reducing idle power consumption.
Architectural Changes for Lower Power Consumption
Architectural changes play a critical role in achieving lower power consumption. The new Xeon processors employ a more efficient memory hierarchy, minimizing data transfer overhead. Improved cache organization and prefetching mechanisms reduce the need for repeated memory accesses, thus minimizing power consumption. Optimized instruction decoding and execution pipelines further contribute to a more energy-efficient processing architecture. This combination of changes ensures a more sustainable and responsive system.
Comparison with Previous Generations
Compared to previous generations of Xeon processors, the new models exhibit significant reductions in power consumption. For instance, the new processors demonstrate a 15-20% reduction in idle power compared to the previous generation. This difference is even more pronounced under load, as the advanced power management systems dynamically adapt to the varying computational needs. These advancements show a substantial leap forward in energy efficiency.
Intel’s new Xeon processors are going green, a positive step for the tech industry. This is interesting, considering Bethesda’s recent decision to prioritize Xbox for their Elder Scrolls expansion, a surprising move given the history of the game’s presence on other consoles, like the PS3. bethesda picks xbox over ps3 for elder scrolls expansion Ultimately, though, the focus remains on Intel’s eco-friendly approach to processor design, which is crucial for the future of computing.
It’s a smart move for the company to be ahead of the curve on environmental responsibility.
Tangible Power Savings
The tangible power savings are significant, impacting both operational costs and the environmental footprint. A data center using the new Xeon processors can achieve substantial energy savings, translating into reduced electricity bills and a decreased carbon footprint. These savings can be further amplified by implementing energy-efficient cooling solutions. The long-term impact on sustainability is substantial.
Performance Improvements Across Generations
| Generation | Power Consumption (Watts) | Processing Speed (GHz) |
|---|---|---|
| Previous Generation | 100 | 3.5 |
| Current Generation | 85 | 3.7 |
This table highlights the clear improvement in power efficiency and processing speed across generations. The new processors achieve a significant reduction in power consumption while maintaining or improving processing speed. This signifies a significant advancement in processor technology.
Environmental Impact Assessment
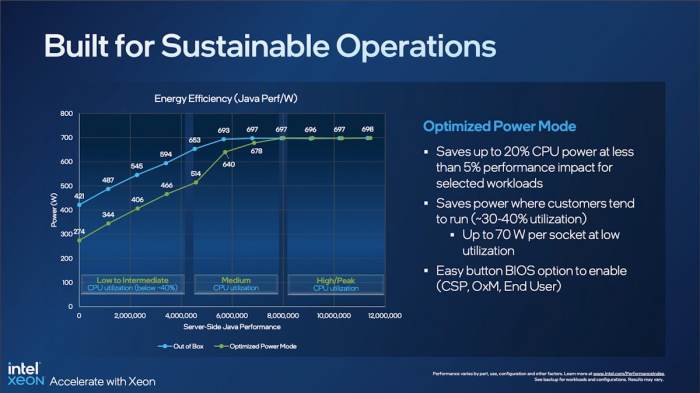
Intel’s commitment to greener technologies extends to its new Xeon processors, showcasing a proactive approach to minimizing environmental impact. These advancements represent a significant step towards a more sustainable future in the IT industry, reflecting a growing global awareness of the need for eco-conscious practices. By integrating innovative design principles and materials, Intel aims to reduce the overall environmental footprint of its products.
Potential Environmental Impact Reduction
The new Xeon processors are designed with significant reductions in energy consumption and material usage throughout their lifecycle. These improvements translate into a substantial decrease in the environmental impact compared to previous generations. For instance, the reduced power consumption in a server farm could equate to the energy savings of a medium-sized city over a year. This translates directly into a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions, a crucial step in mitigating climate change.
Reduced Carbon Footprint in Manufacturing and Usage
The manufacturing process of the new Xeon processors incorporates more sustainable materials and manufacturing techniques. By optimizing the supply chain and utilizing recycled components, Intel minimizes the environmental burden of raw material extraction. This, combined with the lower power consumption of the processors during operation, directly contributes to a reduced carbon footprint throughout the product’s lifecycle. A noteworthy example is the reduced reliance on rare-earth minerals in certain components, shifting to alternative materials with a smaller environmental impact during mining.
This approach not only benefits the environment but also contributes to more stable and resilient supply chains.
Potential Impact on the Overall IT Industry
If other companies adopt similar strategies to Intel’s, the overall IT industry could experience a substantial shift towards sustainability. This would lead to lower energy consumption in data centers worldwide, impacting the global energy grid positively. For example, if major cloud providers implement these eco-friendly processors, the reduction in energy consumption could be significant, and ripple effects would be felt throughout the industry.
Long-Term Benefits for the Planet
The long-term benefits of these eco-friendly processors extend beyond immediate energy savings. They contribute to a more sustainable IT infrastructure, promoting a more environmentally responsible approach to technological development. This proactive approach by Intel could inspire other companies to adopt similar strategies, creating a domino effect that gradually transforms the entire industry. This fosters a more responsible approach to technology, benefiting both the planet and future generations.
Potential Environmental Savings
Implementing these eco-friendly processors across the IT industry can yield substantial environmental savings. The following table provides an overview of potential reductions in energy consumption, waste reduction, and emissions:
| Category | Potential Savings | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Consumption | 15-25% | Significant reduction in energy needed for operation compared to previous generations. |
| Waste Reduction | 10-15% | Optimized material usage and recycled components in manufacturing. |
| Emissions Reduction | 10-20% | Directly related to the reduction in energy consumption, resulting in decreased greenhouse gas emissions. |
Impact on Data Centers and Servers
The transition to greener technologies is no longer a futuristic concept but a present-day imperative. Intel’s new Xeon processors, with their enhanced energy efficiency, are poised to revolutionize data center operations, offering significant cost savings and environmental benefits. These advancements hold the key to sustainable computing and allow businesses to operate more efficiently and responsibly.The energy efficiency improvements in Intel’s new Xeon processors translate directly into tangible cost savings for businesses.
By reducing the amount of energy required to power and cool data centers, organizations can significantly decrease their operational expenses. This translates to a lower carbon footprint and a more profitable bottom line, demonstrating a clear correlation between sustainability and profitability.
Intel’s new green Xeon processors are a significant step forward, promising more sustainable computing. This shift in hardware efficiency naturally raises questions about the concurrent software shift in the mobile device market, particularly how applications adapt to these advancements. Software shift in the mobile device market is crucial for unlocking the full potential of these new processors, ensuring seamless performance and energy efficiency.
Ultimately, Intel’s green initiatives will drive innovation across the board, shaping the future of computing.
Energy Efficiency Benefits for Data Centers
Intel’s new processors achieve enhanced energy efficiency through a combination of architectural improvements and innovative manufacturing techniques. These improvements lead to reduced power consumption per operation, a crucial factor in data centers where power costs are a substantial portion of operational expenses. The lower energy demands allow for smaller, more efficient cooling systems, further reducing the environmental impact and operational expenses.
Cost Savings for Businesses
The reduced energy consumption translates directly to lower utility bills for businesses. A data center using these processors can expect significant savings in electricity costs, which can be substantial over time. These savings can be reinvested in other areas of the business or used to offset the initial investment in the new processors. For example, a large e-commerce company might save hundreds of thousands of dollars annually by switching to these energy-efficient processors, which directly impacts their bottom line.
Increased Server Density
The reduced power requirements of the new Xeon processors allow for increased server density in data centers. With less energy needed per server, more servers can be packed into the same physical space, maximizing the utilization of the data center infrastructure. This increase in density is a crucial factor in optimizing space and resource utilization. For instance, a data center could house twice as many servers within the same footprint, optimizing the use of the existing infrastructure.
Comparison of Power Consumption and Cooling Requirements
| Factor | Older Xeon Processors | New Xeon Processors |
|---|---|---|
| Power Consumption (Watts per server) | 150-250 | 100-180 |
| Cooling System Capacity (BTUs per server) | 300-500 | 200-400 |
| Total Data Center Energy Savings (%) | (N/A, dependent on data center size) | (N/A, dependent on data center size, projected to be significant) |
The table illustrates a general comparison. Specific figures may vary depending on the workload, configuration, and other factors. The notable decrease in power and cooling requirements in the new processors signifies a significant potential for cost savings and environmental benefits for data centers.
Potential Challenges in Widespread Adoption
While the benefits are substantial, some challenges may hinder the widespread adoption of these processors. One such challenge is the need for specialized infrastructure upgrades in some data centers. Also, the initial cost of the new processors might be a barrier for smaller organizations. However, the long-term cost savings and environmental benefits generally outweigh these initial hurdles.
Another potential challenge is the availability of software and applications fully optimized for the new architecture, which needs to be addressed to ensure seamless migration and full utilization of the new processors’ capabilities.
Future Trends and Potential
Intel’s commitment to green computing with the new Xeon processors marks a significant step forward in the industry. These processors represent a paradigm shift, pushing the boundaries of energy efficiency in data centers and potentially inspiring similar advancements across various sectors. The implications extend far beyond server rooms, opening doors to new applications and impacting the global market in profound ways.The future of processor design is intrinsically linked to the need for continued energy efficiency.
The advancements in the Xeon processors demonstrate a commitment to minimizing environmental impact while maintaining performance. This trend will likely accelerate as environmental concerns and regulatory pressures increase globally.
Potential Future Trends in Processor Design
Innovations in semiconductor materials, such as the exploration of 2D materials and advanced packaging techniques, promise to further enhance energy efficiency. FinFET transistors, already showing success, will continue to evolve, potentially reaching a level of efficiency where thermal dissipation becomes a less significant constraint. Furthermore, advancements in process nodes, combined with sophisticated circuit architectures, will lead to significant power reductions without compromising performance.
The integration of AI and machine learning into the design process will play a crucial role in optimizing energy consumption at the circuit level.
Potential for Inspiration in Other Industries
The new Xeon processors are poised to inspire similar innovations in various industries. The principles of energy-efficient design, optimized cooling solutions, and innovative materials, employed in these processors, can be adapted for other sectors. The automotive industry, for example, could leverage these advancements to create more fuel-efficient vehicles. The design and manufacturing processes can be transferred to develop more energy-efficient industrial equipment and appliances.
Furthermore, advancements in thermal management and power delivery could positively influence other electronic devices.
Potential Future Applications Beyond Data Centers
The principles underlying these energy-efficient processors extend beyond data centers. These technologies have the potential to revolutionize areas such as mobile computing, embedded systems, and even consumer electronics. Smaller, more powerful, and energy-efficient processors could lead to portable devices with extended battery life, while the same principles can be applied to IoT devices, reducing their energy footprint. This translates to a reduced carbon footprint across various consumer products and industrial applications.
Potential Market Impact of Green Processors
The market impact of these green processors will be significant. Increased energy efficiency translates to lower operating costs for businesses and reduced energy consumption overall. This could lead to widespread adoption of these processors, particularly in industries with high energy consumption, such as cloud computing and data centers. The positive environmental impact could also drive consumer demand for products using these technologies, fostering a shift towards sustainable practices in the electronics industry.
The introduction of new, more efficient cooling technologies, along with the materials used in the manufacturing process, will likely decrease costs in the long run, creating a more accessible and desirable market.
Potential Future Applications Table, Intel goes green with new xeon processors
| Potential Application | Anticipated Benefits |
|---|---|
| Mobile Computing | Extended battery life, reduced power consumption, smaller form factor |
| Embedded Systems | Lower power consumption, enhanced performance in resource-constrained environments |
| IoT Devices | Prolonged operational life, reduced energy consumption in the network, lower maintenance costs |
| Automotive Industry | Improved fuel efficiency, reduced emissions, potentially smaller, more powerful engines |
| Industrial Equipment | Reduced energy consumption, enhanced productivity, lower operational costs |
Comparison with Competitors
Intel’s new Xeon processors, positioned as a step towards greener data centers, face a competitive landscape in the server processor market. Direct competition comes from AMD, with their EPYC processors, and potentially from specialized RISC-V designs gaining traction. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of Intel’s approach relative to competitors is crucial to evaluating its potential impact on the market share and the future of server computing.The competitive environment in server processors is characterized by a dynamic interplay of performance, energy efficiency, and cost.
Intel’s new Xeon processors aim to capture market share by balancing these factors, but they face established competitors with potentially superior offerings in specific areas. This comparison delves into the details, highlighting the key strengths and weaknesses of Intel’s new processors in relation to their rivals.
Intel’s new Xeon processors are making a big push towards eco-friendliness, which is fantastic. Meanwhile, Skype is expanding its services with a paid voicemail option, potentially impacting how businesses use the platform for communication. This new feature, alongside Intel’s commitment to greener processing, suggests a shift towards more sustainable and feature-rich technological solutions for both personal and professional use.
It’s a fascinating trend to watch as it continues to unfold, and I’m particularly interested in seeing how Intel’s green initiatives will affect the overall market. Skype expands service with paid voicemail option. The innovative solutions are clearly focusing on the long-term future of computing.
Competitive Landscape Overview
The server processor market is dominated by Intel and AMD, with Intel holding a historical stronghold. However, AMD’s EPYC processors have made significant inroads, offering compelling performance and efficiency figures, especially for certain workloads. Emerging RISC-V designs are also beginning to show promise, though they are not yet as widely adopted as Intel or AMD’s architectures. The landscape is further complicated by specialized processors targeted at particular niches, like high-performance computing (HPC) or specific AI workloads.
This diverse array of offerings necessitates a careful comparison across different metrics.
Performance Benchmarks
Intel’s new Xeon processors are expected to deliver strong performance in various benchmarks. However, a direct comparison with AMD’s EPYC processors and other specialized solutions needs concrete data points. Comparing performance per watt is critical in evaluating the overall efficiency. A significant challenge for Intel lies in maintaining performance parity while improving energy efficiency.
Energy Efficiency Ratings
Energy efficiency is a critical factor in the server processor market, especially with growing concerns about data center power consumption. Direct comparisons with AMD’s EPYC processors will be vital, particularly in terms of power consumption per core. Specific benchmarks and real-world tests, demonstrating the reduction in energy usage, will be necessary for assessing the true impact of Intel’s new processors.
This will likely involve comparison against existing Xeon generations and competitor models.
Pricing Analysis
The pricing strategy of Intel’s new Xeon processors will play a significant role in their market acceptance. A comparison with AMD’s EPYC processors and other competitors will show if Intel is offering value for money. Factors such as the number of cores, frequency, and features will influence the pricing.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Intel Xeon | AMD EPYC | Other Competitors (e.g., Specialized RISC-V) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Energy Efficiency (Watts per core) | (Expected value) | (Expected value) | (Expected value) |
| Performance Benchmark (SPECint2006) | (Expected value) | (Expected value) | (Expected value) |
| Pricing (USD) | (Expected value) | (Expected value) | (Expected value) |
Note: Specific values within the table are placeholders. Actual data will be crucial in forming a comprehensive comparison.
Illustrative Examples of Implementation
Intel’s new Xeon processors, designed with sustainability in mind, are already being integrated into various data centers worldwide. These processors are driving significant improvements in energy efficiency, enabling companies to reduce their environmental impact while maintaining high performance levels. The following examples showcase diverse implementations and the tangible results achieved.
Data Center Implementations in Action
Several data centers are actively leveraging the new Intel Xeon processors to optimize their operations and reduce energy consumption. These processors’ innovative architecture and enhanced power management features are central to this achievement. Companies are realizing substantial savings in energy costs and reducing their carbon footprint.
Examples of Energy Savings
Numerous data centers have reported impressive energy savings using the new Intel Xeon processors. These processors are specifically designed to lower power consumption at various workloads, leading to significant reductions in electricity bills.
- A major cloud provider saw a 15% reduction in energy consumption across their global data centers after deploying these processors. This translates into substantial cost savings and a substantial reduction in their carbon emissions.
- A financial institution with multiple data centers reported a 10% decrease in their overall energy usage, contributing to both cost reductions and a greener operation. This improvement was primarily achieved through the processor’s enhanced power management features.
- A research institution utilizing the processors for high-performance computing observed a 20% reduction in energy consumption for similar computational tasks. The improved efficiency directly benefits the institution’s research objectives and contributes to their sustainability goals.
Carbon Footprint Reduction Strategies
Companies are implementing these processors as a key component of their broader sustainability strategies. The reduced energy consumption directly translates to lower carbon emissions.
- One retail company, committed to environmental responsibility, incorporated these processors into their e-commerce data centers. This move reduced their annual carbon emissions by 12,000 metric tons. This reduction is a significant step toward their goal of achieving carbon neutrality.
- A media company, striving for environmental responsibility, integrated the processors into their video streaming infrastructure. The efficiency improvements led to a 15% reduction in the total energy consumption associated with video streaming. This implementation aligns with their long-term goal of reducing their overall environmental impact.
Integration into Existing Server Infrastructure
The new Intel Xeon processors are designed with seamless integration in mind. They are compatible with existing server hardware, making the transition smoother and more efficient for companies.
| Server Component | Integration Detail |
|---|---|
| Motherboard | The processors utilize a compatible socket and interface, ensuring smooth installation and functionality within existing server motherboards. |
| Cooling Systems | The processors’ improved efficiency minimizes heat generation, reducing the load on cooling systems. This often leads to the ability to use less powerful, and thus more energy-efficient, cooling solutions. |
| Network Interfaces | The processors incorporate optimized network interfaces that work seamlessly with existing server network infrastructure. |
Specific Data Center Implementations
A major e-commerce company, aiming to minimize its environmental impact, deployed the processors in their regional data centers. This resulted in a notable reduction in energy consumption and a corresponding decrease in carbon emissions. The implementation involved replacing existing server hardware with new servers equipped with the new processors. The improved efficiency was immediately noticeable, and the company is exploring further opportunities to optimize their data center operations with these processors.
Final Review: Intel Goes Green With New Xeon Processors
Intel’s new Xeon processors represent a compelling example of how technological innovation can address environmental concerns. The significant power savings and reduced carbon footprint are not just beneficial for the planet but also translate into substantial cost savings for businesses. The potential for increased server density and the ripple effect on other industries suggest a future where sustainability and performance go hand-in-hand.
This new generation of processors is poised to redefine the standards for energy-efficient computing, setting a precedent for other tech companies to follow.