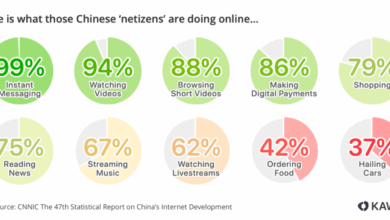
Teens & Social Media 55% Use
55 percent of us teens use social networking sites, a statistic that highlights the profound impact of these platforms on our youth. This article delves into the prevalence of social media use among teens, exploring its effects on development, academic performance, social interactions, body image, mental health, and privacy. We’ll examine the types of platforms preferred, compare usage trends across demographics, and analyze the positive and negative consequences of this digital integration in teenage life.
The research reveals a complex relationship between teens and social media, one that presents both opportunities and challenges. From fostering connections to potentially harming mental well-being, the impact is significant. We’ll unpack these findings, using data and analysis to offer a balanced perspective on this increasingly important aspect of teenage life.
Teen Social Media Usage Prevalence
The ubiquitous presence of social networking sites in the lives of teenagers is undeniable. Understanding the extent of this usage is crucial for comprehending the impact on their development and well-being. This exploration delves into the statistic of 55 percent of US teens using social networking sites, examining its context, historical trends, and comparative data from other regions.
Detailed Explanation of the Statistic
The statistic “55 percent of US teens use social networking sites” signifies a significant portion of American adolescents actively engaging with online platforms. This engagement encompasses a wide range of activities, from sharing personal updates and photos to interacting with friends and joining online communities. It highlights the pervasiveness of social media in contemporary teen life.
So, 55 percent of us teens are glued to social media. It’s a pretty significant number, right? That’s why developments like Ask Jeeves launching image search technology in Germany, as detailed in this article ask jeeves launches image search technology moves into germany , are fascinating. They show how technology is constantly evolving, which could, in turn, affect how we use social media.
And, of course, how teens, who are already so active on social media, react to this new innovation.
Historical Trends in Teen Social Media Use
Historical data suggests a gradual increase in teen social media use over the past two decades. Early adoption focused on platforms like MySpace and Facebook, which evolved into the more visually-driven and interactive platforms prevalent today, such as Instagram and TikTok. The proliferation of smartphones and faster internet speeds further accelerated this trend, making social media increasingly accessible and integrated into daily routines.
Comparison to Data from Other Countries or Demographics
Comparing this statistic with similar data from other countries is important for understanding global trends. While specific figures vary by nation, studies consistently show a high prevalence of social media use among teenagers globally. Factors like cultural norms, technological infrastructure, and socio-economic conditions influence these differences. Further research is needed to identify the specific factors driving these variations.
Methodology Used to Collect Data
The precise methodology for collecting data on teen social media usage varies depending on the source. Common methods include surveys, polls, and observational studies. These methods often involve sampling representative groups of teens to collect data on their social media habits. Accuracy is contingent upon the survey’s sample size and the representativeness of the sample population, as well as the honesty and accuracy of responses from participants.
Data on Social Media Use Across Different Age Groups
Unfortunately, precise age-based breakdowns of social media usage for US teens are not consistently available in publicly accessible data sources. Gathering such detailed information requires large-scale, longitudinal studies, which are often resource-intensive and not readily accessible. While broad trends can be observed, more specific age-group data remains a research area.
Impact on Teen Development
Social networking sites have become an undeniable part of the teenage experience, significantly impacting their development in ways both positive and negative. Understanding these effects is crucial for parents, educators, and teens themselves to navigate the digital landscape effectively. This exploration delves into the multifaceted influence of social media on adolescent growth.The pervasive nature of social media platforms often leads to a blurring of lines between online and offline interactions.
This constant connectivity, while providing opportunities for connection and information sharing, also presents challenges that can affect mental health and overall well-being. Teens are navigating a complex world, and social media plays a significant role in shaping their identities, relationships, and future trajectories.
Potential Positive Effects of Social Networking Sites
Social media platforms can offer opportunities for social connection and support, particularly for teens who may face isolation or challenges in their immediate surroundings. Online communities can provide a sense of belonging and support, fostering a sense of shared identity among like-minded individuals. This can be particularly helpful for teens who may be navigating difficult circumstances or facing unique challenges, such as those with specific interests or marginalized identities.
Whoa, 55 percent of us teens are on social media! It’s wild how much our lives revolve around these platforms. Meanwhile, the MPAA’s crackdown on peer-to-peer networks, like their lawsuits and arrests against various file-sharing services here , highlights the complex relationship between technology and societal norms. Still, 55 percent of us teens use social networking sites, a massive part of our digital lives, showing how intertwined our online and offline worlds have become.
Moreover, social media platforms can be used as a tool for education and learning. Access to diverse perspectives and information can broaden teens’ understanding of the world.
Potential Negative Effects of Social Networking Sites
The constant exposure to curated, often idealized, representations of others’ lives can lead to feelings of inadequacy and low self-esteem. The pressure to maintain an online persona can negatively impact self-image and contribute to anxiety and depression. Cyberbullying and online harassment are significant concerns, impacting teens’ mental health and emotional well-being. Excessive social media use can lead to decreased face-to-face interaction, potentially hindering the development of crucial social skills.
Impact on Mental Health and Well-being
The correlation between social media use and mental health issues is a complex area of study. Studies have shown a potential link between excessive social media use and increased rates of anxiety, depression, and body image issues among adolescents. The constant pressure to present a perfect online persona and the fear of missing out (FOMO) can significantly affect a teen’s emotional well-being.
Mental health professionals often highlight the need for mindful social media use and balanced digital interactions to maintain good mental health.
Factors Contributing to Differing Experiences with Social Media
Teen experiences with social media are diverse, influenced by a range of factors. These factors include socioeconomic status, access to technology, cultural background, personality traits, and individual coping mechanisms. Teens from different socioeconomic backgrounds may have unequal access to reliable internet connections or devices, potentially creating disparities in their online experiences. Furthermore, individual coping mechanisms and personality traits can significantly impact how teens respond to the pressures and challenges of social media use.
For instance, individuals with higher levels of self-esteem may be less susceptible to negative impacts.
Pros and Cons of Social Media Use for Teens
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Enhanced social connections, support systems, and access to information | Cyberbullying, online harassment, pressure to present a perfect image, and FOMO |
| Opportunities for learning and education through diverse perspectives | Negative impact on self-esteem and body image, potential for decreased face-to-face interaction and social skills development |
| Increased access to diverse communities and support networks | Addiction, decreased sleep, and mental health issues |
| Platforms for expressing creativity and connecting with like-minded individuals | Potential for comparison and unrealistic expectations, and mental health problems |
Types and Platforms of Social Networking Sites: 55 Percent Of Us Teens Use Social Networking Sites
Social media has become an undeniable part of teenage life, profoundly impacting their communication, social interactions, and development. Understanding the diverse landscape of social networking sites teens use is crucial for comprehending their online experiences and potential effects. Different platforms cater to various interests and needs, creating a complex interplay of influence and engagement.The plethora of social networking sites available today offers teens a vast array of options, ranging from general-purpose platforms to niche communities focused on specific interests.
So, 55 percent of us teens are hooked on social networking sites, which is a pretty big deal. It’s interesting to consider how that compares to the recent wave of new bagel variants rolling in – like, seriously, new bagel variants roll in waves of innovation! Still, I think the social media engagement among teens is definitely a major factor in how we connect and communicate nowadays.
Choosing a platform often reflects a teen’s social circles, personal preferences, and even cultural influences. This exploration will delve into the characteristics of popular platforms, highlighting their unique features and functionalities. It will also address how platform choices may differ across demographics.
Popular Social Networking Sites Used by Teens
Teens engage with a wide spectrum of social media platforms. Understanding these platforms and their characteristics provides valuable insights into the digital environment teens inhabit. These platforms offer varying degrees of functionality, impacting how teens interact and form relationships online.
- Facebook: A widely used platform for connecting with friends and family, sharing updates, and participating in groups. Its robust features include messaging, event creation, and detailed profile customization, offering a comprehensive social networking experience. The platform has been around for a while, allowing users to build extensive networks.
- Instagram: Known for its visual focus, Instagram emphasizes photos and videos. This platform facilitates sharing personal moments, exploring visual trends, and connecting with influencers. Its popularity among teens stems from its visual appeal and capacity for self-expression.
- TikTok: A platform predominantly based on short-form video content, TikTok has gained immense popularity among teens for its creative expression and entertainment value. Users create and share videos, often incorporating trending sounds and challenges, fostering a sense of community through shared content.
- X (formerly Twitter): A platform centered on microblogging and real-time updates. Users share short messages, engage in conversations, and follow news and personalities. X offers a fast-paced environment for information sharing and direct interaction with public figures.
- YouTube: A platform primarily for sharing video content, ranging from educational materials to entertainment and music. Its accessibility and vast library of content cater to diverse interests, allowing teens to discover new channels and creators.
- Snapchat: This platform is characterized by its ephemeral messaging and visual storytelling. Users share photos and videos that disappear after a set time, creating a sense of immediacy and intimacy. Its unique features cater to teens’ desire for spontaneous interaction.
Comparison of Social Media Features and Functionalities
Different platforms offer varying sets of features, impacting user experience and engagement.
| Platform | Primary Feature | Functionality | User Interaction |
|---|---|---|---|
| Connecting with friends and family | Messaging, groups, events, detailed profiles | Building extensive networks, sharing updates | |
| Visual sharing | Photo/video sharing, stories, reels | Visual expression, exploring trends, connecting with influencers | |
| TikTok | Short-form video | Video creation, trending sounds, challenges | Creative expression, community engagement |
| X | Microblogging | Short messages, conversations, following | Real-time updates, engaging with personalities |
| YouTube | Video content | Educational, entertainment, music | Discovering creators, exploring diverse content |
| Snapchat | Ephemeral messaging | Photos/videos disappearing after time | Spontaneous interaction, visual storytelling |
Platform Variations Across Demographics
Platform preferences can vary based on age, interests, and cultural background. Factors like language, local trends, and peer influences can significantly affect platform choices. For instance, younger teens might gravitate towards platforms emphasizing short-form content, while older teens might prefer platforms offering more nuanced interactions. Cultural context also plays a role in platform popularity. These factors shape the digital landscape for teens and impact how they navigate and interact within it.
Social Media Use and Academic Performance
Navigating the digital age, teenagers are deeply intertwined with social media. This constant connectivity, while offering opportunities for connection and information, presents a complex relationship with academic performance. Understanding this interplay is crucial for educators and parents alike to support teenagers in balancing their online and offline lives effectively.
The potential correlation between social media use and academic performance is multifaceted and not straightforward. While some teens might find social media platforms beneficial for research or collaboration, others might experience distractions that negatively impact their studies. The key lies in understanding the nuances of this relationship, including the various factors that mediate this connection, and the specific ways social media use impacts different academic tasks.
Potential Correlation and Methods of Study
Numerous studies have investigated the correlation between social media use and academic performance. These studies often use quantitative methods, like surveys and statistical analysis, to explore the relationship between the time spent on social media and grades, or the perceived impact of social media on study habits. Researchers also utilize qualitative methods, such as interviews and focus groups, to understand the subjective experiences of teenagers regarding their social media use and its impact on their academic journey.
These varied approaches provide a more comprehensive understanding of the complexities of the relationship.
Potential Mediating Factors
Several mediating factors can influence the relationship between social media use and academic performance. These factors include the individual’s personality traits, their learning style, and the specific social media platforms they use. For example, a teenager who is easily distracted might struggle to maintain focus on their studies when frequently bombarded with notifications and updates. Alternatively, a teenager who uses social media to connect with peers for study groups may experience a positive impact on their academic performance.
Examples of Positive and Negative Impacts
Social media use can have both positive and negative impacts on academic tasks. Positive examples include using social media platforms to find study resources, collaborate with peers on projects, or access educational content. Negative impacts can include procrastination, reduced focus, and time spent on non-academic activities.
Potential Effects on Grades and Academic Success
| Aspect | Positive Effects | Negative Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Time Management | Utilizing social media for study groups and collaborative projects can improve time management skills. | Excessive social media use can lead to poor time management, neglecting academic tasks. |
| Information Access | Social media platforms can be a valuable source of information for research and academic projects. | Misinformation and unreliable sources on social media can hinder academic accuracy and research integrity. |
| Collaboration | Social media platforms can facilitate communication and collaboration among students for study sessions or project work. | Social media interactions can lead to distractions, reducing focus on academic work. |
| Motivation | Social media can motivate some students to achieve academic goals through peer support or online challenges. | Social media comparisons can lead to feelings of inadequacy and low self-esteem, impacting motivation for academic tasks. |
| Stress | In some cases, social media can be a source of relaxation and stress relief for students. | Excessive use can lead to stress and anxiety related to social comparisons or cyberbullying. |
Social Media and Social Interactions
Social media platforms have become an undeniable part of teenage life, significantly impacting how teens interact and build relationships. While offering opportunities for connection and communication, these platforms also present unique challenges and potential pitfalls. Navigating this digital landscape requires understanding both the positive and negative influences on social interactions.Social networking sites can act as a powerful tool for fostering social interactions, connecting teens with peers across geographical boundaries, and facilitating the formation of online communities based on shared interests.
However, the nature of online interactions differs significantly from face-to-face interactions, potentially leading to misunderstandings and misinterpretations. This difference, along with the potential for cyberbullying, demands careful consideration and responsible use.
Facilitating Social Interactions
Social media platforms provide a space for teens to connect with friends, family, and individuals with similar interests. Instant messaging, group chats, and social media posts allow for constant communication, strengthening existing bonds and building new ones. Sharing experiences, thoughts, and feelings online can foster a sense of belonging and support among peers. This is particularly important for teens who may face social challenges in their offline lives or those who live in remote areas.
Differences in Online and Offline Interactions
Online interactions often differ significantly from in-person interactions. Tone and intent can be easily misinterpreted in text-based communication. Emojis and other digital cues may not fully convey the nuances of in-person communication, leading to misunderstandings. The lack of nonverbal cues, such as facial expressions and body language, can hinder the development of empathy and emotional intelligence.
Impact on Social Skills and Relationships
Social media can impact the development of social skills in various ways. Over-reliance on online communication can sometimes hinder the development of crucial in-person communication skills, like active listening and nonverbal cues. However, participation in online discussions and interactions can encourage self-expression and confidence. The quality of relationships formed online can vary, ranging from superficial connections to deep and meaningful bonds.
Cyberbullying and Harassment
The anonymity and reach of social media platforms create a fertile ground for cyberbullying and harassment. Teens may face hurtful comments, threats, or exclusion from online groups, which can significantly impact their mental health and well-being. The permanence of online content can also cause lasting damage, as posts and messages can be shared and re-shared, potentially causing significant harm to the victim.
Table of Online and Offline Social Interactions
| Interaction Type | Online Description | Offline Description |
|---|---|---|
| Friendship Formation | Discovering shared interests through online groups, commenting on posts, and engaging in online conversations. | Developing friendships through shared experiences, activities, and face-to-face interactions. |
| Communication | Sending messages, sharing photos, and engaging in online discussions. | Talking in person, using body language and facial expressions to convey meaning. |
| Social Events | Planning events and coordinating through social media platforms. | Organizing gatherings and activities in person. |
| Conflict Resolution | Attempting to resolve conflicts through online discussions and messages. | Addressing conflicts directly and constructively in person. |
Social Media and Body Image
Social media has become an undeniable part of teenage life, offering connections and opportunities for self-expression. However, this digital landscape can also exert a powerful influence on how teens perceive their bodies. The curated and often idealized portrayals of beauty prevalent online can have a significant impact on developing self-esteem and body image. This exploration dives into the complexities of this relationship, examining the potential pitfalls and highlighting constructive strategies.The constant exposure to filtered images and meticulously crafted online personas can create a distorted view of reality.
Teens, particularly vulnerable during their developmental years, may compare themselves to these unrealistic standards, leading to feelings of inadequacy and low self-worth. This comparison isn’t just theoretical; it’s a tangible experience for many. The pressure to conform to a specific aesthetic can manifest in various ways, from unhealthy dieting practices to body dissatisfaction.
Unrealistic Beauty Standards and Their Impact
The beauty standards often presented on social media are frequently unrealistic and unattainable. These standards, often idealized and heavily edited, can negatively influence teens’ self-perception. They may feel pressured to conform to specific body types, skin tones, or appearances that are not representative of the diversity of the human population. This can lead to feelings of inadequacy and anxiety, impacting their mental and emotional well-being.
For instance, the prevalence of highly edited photos and videos on platforms like Instagram and TikTok can lead to unrealistic expectations about what constitutes an acceptable body image.
Factors Contributing to Teen Body Image Perception Online
Several factors contribute to a teen’s perception of their body image online. The constant exposure to filtered and edited images creates a sense of comparison and often leads to dissatisfaction with their own appearance. Social validation from online interactions plays a role, with teens often seeking approval and validation from their peers on social media platforms. The pressure to maintain a perfect online persona can also influence body image perceptions.
This includes the fear of judgment and criticism from online communities.
Promoting Positive Body Image Messages on Social Media
Social media can be a powerful tool for promoting positive body image messages. Platforms can be used to showcase diverse body types and appearances, challenging the narrow definition of beauty often presented. Creating content that celebrates individuality and self-acceptance can encourage teens to embrace their unique qualities and appreciate their bodies. This involves encouraging genuine self-expression and reducing the emphasis on superficial standards.
Sharing personal stories and experiences related to body image can foster empathy and understanding within online communities.
Table: Factors Contributing to Body Image Issues for Teens, 55 percent of us teens use social networking sites
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Exposure to Filtered Images | Constant exposure to digitally altered images can lead to unrealistic expectations and dissatisfaction with one’s own appearance. |
| Social Validation Seeking | Teens often seek approval and validation from peers online, potentially leading to feelings of inadequacy when they do not meet perceived standards. |
| Pressure to Maintain a Perfect Persona | The need to present a flawless image online can cause stress and anxiety, impacting body image perception. |
| Comparison with Others | Comparing oneself to others online, especially when those comparisons are based on curated and idealized images, can negatively impact self-esteem and body image. |
Social Media and Mental Health

Navigating the digital world can be a double-edged sword for teens. While social media offers opportunities for connection and community, it also presents unique challenges to mental well-being. Understanding the potential links between social media use and mental health conditions, along with effective coping strategies, is crucial for supporting teens in this digital age.Social media platforms have become increasingly intertwined with adolescent lives, influencing self-perception, social interactions, and overall mental health.
The constant exposure to curated online personas, often highlighting idealized versions of reality, can lead to social comparison and feelings of inadequacy. Moreover, cyberbullying and online harassment can have devastating effects on a teen’s emotional well-being. Recognizing these potential pitfalls and equipping teens with the tools to navigate them is vital.
Potential Links Between Social Media Use and Mental Health Conditions
Teens experiencing increased social media use often report higher rates of anxiety and depression. This correlation may stem from several factors, including the pressure to maintain an online persona, constant exposure to potentially unrealistic standards of beauty and success, and the potential for cyberbullying. Research consistently demonstrates a relationship between heavy social media use and negative mental health outcomes.
It’s crucial to understand that this isn’t a definitive cause-and-effect relationship, but rather a complex interplay of factors.
Social Comparison and its Effects
Social comparison, the process of evaluating oneself in relation to others, is amplified on social media. Teens often compare their lives, achievements, and appearances to the seemingly perfect lives presented by others online. This can lead to feelings of inadequacy, low self-esteem, and anxiety. The curated nature of online profiles, often highlighting only the positive aspects of life, can create a distorted view of reality, making it challenging for teens to maintain a healthy sense of self-worth.
Cyberbullying and its Impact
Cyberbullying, the use of electronic communication to bully or harass another person, can have a profound and lasting negative impact on a teen’s mental health. The anonymity and reach of online platforms can exacerbate the emotional distress caused by such interactions. Victims of cyberbullying may experience feelings of isolation, fear, depression, and even suicidal ideation. It’s essential to recognize the pervasive nature of cyberbullying and provide teens with resources and support to address these issues.
Coping Strategies for Negative Online Experiences
Developing healthy coping mechanisms is crucial for teens navigating negative online experiences. These strategies can include setting limits on social media use, disconnecting from the internet when overwhelmed, and seeking support from trusted adults or peers. Recognizing that online interactions aren’t always reflective of reality is vital for maintaining a healthy perspective. It’s also important to teach teens how to identify and challenge negative thoughts and feelings that may arise from online interactions.
Positive Online Communities for Teens
Positive online communities can provide teens with valuable support and connection. These communities can foster a sense of belonging, encourage positive self-expression, and provide opportunities for learning and growth. Examples of positive online spaces include supportive forums for specific interests, online clubs focusing on shared hobbies, and social media groups centered around positive messages. Engaging in these communities can counteract the negative influences of social media.
Positive and Negative Influences of Social Media on Teen Mental Health
| Positive Influences | Negative Influences |
|---|---|
| Connection with peers and like-minded individuals | Social comparison leading to low self-esteem |
| Access to information and resources | Cyberbullying and harassment |
| Opportunities for self-expression and creativity | Pressure to maintain an idealized online persona |
| Support networks for shared interests | Distorted view of reality and unrealistic expectations |
| Increased awareness of social issues | Increased anxiety and depression |
Social Media and Privacy
Social media has become an integral part of teenage life, connecting them with friends, family, and the wider world. However, this interconnectedness comes with a crucial consideration: online privacy and security. Understanding the risks and implementing protective measures is essential for teens to navigate the digital landscape safely and responsibly.Protecting your personal information online is paramount for a safe and positive digital experience.
Sharing sensitive details without considering the potential consequences can expose you to various risks, including identity theft, harassment, and cyberbullying. Understanding these risks is the first step towards safeguarding your privacy.
Importance of Online Privacy and Security for Teens
Protecting personal information online is crucial for teens to avoid potential risks. Online safety isn’t just about avoiding trouble; it’s about fostering a positive and secure online experience. A strong understanding of privacy and security practices allows teens to fully participate in the digital world while minimizing vulnerabilities.
Potential Risks of Sharing Personal Information Online
Sharing personal information online can lead to various risks. The consequences of carelessly sharing details can range from minor inconveniences to serious security breaches. Knowing the potential pitfalls is essential for developing responsible online habits. For instance, posting precise locations or sharing sensitive details like financial information can attract unwanted attention and potential threats. Specific risks include identity theft, cyberbullying, harassment, and even physical harm in extreme cases.
Scams and phishing attempts are also prevalent online and can lead to financial loss. The risks are not limited to malicious actors; even well-intentioned actions can lead to privacy issues if the information is shared without considering its potential impact.
Strategies for Protecting Online Privacy
Protecting online privacy involves a multifaceted approach. This includes understanding privacy settings, being mindful of what you share, and practicing responsible online behavior. One crucial strategy is to review and adjust privacy settings on social media platforms regularly. This involves limiting the visibility of your posts, controlling who can see your profile, and ensuring that sensitive information is not easily accessible to the public.
Using strong passwords, enabling two-factor authentication, and being cautious about suspicious links are additional crucial steps in safeguarding your online presence.
How Teens Can Use Social Media Safely and Responsibly
Using social media safely and responsibly is about cultivating good digital citizenship. Teens should be mindful of the information they share and the interactions they have online. This involves critical thinking, awareness of potential risks, and the application of safe practices. Respecting others’ boundaries and avoiding harmful content are crucial elements of responsible social media use.
Table of Privacy Settings and Security Tips for Teens
| Social Media Platform | Privacy Settings | Security Tips |
|---|---|---|
| Adjust privacy settings for posts, friends, and profile information. Use Facebook’s privacy check tools. | Use strong passwords, enable two-factor authentication, be cautious about friend requests. | |
| Control who can see your posts, stories, and profile. Review privacy settings for direct messages. | Use strong passwords, enable two-factor authentication, be cautious about friend requests. | |
| TikTok | Adjust privacy settings for videos, comments, and profile information. Limit access to certain content. | Use strong passwords, enable two-factor authentication, be cautious about suspicious links. |
| Snapchat | Control who can view your stories and messages. Review privacy settings for direct messages. | Use strong passwords, enable two-factor authentication, be cautious about friend requests. |
Ultimate Conclusion
In conclusion, the pervasive use of social networking sites by teens – 55% – underscores the need for a comprehensive understanding of its multifaceted influence. While offering avenues for connection and self-expression, it also presents potential risks to mental health, body image, and academic performance. Navigating this digital landscape requires a thoughtful approach that fosters responsible use, emphasizes critical thinking, and equips teens with the tools to thrive in the digital age.