MSN vs AOL A Never-Was Battle
Msn vs aol the battle that never was – MSN vs AOL: the battle that never was. Stepping back to the late 90s and early 2000s, the internet was a far cry from today’s ubiquitous digital landscape. AOL and MSN, alongside CompuServe, were the gatekeepers to this nascent online world. This exploration dives into the context, features, marketing, rise and fall of these services, their impact on the internet ecosystem, and the cultural footprint they left behind.
We’ll examine their often-overlooked differences and explore why the supposed “battle” was more of a parallel evolution.
This detailed look at MSN and AOL will compare their core services, from email and news to the technical nuances of their platforms. We’ll dissect their marketing strategies, subscription models, and the factors that contributed to their ultimate fates. The analysis delves into the changing internet landscape, evolving user preferences, and the lasting impact these services had on shaping the digital world we know today.
Introduction to the Context
The late 1990s and early 2000s witnessed a dramatic shift in how people accessed and interacted with the internet. Online services, rather than just web pages, became the primary gateways for millions, offering a structured environment beyond simple browsing. This era saw the rise of powerful players vying for user attention and market share, creating a vibrant, albeit sometimes chaotic, online landscape.This period was characterized by rapid technological advancements, creating a demand for services that could manage the increasing complexity of the internet.
These online services provided not just access but also a sense of community, shaping user expectations and creating a distinct internet culture. Understanding the competitive landscape and business models of these providers helps us appreciate the impact of this era on modern technology and digital society.
Key Players in the Online Space, Msn vs aol the battle that never was
AOL, MSN, and CompuServe dominated the online service landscape during this period. AOL, through aggressive marketing and bundled services, rapidly achieved a massive user base. MSN, a product of Microsoft, leveraged its existing software ecosystem to integrate its online service into a comprehensive platform. CompuServe, an early pioneer, had a loyal following but struggled to keep pace with the evolving market.
Prevailing Internet Culture and User Expectations
The internet culture of the late 1990s and early 2000s was characterized by a sense of discovery and excitement. Users were eager to explore the possibilities of online communication, community, and information access. Online services like AOL offered not just email and news but also chat rooms, forums, and games, fostering a sense of community. Users expected these services to be user-friendly, reliable, and comprehensive, incorporating essential tools and functionalities.
These expectations played a crucial role in the competitive dynamics between providers.
Competitive Landscape and Driving Factors
The rivalry between AOL, MSN, and CompuServe was intense. AOL’s aggressive marketing campaigns and bundled deals with internet service providers positioned it as a dominant force. MSN, relying on Microsoft’s established brand and software ecosystem, targeted a different segment of the market. The availability of dial-up internet connections, often limited by speed and availability, contributed to the competitive landscape.
User acquisition, retention, and feature development became key battlegrounds.
Remember the heated debates about MSN vs AOL? It was a clash of titans, but ultimately, a non-event. Fast forward to today, and the music industry is undergoing a similar shift. Buy.com debuts legit music downloads strings attached , which feels like a surprisingly modern take on the digital download wars. The parallels to the AOL/MSN era are intriguing, though, ultimately, this new era has different players and a different landscape.
So, while the past may feel familiar, the future unfolds in its own way.
Business Models Employed
Each provider employed a unique business model. AOL’s strategy revolved around bundled services, including internet access and software, to attract and retain subscribers. MSN capitalized on Microsoft’s extensive software portfolio, integrating its online service seamlessly with products like Windows and Outlook. CompuServe focused on offering a wide range of services, including forums, chat rooms, and databases, catering to a diverse user base.
Comparing Features and Services
The digital landscape of the late 1990s and early 2000s saw a fierce competition between MSN and AOL for internet dominance. This competition manifested in a variety of services and features, each vying for user attention and market share. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of these services is crucial to grasping the evolving nature of online experiences during this period.This comparison delves into the core offerings of MSN and AOL, examining their email, news, and other services, their technical platforms, and the overall user experiences.
This analysis will also illuminate the varying pricing and subscription models that shaped their appeal to consumers.
Email Services
The email services offered by MSN and AOL were foundational to their user bases. MSN Hotmail, a pioneering webmail service, provided a user-friendly interface for sending and receiving emails. AOL’s email service, though initially a strong competitor, gradually faced challenges adapting to the evolving webmail standards.
Remember the endless debate about MSN vs. AOL? It was a digital duel that never really materialized as a significant clash. Meanwhile, tech giants like SGI were pushing the boundaries of computing, like their groundbreaking sgi introduces quad processor workstation , showcasing the advancements in processing power. The focus on these powerful machines, though, probably overshadowed the more superficial battle of online services like MSN and AOL, a battle that was never really a battle at all.
- MSN Hotmail offered a superior user experience due to its web-based nature. Users could access their emails from any computer with an internet connection, offering unparalleled convenience compared to the desktop-based email clients prevalent at the time. This accessibility and ease of use proved crucial for a wider user base.
- AOL’s email service, initially popular, struggled to compete with the increasing popularity of webmail. The transition to a more user-friendly webmail system for AOL email was slower, and the desktop-centric nature of its early offerings proved less adaptable as internet use evolved.
News and Information Services
Both MSN and AOL attempted to establish themselves as comprehensive news and information hubs. MSN integrated news feeds directly into its portal, offering a consolidated experience. AOL, while providing news, focused on a different approach, integrating it with its community features.
- MSN’s news integration within its portal offered a streamlined approach to news consumption. Users could access news from various sources within the MSN environment, fostering a centralized information hub. This consolidation and accessibility contributed to a smoother user experience.
- AOL’s news service was more closely tied to its online community features. Users could access news within the AOL community, but the integration wasn’t as seamless or comprehensive as MSN’s. This approach emphasized the social aspect of news consumption rather than a purely informational one.
Platform and Interface Differences
The technological foundations of MSN and AOL differed significantly. MSN benefited from a more open architecture, allowing for easier integration with other services. AOL, while influential in its early days, relied on a more closed system, impacting its ability to evolve with the changing internet landscape.
- MSN leveraged a more open platform architecture, allowing for easier integration with various software and services. This openness fostered innovation and broader compatibility, enabling users to connect with a wider array of tools.
- AOL’s platform was more tightly controlled, leading to a less flexible and adaptable environment. While effective in its time, this closed system hindered integration with other applications and services, eventually hindering its ability to compete with the increasingly interconnected nature of the internet.
User Experience and Perception
The perceived user experience of MSN and AOL varied. MSN’s integrated approach, encompassing various services within one portal, fostered a sense of convenience. AOL’s community focus emphasized a different kind of user experience, centered around social interaction and group communication.
- MSN’s user experience emphasized convenience, providing a unified platform for accessing diverse services. This centralized approach made it easy for users to navigate various features.
- AOL’s user experience emphasized a strong sense of community, allowing users to connect with others through shared interests. This social aspect of the AOL platform played a vital role in its appeal to certain user groups.
Pricing and Subscription Models
The pricing and subscription models of MSN and AOL differed significantly, reflecting their distinct approaches to service delivery. MSN adopted a more diverse approach, offering various tiers of access and services, while AOL prioritized a simpler, bundled subscription.
| Feature | MSN | AOL |
|---|---|---|
| Basic Access | Free with limited features | Free with limited features |
| Premium Access | Tiered subscriptions based on features | Bundled subscription with integrated services |
| Pricing Details | Variable based on tier | Fixed monthly fee |
Marketing and User Acquisition
The battle for internet dominance in the late 1990s and early 2000s was fiercely fought, and a significant part of that battle was waged through marketing and user acquisition strategies. MSN and AOL, titans of their time, employed various tactics to attract and retain users. Understanding these strategies provides valuable insight into the competitive landscape and the evolving nature of online services.MSN and AOL’s marketing campaigns were pivotal in shaping the early internet experience for millions.
These efforts were crucial in defining their respective brand identities and influencing user choices in a rapidly changing digital environment. Their approaches varied, but both companies understood the importance of building a strong brand presence and a loyal user base.
Marketing Strategies Employed by MSN and AOL
MSN, positioned as a comprehensive portal, focused on providing a one-stop shop for news, email, and entertainment. AOL, on the other hand, emphasized community building, creating a sense of belonging through its instant messaging service. These distinct approaches reflected their target demographics and the evolving needs of online users.
Promotional Campaigns and Branding Efforts
MSN leveraged its strong ties with Microsoft, employing a multi-pronged approach. Advertising campaigns highlighted the integration of MSN services with other Microsoft products. This strategy aimed to attract existing Microsoft users. AOL, through its iconic dial-up modem service, built a unique brand identity around community and instant messaging. Promotional materials often portrayed AOL as a social hub.
Tactics Used to Build Brand Loyalty
Both companies implemented loyalty programs and incentives to retain existing users. MSN offered various free services and exclusive content to encourage continued use. AOL focused on enhancing its instant messaging platform and expanding its online community features. These strategies helped foster a sense of loyalty and brand attachment among users.
User Acquisition Strategies and the Competitive Landscape
MSN’s aggressive user acquisition strategies, often coupled with free offerings, created a significant competitive pressure on AOL. The competitive landscape was further influenced by the growing popularity of other internet providers. The ability to attract and retain users directly impacted the market share and influence of each company.
Table Illustrating Marketing Campaigns
| Company | Campaign Focus | Key Tactics | Target Audience |
|---|---|---|---|
| MSN | Comprehensive Portal | Integration with Microsoft products, free services, exclusive content | Existing Microsoft users, individuals seeking a one-stop online experience |
| AOL | Community Building | Instant messaging, online forums, community features | Individuals seeking social connections and online communities |
The Rise and Fall of the Services

The battle for online dominance between MSN and AOL, though never a direct, head-to-head conflict, was a fascinating study in how technological advancements and shifting user preferences shaped the digital landscape. Both services, initially pioneers in their respective eras, ultimately succumbed to the changing tide of internet access and user demands. Understanding their trajectories offers valuable insights into the evolution of online services and the forces that drive their success or failure.
Key Events in the Development and Decline of MSN
MSN, Microsoft’s foray into the online service arena, saw its initial success fueled by the burgeoning popularity of the internet and Microsoft’s existing stronghold in the software market. Its early offerings, including email, instant messaging, and web portal features, appealed to a wide audience. However, the company’s evolution didn’t always reflect smooth sailing. The rise of social media platforms and more user-friendly internet browsing experiences gradually shifted user preferences, leading to MSN’s decline in popularity.
- 1995-2000: MSN launched, offering a suite of services including email, instant messaging, and web browsing. This period witnessed rapid growth, capitalizing on Microsoft’s influence and the increasing internet adoption rate.
- 2000-2005: MSN faced competition from emerging internet service providers and new social networking sites. The introduction of more user-friendly interfaces and broader functionalities began to chip away at MSN’s market share.
- 2005-2010: The increasing popularity of social networking platforms like Facebook and Twitter significantly altered user habits. MSN struggled to adapt to these shifts, losing further ground to more modern, social-centric services.
- 2010-Present: MSN evolved into a more integrated component of Microsoft’s ecosystem, becoming less of a standalone service and more of a tool within other Microsoft products. This transition reflects the changing nature of online services, emphasizing interoperability and integrated user experiences.
Key Events in the Development and Decline of AOL
AOL, initially a pioneering internet service provider, experienced a period of phenomenal growth, fueled by its innovative approach to internet access and user-friendly software. However, its dominance proved unsustainable as the internet landscape transformed. The company’s struggle to adapt to changing user expectations and the rise of broadband internet access ultimately led to its decline.
- 1980s-1990s: AOL emerged as a leader in dial-up internet access, offering a user-friendly interface and a comprehensive suite of online services, including email and instant messaging. This period saw AOL achieve significant market penetration.
- Late 1990s-2000s: The rise of broadband internet access and the increasing sophistication of internet users created challenges for AOL’s dial-up-centric model. The company struggled to maintain its competitive edge as users migrated to faster, more versatile connections.
- 2000s-Present: AOL adapted by acquiring and integrating other online services, including media properties. However, this diversification did not fully address the core issue of the company’s outdated business model. The company has transitioned into a subsidiary of Verizon and now primarily operates within the digital media sphere.
Impact of Evolving Internet Technologies
The transition from dial-up to broadband internet access fundamentally altered the landscape for online service providers. Broadband offered significantly faster speeds and greater bandwidth, enabling more complex and interactive online experiences. This shift significantly impacted the services offered by providers like MSN and AOL, requiring them to adapt their offerings to accommodate the enhanced capabilities.
Changing User Preferences and Needs
User preferences and needs evolved significantly alongside the advancements in internet technologies. The shift from a simple internet experience to a more interactive and social one led to a demand for more user-friendly interfaces and integrated social features. MSN and AOL, initially successful with their simpler offerings, found it increasingly challenging to adapt to these evolving expectations.
Key Milestones and Turning Points
| Service | Milestone | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| MSN | 2005 Launch of Windows Live | Shift towards integration with other Microsoft products. |
| MSN | 2010s Shift to an integrated platform | Reflects the increasing emphasis on interoperability and integrated user experiences. |
| AOL | Acquisition of numerous media companies | Attempts to diversify and adapt to changing media landscape. |
| AOL | 2000s Loss of market share to broadband providers | Indicates the difficulty in adapting to changing technological landscapes. |
Impact on the Internet Ecosystem
MSN and AOL, while eventually fading from prominence, profoundly shaped the internet landscape. Their rise and fall are a fascinating case study in the evolving nature of online services and the ever-shifting needs of users. Their impact extended beyond their specific offerings, influencing the broader ecosystem, from communication protocols to the very design of the web experience.Their legacy is complex, encompassing both positive contributions and the pitfalls of early internet innovation.
They fostered a period of rapid growth and accessibility, but also demonstrated the transient nature of technological trends and the importance of adapting to changing user expectations.
Remember the MSN vs AOL showdown? It was a fascinating, but ultimately fizzled-out battle for internet supremacy. While those days are long gone, the need to safeguard our digital history is as relevant as ever. We need to proactively upgrade and archive the ongoing threat of data extinction upgrade and archive the ongoing threat of data extinction.
The lesson from that forgotten internet war is that digital data, like a well-maintained historical archive, needs constant care and attention. Ultimately, the fight for digital preservation is far more significant than any outdated internet service provider rivalry.
Influence on Online Communication and Interaction
MSN Messenger and AOL Instant Messenger (AIM) revolutionized online communication. Before these platforms, interacting with others online was limited and cumbersome. These instant messaging services democratized communication, allowing people to connect in real-time across geographical boundaries. This facilitated the formation of online communities and friendships, impacting social interactions in ways that were previously unimaginable. The adoption of these services demonstrated the increasing importance of real-time communication in the digital age.
Impact on Web Browsers and Related Technologies
The rise of MSN and AOL coincided with the evolution of web browsers. Their integrated services, often bundled with their respective browsers, highlighted the importance of a seamless user experience. These companies recognized the need for user-friendly interfaces and integrated services. This fostered competition in the browser market, leading to advancements in features and usability. The demand for reliable and efficient web browsing tools increased significantly, driving innovation in browser development and functionality.
Shaping the Future of Online Services and Content
MSN and AOL’s initial success demonstrated the viability of providing a comprehensive suite of online services. Their offerings included email, news, games, and more, all bundled into a single platform. This approach anticipated the trend toward integrated online experiences. While their specific models didn’t fully endure, the concept of offering diverse services under a single umbrella influenced the evolution of online platforms.
The ambition of providing a holistic online experience shaped the way people interacted with the internet.
Long-Term Consequences of the Rise and Fall
| Aspect | Positive Consequences | Negative Consequences |
|---|---|---|
| User Experience | Increased accessibility to online services, fostering a sense of community. | Potential for fragmentation of the internet ecosystem. |
| Market Competition | Stimulated innovation and competition in the online services market. | Limited user choice and flexibility in some cases, especially with bundled services. |
| Content Delivery | Early examples of online news and entertainment delivery models. | Potential for biased content delivery based on platform priorities. |
| Technological Advancements | Prompted innovation in areas like instant messaging and online communication. | Limited scalability of specific models as user needs evolved. |
| Overall Impact | Facilitated the transition to a more integrated and user-friendly online environment. | Failed to fully anticipate and adapt to the evolving needs and preferences of internet users. |
Cultural Impact and User Perceptions: Msn Vs Aol The Battle That Never Was
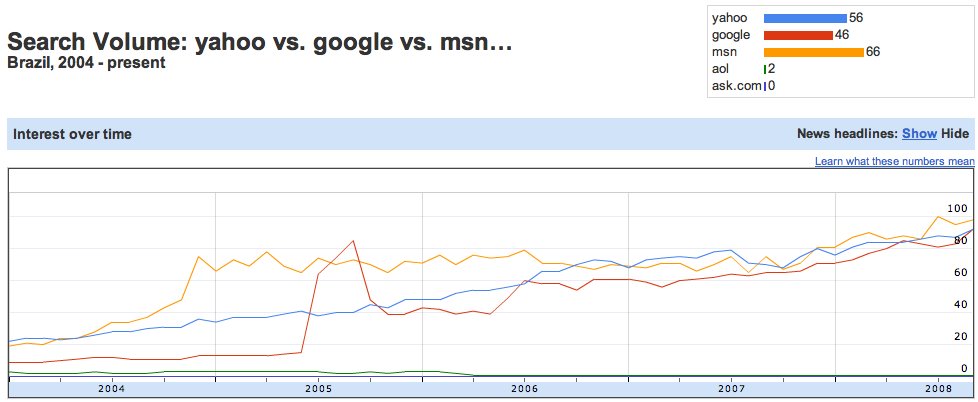
MSN and AOL, while now fading into the digital past, left indelible marks on popular culture and internet usage. Their rise and fall mirrored the evolving relationship between technology and society, shaping user expectations and impacting online interactions. Understanding their cultural impact requires examining how these services were perceived by various demographics, how they influenced social behavior, and how they reshaped the internet experience as a whole.Beyond simply providing email and internet access, these services became deeply ingrained in daily routines, influencing how people communicated, sought information, and even formed communities.
Their perceived value, both positive and negative, shaped individual and collective online behaviors.
Influence on Popular Culture
The integration of MSN and AOL into daily life fostered a unique set of online habits. The ubiquitous presence of their interfaces, with chat features and personalized content feeds, fundamentally altered communication styles. Users learned to express themselves through online avatars and interactions, often adopting distinct personas within these virtual spaces. This created a blend of online and offline social circles, with interactions frequently bridging the two.
For example, the rise of instant messaging led to a new form of casual communication, which, in turn, affected interpersonal dynamics.
Social Impact on Users
The services fostered a sense of community, albeit often within a specific online ecosystem. Users interacted within AOL Instant Messenger or MSN Messenger, forming friendships and networks that were deeply rooted in these platforms. The ability to connect with others, regardless of geographical location, provided a sense of global accessibility. This sense of interconnectedness was a significant factor in the services’ widespread adoption and the impact they had on personal relationships.
This interconnectedness was often limited to those within the platform’s specific community, shaping social interaction patterns.
Demographic Perceptions of MSN and AOL
Different demographics reacted differently to MSN and AOL. Younger users often embraced the novelty and accessibility of these platforms, seeing them as central to their social lives. Older users, however, might have viewed these services with a degree of skepticism or apprehension. This varied reaction to the platforms is illustrated by the different ways these services were used across age groups.
The cultural impact of MSN and AOL wasn’t uniform; it was shaped by generational differences and personal preferences.
Role in Shaping the Internet Experience
MSN and AOL were pioneers in the design and implementation of user interfaces for online services. Their platforms introduced the concept of personalized news feeds and integrated communication tools, influencing the design of subsequent online platforms. This led to a significant shift in the way users navigated the internet. The availability of chat, email, and information in one platform was a revolutionary concept for its time, paving the way for more complex and interconnected online experiences.
Cultural Influences Comparison Table
| Feature | MSN | AOL |
|---|---|---|
| Ease of Use | Intuitive interface, allowing users to easily navigate between different features. | Initially, the interface was complex for some users. However, they adapted. |
| Social Interaction | Fostered a sense of community through integrated messaging and forums. | Facilitated communication through instant messaging and online communities. |
| Personalization | Personalized news feeds and customizable profiles. | Personalized content and user profiles were a key feature. |
| Cultural Impact | Significant impact on internet usage, especially among younger users. | Broad cultural impact, influencing communication and internet culture. |
Last Point
In retrospect, the “battle” between MSN and AOL wasn’t a head-to-head clash but rather two distinct responses to a burgeoning digital world. Their rise and fall highlight the rapid pace of technological advancement and changing user needs. The strategies, successes, and failures of these early online services provide valuable insights into the evolution of the internet and its lasting influence on our lives.
They were a significant part of the history of the internet, though their direct competition didn’t shape the future in the same way that other events did.