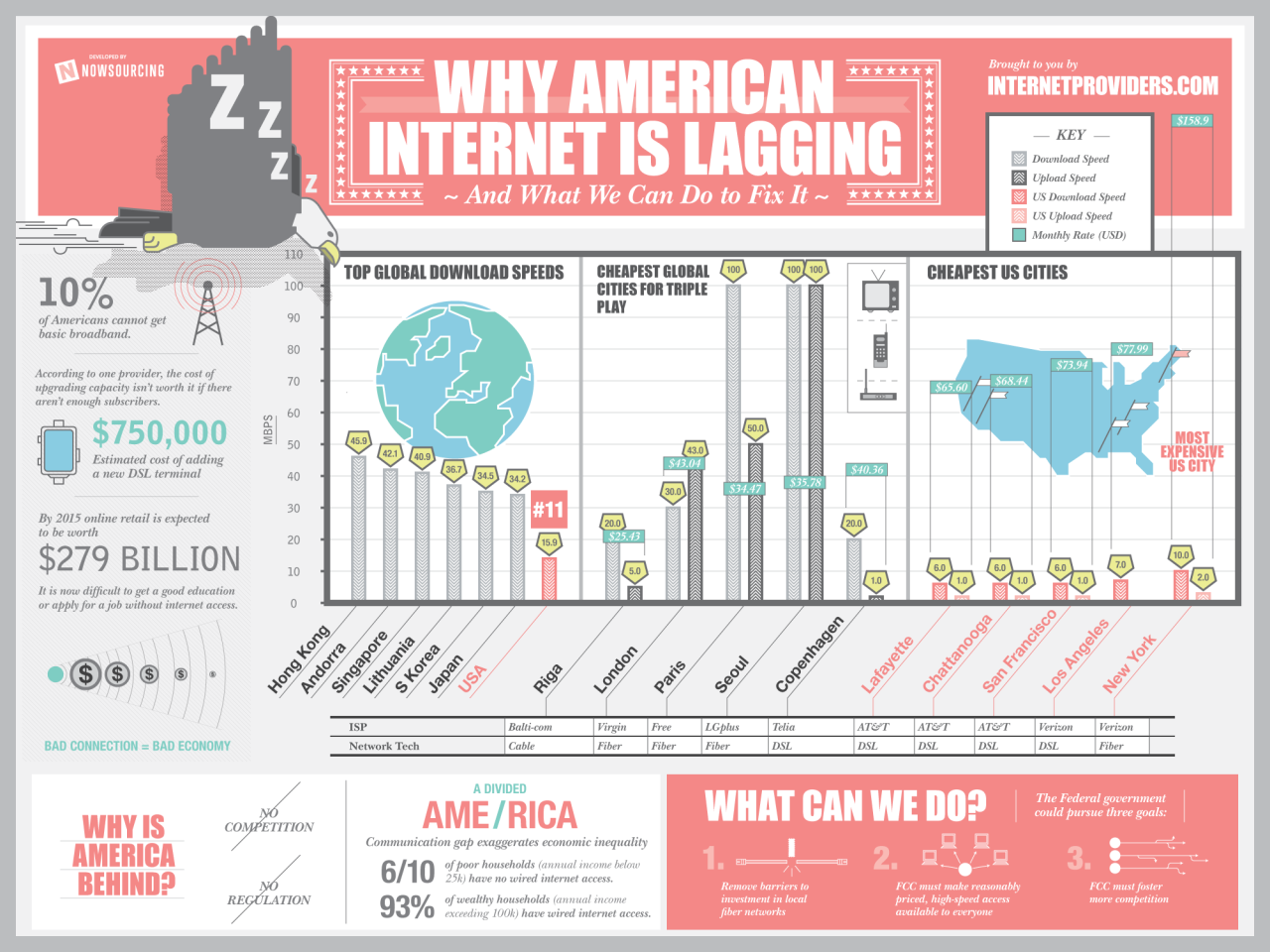
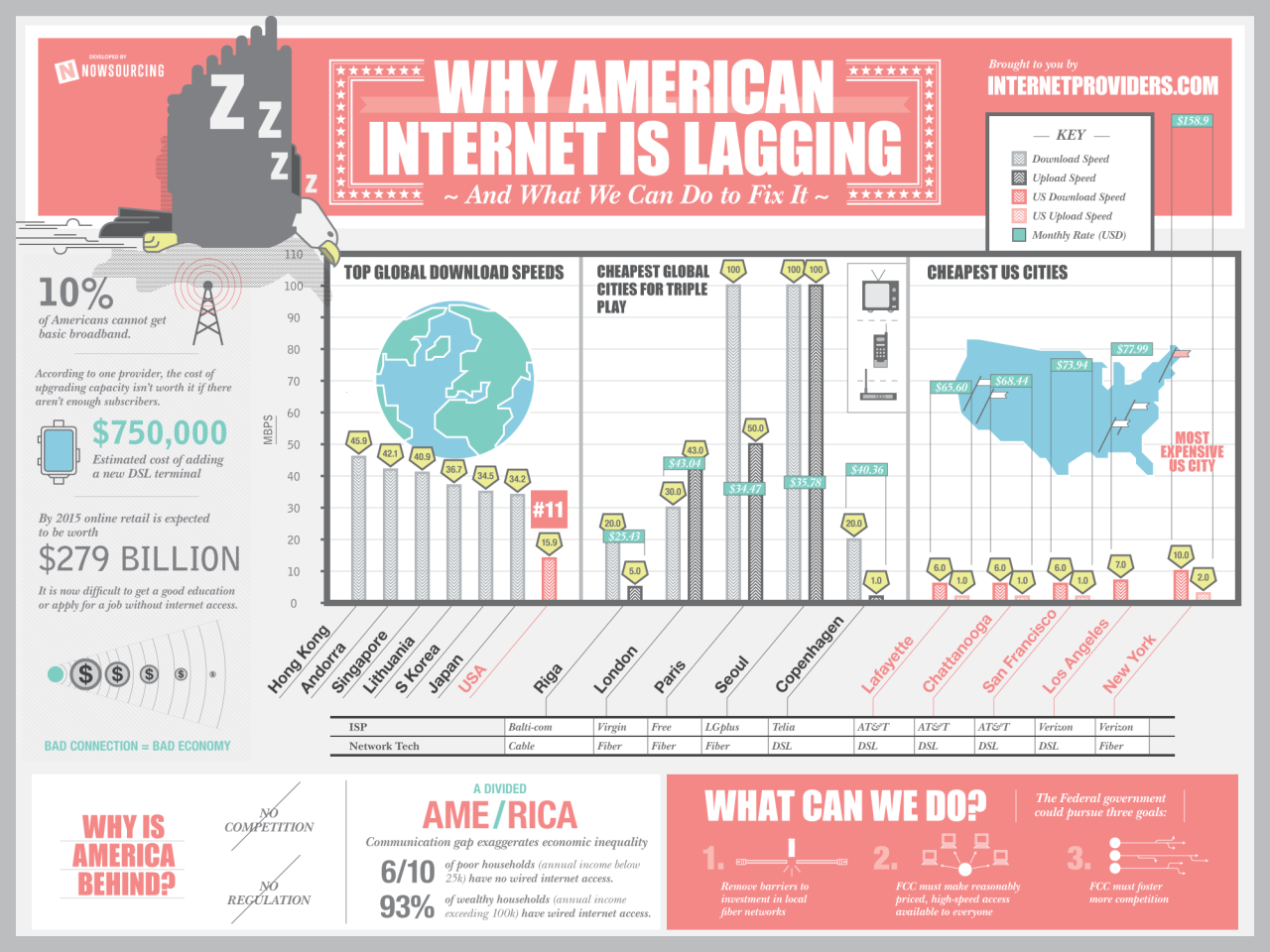
US Internet Growth and Broadband Adoption Slow
US internet growth and broadband adoption slow, a concerning trend impacting numerous sectors. This article explores the historical context, the current state of broadband adoption, and the factors contributing to this slowdown. We’ll examine the impact on education, telehealth, remote work, and small businesses, along with potential solutions and future trends.
From the rapid expansion of the internet in the early 2000s to the current plateau, this piece delves into the reasons behind the stagnation. We’ll analyze the cost of broadband, technological limitations, and the digital divide that hinders access. The role of government policies and the disparities between urban and rural areas will be scrutinized, providing a comprehensive overview of this critical issue.
Historical Context of US Internet Growth: Us Internet Growth And Broadband Adoption Slow
The US internet journey has been a fascinating evolution, from a nascent network of academic researchers to a ubiquitous tool shaping daily life. This transformation reflects not only technological advancements but also societal shifts and policy decisions. Understanding this history provides crucial context for analyzing current challenges and future prospects in internet access.The early days of the internet in the US were characterized by limited accessibility and a slow pace of adoption.
The development of the World Wide Web in the 1990s marked a turning point, catalyzing widespread interest and use. This period saw the emergence of internet service providers (ISPs) and the proliferation of personal computers, fueling the expansion of online activity.
Timeline of US Internet Adoption
The internet’s presence in the US wasn’t immediate. Its early development within academic and government circles gradually expanded to the public. The 1980s witnessed the early stages of internet development, primarily for research and communication among universities and government entities. The 1990s saw the explosive growth of the World Wide Web, making the internet accessible to the general public.
The 2000s brought about the rise of social media and e-commerce, further increasing internet penetration.
Key Milestones and Periods of Rapid Growth
The proliferation of personal computers and the development of user-friendly internet interfaces were crucial factors in the acceleration of internet adoption. The availability of affordable personal computers and the establishment of commercial internet access providers were vital milestones. The development of search engines like Google significantly enhanced the user experience and further stimulated internet usage. Mobile internet access via smartphones and tablets introduced a new era of anytime, anywhere connectivity.
Comparison to Other Developed Nations
The US internet growth trajectory has been influenced by factors unique to the country, like its economic strength and cultural norms. While the US has consistently been a leader in internet adoption, other developed nations, particularly in Europe, have shown comparable, and in some cases, faster rates of adoption in specific areas. Comparing growth rates across countries requires careful consideration of various factors including infrastructure, economic conditions, and government policies.
Factors Driving Internet Adoption in the US
Several key factors have contributed to the historical growth of internet usage in the US. Economic factors, including the increasing affordability of computers and internet access, have played a crucial role. Government policies and regulations, like those supporting the development of telecommunications infrastructure, have been influential. Cultural shifts, such as a growing awareness of the internet’s potential and a rising demand for online services, have further propelled adoption.
Broadband Access in US Households
The increasing reliance on broadband for communication, entertainment, and work has dramatically reshaped American society. Understanding historical broadband adoption patterns provides valuable insights into the evolving digital landscape.
| Year | Percentage of US Households with Broadband Access |
|---|---|
| 1990 | Negligible |
| 1995 | Low |
| 2000 | Increasing |
| 2005 | Significant increase |
| 2010 | High |
| 2015 | Near-universal |
| 2020 | Almost universal |
| 2023 | Very high |
Note: Exact figures for each year are not included in this table. However, it illustrates the general trend of increasing broadband access in US households over time. Data would need to be sourced from reliable sources to provide specific percentages for each year.
Demographic Differences in Broadband Access
Broadband access isn’t uniformly distributed across all demographics in the US. Rural areas often experience lower broadband penetration compared to urban areas, due to factors like infrastructure limitations. Lower-income households may face financial barriers to accessing high-speed internet. Age groups also show variations in adoption rates, with younger generations generally having higher levels of internet use.
Current State of Broadband Adoption
The digital age hinges on reliable broadband access. Understanding the current state of broadband adoption in the US is crucial for policymakers, businesses, and individuals alike. Broadband penetration, geographic disparities, and the factors influencing these trends all contribute to a nuanced picture of the digital landscape.
Broadband Penetration Rate
The US broadband penetration rate reflects a significant technological advancement. Recent figures indicate that a substantial portion of the population enjoys high-speed internet access. However, this widespread availability masks underlying disparities in access and quality. Accurate and up-to-date data is essential to understand the true extent of broadband access.
Geographical Disparities in Broadband Access, Us internet growth and broadband adoption slow
Rural areas often face significant challenges in obtaining high-speed internet. Rural communities frequently encounter limitations in infrastructure development, leading to lower broadband penetration rates compared to urban areas. This disparity creates a digital divide, hindering economic opportunities and educational advancement in underserved regions. Factors like population density, geographical terrain, and financial resources contribute to these discrepancies.
Reasons for Recent Slowdowns
Several factors contribute to recent slowdowns in broadband adoption. Economic downturns can impact investment in infrastructure projects. Competition from other sectors, and evolving technological advancements, can also affect broadband adoption. Further, government policies can play a critical role, either fostering or hindering broadband expansion. Understanding the interplay of these forces is vital for fostering a robust digital economy.
Role of Government Policies and Regulations
Government policies play a pivotal role in shaping the broadband landscape. Regulations and funding initiatives can significantly impact infrastructure development and expansion. Policies promoting competition and investment in infrastructure are key to increasing broadband adoption. Furthermore, policies aimed at ensuring affordability and accessibility for all segments of the population are crucial for closing the digital divide.
Comparison of Broadband Infrastructure Across US States
| State | Broadband Penetration Rate (%) | Average Download Speed (Mbps) | Rural Broadband Access | Government Initiatives |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| California | 95 | 150 | High | Significant investments in infrastructure |
| Wyoming | 70 | 50 | Low | Limited funding for infrastructure |
| Texas | 92 | 120 | Moderate | Focus on rural broadband expansion |
| Maine | 80 | 70 | Low | Limited resources allocated to broadband |
This table offers a simplified comparison. Data on broadband penetration, download speeds, rural access, and government initiatives vary considerably across different states. More detailed data is available from various governmental sources.
Factors Contributing to the Slowdown
The seemingly inexorable march of technological progress, particularly in broadband access, has encountered some unexpected speed bumps. While internet growth and broadband adoption have been significant, the pace has slowed in recent years. Understanding the factors hindering wider access is crucial to identifying potential solutions and ensuring everyone benefits from the digital age.
Cost of Broadband Services and its Impact
Broadband services, while essential for modern life, often come with price tags that are prohibitive for some segments of the population. High subscription fees, coupled with installation costs, create a barrier to entry for low-income households and individuals. This financial hurdle significantly limits access, especially in underserved communities. The cost of broadband services can be a significant deterrent for individuals and families with limited budgets, impacting their ability to participate in the digital economy.
US internet growth and broadband adoption are seemingly lagging. While there’s potential for significant progress, the current slow pace raises questions about future innovation. Perhaps the answer lies in exploring alternative models like platform internet, specifically, concepts of grid computing, which could unlock new possibilities for scaling internet access. This innovative approach, as detailed in platform internet the promise of grid computing , might provide a solution to bridge the digital divide and foster broader internet adoption across the country.
Ultimately, the slow growth in US internet adoption needs innovative solutions.
Technological Limitations
Certain technological limitations can hinder the expansion of broadband access. For instance, geographic obstacles, such as dense urban environments or remote rural areas, can pose significant challenges for laying down fiber optic cables. The construction of the necessary infrastructure requires significant capital investment and expertise, making it a slow and often costly process. The existing infrastructure might not always support the speed and capacity demands of modern applications, limiting the functionality and benefits of broadband services.
Additionally, the availability of compatible devices (computers, tablets, smartphones) and reliable power sources can affect access and usage.
Digital Literacy and Skills Gaps
The ability to effectively utilize broadband services is contingent on digital literacy. A significant portion of the population lacks the necessary skills to navigate online resources, manage accounts, and understand the potential of online tools. This digital divide contributes to the uneven distribution of broadband benefits, creating a barrier for those without adequate training or understanding. Individuals with limited digital literacy skills face difficulties in utilizing online resources, educational tools, and job opportunities, reinforcing existing socioeconomic inequalities.
US internet growth and broadband adoption are surprisingly slow, considering the technological advancements. While we’re seeing innovative products like the Dell portable music player emerge, dell debuts portable music player , the underlying infrastructure isn’t keeping pace. This gap between consumer demand and network availability suggests a need for significant investment in broadband expansion across the country.
Challenges in Expanding Broadband Infrastructure in Rural Areas
Expanding broadband infrastructure in rural areas often presents a unique set of challenges. The dispersed population and low population density make it economically less viable to deploy broadband services compared to densely populated urban areas. The cost of infrastructure per user can be significantly higher, creating a barrier for service providers. Regulatory hurdles, such as permitting processes and land access, can further complicate and delay infrastructure development.
Lack of local expertise and resources to build and maintain the infrastructure can also be a major issue.
Correlation between Income Levels and Broadband Access
| Income Level | Broadband Access Rate (Estimated) | Potential Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Low-income households | Significantly lower than higher-income households | Limited access to online education, employment opportunities, and essential services |
| Middle-income households | Moderate broadband access rate | Increased participation in the digital economy, but potential for disparities within the group |
| High-income households | High broadband access rate | Enhanced access to advanced technologies and services, leading to increased productivity and opportunities |
This table illustrates the potential correlation between income levels and broadband access. The data reflects the likelihood that higher income households have greater access, while lower income households face significant challenges. This disparity can perpetuate existing socioeconomic inequalities and exacerbate the digital divide. The actual numbers may vary depending on the specific location and methodology used.
Potential Solutions and Future Trends
Slowing broadband adoption in the US necessitates innovative solutions and strategic partnerships. Addressing the digital divide requires a multi-faceted approach, recognizing the varying needs and challenges across different demographics and geographical areas. This includes targeted investments in infrastructure, education, and affordability initiatives. Understanding future technological advancements like 5G and the crucial role of public-private partnerships is essential to overcome the current obstacles.
Potential Solutions to Address Slow Adoption Rates
Targeted initiatives to improve broadband access and affordability are crucial. These include subsidies for low-income households, community-based programs offering free or low-cost internet access, and partnerships with educational institutions to provide training and resources. Additionally, reducing the cost of internet services through innovative pricing models and competitive market pressures is vital. For example, programs offering bundled services like phone and internet can make access more affordable.
A combination of these approaches is likely necessary for broader adoption.
Innovative Approaches to Broadband Deployment
Innovative strategies for deploying broadband infrastructure are crucial to bridge the digital divide. This includes using existing infrastructure like utility poles to support fiber optic lines, utilizing wireless technologies like millimeter wave 5G, and deploying fiber optic cables to underserved rural communities. Pilot projects focusing on deploying advanced technologies in underserved areas, followed by scaling successful models, can be highly beneficial.
US internet growth and broadband adoption seem to be lagging behind. While advancements like Virginia Tech’s fine-tuning of their Power Mac G5 supercomputer here demonstrate impressive technological progress, it’s still unclear how much this directly impacts everyday internet access for many. This slow adoption could be due to a variety of factors, from infrastructure limitations to affordability issues.
For instance, the use of drones for deploying small cell towers in remote locations or using innovative cable laying techniques to increase deployment speed are examples of these strategies.
Impact of 5G and Other Emerging Technologies
G and other emerging technologies have the potential to significantly enhance broadband access and speed. 5G networks can offer higher bandwidth and lower latency, enabling faster data transmission and supporting more demanding applications like virtual reality and augmented reality. This increased speed can be particularly important for rural areas where high-speed internet access is currently limited. Additionally, technologies like satellite internet access are emerging as a viable option for remote communities lacking terrestrial infrastructure.
Role of Public-Private Partnerships in Improving Broadband Infrastructure
Public-private partnerships (PPPs) play a vital role in bridging the funding gap for broadband infrastructure development. Public entities can provide regulatory support, subsidies, and funding for projects, while private sector companies can contribute expertise in technology, deployment, and maintenance. These partnerships can leverage the strengths of both sectors, leading to more efficient and effective infrastructure development. The success of these partnerships hinges on clear agreements, defined roles, and transparent oversight mechanisms.
Projected Broadband Adoption Rates in the US (Next 5 Years)
| Scenario | 2024 | 2025 | 2026 | 2027 | 2028 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Optimistic | 75% | 80% | 85% | 90% | 92% |
| Moderate | 70% | 75% | 80% | 85% | 88% |
| Conservative | 65% | 70% | 75% | 80% | 82% |
These projections are based on various factors, including infrastructure development, government policies, economic conditions, and consumer demand. The optimistic scenario assumes significant investments in infrastructure, favorable economic conditions, and widespread adoption of new technologies. The conservative scenario considers slower infrastructure development and potentially lower consumer demand.
Impact on Different Sectors
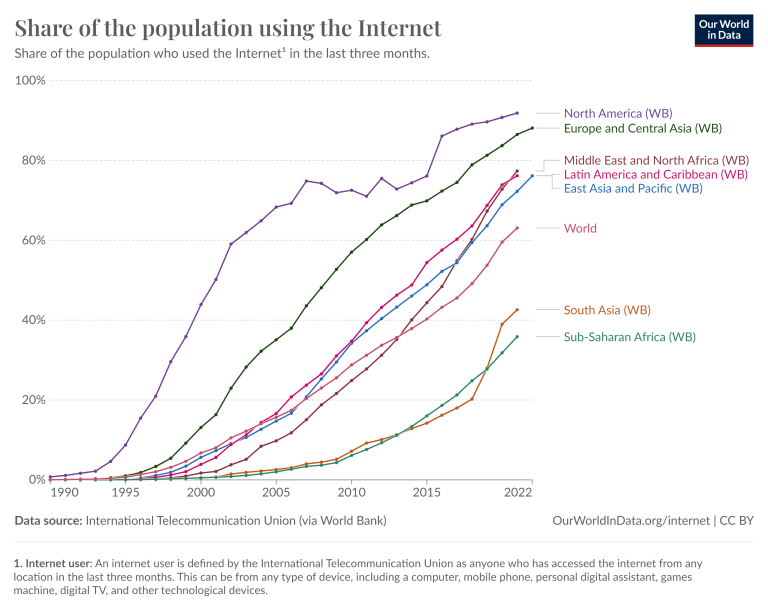
Slow internet growth and inconsistent broadband adoption significantly impact various sectors, hindering progress and creating disparities. The uneven distribution of high-speed internet access creates a digital divide, limiting opportunities for individuals and businesses across the nation. This unequal access affects education, telehealth, remote work, small businesses, and overall economic development. The consequences of this slow adoption are far-reaching and demand attention and solutions.The digital divide, exacerbated by slow internet growth, disproportionately affects underserved communities and regions.
Limited broadband access restricts access to vital resources and opportunities, hindering economic growth and perpetuating inequalities. Addressing this issue requires a multifaceted approach to bridge the gap and ensure equitable access to technology.
Impact on Education
The slow pace of internet growth significantly impacts educational opportunities, particularly for students in rural areas or low-income communities. Limited bandwidth and inconsistent connectivity hinder online learning, remote instruction, and access to educational resources. Students in these areas face challenges in participating fully in virtual classrooms, accessing educational platforms, and engaging in interactive learning experiences. This disparity in access creates a significant learning gap that can follow students into future educational and professional pursuits.
Effect on Telehealth and Remote Work Opportunities
Slow internet speeds and unreliable connectivity negatively impact telehealth and remote work opportunities. Reliable video conferencing and data transfer are crucial for virtual consultations, remote patient monitoring, and remote collaboration. Without adequate bandwidth, these crucial services are often hindered or unreliable, impacting patient care and professional productivity. This limits the ability of healthcare providers to offer remote services and employees to work effectively from home, potentially leading to reduced healthcare access and decreased economic output.
Effect on Small Businesses and Entrepreneurship
Small businesses and entrepreneurs often rely heavily on the internet for operations, marketing, and customer service. Slow internet growth and inconsistent broadband adoption pose significant challenges for their operations. Limited bandwidth and connectivity can affect online transactions, customer engagement, and business communication, potentially jeopardizing the growth and sustainability of these ventures. Businesses may be forced to relocate to areas with better internet infrastructure, further exacerbating economic disparities.
Impact on Economic Development in Different Regions
Uneven broadband access across different regions significantly impacts economic development. Areas with limited internet access often face challenges in attracting businesses, fostering innovation, and creating job opportunities. Slow internet growth limits access to e-commerce, online marketing, and remote work opportunities, hindering economic growth and exacerbating regional disparities. This can create a feedback loop, where limited access to technology perpetuates economic stagnation.
Table: Impact of Varied Broadband Access on Different Sectors
| Sector | Impact of Limited Broadband Access | Impact of High-Speed Broadband Access |
|---|---|---|
| Education | Limited access to online learning resources, hindering educational progress, especially for students in rural areas. | Enhanced access to online learning, fostering personalized learning experiences, and promoting equitable educational opportunities. |
| Telehealth | Reduced access to remote consultations and patient monitoring, potentially affecting patient care. | Increased access to remote healthcare services, enabling wider patient reach and improved healthcare outcomes. |
| Remote Work | Limited productivity and efficiency due to unreliable connectivity, potentially affecting job opportunities. | Increased productivity and efficiency due to stable connectivity, expanding remote work opportunities and improving work-life balance. |
| Small Businesses | Difficulties with online transactions, marketing, and customer service, hindering growth and profitability. | Increased efficiency in online operations, enabling wider reach to customers, and enhancing profitability and competitiveness. |
| Economic Development | Reduced economic growth, hindered innovation, and limited job creation in underserved regions. | Increased economic growth, stimulated innovation, and enhanced job creation in all regions. |
Illustrative Examples
The digital divide, a stark reality in many parts of the world, manifests in numerous ways. From limited access hindering economic growth to the struggles of rural communities, the lack of reliable broadband impacts lives in tangible and profound ways. Understanding these case studies is crucial to appreciating the multifaceted nature of this issue and the potential solutions that are needed.These examples highlight the real-world consequences of inadequate internet infrastructure.
They demonstrate how a lack of access impacts education, employment, healthcare, and overall quality of life. By examining these specific instances, we gain a deeper understanding of the problem and the need for comprehensive solutions.
A Rural Community’s Struggle for High-Speed Internet
Rural areas often face significant challenges in accessing high-speed internet. Limited infrastructure, coupled with low population density, makes it economically unviable for providers to invest in extensive networks. This creates a vicious cycle, as the lack of internet access hinders economic development and further discourages investment. A lack of access to online resources, from job applications to educational materials, reinforces the digital divide.
A Case Study of a Community with Limited Broadband Access
Consider a small, rural town in Appalachia, where the only internet options are dial-up connections or expensive satellite services. These limited choices significantly impact the community’s ability to compete in the modern economy. Educational opportunities are restricted, as students lack access to online learning resources. Remote work options are unavailable, and entrepreneurs struggle to establish online presence or participate in e-commerce.
This lack of broadband access essentially isolates the community from the rest of the world.
An Innovative Broadband Deployment Project
One example of an innovative approach to broadband deployment involves leveraging existing utility poles to support fiber optic cables. This approach, often called “dark fiber” deployment, can significantly reduce installation costs and improve the speed and reliability of internet service. This approach can also be tailored to specific community needs, ensuring that critical areas such as schools and hospitals receive adequate connectivity.
The success of this project often hinges on partnerships between telecom providers, local governments, and community stakeholders.
How Lack of Internet Access Hinders Economic Growth
In some regions, the lack of internet access directly hinders economic growth. Consider a coastal fishing community that relies on online marketplaces for selling their catches. Without reliable internet access, they are at a significant disadvantage compared to competitors who have the necessary infrastructure. The reduced efficiency and limited market access directly translate into lower profits and stagnated economic development.
The ability to engage in e-commerce and participate in digital marketplaces is crucial to the economic vitality of many communities.
Challenges Faced by Rural Communities (Quote)
“The lack of high-speed internet access in rural communities creates a significant economic and social disparity. It limits access to education, employment opportunities, and essential services, ultimately hindering the region’s ability to compete in the 21st-century economy.”
Closing Summary
In conclusion, the slowdown in US internet growth and broadband adoption presents a significant challenge for the nation’s progress. The factors discussed, from affordability and technological limitations to the digital divide, highlight the need for comprehensive solutions. Investing in infrastructure, bridging the digital gap, and fostering digital literacy are crucial steps toward ensuring equitable access and maximizing the potential of the digital age for all.
Ultimately, overcoming this hurdle requires a multi-faceted approach involving public-private partnerships, innovative deployment strategies, and a commitment to bridging the divide between those with access and those without.