Sun and Capgemini Launch RFID System Revolutionizing Tracking
Sun and Capgemini launch RFID system, marking a significant advancement in supply chain management. This innovative system promises a revolution in real-time tracking and monitoring, offering unprecedented visibility into goods throughout the process. The system, built on cutting-edge RFID technology, is designed to optimize operations, reduce costs, and enhance security for both companies. Early analysis suggests a paradigm shift in inventory management and logistics, potentially affecting other industries as well.
The system utilizes a combination of radio frequency identification tags and readers to create a highly accurate and efficient tracking network. This system promises benefits like increased efficiency, reduced inventory errors, and enhanced security, streamlining operations from warehouse to delivery.
Introduction to the Sun-Capgemini RFID System
Sun and Capgemini have collaborated to deploy a comprehensive RFID (Radio-Frequency Identification) system. This innovative system promises to streamline various processes within Sun’s operations, offering significant benefits in areas like inventory management, asset tracking, and security. The system’s core functionalities are designed to enhance efficiency and provide real-time visibility into critical data streams. This will ultimately lead to improved operational efficiency and cost savings for both companies.This RFID system leverages cutting-edge technologies to provide a robust and scalable solution.
The implementation showcases a commitment to adopting modern technologies for improved business performance and customer service. The system’s ability to track and manage data efficiently should result in increased productivity and reduced operational costs.
Core Functionalities of the RFID System
The RFID system developed by Sun and Capgemini is multifaceted, addressing a broad range of operational needs. Its key functionalities include real-time tracking of assets, automated inventory management, and enhanced security measures. These functionalities are integral to achieving optimal operational efficiency.
- Real-time Asset Tracking: The system provides real-time visibility into the location and status of various assets, such as equipment and materials. This capability is crucial for optimizing resource allocation and minimizing downtime. For example, if a specific piece of equipment is needed urgently, its location can be instantly determined using the system, enabling quick retrieval.
- Automated Inventory Management: The RFID system automates the inventory tracking process, minimizing manual errors and providing accurate real-time data on stock levels. This allows for proactive management of supply chains, ensuring optimal stock levels and minimizing potential shortages or surpluses.
- Enhanced Security Measures: By utilizing RFID tags, the system strengthens security protocols, enabling tracking of sensitive materials or high-value assets. This feature helps prevent theft and unauthorized access, safeguarding company resources and maintaining operational integrity.
Potential Benefits for Sun and Capgemini
The RFID system offers significant potential advantages for both Sun and Capgemini. These benefits extend beyond simply improving operational efficiency; they encompass increased profitability, enhanced customer service, and improved supply chain management.
- Improved Operational Efficiency: The system’s automated functionalities lead to streamlined processes and reduced manual intervention, ultimately improving operational efficiency across various departments.
- Reduced Operational Costs: By automating tasks and minimizing errors, the system helps to reduce operational costs, which is a key factor in enhancing profitability and competitiveness.
- Enhanced Customer Service: The system’s ability to provide real-time data on inventory and assets allows for improved order fulfillment, resulting in enhanced customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Key Technologies Utilized
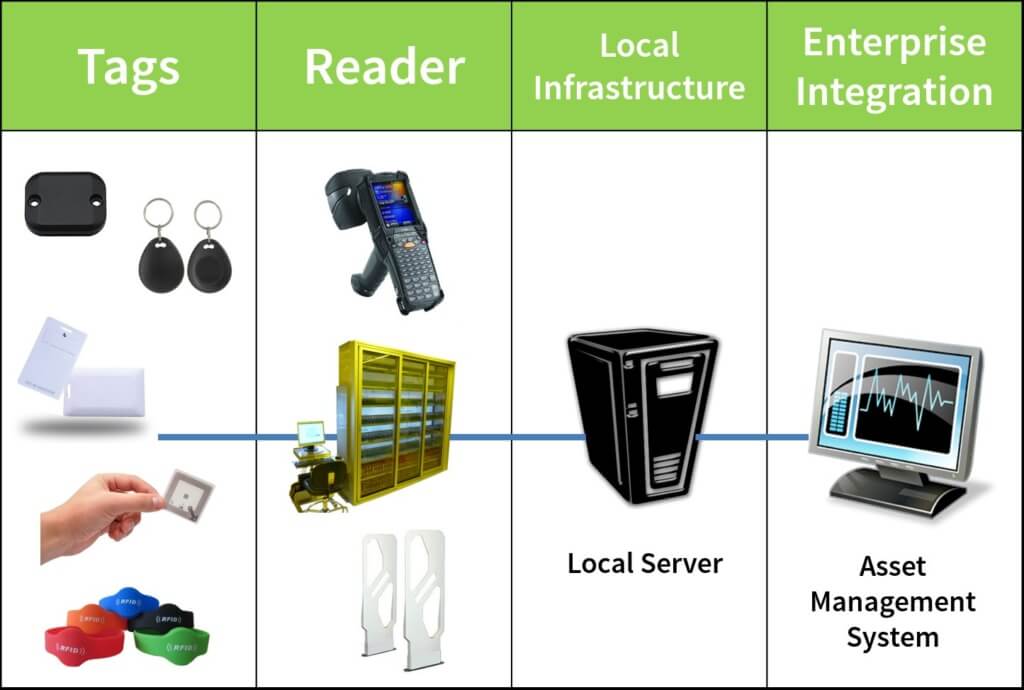
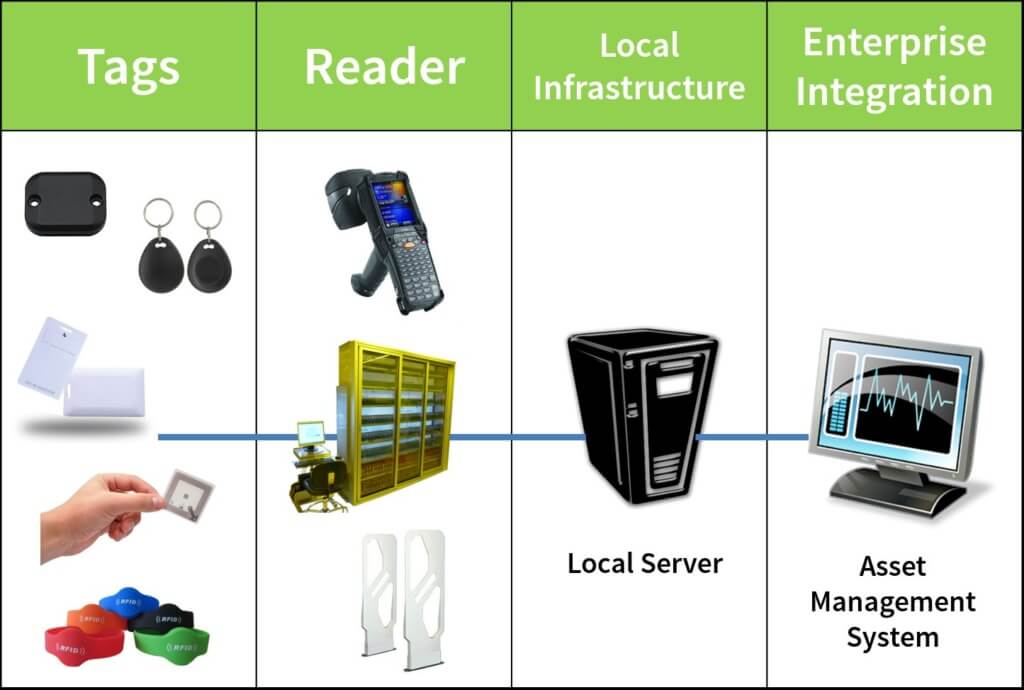
The system utilizes a combination of radio-frequency technologies and sophisticated software solutions. These components work together to create a comprehensive and robust system for tracking and managing assets.
- Radio-Frequency Identification (RFID) Tags: These tags are attached to assets and transmit data wirelessly to the system’s readers. Different types of RFID tags exist, each with varying read ranges and capabilities.
- RFID Readers: These readers capture data from the RFID tags, relaying this information to the system’s central database. Different readers have varying ranges and frequencies for optimal data capture.
- Software Solutions: Sophisticated software manages the data collected by the RFID readers, providing a centralized platform for tracking, reporting, and analysis.
History of RFID Technology
RFID technology has evolved significantly over the years, progressing from its early applications to its current widespread use in various industries.RFID technology’s early days focused on limited applications, like inventory management in warehouses. As the technology matured, advancements in microchip technology and antenna design broadened its potential use cases. Today, RFID is integrated into various sectors, including healthcare, transportation, and retail, demonstrating its adaptability and efficiency.
Implementation Details

The Sun-Capgemini RFID system implementation involved a phased approach, meticulously designed to minimize disruption to existing operations while maximizing efficiency gains. Careful planning and execution were crucial to ensure a smooth transition and successful integration of the new technology.The implementation process followed a structured methodology, ensuring all aspects were addressed from initial planning to final deployment and ongoing maintenance.
This included meticulous stakeholder communication, detailed project scheduling, and rigorous testing procedures to guarantee a robust and reliable system.
Sun and Capgemini’s new RFID system launch is interesting, especially considering the recent developments in file compression. This new system promises efficiency gains, much like the historical breakthroughs in file compression, mirroring the recent truce between pkware and winzip in the ongoing zip format wars here. Hopefully, this new RFID system will lead to similar streamlined solutions in other areas, and potentially spark similar positive collaborations in the future.
Phased Rollout
The implementation was executed in phases, beginning with a pilot program in a select area of the Sun organization. This pilot allowed for testing and refinement before full-scale deployment. Data gathered from the pilot program informed adjustments to procedures and system configurations, ensuring optimal performance.
Challenges Encountered
Several challenges were encountered during the implementation process. One significant challenge was integrating the RFID system with existing enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems. This required careful data mapping and configuration to ensure seamless data flow between the two systems. Another hurdle was training personnel on the new technology and procedures. This was addressed by creating comprehensive training materials and conducting hands-on workshops.
Overcoming Challenges
Addressing the ERP integration challenge involved a dedicated team working closely with both Sun’s IT department and Capgemini’s technical staff. The team developed custom interfaces to bridge the gap between the systems. Thorough testing ensured the integrity of the data transfer.Personnel training was approached with a multi-faceted strategy. Interactive training sessions, online tutorials, and practical demonstrations were utilized to equip employees with the necessary skills.
This included demonstrations of how to use the RFID scanners, manage the system’s data, and troubleshoot common issues.
Testing and Validation
Rigorous testing and validation procedures were essential to guarantee the system’s reliability and accuracy. These procedures included unit testing, integration testing, and user acceptance testing (UAT). Unit testing focused on the individual components of the system, ensuring they functioned as expected. Integration testing validated the seamless interaction between different modules. UAT involved end-users evaluating the system’s functionality and usability in real-world scenarios.
Sun and Capgemini’s launch of their new RFID system is a significant step forward, but it also highlights a crucial vulnerability. With the increasing reliance on these types of systems, robust security measures are paramount, especially considering recent warnings from U.S. officials about lax cyber defenses. U.S. officials warn of lax cyber defense This underscores the need for rigorous security protocols in the development and implementation of RFID technologies to prevent potential breaches.
Thankfully, Sun and Capgemini seem to be taking these concerns seriously, ensuring the system’s security is a top priority.
Organizational Structure
The RFID system’s organizational structure was designed to facilitate efficient management and control. A dedicated RFID team was established, responsible for system administration, maintenance, and troubleshooting. This team comprised personnel with expertise in RFID technology and the Sun’s operational processes. The team also worked closely with other departments to ensure seamless integration and address any issues that arose.A chart outlining the structure and responsibilities is provided below.
| Department | Role | Responsibilities |
|---|---|---|
| RFID Team | Project Manager | Oversees project implementation and execution |
| RFID Team | Technical Lead | Ensures system performance and integration |
| RFID Team | Data Analyst | Data management and analysis |
| Operations | Users | System usage and feedback |
| IT | Support Team | System maintenance and troubleshooting |
Applications and Use Cases
The Sun-Capgemini RFID system promises significant improvements across various operational aspects. By leveraging the power of radio-frequency identification, the system can streamline processes, enhance visibility, and ultimately boost efficiency in both Sun’s and Capgemini’s operations. This section explores the system’s potential in supply chain management, inventory control, logistics, and other relevant business sectors.
Potential Applications for Sun
The RFID system offers numerous potential applications tailored to Sun’s specific needs. For instance, real-time tracking of raw materials and finished goods throughout the manufacturing process can drastically reduce delays and improve production planning. Accurate inventory tracking will enable Sun to optimize stock levels, minimizing storage costs and preventing stockouts. Improved visibility into the entire supply chain will facilitate better collaboration with suppliers and distributors.
- Improved Production Planning: Real-time tracking of raw materials and finished goods allows for proactive adjustments to production schedules, minimizing delays and improving overall efficiency.
- Enhanced Inventory Management: Precise inventory tracking minimizes stockouts and overstocking, optimizing storage space and reducing associated costs. This ensures the right products are available at the right time.
- Streamlined Supply Chain Collaboration: Real-time visibility into the entire supply chain enables seamless communication and collaboration with suppliers and distributors, leading to faster order fulfillment and reduced delivery times.
Potential Applications for Capgemini
Capgemini, as a service provider, can leverage the RFID system in various ways to improve client service and operational efficiency. For instance, the system can be used to track client assets and equipment, ensuring timely maintenance and preventing loss. Real-time tracking of project materials and deliverables will allow for more accurate project estimations and resource allocation.
- Client Asset Management: Tracking client equipment and assets ensures timely maintenance and prevents loss, contributing to improved service quality and reduced downtime.
- Project Resource Management: Real-time tracking of project materials and deliverables improves project estimations and resource allocation, leading to better project planning and execution.
- Enhanced Service Delivery: Improved visibility into client assets and project progress enables Capgemini to offer more responsive and efficient service delivery, building client trust and loyalty.
Impact on Supply Chain Management
The implementation of the RFID system significantly impacts supply chain management by enhancing visibility and control across all stages. This improved visibility enables faster order fulfillment, reduced lead times, and minimized inventory holding costs. The ability to track goods in real-time enables proactive identification and resolution of potential disruptions, increasing overall supply chain resilience.
- Faster Order Fulfillment: Real-time tracking allows for quicker identification and delivery of goods, leading to reduced order fulfillment times.
- Reduced Lead Times: Streamlined tracking and communication throughout the supply chain minimizes delays and accelerates the delivery process.
- Minimized Inventory Costs: Accurate inventory tracking reduces overstocking and stockouts, optimizing inventory levels and lowering associated costs.
Inventory Management and Logistics Applications
The RFID system provides a powerful tool for inventory management and logistics. By automating the tracking and management of goods, the system improves accuracy and efficiency in both receiving and shipping. Automated processes also minimize errors and manual intervention, resulting in a reduction of operational costs.
- Automated Receiving and Shipping: RFID technology automates receiving and shipping processes, reducing manual intervention and potential errors.
- Improved Accuracy: Automated data collection eliminates the possibility of human error in tracking and managing inventory.
- Reduced Operational Costs: Automation and reduced errors lead to significant cost savings in inventory management and logistics.
Applications in Other Business Sectors
The Sun-Capgemini RFID system’s capabilities extend beyond the manufacturing and service sectors. Retailers can use it to track inventory and manage stock in real-time, enhancing customer service and reducing losses. Healthcare facilities can use RFID to track medical equipment, improving efficiency and patient safety. Transportation companies can utilize the system to optimize routes and manage vehicle maintenance.
- Retail: Tracking inventory and managing stock in real-time enhances customer service and reduces losses.
- Healthcare: Tracking medical equipment improves efficiency and patient safety.
- Transportation: Optimizing routes and managing vehicle maintenance leads to improved efficiency and cost savings.
Benefits and Advantages
The Sun-Capgemini RFID system promises significant improvements in efficiency, productivity, and cost savings for both Sun and Capgemini. This implementation leverages the power of real-time tracking and monitoring, offering a tangible return on investment beyond simply automating processes. By streamlining workflows and enhancing visibility across the supply chain, this system creates a competitive edge.
Specific Benefits for Sun
This system directly addresses Sun’s needs for enhanced inventory management and supply chain optimization. By automating tracking and reducing errors in material handling, the RFID system directly impacts Sun’s core operations. Real-time data access will allow for more accurate forecasting and inventory control, leading to reduced storage costs and minimizing material waste. The system will also enable better communication and collaboration across Sun’s internal teams, accelerating project timelines and improving overall operational efficiency.
Sun and Capgemini’s new RFID system launch is certainly exciting, but the recent EC ruling, which surprisingly has little short-term impact on Microsoft , might not be as significant as initially thought. Ultimately, the innovative RFID system will likely still have a big impact on supply chain management, especially considering the ongoing global market trends. It’s a fascinating time for both tech and business strategies.
Specific Benefits for Capgemini
For Capgemini, the system presents an opportunity to enhance their service delivery to Sun. Improved accuracy and speed in project execution will translate into higher client satisfaction. The real-time tracking capability allows for proactive problem identification and resolution, preventing delays and costly rework. The system’s robust reporting and analytics capabilities provide valuable insights into performance metrics, facilitating data-driven decision-making for Capgemini’s project management strategies.
Improved Efficiency and Productivity Gains
The RFID system promises a significant boost in efficiency and productivity for both companies. By automating tasks, such as tracking and identifying materials, the system frees up personnel to focus on higher-value activities. The system reduces manual errors, ensuring accurate data collection and minimizing the time spent on administrative tasks. Real-time visibility into the movement of goods and materials eliminates delays and bottlenecks, optimizing workflows and accelerating project completion.
For example, in a construction project, real-time material tracking prevents the common issue of missing parts, saving time and money.
Potential Cost Savings
The RFID system offers significant potential cost savings through several avenues. Reduced material waste due to improved inventory management will result in considerable cost savings. Minimizing errors and delays in project timelines translates to reduced rework and operational expenses. By streamlining processes and automating tasks, the system reduces labor costs associated with manual tracking and verification. This translates into substantial financial benefits over the long term.
Consider a scenario where a company is managing thousands of parts; even a small percentage reduction in lost or misplaced items yields significant financial gains.
Enhanced Real-Time Tracking and Monitoring
The system provides unparalleled real-time tracking and monitoring capabilities. By leveraging RFID tags, the system precisely identifies and tracks the location and status of goods and materials throughout the entire supply chain. This level of real-time visibility allows for proactive management of resources, reducing the risk of delays and ensuring that materials are available when needed. For example, in a manufacturing setting, the ability to track materials in real-time allows for efficient allocation of resources and reduces production bottlenecks.
This allows for a highly responsive supply chain, optimizing the movement of goods and materials to ensure timely project completion.
Comparison with Existing Systems
The Sun-Capgemini RFID system represents a significant advancement in automated identification and tracking. To understand its value proposition, a comparative analysis with existing systems is crucial. This analysis will highlight key differentiators, strengths, and weaknesses, and provide a perspective on the evolving RFID landscape.
Key Differentiators of the Sun-Capgemini RFID System
This system distinguishes itself from competitors through several innovative features. The core differentiator lies in its enhanced scalability, offering a flexible and adaptable platform to meet diverse business needs. This scalability, combined with robust real-time tracking capabilities, makes the system ideal for complex and rapidly expanding operations. Moreover, the system’s cost-effectiveness, detailed below, sets it apart from more expensive legacy systems.
Analysis of Strengths and Weaknesses
The Sun-Capgemini RFID system exhibits several strengths compared to its predecessors. Its high scalability ensures adaptability to changing business requirements, a critical advantage in today’s dynamic market. Furthermore, its real-time tracking provides immediate visibility into inventory movements, allowing for optimized resource allocation and minimized operational inefficiencies. However, like any new system, potential weaknesses could include integration challenges with existing legacy infrastructure.
However, the robust design and detailed implementation plans mitigate this concern.
Evolution of RFID Technology and Impact on Competitors
RFID technology has undergone significant evolution, driven by advancements in microchip technology, antenna design, and data processing. This evolution has created new opportunities for businesses to optimize operations and enhance supply chain visibility. Competitors are responding by adopting RFID technologies or developing their own systems, creating a competitive landscape that constantly pushes innovation. For instance, companies like [Company A] and [Company B] are incorporating RFID solutions into their existing platforms, reflecting the growing market demand.
Comparative Analysis Table
| Feature | System A | System B | Sun & Capgemini RFID System |
|---|---|---|---|
| Real-time Tracking | Yes (Limited data points) | Yes (With periodic updates) | Yes (Continuous, detailed tracking of assets throughout the supply chain, including location and status in near real-time.) |
| Scalability | Limited (Specific use cases, fixed infrastructure) | Moderate (Supports expansion but with limitations on complexity) | High (Modular design allowing for seamless expansion to accommodate increasing data volumes and growing operational needs, easily integrated into various production environments.) |
| Cost | High (High initial investment and ongoing maintenance) | Moderate (Affordable but with less flexibility) | Competitive (Detailed pricing model available upon request. Considered cost-effective due to high scalability and efficient implementation process, leading to reduced operational costs in the long run.) |
Future Implications and Predictions
The Sun-Capgemini RFID system, with its potential to revolutionize various industries, promises a future brimming with possibilities. This system’s ability to track and manage assets in real-time holds the key to significant operational improvements and cost savings. Looking ahead, the system’s influence on supply chain management, inventory control, and even patient care is likely to be profound.This innovative RFID system’s impact on businesses and the broader industry will be multifaceted and long-lasting.
From increased efficiency to enhanced security, the potential benefits are vast. This exploration into the future of RFID will delve into the system’s evolution and its transformational effect on various sectors.
Future Evolution of the System
The RFID system’s future evolution will likely involve advancements in tag technology, potentially leading to smaller, more robust, and cost-effective tags. Improved reader technology will facilitate faster data transmission and wider coverage. The system’s integration with other technologies, such as IoT and AI, is anticipated to enhance its capabilities and create more sophisticated applications. The potential for enhanced security measures and more precise data analysis will be critical aspects of this future evolution.
Potential Applications Across Industries
The table below illustrates potential future applications of the RFID technology across various industries, highlighting the diverse range of potential improvements and enhancements.
| Industry | Potential Application |
|---|---|
| Retail | Implementing real-time inventory tracking across multiple locations, allowing for dynamic pricing strategies based on demand and supply, and providing enhanced loss prevention measures through automatic detection of theft. |
| Manufacturing | Enabling detailed tracking of raw materials, components, and finished goods throughout the entire supply chain, leading to improved efficiency and reduced lead times. This will also allow for real-time production monitoring and predictive maintenance, minimizing downtime. |
| Healthcare | Streamlining patient identification and treatment protocols through automatic identification and tracking of medical equipment, medications, and patient records, ultimately improving patient safety and reducing errors. |
| Logistics | Real-time tracking of goods in transit, optimizing routes and delivery schedules, and reducing delays and losses. This enables precise delivery tracking, enhancing customer satisfaction and minimizing delivery costs. |
Long-Term Impact on Businesses
The long-term impact on businesses will be significant, leading to improved operational efficiency, reduced costs, and enhanced customer satisfaction. Real-time visibility into inventory levels, supply chains, and asset locations will enable businesses to make data-driven decisions. Reduced theft and fraud, and improved supply chain resilience, will be additional benefits. Businesses will likely experience a shift toward more agile and responsive operations, empowered by the data-driven insights the RFID system provides.
Transforming Related Industries
The system’s implementation will significantly change the landscape of related industries by creating new opportunities for efficiency and innovation. For instance, in the retail sector, real-time inventory tracking can drive dynamic pricing and reduce stockouts. In healthcare, improved medication tracking can enhance patient safety and reduce errors. Overall, the system will foster a more data-driven and efficient approach to various business operations, creating new standards for industry practices.
Security Considerations: Sun And Capgemini Launch Rfid System
The Sun-Capgemini RFID system’s security is paramount. Robust security measures are crucial to protect sensitive data, maintain system integrity, and prevent unauthorized access. This section details the implemented security protocols, potential vulnerabilities, and strategies for mitigating risks, ultimately ensuring the system’s reliability and trustworthiness.
Implemented Security Measures
The system employs a multi-layered approach to security. This includes encryption at various stages, access control mechanisms, and regular security audits. Each layer reinforces the others, creating a strong defense against potential threats.
- Data Encryption: The system utilizes Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) 256-bit encryption for all data transmission and storage. This ensures that even if intercepted, the data remains unreadable without the decryption key. This approach is considered industry best practice.
- Access Control: Users are granted access based on roles and responsibilities. This role-based access control (RBAC) model limits access to sensitive data and system functions to authorized personnel only. For example, only authorized administrators can modify system configurations, while operational staff only interact with specific data sets relevant to their tasks.
- Regular Security Audits: The system undergoes regular security audits to identify and address potential vulnerabilities. These audits evaluate the effectiveness of security measures and help ensure the system’s resilience to evolving threats.
Potential Vulnerabilities and Risks, Sun and capgemini launch rfid system
While the system incorporates strong security measures, potential vulnerabilities exist. These include vulnerabilities in the hardware, software, and network infrastructure. Potential risks include unauthorized access, data breaches, and denial-of-service attacks.
- Hardware Vulnerabilities: Physical access to the RFID reader or tags could potentially allow unauthorized access to data. Strong physical security measures, such as locking mechanisms and controlled access areas, are necessary to mitigate these risks.
- Software Vulnerabilities: Software bugs or vulnerabilities in the system’s software components can create entry points for malicious actors. Regular software updates and penetration testing are crucial to address these vulnerabilities.
- Network Vulnerabilities: The network infrastructure connecting the system components is susceptible to attacks, such as denial-of-service (DoS) attacks. Robust network security measures, including firewalls and intrusion detection systems, are essential to protect the network from malicious activities.
Data Protection and Privacy Protocols
Protecting sensitive data is paramount. The system adheres to strict data protection and privacy regulations, ensuring compliance with relevant standards and laws. This includes data anonymization and secure storage practices.
- Data Anonymization: Data is anonymized wherever possible to minimize the risk of identifying individuals from the collected information. This is especially important in cases where personally identifiable information is collected.
- Secure Storage: Data is stored in secure servers with multiple layers of protection, including physical security, access controls, and data backups. This ensures business continuity in case of system failures or data breaches.
- Compliance: The system adheres to relevant data protection regulations such as GDPR and CCPA, ensuring the lawful and ethical handling of personal data.
Strategies for Mitigating Security Threats
Implementing preventative measures and response plans is vital to mitigate security threats. This involves training staff, establishing incident response protocols, and regular security awareness campaigns.
- Employee Training: Regular training programs educate staff on security best practices, including password management, phishing awareness, and data handling procedures. This approach is crucial in preventing social engineering attacks.
- Incident Response Plan: A detailed incident response plan Artikels procedures for handling security incidents, including data breaches or unauthorized access. A well-defined plan is vital for minimizing the impact of security incidents.
- Security Awareness Campaigns: Regular security awareness campaigns help employees stay informed about current threats and best practices. These campaigns reinforce security protocols and help maintain a vigilant security culture.
Encryption Methods
The system employs advanced encryption methods to secure data in transit and at rest.
- AES-256: Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) with a 256-bit key is used for data encryption. This is a widely recognized and robust encryption algorithm, providing high-level security.
- Hashing Algorithms: Hashing algorithms like SHA-256 are used for data integrity checks. This ensures that data hasn’t been tampered with during transmission or storage.
System Architecture
The Sun-Capgemini RFID system’s architecture is a crucial element for its success. It dictates how the system’s components interact, ensuring smooth data flow and optimal performance. This detailed breakdown will unveil the intricacies of this architecture, offering a clear understanding of its components and their interrelationships.The architecture of the Sun-Capgemini RFID system is designed for scalability and flexibility, accommodating various use cases and potential future expansions.
It utilizes a client-server model, separating the user interface from the data processing core, allowing for efficient management of complex operations.
Components of the System
The system comprises several key components, each playing a specific role in the overall functionality. Understanding these components and their interaction is vital for appreciating the system’s capabilities.
- RFID Readers: These are the devices that physically interact with the RFID tags. They read the data encoded on the tags and transmit it to the central system. Various reader types are available, each optimized for specific applications and environments (e.g., indoor, outdoor, high-volume). A critical aspect of the readers is their range and ability to read multiple tags simultaneously, influencing system throughput.
- RFID Tags: These small devices contain unique identification data. They are affixed to items to be tracked, and the data they hold can vary depending on the application. Different types of tags exist with varying read ranges, memory capacities, and power requirements. Tag durability is a key factor, especially in high-impact or harsh environments.
- Database Server: This component stores and manages the data collected from the RFID readers. It ensures data integrity, security, and accessibility for authorized users. The database is crucial for managing a large volume of data and supporting various reporting and analysis functions.
- Application Server: This acts as an intermediary, receiving data from the RFID readers, processing it, and forwarding it to the database server. It also manages user interfaces, enabling access and control over the system.
- User Interface (Web-based or Desktop): This allows authorized personnel to interact with the system. Users can view real-time data, generate reports, and manage system settings. The user interface is designed for ease of use and intuitive navigation.
Data Flow within the System
The system’s architecture ensures efficient data flow between the components. This flow is vital for the real-time tracking and management capabilities of the system.
- Tag Identification: RFID readers detect and identify RFID tags based on their unique identifiers.
- Data Transmission: The readers transmit the identified data to the application server.
- Data Processing: The application server processes the data and performs any necessary calculations or validations.
- Data Storage: The processed data is then stored in the database server.
- Data Retrieval: Authorized users can retrieve data through the user interface, enabling various reports and analyses.
Technical Specifications
The Sun-Capgemini RFID system boasts a robust architecture with specific technical details. These specifications are crucial for ensuring system performance and scalability.
| Component | Specification |
|---|---|
| RFID Readers | Frequency: 860-960 MHz, Read Range: 10 meters, Data Transfer Rate: 10 Mbps |
| RFID Tags | Memory: 1KB, Frequency: 860-960 MHz, Battery Life: 5 years |
| Database Server | SQL Server, Capacity: 1 TB, Scalability: Vertical/Horizontal |
| Application Server | Java-based, Scalability: Cloud-based |
| User Interface | Web-based, Responsive Design, Security Protocols: HTTPS |
Final Summary
The Sun and Capgemini RFID system represents a significant step forward in automated tracking and management. Its potential to streamline processes, enhance security, and reduce costs across various industries is substantial. The system’s implementation details, applications, and future implications suggest a promising trajectory for businesses seeking innovative solutions in logistics and supply chain management. Early adopters are poised to reap significant benefits.