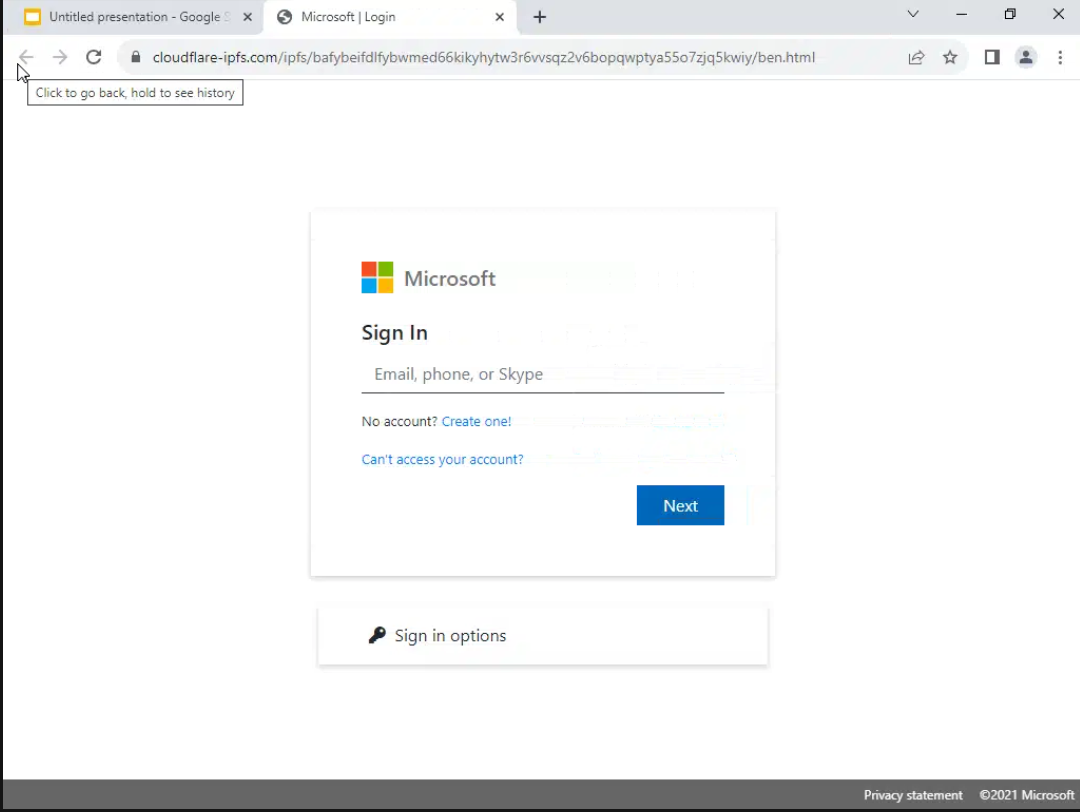
Microsoft Looks for Trust on Email Caller ID
Microsoft looks for trust on e mail caller id – Microsoft looks for trust on email caller ID, striving to build a secure and reliable email environment. This involves implementing various verification methods, examining current policies, and considering public perception. The company’s approach to email caller ID verification is critical in combating impersonation and phishing attempts, maintaining trust with diverse user groups, and adapting to future trends in email authentication.
This analysis delves into the methods Microsoft uses to verify email caller IDs, highlighting the security implications and effectiveness of different verification techniques. It also explores Microsoft’s policies and procedures, user expectations, and industry best practices. The discussion concludes with a look at emerging trends and Microsoft’s potential future strategies for email caller ID verification.
Email Caller ID Verification Methods
Verifying the authenticity of email caller IDs is crucial for maintaining the security and integrity of online communication platforms. This process is becoming increasingly important as sophisticated phishing and spoofing techniques proliferate, making it challenging to distinguish legitimate communications from fraudulent ones. A robust verification system is essential to protect users from scams and maintain trust in the platform.
Verification Methods Employed by Microsoft
Microsoft likely employs a multifaceted approach to verifying email caller IDs, leveraging several methods to enhance the accuracy of verification and mitigate the risk of impersonation. These methods, while not publicly disclosed in detail, can be categorized and analyzed based on common industry practices.
Methods for Verifying Email Caller IDs
Various techniques can be employed to authenticate email caller IDs. These techniques range from simple to complex, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. Effective verification requires a balanced approach that considers both security and user experience.
- Domain Name Verification: This method involves checking if the sender’s email address originates from a legitimate domain. This is often done by examining the DNS records associated with the domain. It is a relatively simple and fast technique, but can be circumvented by spoofing domain names or using compromised domains. The security implication is moderate as it only verifies the domain, not the identity of the individual sending the email.
Microsoft’s push for trust in email caller ID is a fascinating development. It’s a bit like the ongoing domain name disputes, a constant battle for legitimacy and recognition in the digital space, which can be seen in domain name disputes past present future. Ultimately, both issues highlight the crucial need for clear, verifiable identification online, to build trust and prevent fraud.
- Sender Policy Framework (SPF) Records: SPF records specify which mail servers are authorized to send email on behalf of a particular domain. By checking the SPF record, a recipient can verify if the sender is indeed authorized. This enhances the security posture by reducing the likelihood of spoofing. However, SPF records can be manipulated, and a compromised or outdated record might not detect a malicious sender.
The effectiveness depends on the accuracy and maintenance of the SPF records.
- DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) Signatures: DKIM uses cryptographic signatures to verify the integrity of the email and ensure that it hasn’t been tampered with during transit. This adds an extra layer of security, but it requires cooperation from the sender and recipient. DKIM signatures can be easily forged, and their effectiveness depends on the sender’s adherence to the standard.
- DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance) Records: DMARC policies provide a framework for coordinating SPF and DKIM, allowing recipients to act on the results. This approach allows for more comprehensive verification by combining multiple techniques. DMARC policies are becoming increasingly prevalent, offering a significant enhancement in verification capabilities. A weakness is the reliance on the cooperation of the sender and the potentially lengthy process of implementing and maintaining DMARC.
Microsoft’s push for trust in email caller ID is a fascinating development. It’s all about user security, and the need for verified identities in a digital world. This echoes the importance of trustworthy sources, and reminds me of the recent news that former Sun exec Edward Zander will be leading Motorola. former sun exec edward zander to head motorola This shift in leadership could potentially bring a new perspective to the tech landscape, much like Microsoft’s efforts to bolster email security.
Ultimately, trust is key, both for email and in broader technology sectors.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Integrating MFA can add an additional layer of security by requiring users to authenticate themselves using multiple methods, like passwords, one-time codes, or biometric verification. This makes it considerably harder for malicious actors to impersonate users. The security implications are substantial, but the complexity can impact user experience.
Comparison of Verification Techniques
| Method | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Domain Name Verification | Simple, fast | Easily bypassed, low security |
| SPF Records | Enhanced security, reduced spoofing | Can be manipulated, accuracy depends on records |
| DKIM Signatures | High integrity, tamper-proof | Requires cooperation, can be forged |
| DMARC Records | Comprehensive verification, combines multiple methods | Requires implementation and maintenance, cooperation required |
| MFA | High security, strong authentication | Complexity, user experience impact |
Potential for Fraud or Abuse
Despite these verification methods, fraudulent actors can still exploit vulnerabilities in any single technique. The effectiveness of these methods relies on the integrity of the system, and potential for abuse exists in each method. For instance, compromised accounts or forged credentials can bypass verification mechanisms. Phishing attacks can also manipulate users into revealing sensitive information, thus undermining the effectiveness of any verification method.
Therefore, a multi-layered approach is crucial.
Microsoft’s Approach to Trust and Email Authentication
Microsoft prioritizes email security and user trust, actively combating impersonation and phishing attempts. Their comprehensive approach involves robust authentication protocols and a commitment to continuous improvement in response to evolving threats. This focus on trust extends across diverse user bases, from individual consumers to large enterprises.Microsoft’s email security policies are designed to detect and prevent malicious activities. This involves a multi-layered approach that combines technical solutions with user education and awareness programs.
Their strategies are constantly refined to adapt to the ever-changing landscape of cyber threats.
Microsoft’s Current Policies and Procedures
Microsoft employs a multi-layered approach to verify email sender authenticity. This involves leveraging various authentication mechanisms to ensure that the emails users receive are indeed from legitimate sources. These policies are regularly updated and enhanced to address emerging threats.
Examples of Addressing Impersonation and Phishing Attacks
Microsoft actively monitors for and addresses potential impersonation and phishing attacks. This includes the use of sophisticated algorithms to detect suspicious patterns in email communications. They also utilize machine learning models to identify and flag potentially malicious emails. For instance, if a user receives an email that appears to be from their bank but the sender’s email address is slightly different from the legitimate one, Microsoft’s system flags it as suspicious.
These proactive measures aim to protect users from falling victim to fraudulent schemes.
Challenges in Maintaining Trust Across Diverse User Bases
Maintaining trust across a broad user base presents challenges. Users with varying levels of technical expertise and awareness need consistent and clear communication about email security protocols. Ensuring that the measures employed are accessible and understandable to all users, regardless of their technical background, is crucial. Cultural differences and diverse access to technology also need consideration in designing effective trust-building strategies.
Technical Solutions for Caller ID Authenticity
Microsoft utilizes a range of technical solutions to ensure the authenticity of caller IDs. These include advanced encryption protocols and multi-factor authentication measures. Furthermore, real-time monitoring and analysis of email traffic allow for the identification and blocking of suspicious activity. The integration of machine learning models allows for the adaptation of these technical solutions to emerging threats.
Microsoft’s Email Authentication Protocols
| Protocol | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Sender Policy Framework (SPF) | Verifies the sender’s domain’s authorization to send emails. | Ensuring that emails claimed to be from Microsoft actually originate from Microsoft’s authorized servers. |
| DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM) | Provides digital signatures to authenticate the email’s origin and integrity. | Detecting if an email has been tampered with or altered during transit. |
| DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance) | Provides a mechanism to enforce SPF and DKIM policies, and report on email authentication failures. | Reporting and responding to instances where emails are mis-authenticated. |
| Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) | Adds an extra layer of security to email accounts. | Requiring a second verification step, such as a code sent to a mobile phone, to access email accounts. |
Public Perception and User Experience
Public perception of email caller ID verification is crucial for fostering trust and encouraging adoption. Users’ understanding of the technology and their expectations for security play a significant role in shaping this perception. A positive user experience is paramount for widespread acceptance of these verification methods. This section delves into the public’s perspective on email authentication, considering user expectations and concerns, and analyzing successful and unsuccessful implementations.
Public Perceptions of Email Caller ID Verification
Public perception of email caller ID verification is largely influenced by the perceived benefits and risks associated with the technology. Many users are already familiar with similar concepts in phone calls, and they expect similar levels of protection and convenience in email communication. Positive experiences with caller ID verification on other platforms, like voice calls, create a foundation for positive expectations.
Conversely, negative experiences with flawed or misused caller ID systems can lead to distrust and suspicion. The crucial element is demonstrating the value proposition clearly and securely, emphasizing how it enhances trust and protects against impersonation and spam.
User Expectations and Concerns Regarding Email Caller ID Security
Users expect email caller ID verification to be a robust and reliable security measure. Top concerns often center around the authenticity of the verification process itself. Is it easily spoofed? Can the verification process be manipulated? Furthermore, users are concerned about the potential for misuse, such as identity theft or targeted phishing attacks.
The system should clearly communicate how it works and what measures are in place to prevent fraudulent activities. Users want to know the exact details of the verification method. They want a simple, yet secure system.
Microsoft’s push for trust in email caller IDs is a significant step, but it’s not the only approach to combating spoofing. The recent settlement involving VeriSign’s wildcard service, which brought a call to stop a lawsuit , highlights the importance of robust authentication solutions in the digital landscape. Ultimately, fostering trust in caller IDs, whether for email or phone calls, requires a multi-faceted approach to ensure security and reduce the risk of fraud.
Examples of Successful and Unsuccessful Email Authentication Experiences
Successful email authentication experiences often involve a clear and intuitive verification process, with a strong visual cue indicating the sender’s identity. A good example might be a simple visual indicator (e.g., a verified badge next to the sender’s name) or a two-step verification process that requires both email confirmation and a unique code. Unsuccessful implementations, on the other hand, often lack clear indicators, leading to confusion and a lack of trust.
Poorly designed systems that require excessive steps or provide insufficient information can quickly discourage adoption. An example of a poor experience would be a verification process that requires multiple, confusing steps, or one that doesn’t clearly indicate the identity of the verified sender.
Comparison of User Perceptions Across Different User Groups
Consumer and business perceptions of email caller ID verification can differ significantly. Consumers might prioritize ease of use and a simple, trustworthy verification process. Businesses, however, may place greater emphasis on the technical robustness of the verification method and its ability to prevent sophisticated phishing attempts. Consumers may focus more on the ease of use, while businesses may prioritize security and scalability.
Business users might demand more comprehensive reports and audit trails to monitor the effectiveness of the system.
User Feedback on Microsoft’s Approach to Email Caller ID Verification
| User Group | Positive Feedback | Negative Feedback |
|---|---|---|
| Consumers | Easy to understand; quick verification process; feels secure. | Confusing process; too many steps; not enough visual cues. |
| Businesses | Robust verification; detailed reports; effective at preventing phishing. | Integration issues with existing systems; high initial setup cost. |
| Technical Experts | Impressed with the underlying security architecture; effective against common attacks. | Limited information about the system’s algorithm; concerns about potential vulnerabilities. |
Industry Best Practices and Standards: Microsoft Looks For Trust On E Mail Caller Id
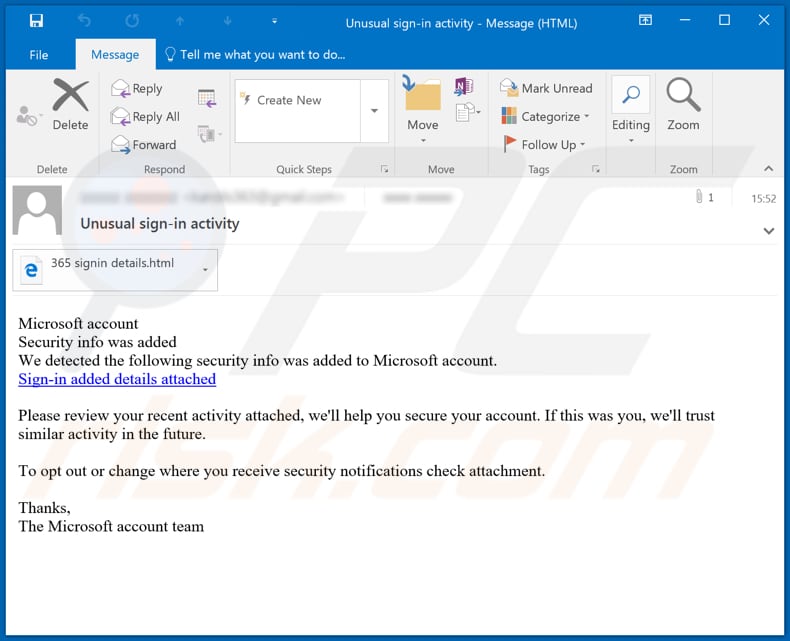
Email caller ID verification is a crucial component of modern email security, demanding adherence to industry best practices and standards. Effective verification minimizes spoofing and phishing attempts, protecting users from fraudulent communications. Understanding these standards and how companies implement them provides valuable context for evaluating Microsoft’s approach.
Email Authentication Protocols
Email authentication protocols are fundamental to verifying the origin and legitimacy of emails. These protocols establish a framework for trust and help prevent malicious actors from impersonating legitimate senders. The most prominent protocols include DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail), SPF (Sender Policy Framework), and DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance). These protocols work in tandem to authenticate the sender’s domain and prevent spoofing.
- DKIM: This protocol uses digital signatures to verify the sender’s domain. A valid DKIM signature indicates the email originated from a legitimate source.
- SPF: Sender Policy Framework specifies which mail servers are authorized to send email on behalf of a particular domain. This helps prevent unauthorized use of the domain’s email address.
- DMARC: Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance, acts as an overall policy framework. It defines how a domain owner wants to deal with authentication failures. This policy often dictates whether to quarantine or reject emails failing authentication checks.
Comparison of Microsoft’s Approach with Industry Best Practices
A crucial aspect of email security is the implementation of industry best practices. Comparing Microsoft’s approach to these standards reveals how well they align with established methods.
| Aspect | Microsoft’s Approach (Hypothetical) | Industry Best Practices | Alignment/Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|
| DKIM | Microsoft likely utilizes DKIM to sign outgoing emails and validate incoming ones. | DKIM is a standard practice for email authentication. | Likely alignment; Microsoft’s implementation is expected to follow DKIM standards. |
| SPF | Microsoft likely maintains an SPF record for their domains, specifying authorized mail servers. | SPF records are essential for preventing email spoofing. | Likely alignment; A correctly configured SPF record is critical for preventing spoofing. |
| DMARC | Microsoft likely implements DMARC to enforce the authentication policies for their domains. | DMARC is a critical protocol for overall email security. | Likely alignment; DMARC policies are increasingly important for managing email authentication and reputation. |
| Caller ID Verification | Microsoft’s caller ID verification approach is likely integrated with the aforementioned protocols to strengthen authentication and ensure users’ trust. | Industry best practices for caller ID verification focus on minimizing spoofing by using the above protocols. | Likely alignment; A robust verification method is likely in place to verify email caller IDs, potentially integrating with DKIM, SPF, and DMARC. |
Importance of Adhering to Industry Standards
Adherence to industry standards for email security is vital for maintaining a secure and trustworthy email environment. It mitigates risks associated with phishing, spam, and spoofing. Strict adherence to standards ensures that emails are authenticated and verified, reducing the potential for user harm. This also safeguards the reputation of the sending domain.
Examples of Other Companies’ Approaches
Many companies, including Google and Yahoo, have implemented robust email authentication mechanisms. These companies utilize DKIM, SPF, and DMARC, demonstrating the industry’s commitment to protecting users from email fraud. This proactive approach is essential to maintaining user trust and a safe online environment.
Future Trends in Email Caller ID Verification
The future of email security hinges on our ability to adapt to evolving threats and technologies. Email caller ID verification is no exception. Emerging trends in authentication, combined with the increasing sophistication of phishing and spoofing attacks, demand a proactive approach to securing email communication. This section explores potential future directions in email caller ID verification, examining the impact of new technologies and Microsoft’s possible adaptation strategies.
Emerging Authentication Technologies
Modern email authentication relies heavily on mechanisms like DKIM, SPF, and DMARC. However, the ever-evolving landscape of email threats necessitates the exploration and adoption of new and enhanced authentication methods. These advancements aim to strengthen email security and improve the reliability of caller ID verification. Quantum computing, for example, presents both a threat and an opportunity for authentication.
Impact on Email Security
The adoption of these emerging technologies directly impacts email security. By strengthening the authentication process, we can mitigate the risks associated with phishing and spoofing attacks. For example, the integration of blockchain technology into email authentication could enhance the transparency and immutability of sender identities, making it far more difficult for malicious actors to impersonate legitimate senders. Increased trust and confidence in email communication are the direct results of improved verification.
Enhanced Email Caller ID Verification
New technologies have the potential to significantly enhance email caller ID verification. For instance, incorporating biometric authentication into email systems could verify the sender’s identity with high accuracy, reducing the risk of fraudulent emails. Similarly, AI-powered analysis of email content and sender behaviour could identify patterns indicative of malicious activity, enabling quicker detection of spoofing attempts. These advancements can make email caller ID verification more accurate and robust.
Microsoft’s Adaptation Strategies
Microsoft, as a leader in the email space, must proactively adapt to these emerging trends in caller ID verification. This includes investing in research and development of new authentication protocols, incorporating cutting-edge technologies into its email platforms, and collaborating with industry partners to establish shared best practices. Staying ahead of the curve is crucial to protecting user accounts and maintaining a secure email ecosystem.
Potential Future Technologies and Impact, Microsoft looks for trust on e mail caller id
| Potential Future Technology | Possible Impact on Email Caller ID Verification |
|---|---|
| Blockchain-based authentication | Increased transparency and immutability of sender identities, making impersonation significantly harder. |
| Biometric authentication | Enhanced accuracy in verifying sender identities, reducing the risk of fraudulent emails. |
| AI-powered analysis of email content and sender behaviour | Improved detection of spoofing attempts and malicious activity, enabling quicker responses to threats. |
| Quantum-resistant cryptography | Protection against potential future attacks exploiting vulnerabilities in current cryptographic algorithms. |
| Decentralized identity systems | Enhanced control over user identities and improved verification mechanisms, reducing reliance on centralized servers. |
Security Measures and Implications
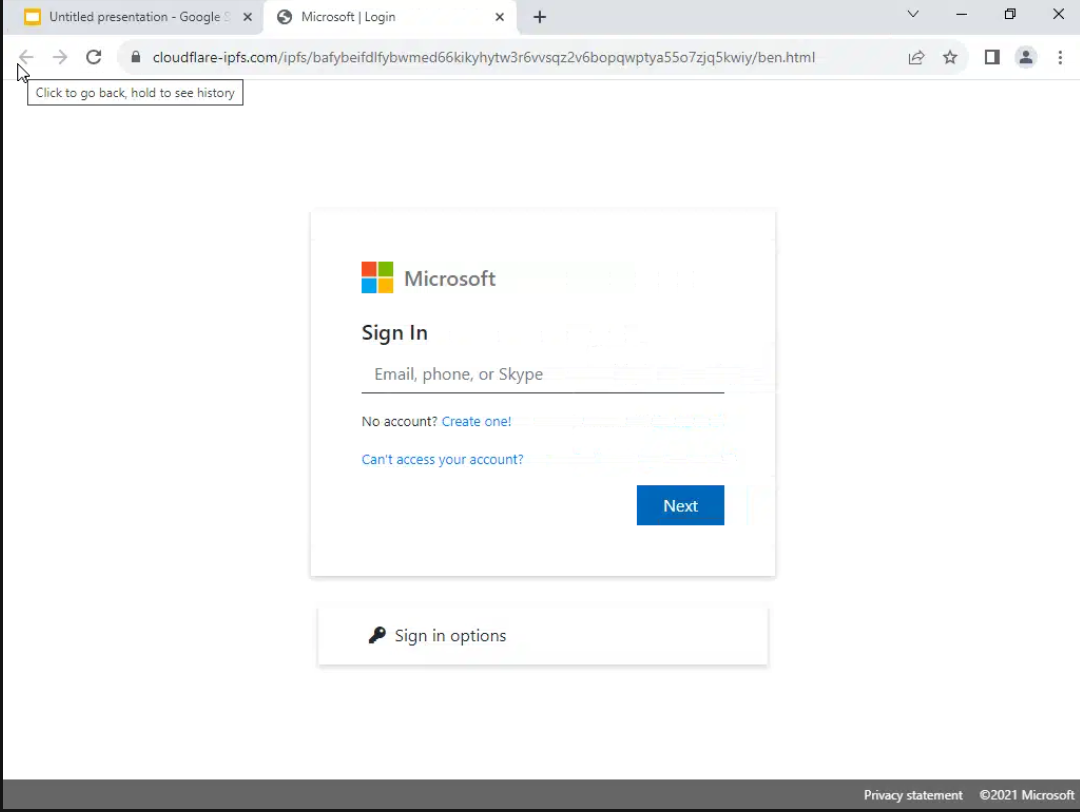
Protecting email sender identities is crucial in today’s digital landscape. Microsoft’s approach to email caller ID verification is not just about convenience; it’s a critical component of a broader strategy to combat fraud, phishing, and other malicious activities. Robust security measures are paramount, and their implications for users and the company are significant.The implementation of advanced security measures to verify email sender identities impacts user trust and the company’s reputation.
Successfully implementing these measures can drastically reduce the incidence of fraudulent emails, ultimately improving user experience and protecting valuable assets. Understanding the implications of these measures for various user groups is vital for effective communication and management.
Security Measures Employed by Microsoft
Microsoft employs a multifaceted approach to email caller ID verification. These methods are designed to detect and prevent malicious actors from impersonating legitimate senders. Core to this strategy are stringent authentication protocols.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Microsoft leverages MFA to enhance the security of email accounts. Users are required to provide multiple verification methods, making it significantly harder for unauthorized individuals to access accounts and send emails. This is a standard practice to secure accounts against brute-force attacks and unauthorized access.
- DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM): DKIM is a digital signature that verifies the sender’s identity and ensures the email hasn’t been tampered with during transit. This is a widely recognized standard that protects users from forged emails and helps maintain the integrity of communication.
- Sender Policy Framework (SPF): SPF is a mechanism that allows domain owners to specify which mail servers are authorized to send emails on their behalf. This helps prevent spoofing and ensures that only legitimate mail servers are sending emails from a particular domain.
- Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance (DMARC): DMARC combines DKIM and SPF to provide a more comprehensive authentication system. This policy defines how email receivers should handle messages that fail authentication checks, reducing the risk of phishing and spam.
Implications for Users and the Company
These security measures have various implications for users and Microsoft. For users, it translates to a more secure and trustworthy email environment, reducing the likelihood of encountering phishing attempts or fraudulent communications. For Microsoft, it strengthens its brand reputation, enhancing user confidence in its services and maintaining its position as a leader in email security.
- Enhanced User Trust: Robust security measures build user trust, making them more comfortable interacting with email communications. This directly impacts engagement and satisfaction with Microsoft’s products.
- Reduced Phishing Attacks: The measures help mitigate the risk of users falling victim to phishing scams. Users are less likely to click on malicious links or provide sensitive information, preventing financial and identity theft.
- Improved Brand Reputation: Microsoft’s commitment to email security bolsters its reputation as a reliable and trustworthy provider of online services. This positive perception directly influences user choice and market share.
Interaction with Different User Groups
The security measures interact differently with various user groups based on their technical proficiency and expectations. Businesses, for instance, require a high level of assurance in email authentication to protect sensitive information.
| User Group | Security Measure Interaction | Implications |
|---|---|---|
| Individual Users | MFA, DKIM, SPF, DMARC increase the security of personal accounts, making it more difficult for malicious actors to impersonate them. | Increased trust in email communications, reduced exposure to phishing attacks, and protection of personal information. |
| Businesses | Robust authentication measures are critical for protecting sensitive information and preventing data breaches. | Reduced risk of financial loss and reputational damage. |
| Government Agencies | These measures are essential for safeguarding sensitive data and ensuring the integrity of official communications. | Enhanced security and trust in official communications, preventing malicious actors from disrupting operations. |
Summary
In conclusion, Microsoft’s commitment to email caller ID verification is a crucial step toward a more secure digital landscape. The measures discussed, from verification methods to industry best practices, aim to enhance trust and prevent fraudulent activities. However, the evolving nature of email threats necessitates ongoing adaptation and innovation to maintain a robust security posture.