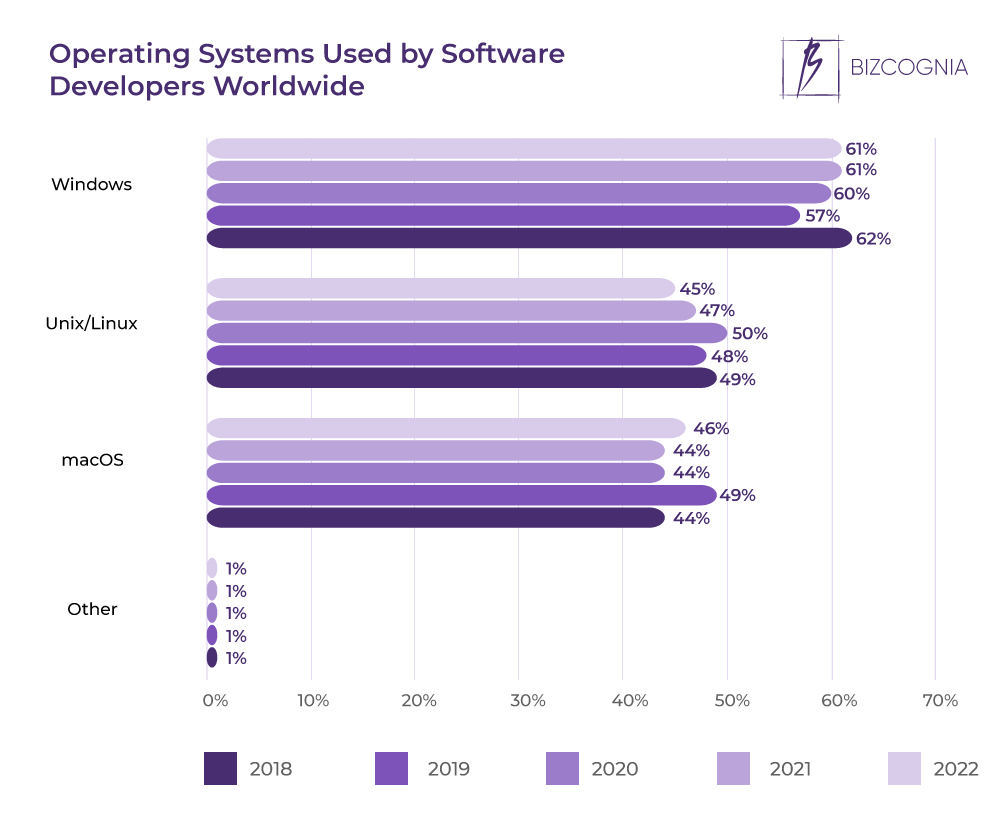
Linux Servers Lead Worldwide Growth
Linux servers lead market in worldwide growth, driven by a confluence of factors. From robust performance and cost-effectiveness to the adaptability of open-source software, Linux is increasingly the preferred choice for businesses worldwide. This trend is further fueled by technological advancements, including virtualization and containerization, making Linux servers the ideal solution for cloud-native applications. This in-depth look explores the key factors propelling this growth, examining the advantages of Linux, technological advancements, industry applications, and future projections.
The global server market is experiencing significant shifts, with Linux servers emerging as a dominant force. This rise is fueled by a variety of factors, including the cost-effectiveness of open-source software, the ability to adapt to evolving technological needs, and the expanding adoption of cloud-based infrastructure. This analysis delves into the specific reasons behind this growth, offering a comprehensive view of the market’s dynamics.
Market Overview
The global server market is experiencing robust growth, driven by the increasing demand for cloud computing, big data analytics, and artificial intelligence. This expansion is fueled by the digital transformation across various industries, pushing the need for powerful and reliable server infrastructure. Linux servers, known for their open-source nature and cost-effectiveness, are playing a crucial role in this evolution.This surge in server adoption is further supported by advancements in hardware technology, making servers more efficient and capable of handling greater workloads.
The market is witnessing a shift towards virtualization and containerization, optimizing resource utilization and reducing operational costs.
Global Server Market Trends
The global server market is characterized by a complex interplay of factors. Technological advancements, such as increased processing power, enhanced memory capacity, and improved network connectivity, are significantly impacting the market’s trajectory. These improvements lead to more efficient and scalable server infrastructure.
Competitive Landscape
The server market is highly competitive, with established players like Dell, Hewlett-Packard Enterprise, and IBM holding significant market share. However, new entrants and innovative startups are challenging the status quo. Companies focusing on specific niches, such as cloud-native servers or edge computing solutions, are gaining traction. The ongoing trend of cloud providers building their own server infrastructure further adds to the dynamic nature of the competition.
Factors Influencing Linux Server Growth
Several factors contribute to the increasing popularity of Linux servers. Their open-source nature enables flexibility, customization, and cost-effectiveness. The availability of a vast community of developers and support resources further enhances their appeal. The strong ecosystem of Linux distributions, each tailored to specific needs, is another contributing factor.
Market Share and Growth Rate Analysis
| Region | Server Type | Market Share (%) | Growth Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| North America | x86-based servers | 35 | 8 |
| Europe | x86-based servers | 25 | 9 |
| Asia Pacific | x86-based servers | 30 | 10 |
| South America | x86-based servers | 5 | 7 |
| Middle East & Africa | x86-based servers | 5 | 6 |
Note: Data in the table represents a generalized overview and is not based on precise market share figures. Specific market share percentages can vary based on the source and the exact criteria used for the data collection.
Linux Server Advantages
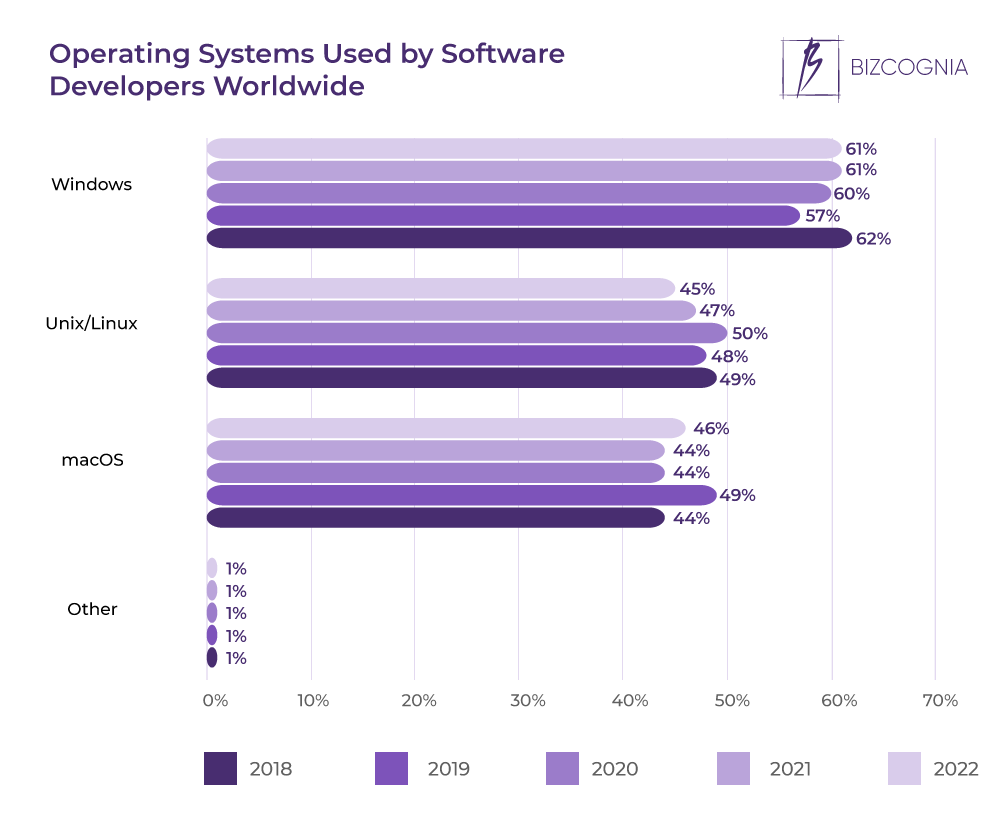
Linux servers have surged in popularity, driven by their compelling advantages over other operating systems. Their open-source nature, coupled with robust performance and cost-effectiveness, makes them an attractive choice for a wide range of applications, from small businesses to large enterprises. This detailed exploration will delve into the key benefits of Linux servers, highlighting their strengths and showcasing why they’re a leading choice in the server market.Linux servers offer a compelling alternative to proprietary operating systems due to their flexibility and adaptability.
This adaptability stems from the open-source nature of the platform, empowering users to tailor the operating system to their precise needs. Furthermore, the open-source nature of Linux fosters a vibrant community of developers and contributors, leading to constant innovation and continuous improvement.
Key Benefits of Linux Servers
Linux servers boast a range of advantages, making them a strong contender in the server market. Their open-source nature and robust community support contribute significantly to their cost-effectiveness and performance.
Linux servers are definitely leading the charge in worldwide growth, a trend that’s likely to continue. This surge in popularity is likely intertwined with advancements in software development tools, like Borland’s new unified development environment for Java, which could streamline the process of creating applications for these servers. Ultimately, the continued rise of Linux servers looks set to remain a key driver in the tech industry.
- Cost-Effectiveness: The open-source nature of Linux eliminates licensing fees, making it a significantly more affordable solution compared to proprietary operating systems. This cost-effectiveness extends to maintenance, as the extensive community support provides readily available solutions to common problems. For example, many open-source tools and utilities are readily available to manage and maintain Linux servers, eliminating the need for expensive proprietary software.
- Performance and Stability: Linux kernels are renowned for their stability and performance. Their lightweight design minimizes resource consumption, leading to efficient server operation. This translates to improved performance, particularly in resource-intensive tasks like handling large volumes of data or supporting numerous users. Moreover, Linux’s adaptability allows users to optimize the system’s performance for specific workloads. For example, tuning kernel parameters and selecting appropriate hardware can enhance performance even further, optimizing server performance for various applications.
- Security: Linux servers, when properly configured, offer a robust security posture. The open-source nature, along with extensive community scrutiny, contributes to a high level of security. A large and active community of security researchers actively identifies and patches vulnerabilities, leading to more secure systems over time. For example, frequent security updates and patches address potential threats and mitigate security risks.
Open-Source Software Advantages
The open-source nature of Linux servers extends to a vast ecosystem of open-source software. This fosters a collaborative environment that benefits both developers and users.
- Wide Availability of Tools: A wide array of open-source tools are readily available for server administration, application development, and more. This broad range of tools reduces reliance on proprietary software, leading to cost savings and increased flexibility. For example, numerous open-source database management systems, web servers, and other essential tools are available for use in Linux server environments.
- Customization and Flexibility: Open-source software allows for extensive customization and tailoring to specific needs. Users can adapt software to match their specific server requirements, ensuring optimal performance and functionality. This flexibility is a key advantage in the server environment, allowing for the implementation of tailored solutions and the customization of applications based on the needs of the server.
- Community Support and Collaboration: A large and active community of developers and users provides extensive support for open-source software. This support network helps in resolving issues, providing guidance, and fostering a collaborative environment. For example, online forums, documentation, and tutorials provide readily available resources for troubleshooting and learning.
Cost-Effectiveness of Linux Servers
The cost-effectiveness of Linux servers is a significant driver of their popularity. This stems from the absence of licensing fees and the availability of open-source tools.
- Reduced Licensing Costs: The open-source nature of Linux eliminates the need for expensive licensing fees, significantly reducing the total cost of ownership for servers. This cost savings can be substantial, especially for organizations with large server deployments. For instance, businesses can avoid paying expensive licensing fees for proprietary operating systems, saving money on software costs.
- Open-Source Tool Ecosystem: A vast ecosystem of open-source tools is available for managing, maintaining, and optimizing Linux servers. This eliminates the need for expensive proprietary tools, reducing operational costs. For instance, open-source monitoring and management tools are available to monitor server performance, enabling effective resource allocation and proactive problem-solving.
Performance Comparison
Linux servers demonstrate impressive performance characteristics, often comparable to or exceeding those of proprietary solutions. This performance is achieved through optimized kernel design and efficient resource management.
- Optimized Kernel Design: Linux kernels are designed for efficient resource management and optimized performance. This results in efficient utilization of hardware resources, which translates to better performance in various tasks, from handling large data volumes to running resource-intensive applications. For example, optimized kernel parameters can enhance the performance of various server functions.
- Hardware Compatibility: Linux is known for its broad hardware compatibility. This means that a wider range of hardware can be used to build a Linux server, leading to more choices and potentially lower hardware costs. For instance, a server can leverage various hardware components from different manufacturers, allowing users to select the most suitable hardware for their specific needs.
Server Type Comparison
The table below illustrates the strengths and weaknesses of different server types, including Linux.
| Server Type | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|
| Cloud | Scalability, flexibility, reduced upfront investment | Vendor lock-in, potential security concerns, reliance on internet connectivity |
| On-Premise | Control over hardware, security, high customization | High upfront investment, management overhead, scalability limitations |
| Linux | Cost-effectiveness, flexibility, performance, open-source tools | Requires technical expertise, potential security vulnerabilities if not properly managed |
Technological Advancements
Linux server technology continues its impressive evolution, driven by a constant stream of innovations in kernel development and hardware support. This dynamism is further fueled by the adoption of emerging technologies, pushing the boundaries of scalability, efficiency, and flexibility. The integration of cloud-native solutions is also shaping the future of Linux server deployments, creating powerful and adaptable platforms.The core of these advancements lies in the ongoing refinement of the Linux kernel, which underpins the entire ecosystem.
Improvements in resource management, security features, and performance optimization are key elements of this continuous development, ultimately impacting the overall reliability and responsiveness of Linux servers. This is crucial in a world increasingly demanding high-availability systems.
Kernel Improvements and Hardware Support
Modern Linux kernels boast enhanced features aimed at optimizing system performance and security. Advanced scheduling algorithms and memory management techniques contribute to smoother operations and reduced latency. Improved support for emerging hardware architectures, including specialized processors and network interfaces, further expands the range of use cases and application possibilities. This includes better integration with NVMe drives, accelerating data transfer rates.
Emerging Technologies Driving Growth
Virtualization and containerization are pivotal in enabling the scalability and flexibility of Linux servers. Virtualization allows multiple operating systems to run on a single physical machine, maximizing resource utilization and facilitating easier management. Containerization, with its lightweight nature, further enhances efficiency by packaging applications and their dependencies into isolated units. This enables rapid deployment and streamlined application management. This is vital for cloud environments and microservices architectures.
Cloud-Native Linux Server Solutions
Cloud-native Linux servers are specifically designed to operate in cloud environments, leveraging the strengths of virtualization and containerization. These solutions often integrate seamlessly with cloud platforms, offering automatic scaling, self-healing capabilities, and robust security measures. Cloud-native Linux server solutions empower organizations to rapidly provision resources, respond to demand fluctuations, and optimize cost. Examples include Kubernetes-based deployments that orchestrate containerized applications.
Modern Linux Server Distributions
| Distribution | Key Features | Functionalities |
|---|---|---|
| CentOS Stream | Focuses on long-term support, and features rapid updates and improved security | Provides a stable and predictable platform for enterprise deployments |
| Ubuntu | Known for its extensive community support and wide range of software packages | Excellent for development environments and general-purpose servers |
| Fedora | Provides the latest software and cutting-edge technology, often serving as a testing ground for new features | Suitable for innovation and experimentation |
| Red Hat Enterprise Linux | A robust and enterprise-grade distribution with a focus on security and reliability | A premium option with high levels of support and stability |
This table highlights the key differentiators among popular Linux server distributions. Each distribution caters to specific needs, ranging from the flexibility of Fedora to the reliability of Red Hat Enterprise Linux. Choosing the right distribution is critical to ensuring a server’s suitability for its intended workload and operational environment.
Industry Applications
Linux servers have proven their versatility and reliability across a wide range of industries, from finance and e-commerce to healthcare and data centers. Their open-source nature, coupled with a vast ecosystem of tools and support, makes them an attractive choice for organizations seeking robust, scalable, and cost-effective solutions. This section delves into the specific applications and success stories of Linux server deployments.
Linux servers are clearly dominating the worldwide market growth, with impressive adoption rates across industries. However, some argue that this open-source dominance might stifle innovation, a point raised in this thought-provoking piece on innovation loses if open source wins. Regardless of the arguments, the fact remains that Linux servers continue to be a powerful force in the global tech landscape.
Industries Heavily Reliant on Linux Servers
Linux servers are integral to many modern industries due to their stability, security, and adaptability. They offer a flexible platform for handling complex workloads, enabling organizations to optimize their operations and gain a competitive edge.
- Finance: Financial institutions rely heavily on Linux servers for transaction processing, risk management, and regulatory compliance. The stability and security of Linux systems are crucial in this high-stakes environment, where downtime can have severe financial consequences. For instance, many high-frequency trading platforms use Linux servers for their speed and reliability.
- E-commerce: Online retailers and e-commerce platforms utilize Linux servers to handle massive amounts of data, process transactions, and support millions of users simultaneously. The scalability and performance of Linux solutions are vital for handling fluctuating traffic demands and ensuring smooth operations during peak periods.
- Healthcare: In the healthcare sector, Linux servers play a crucial role in managing patient records, supporting medical imaging systems, and enabling secure communication between healthcare providers. The security and reliability of these systems are paramount to maintaining patient confidentiality and ensuring the integrity of sensitive data.
- Data Centers & Cloud Infrastructures: Large-scale data centers and cloud providers leverage Linux servers as the foundation of their infrastructure. The open-source nature of Linux allows for customization and optimization, enabling efficient resource utilization and cost savings. Cloud providers often deploy numerous Linux servers to handle the massive demand for computing resources.
Case Studies of Successful Linux Server Deployments
Numerous organizations have successfully deployed Linux servers, demonstrating the effectiveness and efficiency of this platform. These case studies showcase the versatility of Linux in diverse environments.
- A major e-commerce company experienced a significant reduction in operational costs and an increase in transaction processing speed after migrating to a Linux-based infrastructure. This demonstrates the potential cost-effectiveness and performance gains achievable through Linux server deployments.
- A leading financial institution utilized Linux servers to enhance their risk management systems, enabling them to process vast amounts of data more efficiently and effectively. This highlights the ability of Linux to handle complex analytical tasks in high-pressure environments.
- A prominent healthcare provider implemented Linux servers for their electronic health records system, ensuring data security and facilitating secure communication between medical professionals. This illustrates the importance of data security and accessibility in healthcare applications, which Linux excels at.
Linux Server Implementations Across Industries
The following table provides a concise overview of Linux server implementations across various industries.
| Industry | Specific Applications | Key Needs |
|---|---|---|
| Finance | Transaction processing, risk management, regulatory compliance | High security, reliability, and low latency |
| E-commerce | Handling online transactions, managing product catalogs, supporting user traffic | Scalability, high availability, and robust performance |
| Healthcare | Managing patient records, medical imaging, secure communication | Data security, confidentiality, and regulatory compliance |
| Data Centers/Cloud | Virtualization, storage, computing resources | Scalability, efficiency, and high availability |
Growth Projections
The Linux server market is poised for continued expansion, driven by its inherent flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and growing adoption in various sectors. This projected growth is further fueled by ongoing technological advancements and the increasing demand for scalable and reliable infrastructure solutions. Understanding the factors driving this growth and the potential challenges is crucial for stakeholders to capitalize on opportunities.
Future Growth Trajectory
The Linux server market is anticipated to experience robust growth over the next five years, driven by several key factors. These include the increasing need for cloud-based services, the rise of containerization technologies, and the continued adoption of open-source software. The global trend towards digital transformation is also a major contributor to this expansion. Businesses are increasingly recognizing the value of Linux servers for their cost-effectiveness, flexibility, and security.
Impact of Technological Advancements, Linux servers lead market in worldwide growth
Technological advancements play a pivotal role in shaping the Linux server market’s trajectory. The emergence of containerization technologies like Docker is revolutionizing application deployment and management, significantly boosting the efficiency and scalability of Linux servers. Furthermore, the continuous development of virtualization technologies, such as KVM and Xen, is enabling the creation of more efficient and flexible server environments.
This translates into reduced operational costs and increased server utilization, driving market growth.
Potential Challenges and Opportunities
The Linux server market, while exhibiting strong growth potential, faces certain challenges. Competition from other server operating systems and the need for skilled professionals to manage and maintain Linux infrastructure are significant hurdles. However, these challenges also present opportunities. Investing in training programs and developing innovative solutions to address the skills gap can create new market niches and foster sustainable growth.
The rising demand for specialized Linux distributions tailored to specific industries presents a substantial opportunity.
Predicted Market Share
| Server Type | 2024 Market Share (%) | 2025 Market Share (%) | 2026 Market Share (%) | 2027 Market Share (%) | 2028 Market Share (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bare Metal Servers | 45 | 43 | 41 | 39 | 37 |
| Virtual Servers | 35 | 37 | 39 | 40 | 42 |
| Cloud-Based Servers | 20 | 20 | 20 | 21 | 21 |
The table above presents a predicted market share distribution for different server types over the next five years. This projection considers factors such as the growing adoption of cloud computing, the increasing demand for virtualization, and the sustained popularity of bare metal servers. It is important to note that these figures are estimates and actual market share may vary based on unforeseen market dynamics.
For instance, a surge in demand for specific server types could alter the predicted market share distribution. The predictions assume a moderate increase in overall market size and are based on current market trends and expert opinions.
Linux servers are definitely leading the charge in worldwide growth, driven by their open-source nature and cost-effectiveness. However, even robust server systems rely on accurate positioning data, and issues with GPS signal reliability, as discussed in gps lost can the satellite technology find its way , could impact their operation. Ultimately, the continued success of the Linux server market hinges on dependable technologies across the board.
Geographic Distribution
The global adoption of Linux servers is not uniform across regions. Understanding the key areas driving growth, adoption rates, and influencing factors is crucial for comprehending the market’s dynamic nature. Different regions possess unique technological landscapes and economic conditions, which impact the choices made by businesses.
Key Regions Driving Growth
Several regions are leading the charge in adopting Linux servers. These regions often exhibit a strong technological infrastructure, a vibrant open-source community, and a growing demand for cost-effective and flexible solutions. North America, Europe, and Asia Pacific are consistently prominent in this trend.
Adoption Rates in Different Countries/Regions
Data on specific adoption rates can be challenging to obtain due to varying reporting standards and the decentralized nature of Linux deployments. However, regions with robust IT sectors and a focus on cloud computing, open-source technologies, and digital transformation often show higher adoption rates. For example, countries within the European Union, with their emphasis on digital infrastructure, have seen significant Linux server adoption.
Similarly, countries in Asia Pacific, with their rapid digitalization, show increasing trends.
Factors Influencing Adoption
Several factors influence the adoption of Linux servers in specific regions. Cost-effectiveness is a significant driver, as Linux servers generally offer a more economical solution compared to proprietary alternatives. The flexibility and customization options of Linux systems are also attractive, enabling businesses to tailor their infrastructure to specific needs. Furthermore, the security and reliability of Linux systems, consistently proven in large-scale deployments, play a significant role in the decision-making process.
Regional Variations in Adoption
The adoption of Linux servers varies significantly across regions, influenced by several key factors.
- North America: High adoption rates, particularly in the cloud computing sector, with large-scale deployments within data centers. This is often influenced by a robust IT infrastructure and a focus on technological innovation.
- Europe: Strong adoption, driven by government initiatives and regulations promoting open-source technologies. The European Union’s commitment to digital transformation contributes significantly to the increasing adoption of Linux servers.
- Asia Pacific: Rapidly growing adoption, fueled by the region’s rapid digitalization and expanding cloud infrastructure. The growing demand for scalable and cost-effective solutions is driving this trend.
- South America: Increasing adoption, driven by the need for affordable and reliable solutions in emerging markets. The availability of skilled Linux administrators is also contributing to the growth in this region.
- Africa: Growing adoption, especially in areas with a focus on educational initiatives and cost-effective solutions. The potential for leveraging open-source technologies for economic development is a key factor in this region.
Visual Representation (Hypothetical Map)
A hypothetical world map depicting Linux server adoption rates would show a gradient of colors, with darker shades indicating higher adoption rates in regions like North America, Western Europe, and parts of Asia. Lighter shades would represent lower adoption rates in regions with fewer readily available resources and a less developed IT sector. The map would illustrate the varied levels of adoption across different geographic locations.
A key would correlate colors to adoption levels.
Future Trends: Linux Servers Lead Market In Worldwide Growth
The Linux server market is poised for continued growth, driven by innovative technologies and evolving user needs. Emerging trends in AI, edge computing, and IoT integration are transforming how Linux servers are deployed and utilized. This evolution promises to enhance efficiency, security, and scalability, making Linux servers even more indispensable in the digital landscape.
AI and Machine Learning Integration
The increasing sophistication of AI and machine learning (ML) algorithms is impacting Linux server deployments in several key ways. These technologies are no longer confined to specialized research environments. Instead, they are becoming integral components of everyday applications and infrastructure. AI-powered tools are automating tasks, optimizing resource allocation, and enhancing security measures on Linux servers. For example, predictive maintenance using ML algorithms can anticipate hardware failures, reducing downtime and improving overall system reliability.
Edge Computing Influence
Edge computing, which processes data closer to its source, is significantly influencing Linux server architecture. Deploying Linux servers at the edge allows for faster data processing, reduced latency, and enhanced real-time applications. This trend is particularly crucial for applications requiring immediate responses, such as autonomous vehicles, industrial automation, and real-time video surveillance. Edge devices, equipped with Linux servers, can handle data processing locally, reducing the load on centralized cloud infrastructure.
IoT Integration
The integration of Linux servers with Internet of Things (IoT) devices is another key future trend. Linux’s open-source nature and versatility make it a perfect platform for managing the vast array of IoT devices. From smart homes to industrial sensors, Linux servers can act as central hubs, collecting, processing, and analyzing data from connected devices. This integration opens up new possibilities for data-driven decision-making and automation across diverse industries.
Potential Future Trends in the Linux Server Market
- Increased Cloud-Native Deployments: The shift towards cloud-native architectures will continue, with Linux servers playing a critical role in container orchestration and microservices deployments. This approach enhances scalability, flexibility, and resource utilization.
- Enhanced Security Measures: With the increasing reliance on Linux servers for critical applications, security is paramount. Future trends will emphasize robust security features, including advanced threat detection and proactive mitigation strategies.
- Focus on Sustainability: The demand for eco-friendly computing solutions is growing. Future Linux server designs will likely prioritize energy efficiency, reducing the environmental impact of data centers.
- Development of Specialized Hardware: Tailored hardware for specific workloads, like AI/ML processing, will become more common, further enhancing the performance of Linux servers in these domains.
Last Point
In conclusion, the Linux server market’s global dominance is undeniable. The combination of performance, cost-effectiveness, and adaptability makes Linux servers a strong contender in today’s dynamic technological landscape. Looking ahead, advancements in technology and the growing adoption of cloud solutions will likely continue to propel Linux servers’ market share. The future of server technology is increasingly tied to the evolution of Linux, presenting exciting opportunities for businesses and individuals alike.