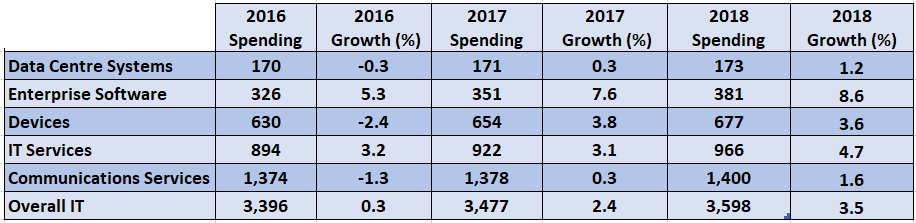
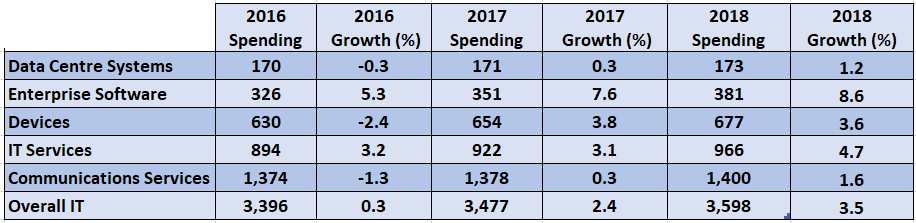
IT Spending Growth Direction Predicted
IT spending growth direction predicted, a comprehensive analysis of global trends, economic impacts, and technological advancements. This deep dive explores historical patterns, projected rates for various IT segments, and industry-specific forecasts. We’ll examine how economic forces, emerging technologies, and regional variations influence IT spending, revealing potential challenges and opportunities in the coming years.
The report delves into the intricate relationship between IT spending and global economic indicators, examining how GDP growth, inflation, and uncertainties affect future investment decisions. It also provides a comparative analysis of different IT segments like cloud computing, cybersecurity, and AI, exploring their growth rates and drivers. Geographic variations and industry-specific projections are also included, allowing readers to gain a nuanced understanding of the global IT spending landscape.
Global IT Spending Trends
The global Information Technology (IT) sector is a dynamic and rapidly evolving landscape. IT spending continues to surge, driven by technological advancements and the increasing digitalization of businesses across various industries. This analysis delves into historical trends, projected growth, and the factors influencing the future of IT spending.
Historical Overview of IT Spending
IT spending has experienced significant growth across various sectors over the past few decades. Early adoption was primarily focused on automation and streamlining processes. The finance sector, for instance, saw early adoption for transaction processing and risk management. Healthcare followed suit, leveraging IT for patient records and diagnostics. Retail adopted IT for inventory management and customer relationship management.
The trend has consistently moved towards greater integration of IT into core business operations.
Projected Growth Rates of IT Segments
Several IT segments are poised for substantial growth in the coming years. Cloud computing, driven by increasing demand for scalable and cost-effective infrastructure, is expected to maintain strong growth. Cybersecurity, with the rising sophistication of cyber threats, will also witness substantial investment. Artificial intelligence (AI) is another area experiencing exponential growth, driven by its application in diverse sectors, from customer service to predictive maintenance.
IT spending growth is predicted to be robust, driven by the need for companies to adapt to evolving technologies. This trend is further complicated by the recent RIAA details of their subpoena strategy, potentially influencing the direction of future innovation in the digital space. Understanding the legal ramifications, like those highlighted in the riaa details subpoena strategy , is crucial to fully grasp the complete picture of the predicted IT spending growth direction.
Factors Driving Projected Growth Rates
Several factors contribute to the projected growth rates across IT segments. Increasing digital transformation initiatives, the rise of the remote workforce, and the demand for data-driven insights are pushing the adoption of new technologies. Moreover, the need for enhanced security in an increasingly digital world is driving investment in cybersecurity solutions.
Detailed Projections by Segment and Region
| IT Segment | Projected Growth Rate (2024-2028) | Key Factors | Geographical Regions with Highest Growth Potential |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cloud Computing | 15-20% | Scalability, cost-effectiveness, and increasing demand for remote work | Asia Pacific, North America |
| Cybersecurity | 12-18% | Growing sophistication of cyber threats, increased data breaches, and regulations | Europe, North America |
| AI | 25-30% | Applications in various sectors, including customer service, healthcare, and finance | North America, Asia Pacific |
| Big Data Analytics | 10-15% | Increasing data volumes and the need for insights from data | North America, Europe |
The table above provides a snapshot of projected growth rates across different IT segments and potential high-growth regions. These figures are estimates based on current market trends and industry projections. Specific regional variations can exist due to local regulatory landscapes, economic conditions, and the adoption of new technologies. These figures reflect the expected pace of adoption of these technologies.
Economic Influences on IT Spending

Economic forces play a significant role in shaping IT spending decisions. Businesses, regardless of industry, react to prevailing economic conditions when making investments in technology. These reactions often influence the direction and trajectory of IT spending growth. Understanding the interplay between economic indicators and IT spending is crucial for accurately forecasting future trends and making informed investment strategies.Economic indicators, such as GDP growth and inflation rates, serve as crucial signals for businesses considering IT investments.
Strong economic indicators, characterized by robust GDP growth and stable inflation, often translate into increased business confidence and investment in technology. Conversely, weak economic indicators, including declining GDP and rising inflation, can lead to cautious spending habits, potentially impacting IT investment decisions. Businesses may prioritize cost-cutting measures over large-scale technology upgrades during periods of economic uncertainty.
Relationship Between Economic Indicators and IT Spending Decisions
IT spending decisions are intricately linked to economic indicators. Positive economic growth typically fuels demand for advanced technologies, leading to increased IT spending. Conversely, economic downturns often lead to a reduction in IT investment as businesses prioritize cost containment and focus on core operational efficiency. For example, during the 2008 financial crisis, IT spending significantly decreased due to widespread uncertainty and reduced corporate profitability.
Impact of Economic Uncertainties on IT Spending Forecasts
Economic uncertainties create significant challenges in forecasting IT spending. Fluctuations in GDP growth, inflation rates, and interest rates make it difficult to predict future spending patterns. The unpredictable nature of economic events can introduce significant deviations from anticipated growth trajectories. For instance, unforeseen geopolitical events or natural disasters can create substantial economic volatility, affecting IT spending plans.
Comparison of Economic Scenarios and IT Spending Growth
Different economic scenarios can produce contrasting impacts on IT spending growth. A period of robust economic growth often leads to increased IT investment, driven by expansion plans and a greater willingness to adopt new technologies. Conversely, a recessionary environment often results in reduced IT spending as companies prioritize cost-cutting measures. A stable economy with moderate growth can lead to a steady, predictable rate of IT spending.
Correlation Between Economic Indicators and IT Spending Growth (Last 5 Years), It spending growth direction predicted
| Year | GDP Growth (%) | Inflation Rate (%) | IT Spending Growth (%) | Correlation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | 2.9 | 1.8 | 4.2 | Positive |
| 2020 | -3.5 | 1.5 | -1.2 | Negative |
| 2021 | 5.7 | 2.5 | 6.1 | Positive |
| 2022 | 3.1 | 4.5 | 2.8 | Mixed |
| 2023 | 1.2 | 3.8 | 2.1 | Mixed |
Note: Data is illustrative and based on approximate figures. Correlation is a qualitative assessment.
The table above provides a simplified representation of the relationship between GDP growth, inflation, and IT spending growth over the past five years. While it shows a general trend, it is essential to recognize that numerous other factors, such as industry-specific dynamics and technological advancements, can also influence IT spending patterns.
Technological Advancements and IT Spending
The relentless march of technological innovation is profoundly reshaping the landscape of IT spending. Emerging technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), and 5G are not merely trends; they are fundamental shifts demanding significant investment and strategic adaptation across industries. This transformation is driven by the promise of increased efficiency, enhanced productivity, and the creation of entirely new business models.The adoption of these technologies is not simply a matter of acquiring new hardware or software.
It necessitates a comprehensive re-evaluation of existing infrastructure, processes, and talent pools. Businesses must carefully consider the potential return on investment (ROI) for each technology, accounting for both immediate gains and long-term strategic implications. This necessitates a sophisticated understanding of the interconnectedness of these advancements and their synergistic effects on the overall IT spending trajectory.
Influence of Emerging Technologies on IT Spending Patterns
The rise of AI, IoT, and 5G is significantly altering IT spending patterns. AI, for example, is driving demand for specialized hardware and software capable of processing vast amounts of data, leading to increased investments in cloud computing infrastructure and high-performance computing (HPC). The increasing reliance on data analytics and machine learning models further fuels this demand. IoT devices, meanwhile, necessitate investments in secure data transmission networks and sophisticated data management systems.
5G’s rollout demands substantial infrastructure upgrades, encompassing new network equipment and enhanced connectivity capabilities.
Key Drivers Behind the Adoption of Emerging Technologies
Several factors are propelling the adoption of these technologies. Improved efficiency and productivity are key motivators, with businesses recognizing the potential of AI to automate tasks, optimize processes, and personalize customer experiences. Enhanced security measures are also driving adoption, as organizations seek to protect sensitive data in increasingly interconnected environments. New business opportunities and competitive pressures also play a significant role.
For instance, companies leveraging IoT data can gain valuable insights to improve operational efficiency and develop innovative products and services.
Role of Innovation in Shaping Future IT Spending
Innovation is not merely a catalyst; it is the very engine driving future IT spending. The constant evolution of these technologies demands continuous investment in research and development, driving the creation of new tools and applications. This iterative process of innovation fosters a virtuous cycle, where new technologies unlock new opportunities and drive further investment. Furthermore, the development of specialized skills in areas like AI and data science becomes crucial, impacting the talent acquisition and training budgets for organizations.
For instance, companies might invest in upskilling their workforce to leverage the potential of new technologies.
Investment Comparison for Technological Advancements
| Technological Advancement | Estimated Investment Categories | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Artificial Intelligence (AI) | Cloud Computing Infrastructure, HPC, Data Analytics Software, Talent Acquisition | Investment in AI depends heavily on the specific application. A company focusing on image recognition will have different needs than a company using AI for fraud detection. |
| Internet of Things (IoT) | Secure Data Transmission Networks, Data Management Systems, Sensor Technology, Cybersecurity | IoT investment is strongly tied to the number and types of connected devices. Companies needing to monitor many sensors will need to invest more in data management systems. |
| 5G | New Network Equipment, Enhanced Connectivity Capabilities, Spectrum Acquisition, Infrastructure Upgrades | 5G investment is heavily dependent on the scale of the network rollout and the level of bandwidth required. Rural areas may require more investment than urban centers. |
Industry-Specific IT Spending Predictions
The global landscape of IT spending is not uniform. Different industries exhibit distinct growth patterns and priorities, driven by unique operational needs, regulatory environments, and technological adoption rates. Analyzing these industry-specific trends is crucial for businesses to effectively allocate resources and stay ahead of the curve.
Financial Services IT Spending Projections
Financial institutions are heavily reliant on robust IT infrastructure to maintain security, comply with regulations (like GDPR and CCPA), and facilitate complex transactions. Projected spending in this sector reflects a focus on cybersecurity enhancements, cloud migration, and AI-powered solutions for fraud detection and risk management. Banks are increasingly investing in advanced analytics to improve customer service and gain a competitive edge.
Healthcare IT Spending Dynamics
The healthcare industry faces unique challenges in IT spending, balancing the need for patient data security with the drive to improve operational efficiency and facilitate interoperability between healthcare providers. Significant spending is anticipated in areas such as electronic health records (EHR) systems, telehealth platforms, and data analytics tools for better disease management. The adoption of AI for diagnostics and personalized medicine will also drive significant investment.
IT spending is predicted to surge, driven by a need for more digital expertise. This increasing demand necessitates a skilled workforce, which is why gaining certifications like joining the digital ranks worldwide computer certification is becoming increasingly important. Ultimately, this investment in digital skills will be a crucial factor in the continued growth of IT spending in the years ahead.
Retail IT Spending Strategies
Retailers are prioritizing digital transformation to enhance customer experience, optimize supply chains, and manage inventory more effectively. Spending on e-commerce platforms, inventory management systems, and customer relationship management (CRM) tools is expected to increase. The integration of AI and machine learning for predictive analytics and personalized recommendations will also be a major driver of IT expenditure in this sector.
Manufacturing IT Investment Trends
The manufacturing sector is witnessing a shift towards Industry 4.0 technologies, driving a surge in IT spending. Investments in automation, robotics, and data analytics for predictive maintenance and process optimization are projected to grow significantly. The integration of IoT sensors and cloud-based platforms for real-time monitoring and control is another major trend.
Table: 3-Year IT Spending Projections (USD Millions)
| Industry | Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Financial Services | 150 | 175 | 200 |
| Healthcare | 120 | 140 | 165 |
| Retail | 80 | 95 | 110 |
| Manufacturing | 100 | 120 | 145 |
Note: These figures are illustrative and based on current market trends. Actual spending may vary depending on specific factors.
Geographic Variations in IT Spending Growth
The global IT spending landscape is far from uniform. Different regions experience varying rates of growth and adoption, influenced by diverse economic conditions, technological priorities, and government policies. Understanding these regional disparities is crucial for businesses seeking to navigate the complexities of the international market and for policymakers striving to foster technological advancement.
Regional IT Spending Growth Expectations
Regional variations in IT spending are significant. While North America consistently holds a substantial portion of global IT expenditure, other regions are experiencing rapid growth. Asia, in particular, is projected to witness robust expansion due to its burgeoning economies and large tech sectors. Europe, though facing economic headwinds in certain areas, is expected to maintain a steady, if not spectacular, rate of growth in IT spending.
These fluctuations are largely driven by a confluence of economic forces and technological innovations unique to each region.
Factors Influencing Regional Variations
Several factors contribute to the divergence in IT spending patterns across the globe. Economic stability and growth rates within each region play a critical role. Stronger economies often demonstrate higher IT investment levels. Government initiatives, including subsidies and tax breaks, significantly influence IT spending. For example, government mandates for digital transformation in public services can substantially increase IT budgets in those regions.
Furthermore, technological adoption rates and local industry needs dictate IT spending priorities. Countries with strong manufacturing sectors, for instance, might allocate more resources to industrial automation software than countries with a predominantly service-based economy.
Comparing IT Spending Strategies
Different countries employ varied strategies for IT spending. Some nations prioritize investing in foundational infrastructure, such as 5G networks and cloud computing resources, to support broader technological advancements. Others focus on specific industry sectors, such as healthcare or finance, where advanced IT solutions are crucial. These differences are directly tied to national priorities and strategic goals. For instance, the US often emphasizes research and development in emerging technologies, while China prioritizes industrial applications of IT.
These strategies, in turn, impact the overall IT spending profile of the region.
Impact of Government Policies on IT Spending
Government policies exert a substantial influence on IT spending within a region. Regulations regarding data privacy and security, for instance, can drive the adoption of specific IT solutions. Furthermore, government mandates for digital transformation in public sectors often stimulate IT spending. Subsidies and tax incentives for technology adoption also significantly impact IT budgets. For example, tax credits for cloud adoption can stimulate investment in cloud-based IT services within a region.
IT Spending Growth Predictions by Region (2024-2028)
| Region | Projected IT Spending Growth (CAGR %) | Key Factors |
|---|---|---|
| North America | 6-7% | Strong economy, continued digital transformation efforts |
| Europe | 5-6% | Steady economic growth, focus on digitalization in some sectors |
| Asia Pacific | 8-9% | Rapid economic expansion, substantial investments in infrastructure and technology |
| Latin America | 7-8% | Rising middle class, increasing demand for digital services |
| Middle East & Africa | 7-9% | Strong economic growth in some countries, investment in infrastructure projects |
Note: CAGR stands for Compound Annual Growth Rate. These figures are estimates and may vary based on economic fluctuations and unforeseen events.
IT spending growth is predicted to be robust, fueled by a need for better security and efficiency. However, recent events, like the spotlight forces exit of new Zealand spam king here , highlight the ever-evolving cybersecurity landscape. This emphasizes the importance of staying ahead of potential threats and adapting strategies for future IT spending. Ultimately, the predicted growth direction remains positive, but with a strong emphasis on proactive security measures.
Challenges and Opportunities for IT Spending Growth
The projected growth in IT spending hinges on organizations effectively navigating a complex landscape of opportunities and challenges. This requires a proactive approach to identifying and mitigating risks, while simultaneously leveraging emerging technologies and market trends. Understanding both the potential pitfalls and the promising avenues for expansion is crucial for success.The future of IT spending is not a straightforward trajectory; rather, it’s a dynamic interplay of factors that can either propel growth or create roadblocks.
Companies must anticipate these challenges and embrace the opportunities to maintain a competitive edge.
Potential Obstacles to Achieving Projected Growth
Several factors could hinder the projected IT spending growth. Economic downturns, inflation, and geopolitical instability can significantly impact budget allocations. Organizations may prioritize essential operational needs over discretionary IT investments, especially during periods of uncertainty. Furthermore, the increasing complexity of IT infrastructure, coupled with the need for skilled personnel, can create significant barriers to entry and implementation.
These challenges can manifest as increased project costs, delays, and ultimately, reduced ROI. For example, the recent global chip shortage impacted numerous industries, demonstrating how external factors can disrupt IT spending plans.
Opportunities Driving IT Spending Growth
Conversely, several powerful forces are driving IT spending growth. The increasing demand for cloud-based solutions, fueled by the rise of remote work and the need for scalability, is a prime example. The need for enhanced data analytics capabilities to extract insights from massive datasets, and the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning into business processes, are further catalysts for IT investments.
These advancements drive productivity gains, improve decision-making, and create new revenue streams. For instance, companies are increasingly investing in AI-powered tools to streamline customer service and automate tasks, highlighting the growing demand for such technology.
Strategies for Navigating Challenges and Capitalizing on Opportunities
Organizations can navigate these challenges and capitalize on opportunities by adopting a strategic and proactive approach to IT spending. This involves meticulous planning, accurate forecasting, and a deep understanding of the specific needs and priorities of the organization. Thorough due diligence in vendor selection, a focus on cloud-based solutions for scalability, and investment in training programs to develop internal IT expertise are vital components of this strategy.
A flexible and adaptable approach to IT spending, allowing for adjustments based on changing market conditions, is also critical. Companies should also consider diversifying their technology sources to mitigate risks associated with supply chain disruptions.
Strategies for Mitigating IT Spending Risks
Implementing effective risk mitigation strategies is crucial to protect investments and ensure successful IT projects. Conducting thorough cost-benefit analyses for proposed projects, establishing clear project timelines and milestones, and implementing robust change management processes can significantly reduce the risks associated with IT spending. Furthermore, building strong relationships with trusted technology partners and exploring alternative solutions can also help mitigate potential disruptions.
For instance, investing in redundancy and disaster recovery solutions can protect critical data and systems from unforeseen events.
Table of Potential Challenges and Opportunities for IT Spending
| Challenges | Opportunities |
|---|---|
| Economic downturns | Growth in cloud-based solutions |
| Inflationary pressures | Data analytics and AI adoption |
| Geopolitical instability | Automation and process improvement |
| Skill shortages | Improved customer experience |
| Project complexity | Innovation and new revenue streams |
| Supply chain disruptions | Scalability and agility |
Future Trends Shaping IT Spending: It Spending Growth Direction Predicted
The IT spending landscape is in constant flux, driven by technological advancements, evolving business needs, and shifting economic conditions. Understanding these future trends is crucial for businesses and investors to strategize effectively and capitalize on emerging opportunities. This section delves into the long-term implications of current trends, predicts future spending evolution, and explores the role of emerging trends in shaping IT spending growth.
Long-Term Implications of Current Trends
Current trends in cloud computing, artificial intelligence, and the Internet of Things (IoT) are significantly impacting IT spending patterns. The increasing adoption of cloud-based services is driving a shift from on-premises infrastructure to subscription-based models. This transition affects both capital expenditure and operational costs. Similarly, AI integration across various sectors is demanding investments in specialized hardware and software.
The IoT’s growth is leading to increased demand for data storage, processing, and management solutions. These long-term implications will continue to reshape the IT spending landscape, with a stronger focus on cloud services, AI-powered tools, and data-centric solutions.
Predictions about Future Evolution of IT Spending
Future IT spending will be characterized by a continued shift towards cloud-based solutions and an increasing emphasis on data-driven strategies. Businesses are increasingly adopting cloud platforms for scalability, cost-effectiveness, and agility. This trend is anticipated to accelerate in the coming years, as more organizations migrate existing applications and infrastructure to the cloud. Data analytics and machine learning are also poised to play a pivotal role, with organizations investing in advanced analytics tools and skilled personnel to extract insights from their data.
The focus will shift from simple data storage to sophisticated data processing and interpretation, leading to increased spending on related technologies.
Role of Emerging Trends in Shaping IT Spending Growth
Emerging trends like blockchain, quantum computing, and the metaverse are expected to significantly impact IT spending in the coming years. Blockchain technology, with its potential for secure and transparent transactions, is attracting investments in related infrastructure and development. Quantum computing, while still in its nascent stages, holds the promise of revolutionizing fields like drug discovery and materials science, necessitating significant investments in research and development.
The metaverse, a virtual world with immersive experiences, is driving demand for advanced networking, graphics processing, and user interface technologies.
Potential Disruptions to the Current IT Spending Landscape
The current IT spending landscape is vulnerable to disruptions from various factors. Cybersecurity threats, with their growing sophistication and frequency, are compelling organizations to invest heavily in robust security measures. The rise of open-source technologies, while potentially lowering costs, may necessitate investments in expertise and support to effectively utilize these solutions. Changes in regulatory environments, particularly concerning data privacy and security, will also impact IT spending decisions.
Future Trends Affecting IT Spending (Next 5-10 Years)
Several factors could significantly impact IT spending in the next five to ten years. The evolution of cloud computing, including the adoption of serverless computing and edge computing, will influence spending. The increasing importance of cybersecurity and the need for robust data protection will lead to higher security-related investments.
| Trend | Impact on IT Spending | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Cloud Computing (Serverless, Edge Computing) | Increased spending on cloud services, reduced on-premises infrastructure | Companies migrating workloads to serverless platforms, setting up edge computing nodes for real-time data processing |
| AI/ML Integration | Investments in AI-powered tools, data scientists, and specialized hardware | Implementing AI-driven automation solutions, enhancing decision-making with machine learning models |
| Cybersecurity Threats | Higher spending on security solutions, security personnel, and threat intelligence | Deploying advanced threat detection systems, implementing security awareness training programs |
| Data Privacy Regulations | Investments in data security infrastructure and compliance measures | Implementing data anonymization techniques, adhering to stricter data privacy regulations |
| Quantum Computing | Investments in research, development, and specialized hardware | Developing quantum algorithms, designing quantum computing infrastructure |
Conclusion
In conclusion, the predicted IT spending growth direction is multifaceted, influenced by a complex interplay of economic factors, technological advancements, and industry-specific demands. While growth is anticipated across various sectors, challenges like economic instability and evolving regulatory landscapes must be considered. Understanding these nuances is critical for organizations seeking to navigate the future of IT investment and capitalize on emerging opportunities.
The analysis offers valuable insights for informed decision-making in the dynamic IT sector.