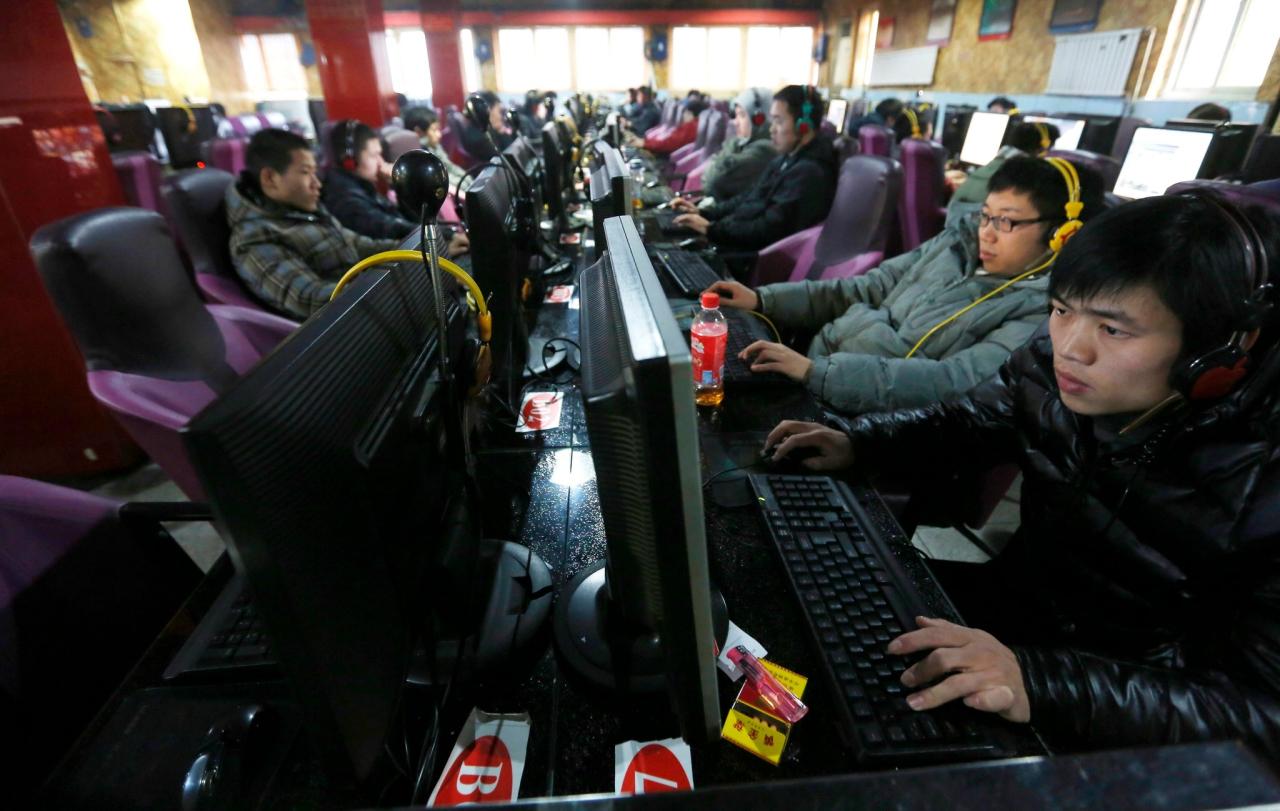
Tech Giants Challenged Chinas Web Censorship
Tech giants challenged to fight chinas web censorship – Tech giants challenged to fight China’s web censorship face a complex web of challenges. From navigating the historical context of global censorship, with its varying approaches and motivations, to understanding China’s specific methods and the economic and political implications, this topic delves into the intricate relationship between tech companies and authoritarian regimes. The ethical considerations for these companies operating in China’s market are undeniable, and the potential conflicts of interest are significant.
How do companies balance profit with their values? What are the potential consequences of compliance or resistance? This deep dive explores these questions and more.
The discussion examines the role of international pressure and legal frameworks in shaping tech companies’ responses. It also explores the diverse strategies companies employ, and the potential risks and rewards of operating in a censored environment. Different tech sectors, like social media and e-commerce, will face varying challenges, and this analysis highlights the potential for innovation and new business models in the face of censorship.
The potential solutions and strategies for navigating these complex situations are also considered, including international collaborations and the role of NGOs.
Global Context of Censorship
Internet censorship, a complex and multifaceted issue, has existed in various forms throughout history. Early forms of control stemmed from government attempts to manage information flow, often motivated by maintaining social order, suppressing dissent, or protecting national security. These early methods were often rudimentary, relying on physical restrictions on communication or direct suppression of certain publications. The rise of the internet, however, dramatically altered the landscape, making censorship more sophisticated and pervasive.The global landscape of internet censorship is characterized by a range of approaches and motivations.
Governments around the world have employed diverse strategies to control information flow, often reflecting their unique political, social, and economic contexts. China, in particular, stands out for the extent and sophistication of its internet controls.
Historical Overview of Internet Censorship
Historically, censorship has taken many forms, ranging from direct suppression of publications to more subtle methods of control. Governments have often justified these measures on grounds of national security, public order, or moral values. The development of the internet has provided new and increasingly sophisticated tools for governments to exert control over information, from content filtering to the use of social media monitoring.
The nature of the internet’s decentralized structure has presented unique challenges to censorship efforts. Despite these challenges, many governments have implemented various strategies to regulate online content.
China’s Approach to Internet Control
China employs a multifaceted approach to controlling its internet space, known as the Great Firewall. This includes a combination of technical measures, such as filtering specific websites and search results, and legal mechanisms, such as strict regulations on online speech and activity. Furthermore, the Chinese government heavily monitors online content, utilizing sophisticated algorithms and human analysts to identify and suppress dissident voices or content deemed harmful to the state.
The Chinese government’s control extends beyond the internet itself, impacting social media platforms and online services. This comprehensive approach has created a highly controlled online environment.
Comparison with Other Countries’ Approaches
Different countries have adopted varying approaches to internet censorship, reflecting their diverse political and social systems. Some countries prioritize freedom of expression, while others prioritize maintaining social order or national security. The approaches often differ in the level of control exerted and the specific methods employed. While China employs a more comprehensive and intrusive approach, other countries use a mix of technical and legal methods.
Examples include filtering systems, legal restrictions on content, and voluntary content moderation by social media platforms. These variations reflect a global spectrum of attitudes toward internet freedom and control.
Economic and Political Implications
China’s censorship policies have significant economic and political implications on a global scale. The control of information flow can limit the free exchange of ideas and hinder innovation. This approach can stifle economic growth and limit the spread of knowledge. Furthermore, it can contribute to political instability and social unrest, as seen in various global contexts.
Table: Internet Censorship Policies
| Country | Specific Restrictions | Methods | Justification |
|---|---|---|---|
| China | Websites, search results, social media | Filtering, monitoring, legal restrictions | National security, social stability |
| Iran | Social media platforms, news outlets | Filtering, blocking, legal restrictions | National security, ideological control |
| North Korea | All forms of internet access | Strict control, limited access | Political control, isolation |
| Russia | Independent news sources, social media platforms | Filtering, legal restrictions, propaganda | National interests, countering dissent |
Tech Giants’ Role and Responsibilities
Navigating the complex landscape of China’s digital sphere presents unique challenges for international tech giants. The nation’s stringent censorship policies and intricate regulatory framework necessitate careful consideration of ethical implications and potential conflicts of interest. Companies must balance profitability with upholding their values and adhering to international standards of freedom of expression.Operating in China’s market demands a nuanced understanding of the legal and societal context.
Companies must navigate a delicate dance between meeting the demands of the Chinese government and maintaining their commitment to user rights and data privacy.
Ethical Considerations in China
Tech companies face a significant ethical dilemma when operating in China. They are expected to comply with censorship requirements, which may conflict with their own values regarding freedom of expression and user privacy. This tension requires careful consideration and transparent communication with stakeholders. Maintaining ethical standards in a market with different cultural norms and regulatory expectations is a constant challenge.
Potential Conflicts of Interest
Companies operating in China’s digital space may face conflicts of interest. The pressure to comply with censorship demands can compromise their commitment to user data protection and freedom of information. These potential conflicts highlight the need for clear ethical guidelines and robust internal mechanisms to mitigate such risks. For example, a social media platform might be pressured to remove content critical of the government, potentially violating user privacy and freedom of expression.
Legal Frameworks Governing Tech Companies
Various legal frameworks govern tech companies’ operations in different jurisdictions. China’s Cybersecurity Law, for instance, imposes stringent obligations on companies handling personal data. Understanding these laws and regulations is critical for compliance and risk management. The legal landscape differs across countries, and companies must adapt their operations to meet the requirements of each jurisdiction. This necessitates a comprehensive legal review and adherence to regional laws.
Role of International Pressure
International pressure plays a crucial role in influencing tech companies’ actions. Advocacy groups and governments often exert pressure on companies to adhere to international standards of freedom of expression and user rights. This pressure, while not always directly enforceable, can influence company policies and actions. Public criticism and boycotts are examples of international pressure.
Strategies Employed by Tech Companies
Tech companies employ various strategies when facing censorship demands. These strategies often involve a combination of compliance, resistance, and lobbying efforts. Negotiating with government agencies, employing legal counsel, and establishing clear internal guidelines are crucial aspects of this process. Furthermore, proactive measures such as establishing local offices with well-versed legal teams can help companies navigate the challenges of a foreign market.
Consequences of Compliance or Resistance
Choosing to comply or resist censorship demands carries potential consequences for tech companies. Compliance may lead to reputational damage and loss of user trust, while resistance could result in fines, sanctions, or even the cessation of operations. The decision to comply or resist must be carefully evaluated based on the specific circumstances and potential risks.
Table: Tech Companies’ Responses to Censorship in China
| Company | Response | Example (Compliance) | Example (Resistance) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Social Media Platform A | Compliance | Removal of posts critical of government policies | None provided |
| Search Engine B | Compliance | Censorship of specific search results | None provided |
| Messaging App C | Resistance (Partial) | Filtering certain types of content | Refusal to remove all content requested |
| E-commerce Platform D | Compliance | Removal of products deemed inappropriate | None provided |
Challenges and Opportunities for Tech Companies
Navigating the Chinese internet market presents unique challenges for tech companies, particularly those operating in the social media and e-commerce sectors. The heavily regulated and censored environment necessitates careful adaptation and strategic decision-making. This intricate landscape necessitates a nuanced understanding of the local context, cultural nuances, and legal frameworks to succeed. This analysis will explore the difficulties, risks, and rewards inherent in operating within a censored environment.The Chinese internet landscape, while presenting immense opportunities for growth, is significantly shaped by stringent censorship policies.
This censorship, designed to maintain social stability and control the flow of information, poses complex challenges for international tech companies seeking to establish a presence. The potential for both significant rewards and substantial risks must be carefully evaluated, with a particular focus on the varying degrees of challenges faced by different types of tech companies.
Tech giants are facing a tough challenge in navigating China’s web censorship, a complex issue with no easy answers. The recent FCC’s move to enforce copy control on digital broadcasts, as detailed in fcc forces copy control of digital broadcasts , highlights the broader struggle to control information flow. Ultimately, these actions raise important questions about the future of global internet access and the power of tech companies in the face of censorship.
Difficulties in Navigating the Chinese Internet Market
Tech companies face substantial hurdles in navigating the Chinese internet market. These challenges stem from the complex regulatory environment, which mandates compliance with stringent censorship policies. Obtaining and maintaining licenses, adhering to content restrictions, and managing data localization requirements can be particularly cumbersome.
Tech giants are facing a real challenge in trying to circumvent China’s web censorship, and it’s a complex issue. Think about the broader implications of reliable location data, like how GPS signals can be disrupted. For instance, if satellite technology suffers failures, as explored in gps lost can the satellite technology find its way , it could impact the very tools needed to get around these restrictions.
Ultimately, these tech companies need innovative solutions to combat censorship, and these challenges highlight the intricate interplay of technology and geopolitics.
Potential Risks and Rewards for Tech Giants
Operating in a censored environment entails significant risks. Companies may face fines, penalties, or even the complete shutdown of their services if they fail to comply with regulations. However, the potential rewards are substantial, particularly in the lucrative e-commerce and social media sectors. Companies that effectively adapt to the unique regulatory environment can gain significant market share and access a large, rapidly growing consumer base.
Comparison of Challenges for Different Tech Companies
Different types of tech companies experience varying degrees of challenges. Social media platforms face the most significant hurdles due to the strict controls on content and information dissemination. E-commerce platforms also face challenges related to data security and localization requirements. However, these challenges are often balanced by the immense market potential within China.
Examples of Adaptation Strategies
Several tech companies have successfully adapted to operating in China. These include employing local partners, developing localized content strategies, and establishing robust compliance mechanisms. These companies recognize the need to adapt to the unique regulatory environment and are often willing to invest significant resources to navigate the challenges.
Innovation and New Business Models
Despite the challenges, the Chinese market presents opportunities for innovation and the development of new business models. Companies can leverage the unique characteristics of the Chinese market to create tailored products and services. This includes adapting existing products to meet the specific needs of the Chinese consumer base.
Tech giants are facing a tough challenge in navigating China’s web censorship. They’re increasingly being asked to actively combat restrictions, but a potential solution might lie in the realm of platform internet and the promise of grid computing. This approach could potentially offer a more distributed and resilient internet infrastructure, potentially giving tech giants new tools to circumvent censorship and create a more open digital landscape.
Ultimately, however, the question remains: can these solutions truly stand up to the complexities of China’s web censorship? See how platform internet the promise of grid computing might help tech giants to effectively address this.
Economic Incentives and Disincentives
Economic incentives for operating in China are substantial due to the large and rapidly growing consumer market. However, disincentives exist due to the strict regulatory environment and potential risks of non-compliance. Companies must carefully weigh these factors when deciding whether to enter or remain in the Chinese market.
Responses to Censorship Policies: Successes and Failures
| Company | Adaptation Strategy | Successes | Failures |
|---|---|---|---|
| Social Media Platform A | Localized content, partnership with local influencers | Increased user engagement, substantial market share | Limited reach due to stringent content controls |
| E-commerce Platform B | Compliance with data localization, strong local partnerships | Significant growth in sales, strong customer base | Difficulties in navigating complex regulatory environment |
| Tech Giant C | Strict compliance with censorship policies, localized services | Strong presence in the market, significant profits | Limited ability to offer services that violate Chinese censorship policies |
| Streaming Platform D | Strict compliance with content regulations, local censorship filters | Large user base in China, high revenue streams | Limited content variety due to censorship, potential loss of international users |
Potential Solutions and Strategies
Navigating the complex landscape of censorship in China presents a significant challenge for tech companies. While maintaining profitability and user engagement, they must simultaneously uphold ethical standards and respect freedom of expression. Finding a balance between these competing priorities requires innovative strategies and a nuanced understanding of the local regulatory environment. This section explores potential solutions and strategies for tech companies operating in China, acknowledging the delicate nature of this challenge.
Strategies for Addressing Censorship Concerns
Tech companies operating in China must develop strategies that enable them to uphold their values while remaining compliant with local regulations. This involves a multifaceted approach, ranging from internal policies to external collaborations. Key areas of focus include proactive content moderation, localization strategies, and maintaining open communication channels with authorities.
- Proactive Content Moderation: Implementing sophisticated content filtering systems that are adaptable to evolving censorship guidelines is crucial. This requires close monitoring of regulatory updates and adjustments to algorithms to avoid violations. This proactive approach helps mitigate the risk of unintentional censorship violations. Examples include employing multiple layers of automated review, integrating human moderators for complex cases, and utilizing machine learning to identify patterns indicative of prohibited content.
- Localization Strategies: Adapting products and services to comply with local customs and preferences is a vital strategy. This includes carefully tailoring content, interfaces, and functionalities to avoid potential conflicts with censorship regulations. Localizing the user experience can also foster trust and engagement within the Chinese market.
- Maintaining Open Communication Channels: Establishing and maintaining open communication channels with relevant government agencies and regulatory bodies is essential for navigating the evolving censorship landscape. These channels can provide crucial insights into evolving guidelines, facilitating proactive compliance and preventing potential misunderstandings.
Mitigating Risks Associated with Censorship, Tech giants challenged to fight chinas web censorship
Minimizing the risks of censorship requires a comprehensive approach, focusing on transparency, resilience, and alternative solutions.
- Transparency and Accountability: Implementing transparent policies and procedures regarding content moderation and censorship compliance builds trust with users and stakeholders. This transparency can help alleviate concerns about potential bias or manipulation in censorship practices.
- Developing Resilient Infrastructure: Creating a robust and adaptable infrastructure capable of handling fluctuating censorship demands is crucial. This may include redundancy in server locations, diverse routing paths, and agile systems for adapting to sudden changes in regulatory requirements. A resilient infrastructure helps maintain service continuity even during periods of heightened censorship.
- Exploring Alternative Solutions: Considering alternative communication channels, such as encrypted messaging platforms or VPN services, could offer users greater freedom of expression. This should be approached cautiously, respecting local regulations and user preferences. For example, utilizing VPNs allows users to access blocked websites, but this should be presented as a service option, not as a default.
International Collaborations and Alliances
International collaborations and alliances can play a crucial role in advocating for internet freedom and supporting tech companies facing censorship challenges.
- Collaborative Advocacy: International organizations and NGOs can work together to advocate for freedom of expression and the rights of internet users. Joint efforts can amplify the impact of individual campaigns and provide support to tech companies facing pressure from censorship regimes.
- Supporting Ethical Operations: International collaborations can support tech companies in developing ethical operating practices in regions with censorship concerns. This can involve providing training, resources, and expertise to help them navigate complex regulatory environments while upholding their values.
Role of International Organizations and NGOs
International organizations and NGOs play a critical role in advocating for internet freedom. They can provide resources, support, and a platform for raising awareness about censorship issues.
- Advocating for Freedom of Expression: International organizations and NGOs can advocate for freedom of expression and the right to access information. They can engage in public awareness campaigns, provide legal support to individuals and organizations, and collaborate with governments to promote digital rights.
- Providing Resources and Support: These organizations can offer resources and support to tech companies facing censorship challenges. This may include training programs, legal consultations, and financial assistance to help them develop ethical and resilient operations.
Examples of Successful Campaigns Advocating for Internet Freedom
Various campaigns have demonstrated the effectiveness of advocating for internet freedom.
- Examples of Successful Campaigns: Numerous campaigns have successfully brought attention to censorship issues and advocated for greater freedom of expression online. Examples include grassroots movements, international advocacy initiatives, and collaborative efforts between NGOs and tech companies.
Potential Solutions Table
| Solution | Pros | Cons | Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Proactive Content Filtering | Reduces risk of violations, adapts to evolving regulations | Potential for misinterpretation, over-filtering, high implementation costs | Employ multiple review layers, human oversight, machine learning, regular audits |
| Localization Strategies | Enhances user engagement, cultural sensitivity | May limit access to global content, slower adaptation to updates | Maintain global functionality where possible, prioritize user feedback |
| International Partnerships | Shared resources, expertise, advocacy power | Potential for conflicts in values, varied approaches | Establish clear guidelines, transparent communication, collaborative strategy development |
| Resilient Infrastructure | Maintains service during censorship events | High initial investment, complex technical implementation | Redundant server locations, diverse routing, agile adaptation tools |
Future Implications and Trends: Tech Giants Challenged To Fight Chinas Web Censorship

The ongoing struggle between global tech giants and China’s stringent internet censorship regime presents a complex and evolving landscape. The future implications of this conflict are multifaceted, impacting not only the Chinese market but the global tech industry as a whole. Understanding these implications is crucial for businesses and policymakers alike.The relationship between tech companies and China’s censorship policies will likely continue to be a delicate balancing act.
Companies will need to navigate the intricate web of regulations and restrictions while maintaining their global operations and user base.
Potential Long-Term Impacts on the Global Tech Landscape
China’s censorship policies, while primarily affecting its domestic market, have global reverberations. The stringent controls on information flow influence the development of global internet standards and protocols. Companies that comply with Chinese censorship practices may face criticism and boycotts from those concerned about human rights and free speech. Conversely, companies that refuse to comply risk losing access to the vast Chinese market, highlighting the inherent tension.
Evolution of the Relationship Between Tech Giants and China’s Censorship
The future relationship between tech giants and China’s censorship will likely be characterized by a continuous negotiation and adaptation. Companies will be compelled to develop sophisticated strategies to navigate the Chinese digital environment, which will include a high degree of compliance with censorship demands while potentially maintaining some semblance of freedom for their global user base. This could involve the development of regionally-specific algorithms or content filters.
The level of compliance will likely depend on the specific company and its priorities.
Role of Emerging Technologies in Shaping the Future of Internet Censorship
Emerging technologies like AI and machine learning are poised to play a significant role in the future of internet censorship. AI algorithms can be employed to identify and filter content deemed objectionable by the Chinese government, leading to more sophisticated and automated censorship systems. This trend could lead to a more refined, albeit intrusive, control over online content.
Conversely, these technologies could also be used by activists and researchers to circumvent censorship, leading to a dynamic struggle between censorship tools and countermeasures.
Impact of New Regulations and Policies on Tech Companies
New regulations and policies regarding data localization, content moderation, and user privacy will further complicate the operations of tech companies in the Chinese market. The enforcement of these regulations could lead to increased compliance costs, potential legal challenges, and limitations on data accessibility for global users. The development of these policies will influence the design of global tech infrastructure and shape the future of the internet.
Potential Future Scenarios for the Relationship Between Tech Giants and China’s Censorship
| Scenario | Description | Potential Risks | Potential Opportunities |
|---|---|---|---|
| Compliance and Adaptation | Companies adjust their services to comply with Chinese censorship regulations. | Loss of user trust, potential for compromised values and ethics, erosion of free speech principles. | Access to the large Chinese market, maintaining revenue streams, and potentially establishing a foothold in the region. |
| Resistance and Withdrawal | Companies refuse to comply with Chinese censorship demands, potentially facing consequences. | Loss of revenue in the Chinese market, reputational damage, and legal challenges. | Strengthening of company values, building a reputation for upholding principles, potentially fostering alternative digital ecosystems outside of China. |
| Strategic Collaboration | Companies develop nuanced approaches to navigate the Chinese market, potentially using local partnerships. | Potential conflicts of interest, compromised values, and the ethical implications of partnerships with censorship-enforcing bodies. | Access to the Chinese market, fostering innovation, and potentially influencing censorship policies in a positive direction. |
| Hybrid Approach | Companies create regionally-specific services, adapting to Chinese censorship while maintaining global standards. | Increased complexity in managing different services, potential for inconsistencies, and difficulties in maintaining global user trust. | Preserving access to the Chinese market, maintaining global operations, and potentially exploring new business models. |
Closing Notes
In conclusion, the ongoing struggle between tech giants and China’s web censorship presents a critical global challenge. The implications extend far beyond China’s borders, impacting the future of the internet and freedom of expression. The discussion highlights the complex interplay of economic incentives, legal frameworks, and ethical considerations. The future of this relationship remains uncertain, but the evolution of technology and global pressure will undoubtedly shape the course of events.
This complex situation demands ongoing vigilance and adaptability from all stakeholders.


