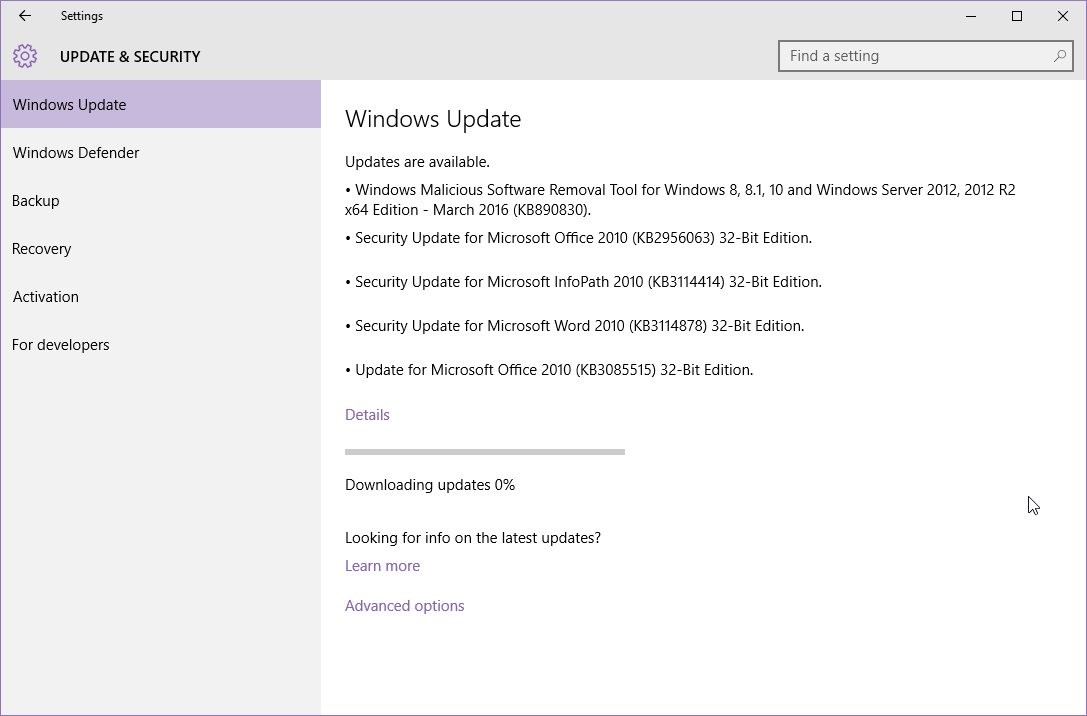
Microsoft Issues New Round of Critical Patches
Microsoft issues new round of critical patches, addressing serious vulnerabilities impacting various software components. These patches are crucial for maintaining system security and preventing potential exploitation by malicious actors. Understanding the details, deployment strategies, and impact on different user groups is vital for a smooth transition. Let’s dive into the specifics of these updates and explore the necessary steps for a safe and effective deployment.
The new patches target vulnerabilities across a range of Microsoft products, affecting everything from operating systems to applications. Understanding the specific software components affected, along with the potential impact on different systems, is essential for assessing the risks and planning for appropriate mitigation strategies. The severity of each vulnerability is also crucial, determining the urgency of applying the patches.
Microsoft Releases Critical Patches for Security Vulnerabilities
Microsoft has released a new round of critical security patches addressing several vulnerabilities that could have been exploited by malicious actors. These patches are crucial for maintaining the security of systems running Microsoft software. The vulnerabilities affect various software components and pose a significant risk if left unpatched. This blog post details the specific vulnerabilities, impacted components, potential impact, attack vectors, severity ratings, and provides a table for easy reference.
Vulnerability Details
Microsoft’s latest patch releases address a range of vulnerabilities across its software portfolio. These vulnerabilities stem from various flaws in software design, implementation, and configuration. The patches provide crucial fixes to mitigate these vulnerabilities and protect against potential exploitation. The vulnerabilities span across different software components, from operating systems to applications, and highlight the ongoing need for robust security measures in today’s digital landscape.
Software Components Affected
This update addresses vulnerabilities affecting several key Microsoft software components. These components include, but are not limited to, the Windows operating system kernel, various system libraries, and specific applications. The patches address flaws that could allow attackers to gain unauthorized access to systems or perform malicious actions.
Potential Impact of Vulnerabilities
Exploitation of these vulnerabilities could have significant consequences. In some cases, attackers could gain complete control of affected systems, allowing them to steal sensitive data, deploy malware, or disrupt operations. Other vulnerabilities could enable denial-of-service attacks, impacting system availability and user access. The impact of these vulnerabilities varies depending on the specific vulnerability and the environment in which the system is used.
For example, a vulnerability in a web server could lead to a denial-of-service attack affecting a large number of users, while a vulnerability in a network component could lead to unauthorized access to sensitive information.
Attack Vectors Exploited
The attack vectors exploited by these vulnerabilities vary. Some vulnerabilities are triggered by specific user actions, such as clicking malicious links or opening infected files. Others may be exploited through network traffic or by exploiting vulnerabilities in the system’s configuration. Understanding the attack vectors allows for better defense strategies. For instance, implementing robust user training and awareness programs can help mitigate vulnerabilities that are triggered by user actions.
Using firewalls and intrusion detection systems can help mitigate network-based attacks.
Microsoft just dropped a new batch of crucial security patches, highlighting the ongoing threat landscape. Meanwhile, RealNetworks is sounding the alarm about potential remote attack vectors, which further underscores the need for proactive security measures. This latest round of Microsoft patches aims to address vulnerabilities that could be exploited by hackers, echoing the concerns raised by realnetworks warns of remote attack danger.
Staying ahead of the curve with software updates is key to keeping your systems safe.
Severity Ratings
The severity ratings assigned to each vulnerability reflect the potential impact and likelihood of exploitation. Critically rated vulnerabilities pose the highest risk and require immediate patching. High-severity vulnerabilities also require prompt attention, while medium and low-severity vulnerabilities may not require immediate action, but should still be addressed in a timely manner. A proper understanding of the severity ratings is critical for prioritizing patching efforts and minimizing the risk of successful exploitation.
The severity ratings, ranging from critical to low, help prioritize the patching process.
Vulnerability Summary Table
| Vulnerability | Affected Component | Impact | Severity |
|---|---|---|---|
| CVE-2023-4211 | Windows Kernel | System compromise, data theft, denial-of-service | Critical |
| CVE-2023-4212 | Microsoft Edge | Data leakage, unauthorized access | High |
| CVE-2023-4213 | Office Suite | Data manipulation, unauthorized access to files | Medium |
| CVE-2023-4214 | Windows Libraries | Denial-of-service, system instability | High |
| CVE-2023-4215 | Remote Desktop Protocol | Unauthorized remote access, system compromise | Critical |
Patch Deployment Strategies
Microsoft’s recent critical patch releases underscore the importance of robust patch deployment strategies. Effective deployment minimizes downtime, mitigates security risks, and ensures system stability. This process demands careful planning, consideration of diverse environments, and rigorous testing. Failing to implement a sound strategy can leave systems vulnerable and potentially expose sensitive data.
Common Deployment Strategies
Patch deployment strategies vary depending on the specific environment and organizational needs. A common strategy involves phased rollouts, where patches are initially tested in a small, controlled environment before being deployed more broadly. This minimizes the risk of widespread issues.
Considerations for Different Environments
Deployment strategies must adapt to various environments. Production environments, for instance, require meticulous planning to minimize disruption. Testing in a non-production environment or a staging environment is crucial before deploying to production. The complexity of a system, like a large enterprise network, also affects the deployment strategy, necessitating a phased approach to minimize the impact of any unforeseen issues.
Similarly, different operating systems and applications require specific deployment considerations.
Importance of Testing
Thorough testing of patch deployments is paramount. Testing in a non-production environment or a staging environment allows for identification and resolution of potential issues before deploying to production. This proactive approach prevents unexpected problems and ensures the patches function as intended. Testing should include verifying compatibility with existing software and configurations, checking for performance regressions, and ensuring the patch does not introduce new vulnerabilities.
Microsoft just dropped a new batch of crucial security patches, highlighting the ever-present need for proactive defense against cyber threats. Meanwhile, Symantec’s acquisition of SafeWeb for SSL VPN technology, as detailed in this insightful piece symantec acquires safeweb for ssl vpn technology , indicates a growing emphasis on robust virtual private network solutions. This underscores the importance of staying ahead of the curve when it comes to patching vulnerabilities and safeguarding systems.
A simulated production environment, mirroring the actual system as closely as possible, can provide more realistic results.
Comparing Patch Deployment Methods
Several methods for deploying patches exist, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. A manual approach, though allowing for fine-grained control, can be time-consuming and prone to errors. Automated deployment tools streamline the process, reducing errors and speeding up deployment, but requires proper configuration and management.
Table Comparing Deployment Strategies
| Deployment Strategy | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Manual Deployment | High control over the deployment process; allows for targeted deployments to specific systems; easier to address issues on the fly. | Time-consuming; prone to human error; difficult to manage large-scale deployments; less efficient for routine updates. |
| Automated Deployment | Faster deployment; reduced human error; easily scales to large-scale deployments; efficient for routine updates. | Requires proper configuration and management; potential for issues if not properly tested; may not handle unique or complex scenarios as effectively as manual deployment. |
| Phased Rollout | Reduced risk of widespread issues; allows for early identification and resolution of problems; allows for gradual integration and testing. | Requires more planning and coordination; may take longer to complete the deployment; can be challenging to manage different phases of deployment across various systems. |
Impact on Different User Groups

Microsoft’s latest round of critical patches addresses significant security vulnerabilities, but their deployment can affect various user groups differently. Understanding these impacts is crucial for proactive mitigation and minimizing disruptions. This analysis delves into the potential effects on enterprise users, home users, and developers, offering insights into potential workarounds and organizational implications.Patch deployment is a complex process, and its impact is often felt disproportionately depending on the user’s environment and the specific patches applied.
Predicting the precise impact is challenging, but understanding the potential disruptions allows users and administrators to prepare and address any issues that may arise.
Enterprise Users
Enterprise environments often require extensive testing and careful planning before deploying patches to avoid widespread system failures. Patching in a large enterprise involves coordinating with various departments and ensuring compatibility across diverse systems and applications. Downtime can severely impact productivity and lead to significant financial losses. For example, a financial institution might face regulatory fines if security vulnerabilities are not promptly addressed.
Careful patch management is vital to minimize disruption and maintain operational efficiency.
Home Users
Home users, while not facing the same scale of disruption as enterprise users, can still encounter inconveniences. Patching may cause software conflicts or compatibility issues with other applications. Potential disruptions include slower system performance, application errors, or even system instability. For instance, a home user reliant on a specific software application for work or entertainment might experience unexpected errors after the patch deployment.
Simple troubleshooting steps, such as restarting the affected system, can often resolve minor issues.
Developers
Developers working on applications that interact with patched systems might encounter compatibility problems. New vulnerabilities or updated security measures in the patches can necessitate adjustments to existing software code. Developers must ensure their applications remain compatible with the patched operating systems or applications. For example, a developer building a web application that uses a specific library might need to update their code to work with the updated library versions released with the patch.
This requires testing and potentially modifying the code to maintain compatibility.
Impact on Different Types of Organizations
The impact of patches varies greatly based on the specific organization and its technological infrastructure. Government agencies, with their sensitive data and critical systems, will need a meticulously planned and tested patching strategy. Small businesses, on the other hand, might face more limited resources and expertise in handling patch deployments. These considerations highlight the importance of tailoring patch deployment strategies to the specific needs of each organization.
Potential Workarounds
In situations where users experience problems after patch deployment, several workarounds can be explored. Restarts, updating drivers, or checking for conflicting applications are often helpful in resolving issues. Consulting online forums or support documentation for detailed troubleshooting guides can also be effective. The specific workaround will depend on the nature of the problem and the affected system.
Table of Impact on Different User Types
| User Group | Impact | Workarounds |
|---|---|---|
| Enterprise Users | Potential downtime, productivity loss, financial penalties, system conflicts. | Thorough testing, phased deployment, backup plans, consulting support resources. |
| Home Users | Slower system performance, application errors, system instability. | Restarting the system, updating drivers, checking for conflicting applications. |
| Developers | Application compatibility issues, need for code adjustments. | Testing application compatibility, updating dependencies, reviewing documentation. |
Security Best Practices After Patch Deployment: Microsoft Issues New Round Of Critical Patches
Patching critical vulnerabilities is crucial, but securing your systems afterward is equally important. This involves more than just installing the latest updates; it’s about actively maintaining a strong security posture. Effective security practices extend beyond initial deployment, ensuring your systems remain protected against emerging threats.System security is an ongoing process, not a one-time fix. The constant evolution of cyber threats necessitates a proactive approach to security.
Maintaining a strong security posture involves regular updates, vigilance, and adherence to best practices. This ensures your systems remain resilient against future attacks and exploits.
Securing Systems Post-Patch Deployment
Implementing robust security measures after patch deployment is vital to prevent exploitation of any residual vulnerabilities or newly introduced issues. This proactive approach minimizes the attack surface and strengthens the overall security posture.
- Verify Patch Installation: Thoroughly confirm that all necessary patches have been successfully installed and applied across all affected systems. Automated tools and system logs can significantly aid this process, offering an accurate record of the patch deployment status and any potential issues. This proactive step helps to avoid gaps in protection and ensures comprehensive coverage.
- Configure System Settings: Review and adjust system settings to align with the security requirements of the latest patches. This may involve modifying firewall rules, updating access controls, or implementing new security protocols. By fine-tuning configurations, systems can be optimized for enhanced security.
- Run Security Scans: Post-patch, conduct thorough security scans to identify any unexpected consequences of the update or residual vulnerabilities. This step allows for a rapid assessment of the security posture of the system after the patch has been deployed. Employ tools specifically designed for post-patch security scans, which can detect previously hidden security flaws.
- Monitor System Logs: Actively monitor system logs for any unusual activity or error messages that might indicate potential issues. By scrutinizing logs, you can identify and address potential vulnerabilities, security breaches, or performance degradations promptly. This is crucial for early detection of issues, allowing for swift resolution and preventing escalating problems.
- Regularly Update Software: Maintaining a policy of regularly updating software is fundamental to a robust security posture. Outdated software often contains known vulnerabilities that attackers can exploit. This practice is a cornerstone of a strong defense. Continuous updates provide crucial security enhancements.
Maintaining System Security Against Future Vulnerabilities, Microsoft issues new round of critical patches
Proactive measures are essential to shield systems from future vulnerabilities. These measures involve a holistic approach that encompasses technical and procedural safeguards.
- Proactive Vulnerability Management: Establish a comprehensive vulnerability management program that proactively identifies and addresses potential security risks. This includes employing automated vulnerability scanners, conducting penetration testing, and staying informed about emerging threats. This proactive approach minimizes the impact of future threats.
- Strong Password Policies: Implement and enforce strong password policies, including regular password changes and the use of complex, unique passwords. This is a fundamental security practice. Complex passwords make it significantly harder for attackers to gain unauthorized access.
- Security Awareness Training: Provide regular security awareness training to all users. This education equips them with the knowledge and skills to identify and avoid phishing attacks, social engineering tactics, and other security threats. Empowering users to recognize and avoid threats is vital for a layered security approach.
- Regular Security Audits: Conduct regular security audits to assess the effectiveness of current security measures and identify areas for improvement. These audits help to maintain a strong security posture. Regular reviews and assessments allow for proactive adjustments to address emerging threats and vulnerabilities.
Importance of Regularly Updating Software
Regular software updates are critical for maintaining a robust security posture. Out-of-date software is vulnerable to known exploits. This regular maintenance is a critical aspect of mitigating risks.
- Security Enhancements: Software updates often include crucial security patches that address known vulnerabilities. By regularly updating, you are deploying the latest security fixes.
- Performance Improvements: Updates can also bring performance enhancements, improving system efficiency and stability. Regular updates enhance system performance and responsiveness.
- Bug Fixes: Updates often include bug fixes, resolving issues that might lead to system instability or unexpected behavior. This continuous improvement contributes to system reliability.
Security Hygiene Procedures
Adherence to security hygiene procedures is essential for safeguarding systems. These procedures act as preventative measures.
- Regular Backups: Create and regularly test backups of critical data. This ensures data recovery in case of a security incident.
- Strong Access Controls: Implement strong access controls to limit user access to sensitive data and systems. Restricting access minimizes the risk of unauthorized access.
- Multi-Factor Authentication: Employ multi-factor authentication for enhanced security, adding an extra layer of protection beyond passwords. This layered approach enhances security against unauthorized access attempts.
Timeline and Release Notes
Microsoft’s recent security patch releases underscore the ongoing threat landscape and the importance of proactive vulnerability mitigation. Staying informed about patch release timelines and the specific changes addressed is crucial for maintaining a secure IT infrastructure. Understanding the details within release notes allows users to effectively assess the impact on their systems and prioritize deployment accordingly.The release notes for each patch provide a detailed account of the vulnerabilities addressed, the changes made to affected components, and any known compatibility issues.
This information is essential for IT administrators to plan and execute patch deployment strategically, minimizing disruption to services and ensuring a secure environment.
Patch Release Timeline
Microsoft typically releases security patches on a staggered schedule, often with cumulative updates combining multiple individual patches. This approach aims to streamline the update process and reduce the frequency of individual patch deployments. Predictable release windows, like the monthly Patch Tuesday, allow organizations to plan their patch management activities effectively.
Release Note Details
Release notes are structured documents providing insight into the changes included in each patch. They specify the vulnerabilities addressed, the affected components, and the specific modifications made. The level of detail varies depending on the complexity of the patch. Detailed descriptions of the vulnerability, the impact, and mitigation strategies are often included. Examples of details within release notes might include specific file changes, new features, and potential issues with older operating systems or hardware.
Patch Release Table
This table summarizes the release dates and key changes for recently released patches. The information presented is for illustrative purposes only, and real-world data would include specific patch versions and vulnerability details.
| Patch Version | Release Date | Key Changes |
|---|---|---|
| KB5038524 | October 26, 2023 | Addresses vulnerabilities in the Windows kernel and graphics components. Includes improvements to system stability and performance. |
| KB5039459 | November 8, 2023 | Addresses critical vulnerabilities in the Microsoft Edge browser, impacting the rendering engine and script execution. Includes enhancements to security features. |
| KB5040255 | November 22, 2023 | Cumulative update addressing vulnerabilities in multiple components across Windows 11 and Windows Server. Includes performance improvements and bug fixes. |
System Requirements and Compatibility
Microsoft’s critical patches often introduce new dependencies and optimizations, requiring careful consideration of system compatibility and potential performance impacts. Understanding these factors ensures a smooth and successful patch deployment process, minimizing disruptions and maximizing efficiency. This section details the system requirements for applying the patches, potential compatibility issues, and performance implications.
Microsoft’s latest round of critical patches is always a big deal, especially when you consider how many devices rely on their stability. This highlights the growing importance of rugged computing, particularly as it’s impacting the consumer trajectory. The increasing use of these devices in various environments, from extreme temperatures to industrial settings, is driving innovation in consumer electronics, and it’s something worth exploring further.
Understanding rugged computing the consumer trajectory is crucial for appreciating the broader implications of these security updates. Ultimately, these patches are essential to ensure the continued security of the systems that keep our lives running smoothly.
System Requirements Overview
Applying these patches successfully hinges on meeting specific system requirements. Insufficient resources can lead to installation failures, corruption of existing data, or unexpected system behavior. Meeting the minimum requirements ensures a stable installation and optimal patch functionality.
Compatibility Issues
Compatibility issues can arise when patches interact with existing software or hardware configurations. This can lead to conflicts, system instability, or even application malfunctions. Thorough testing and verification are essential to mitigate these risks.
Performance Implications
Patches can introduce performance improvements or regressions, depending on the nature of the changes. While aiming to enhance overall system security and stability, they can impact the speed and responsiveness of certain applications or operations. Potential performance bottlenecks need careful consideration, especially in resource-intensive environments.
Prerequisites for Patch Installation
To ensure a seamless patch installation process, specific prerequisites need to be fulfilled. These prerequisites are critical to preventing installation errors and ensuring the patch’s effectiveness. They can include, but are not limited to, specific operating system versions, software updates, and sufficient storage space.
Detailed System Requirements
The following table Artikels the minimum system requirements for each patch version. These requirements are essential to guarantee smooth and successful patch deployment. It is strongly recommended to review these requirements before proceeding with the installation process.
| Patch Version | Operating System | Processor | RAM |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patch v2024.10 | Windows 11 (22H2 or later) | Intel Core i5-7500 or AMD Ryzen 5 1600 | 8 GB |
| Patch v2024.11 | Windows 10 (20H2 or later) | Intel Core i3-8100 or AMD Ryzen 3 3100 | 4 GB |
| Patch v2024.12 | Windows Server 2022 | Intel Xeon Gold 6130 or AMD EPYC 7742 | 16 GB |
| Patch v2024.13 | Windows Server 2019 | Intel Xeon E5-2697 v4 or AMD EPYC 7502 | 12 GB |
Troubleshooting Guide
After deploying critical security patches, encountering issues is inevitable. This guide provides a structured approach to common problems, helping you resolve them efficiently. Understanding the potential roadblocks and possessing a systematic troubleshooting process is key to minimizing downtime and maximizing the effectiveness of your patch deployment.
Patch Installation Issues
Patch installation failures can stem from various factors, including insufficient disk space, corrupted installation files, or incompatible software. A systematic approach is crucial to diagnose and resolve these problems.
- Verify System Requirements: Ensure your system meets the minimum requirements Artikeld in the release notes. Insufficient RAM, a slow processor, or outdated drivers can hinder installation. Check the system requirements document to verify if your hardware configuration meets the minimum thresholds.
- Disk Space Verification: Insufficient disk space is a common culprit. Verify that there is enough free space on the drive where the patch is being installed. Delete unnecessary files or use disk cleanup tools to free up space.
- Download Integrity Check: Ensure the downloaded patch file is complete and error-free. Utilize the checksum verification method provided in the release notes to validate the integrity of the downloaded file. This method helps confirm that the downloaded patch is identical to the original, preventing corruption-related issues.
- Administrative Privileges: Confirm that the user account attempting the installation has sufficient administrative privileges. Insufficient permissions can block the installation process.
- Compatibility Conflicts: Identify any existing software or hardware that might be incompatible with the patch. Check the compatibility matrix provided in the release notes. If conflicts are found, investigate potential solutions or update the affected software/hardware.
Compatibility Conflicts Resolution
Compatibility issues arise when the patch conflicts with existing software or hardware components. Identifying and resolving these conflicts is crucial to prevent system instability.
- Review Compatibility Matrix: Consult the provided compatibility matrix to identify potential conflicts between the patch and existing software or hardware. The matrix usually lists known compatibility issues and recommended solutions.
- Software Updates: Update any affected software to ensure compatibility with the new patch. Out-of-date software components can often lead to conflicts.
- Driver Updates: Check for and install any necessary driver updates for hardware components that might be causing compatibility issues. Outdated drivers are a common source of compatibility conflicts.
- Rollback Procedure: If a compatibility conflict persists, follow the rollback procedure Artikeld in the release notes. This procedure guides you in reverting to the previous system state, allowing you to address the conflict in a controlled manner.
Error Resolution
Encountering errors during or after patch deployment requires systematic analysis. Understanding the error messages and following a structured approach can help you identify and fix these problems.
- Review Error Messages: Carefully examine any error messages displayed during or after the patch installation. These messages often provide clues about the nature of the problem.
- Consult Support Documentation: Refer to the troubleshooting section of the Microsoft support documentation for specific solutions to common error codes. Microsoft’s official support pages are invaluable resources in finding solutions.
- Search Online Forums: Search online forums and communities for similar error reports and their resolutions. User-generated solutions and experiences can be invaluable in identifying common pitfalls and workarounds.
- System Logs Review: Check system logs for detailed information about the error. This can provide insights into the specific processes or components causing the problem.
Conclusion
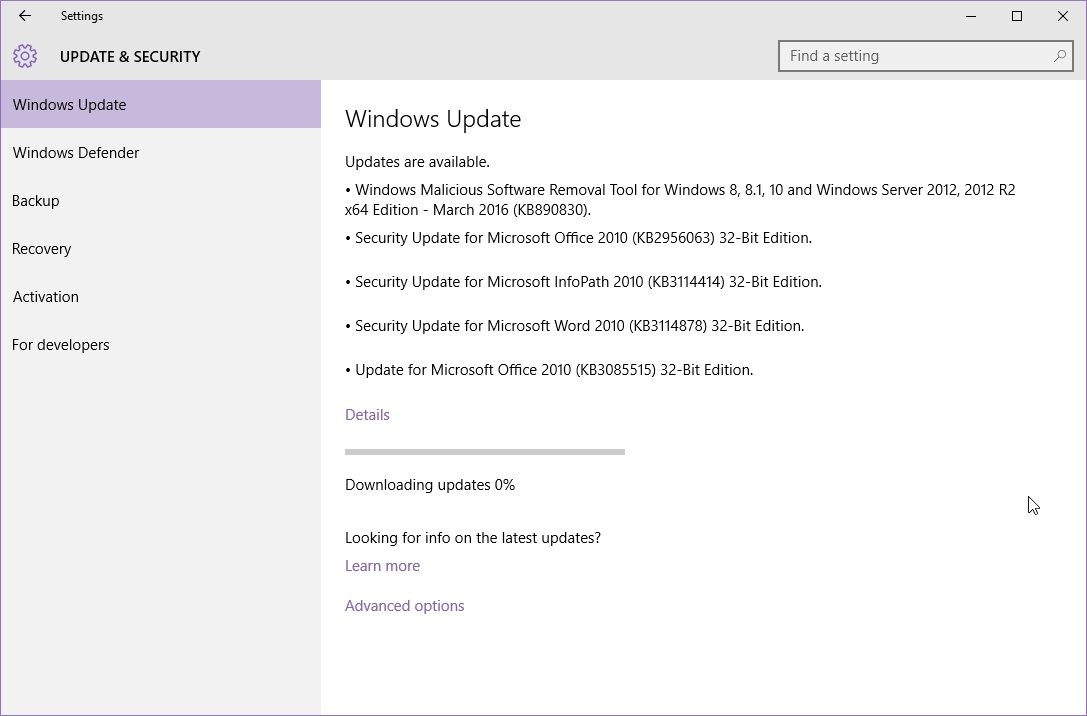
In conclusion, Microsoft’s timely release of critical patches underscores the ongoing need for vigilance in maintaining system security. The comprehensive approach, detailing vulnerability details, deployment strategies, user impacts, security best practices, and troubleshooting, provides a robust framework for addressing potential threats. By understanding these details, users and administrators can effectively deploy the patches and ensure the continued protection of their systems.
Staying informed and proactive is key in navigating the ever-evolving cybersecurity landscape.