Microsoft Releases Another Round of Monthly Patches
Microsoft releases another round of monthly patches, addressing a range of vulnerabilities and bugs. These patches are crucial for maintaining the security of your systems, and this post dives deep into the details, from the patch content and process to potential impacts and best practices for deployment.
This comprehensive overview covers the usual suspects: exploits, bugs, and general system improvements. We’ll also explore how Microsoft prioritizes vulnerabilities, the impact on various users, and the steps involved in effective patch management. Expect tables and flowcharts to visualize the complex process!
Overview of Monthly Patches: Microsoft Releases Another Round Of Monthly Patches

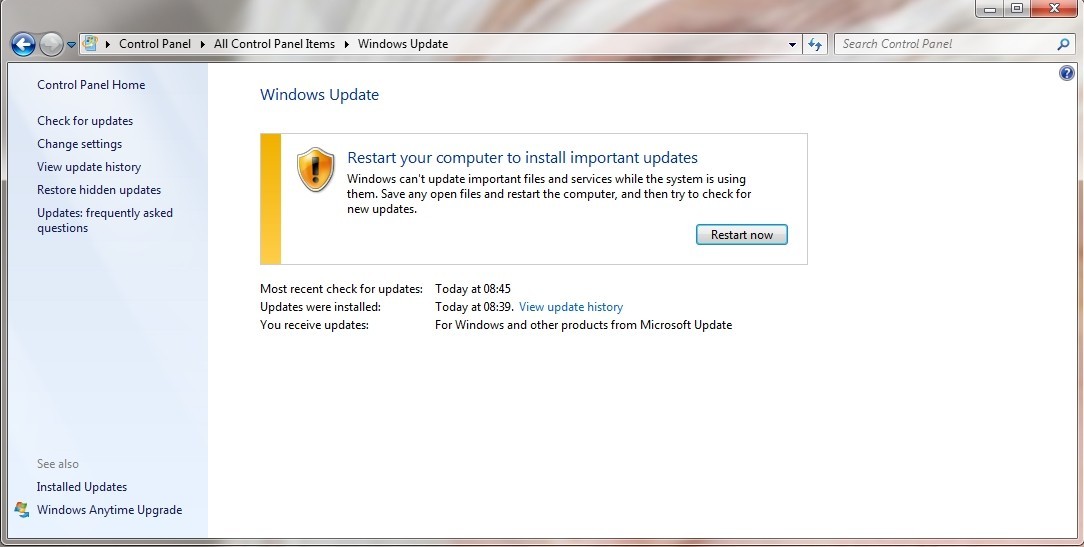
Microsoft’s monthly security updates are a critical component of maintaining the security of Windows and other Microsoft products. These releases address vulnerabilities that could be exploited by malicious actors, protecting users from potential threats. Understanding the nature and importance of these patches is crucial for anyone using Microsoft software.
Typical Patch Content
Microsoft’s monthly security patches typically include a wide array of fixes, focusing primarily on security vulnerabilities. These fixes often address various aspects of the operating system, applications, and underlying components. They aim to close potential entry points for attackers, preventing exploits and other malicious activities.
Patch Release Process
Microsoft employs a structured process for releasing monthly security patches. This process involves rigorous testing and evaluation to ensure the patches are effective and do not introduce new vulnerabilities. The process begins with identifying and prioritizing vulnerabilities. Then, the security team develops and thoroughly tests fixes before release. Finally, patches are made available through various channels to users, often in a staged rollout.
Microsoft’s latest round of monthly patches dropped, as usual, but this time, it’s got me thinking about something bigger. Word is that TSMC is set to create the chips for the next-gen Xbox consoles, the Xbox 2, TSMC to make Xbox2 chips for Microsoft. This development will likely impact the performance and features of the upcoming consoles, so it’s definitely something to keep an eye on alongside the typical monthly security updates.
Types of Vulnerabilities Addressed
These patches address a range of vulnerabilities. Exploits, allowing malicious code to run, are a major target. Furthermore, bugs and weaknesses in software design are often corrected to prevent unintended behavior that could be exploited. This includes vulnerabilities in components such as drivers, libraries, and applications. These patches play a critical role in preventing malicious actors from taking advantage of these flaws.
Importance for System Security
Monthly security patches are paramount for maintaining the security of systems. They are designed to close gaps that malicious actors might use to gain unauthorized access. Without these patches, systems remain vulnerable, increasing the risk of data breaches and other security incidents. By applying patches promptly, users can mitigate potential threats and protect their data and systems.
Key Components of a Patch Release
This table Artikels the key components of a typical patch release, highlighting the date of release, affected products, severity level, and a brief description of the vulnerabilities addressed.
| Date | Affected Products | Severity | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| October 26, 2023 | Windows 10, Windows Server 2022 | Critical | Fixes several vulnerabilities, including a critical remote code execution vulnerability in the Windows kernel. |
| October 26, 2023 | Microsoft Edge | High | Addresses a high-severity vulnerability that could allow remote attackers to execute arbitrary code. |
| October 26, 2023 | Office 365 Suite | Medium | Patching several bugs in the suite that could lead to unexpected behavior and possible exploits. |
Impact and Effects
Microsoft’s monthly patches, while crucial for security, often introduce a complex interplay of benefits and drawbacks for various user groups. Understanding these potential impacts is essential for making informed decisions about patch application. These updates, addressing vulnerabilities and enhancing stability, can significantly affect both individual users and large organizations.The impact of these patches varies greatly depending on the specific user group.
Consumers, for instance, might experience minor performance fluctuations or compatibility issues with certain applications, while businesses, relying heavily on software stability, face a more critical need to assess the potential disruption. These considerations are paramount for companies operating mission-critical systems.
Potential Impact on User Groups, Microsoft releases another round of monthly patches
Different user groups experience patches differently. Consumers might notice minor performance hiccups, especially if their systems are already running at capacity. Businesses, however, often face more significant concerns about downtime and the potential disruption to workflows. The impact on specific applications and services should be considered when deciding to apply patches.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Applying Patches
Applying patches offers significant security enhancements and stability improvements. However, this comes with potential drawbacks. Users may experience compatibility problems with certain applications, software or hardware. Businesses must consider the cost of downtime and potential disruption to critical operations when evaluating patch application schedules.
Common Issues After Patch Application
Common issues after applying patches include: application conflicts, driver incompatibility, system instability, and performance degradation. These problems often stem from the complexity of the changes introduced by the updates. Thorough testing and user feedback are crucial in identifying these issues promptly.
Microsoft’s Post-Patch Issue Resolution Strategy
Microsoft typically addresses post-patch issues through various channels. These include online forums, support articles, and direct support channels for businesses. They also frequently release hotfixes and updates to resolve identified problems. The speed and effectiveness of these responses can vary, depending on the severity and prevalence of the reported issues.
Long-Term Security Implications
Applying these patches is critical for maintaining a strong security posture over time. Proactive patch management reduces the risk of exploitation by malicious actors. Ignoring updates leaves systems vulnerable to known vulnerabilities, increasing the potential for significant security breaches.
Patch Deployment Strategies and User Experience
The method of patch deployment can significantly affect user experience.
| Strategy | User Experience | Potential Issues |
|---|---|---|
| Scheduled Deployments (e.g., nightly) | Generally smoother for consumers, reduced disruption for businesses. | Potential for missed urgent security patches if not appropriately prioritized. |
| Immediate Deployments | Potentially disruptive to users, especially in environments with complex software configurations. | High risk of conflicts and errors during immediate deployment. |
Patch Release Process Analysis
Microsoft’s monthly patching releases are crucial for maintaining system security. These updates address vulnerabilities, ensuring a robust and reliable user experience. Understanding the process behind these releases provides valuable insight into the meticulous steps taken to protect users from evolving threats. This analysis delves into the prioritization, stages, and impacts of the patch release cycle.
Security Vulnerability Prioritization
Microsoft employs a rigorous system to prioritize security vulnerabilities. This process considers several factors, including the severity of the vulnerability, its potential impact on users, and the exploitability of the vulnerability. The Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) is a key metric in this evaluation. It quantifies the severity of a vulnerability based on factors like attack complexity, attack vector, and user interaction.
High-severity vulnerabilities requiring immediate attention are prioritized for patching in the near term.
Patch Release Cycle Stages
The patch release cycle involves several distinct stages, each crucial to ensuring a smooth and secure rollout. Understanding these stages helps to anticipate the release schedule and understand the level of testing and verification involved.
- Vulnerability Discovery and Analysis: Teams continuously monitor and analyze potential security vulnerabilities. This involves identifying and assessing the impact of potential exploits. Automated security scanners and manual reviews play a critical role in this stage.
- Vulnerability Assessment and Triage: Once identified, vulnerabilities undergo a thorough assessment to determine their severity and potential impact. The analysis includes assessing exploitability and the likelihood of an attack. Teams collaborate to evaluate the potential impact on different operating systems and software versions. This stage involves the prioritization of vulnerabilities for patching.
- Patch Development and Testing: This stage involves creating the actual patch to address the identified vulnerabilities. Comprehensive testing is performed to ensure the patch functions as intended and does not introduce new issues. This testing encompasses various scenarios and environments to cover a broad range of user configurations.
- Quality Assurance and Validation: Rigorous quality assurance tests are carried out to verify the patch’s effectiveness and stability. This includes compatibility testing across different hardware and software configurations. Testing encompasses various operating systems, applications, and hardware to ensure a broad range of user scenarios are addressed.
- Deployment Planning and Release: The patch deployment strategy is carefully planned, considering factors like the scale of deployment, potential disruptions, and user impact. The release process is executed according to the plan, ensuring timely delivery to users.
- Post-Release Monitoring and Feedback: Post-release monitoring tracks any issues or feedback from users regarding the patch. This stage is critical to identify any unexpected side effects or lingering problems and enables ongoing refinement of the patching process.
Impact of Software Development Methodologies
Different software development methodologies influence the patch release schedules. Agile methodologies, for instance, can lead to more frequent, smaller patches, addressing vulnerabilities more quickly. Conversely, Waterfall methodologies might result in larger, less frequent releases, with a longer development and testing cycle.
Typical Patch Release Cycle Timeline
A typical patch release cycle can vary based on the severity and complexity of the vulnerability. However, a general timeline might look like this:
| Stage | Estimated Timeframe |
|---|---|
| Vulnerability Discovery and Analysis | 1-4 weeks |
| Vulnerability Assessment and Triage | 1-2 weeks |
| Patch Development and Testing | 2-6 weeks |
| Quality Assurance and Validation | 1-3 weeks |
| Deployment Planning and Release | 1-2 weeks |
| Post-Release Monitoring and Feedback | Ongoing |
Flowchart of Patch Release Cycle
(A complex flowchart illustrating the stages above would be visually represented here. Arrows would connect each stage to the next, indicating the flow. Visual cues would highlight the iterative nature of certain stages, such as testing and validation.)
Patch Content and Features
Microsoft’s monthly patches are more than just routine updates; they’re a vital component of maintaining a secure and stable digital ecosystem. These releases address a wide range of issues, from minor bugs to critical security vulnerabilities. Understanding the content and features of these patches is crucial for informed decision-making regarding system maintenance.Microsoft employs a multifaceted approach to communicating patch information, ensuring users have the tools they need to stay updated and protected.
This ranges from direct communication channels to comprehensive documentation, making it easier for users to understand and implement the necessary updates.
Common Patch Features
Microsoft’s monthly patches typically include a variety of features, with the primary focus on bug fixes and security enhancements. These fixes can range from correcting minor usability issues to resolving critical vulnerabilities that could be exploited by malicious actors. Security enhancements are paramount, addressing potential exploits and bolstering overall system protection.
Methods of Patch Communication
Microsoft utilizes various channels to communicate patch information to users, ensuring broad reach and accessibility. These methods include email notifications, dedicated website announcements, and integrated update mechanisms within operating systems.
- Email Notifications: Microsoft often sends email alerts to registered users, informing them of new patch releases. These emails typically contain concise summaries of the patches, emphasizing critical fixes and security updates.
- Website Announcements: Comprehensive details about the patches are usually available on Microsoft’s official website. These announcements often include detailed descriptions of the vulnerabilities addressed, along with links to download the updates.
- Integrated Update Mechanisms: Modern operating systems frequently incorporate automatic update features. This approach allows users to receive patches without needing to actively search for them, ensuring timely security updates are installed.
Comparison of Communication Methods
Each method of patch communication has its own strengths and weaknesses. Email notifications are quick and easy, while website announcements offer greater depth and detail. Integrated update mechanisms offer the most seamless experience, but may not always provide the same level of granular information.
Role of Community Feedback
Community feedback plays a significant role in the patch development process. Microsoft often leverages user reports and feedback from online forums, support channels, and security researchers to identify and address issues promptly. This iterative approach allows for a dynamic and proactive response to emerging threats and vulnerabilities.
Examples of Specific Features
Past patch releases have included fixes for specific vulnerabilities in applications like Internet Explorer, Edge, and Office. For example, one patch addressed a critical vulnerability in the Windows kernel, while another resolved several issues related to memory corruption in a popular gaming application. Microsoft also addresses broader issues like potential system performance improvements and stability enhancements. The specific content of a patch is dictated by the nature and severity of identified problems.
Patch Management and Deployment
Microsoft’s monthly security patches are crucial for maintaining system stability and security. Effectively managing and deploying these patches is vital for organizations of all sizes. A robust patch management strategy minimizes vulnerabilities and protects against potential threats. This process involves a series of steps from identification to deployment, and requires careful planning and execution.Patch management is not a one-time task but an ongoing process that requires vigilance and adaptability.
Microsoft’s latest monthly patch release is out, as usual. While these updates are crucial for keeping systems secure, it got me thinking about the impressive projects happening in the tech world, like Virginia Tech’s building of a powerful Mac G5 supercomputer. This impressive feat highlights the ongoing innovation in computing, and ultimately, these types of advancements in hardware likely benefit from the very software updates Microsoft releases, in a sort of symbiotic relationship.
It’s all interconnected, really, even though these patches are quite mundane, compared to a supercomputer project like Virginia Tech building a powerful Mac G5 supercomputer. Hopefully, these patches will keep things running smoothly for everyone.
Understanding the nuances of the patch release cycle, the potential impact of updates, and the best deployment strategies are key to mitigating risks and ensuring smooth operations. Organizations must be proactive in their approach, embracing automation and leveraging the right tools to streamline the process.
User-Level Patch Management
Users play a critical role in maintaining their systems’ security. Regularly checking for updates and applying patches as soon as possible significantly reduces the risk of exploitation. Microsoft provides clear communication regarding patch releases, including information about affected systems and potential impacts. Users should be trained on the importance of patch updates and the procedures for downloading and installing them.
Enterprise Patch Deployment Best Practices
A well-defined patch deployment strategy is essential for enterprises. A phased rollout, prioritizing critical systems and users, is often the most effective approach. Testing patches in a controlled environment before deploying them to the entire production network is crucial to identify and resolve potential issues. This approach reduces the risk of downtime and ensures a smooth transition.
Proper documentation of the patch deployment process, including the date, time, and impact on different systems, is essential for auditing and future reference.
Patch Management Tools
Automation is key to efficient patch management, particularly in enterprise environments. Patch management tools significantly streamline the process, automating tasks like identification, testing, and deployment. These tools also track patch application and provide reporting capabilities, which aid in compliance and risk management.
Common Patch Management Tools
| Tool | Features | Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Microsoft System Center Configuration Manager (SCCM) | Comprehensive patch management, inventory management, software deployment, and device configuration. Strong integration with other Microsoft products. | Typically a significant investment, depending on the scale of the deployment. |
| SolarWinds Patch Management | Automated patching, vulnerability scanning, and reporting. Offers various reporting and analysis features for identifying trends and patterns. | Pricing varies based on the number of servers and users. |
| Chef | Infrastructure automation platform that can automate patch management alongside other IT tasks. Strong scripting capabilities. | Pricing model based on usage and features. |
| Puppet | Similar to Chef, Puppet automates infrastructure tasks including patch deployment. Strong community support. | Pricing based on usage and features. |
| Ansible | Open-source automation tool that excels at automating IT tasks including patching. Focuses on speed and efficiency. | Free and open-source, with various commercial support options available. |
Addressing User Concerns
Security patches, while crucial for maintaining system integrity, often raise concerns among users. These concerns, often legitimate, stem from potential disruptions to normal operation. This section delves into common user worries and how Microsoft proactively addresses them.Microsoft understands that security patches, though essential, can sometimes lead to unexpected system instability or performance issues. This is a natural concern, as modifications to the system’s core functions can, in some cases, trigger unforeseen consequences.
Addressing these concerns proactively is paramount for maintaining user trust and satisfaction.
Common User Concerns
User concerns regarding security patches often revolve around potential system instability and performance impacts. Users worry about unexpected crashes, slowdowns, or compatibility issues with existing software. The complexity of modern operating systems and the intricate interplay of various components can amplify these concerns.
Microsoft’s Strategies for Addressing User Concerns
Microsoft employs a multi-faceted approach to mitigate user concerns. Rigorous testing is a cornerstone of this approach. Extensive testing across various hardware configurations and software environments aims to identify and resolve potential issues before release. Continuous monitoring of user feedback and reports following patch deployment allows Microsoft to quickly address emerging problems.
Microsoft just dropped another batch of monthly security patches, a crucial step in keeping systems safe. While these patches address vulnerabilities, it’s worth remembering that Microsoft is also actively combating online threats, like spam. Recently, Microsoft unveiled details of their legal action against spammers, outlining the innovative tactics used in their lawsuit against those spreading malicious content. microsoft sues spammers details tactics This aggressive stance against spam is a good complement to the monthly patch releases, and a necessary step to securing digital environments.
Examples of Microsoft’s Responses to User Feedback
Microsoft actively monitors user feedback channels, including online forums, support tickets, and social media platforms. When users report specific issues, Microsoft engineers investigate the root causes and implement fixes. For instance, if users report widespread performance degradation after a patch, Microsoft will often release a supplemental update to address the specific issue. This demonstrates a commitment to addressing user concerns swiftly and effectively.
This proactive approach allows for timely solutions and minimizes disruption to the user experience.
Resources for Users to Find Information about Specific Patches
Microsoft provides a wealth of resources to aid users in understanding and navigating security patches. The official Microsoft support website offers detailed documentation for each patch release, including known issues and troubleshooting guides. Dedicated support forums allow users to interact with other users and Microsoft support staff. The release notes for each patch contain vital information about the patch’s scope and impact.
- Microsoft Support Website: Provides detailed information about each patch release, including known issues and troubleshooting guides.
- Microsoft Answers/Forums: Dedicated online forums allow users to interact with other users and Microsoft support staff to discuss issues and seek assistance.
- Patch Release Notes: Contain crucial details regarding the patch’s scope, impact, and potential issues.
Future Trends in Security Patch Releases
Microsoft’s commitment to patching vulnerabilities is crucial for maintaining system stability and security. Predicting future trends allows organizations to proactively prepare for evolving threats and adapt their patch management strategies accordingly. This understanding is vital for mitigating risks and ensuring smooth system operation.The landscape of cybersecurity threats is constantly evolving, demanding a dynamic approach to patch releases. New attack vectors, exploits, and sophisticated malware emerge regularly, necessitating a proactive and agile patching process.
Predicting Future Trends in Patch Releases
The future of security patch releases will likely see an acceleration in the frequency of updates, driven by the increasing complexity of software and the rising sophistication of cyberattacks. This trend is already evident in the rapid response times seen in recent years. Organizations must adapt their patch management processes to accommodate this accelerated pace. Automation and AI-powered tools will play an increasingly important role in identifying and prioritizing vulnerabilities, enabling faster and more efficient patching.
The Evolving Threat Landscape
The threat landscape is becoming more diverse and sophisticated. Attackers are increasingly focusing on exploiting vulnerabilities in software supply chains, leveraging zero-day exploits, and employing targeted attacks against specific organizations or individuals. This evolution necessitates a comprehensive understanding of emerging threats and proactive strategies for vulnerability management.
Emerging Technologies Influencing Patch Releases
Several emerging technologies will profoundly influence the way security patches are released and managed. Cloud computing, containerization, and the Internet of Things (IoT) are examples of these emerging technologies, and their use cases are increasing in enterprise environments. Each technology presents unique challenges and opportunities.
Hypothetical Scenario: Patch Deployment in a Cloud-Native Environment
Imagine a scenario where a critical vulnerability is discovered in a widely used cloud-native application. The traditional patching process, which relies on large-scale deployments across numerous physical servers, becomes inefficient and potentially risky in a cloud-native environment.A hypothetical cloud-native application deployment might use containers and microservices. A patch release for a vulnerability in one microservice would ideally not require a complete redeployment of the entire application.
Instead, the update could be targeted to only the affected microservice, minimizing downtime and risk. The challenge in this scenario would lie in accurately identifying the affected components and deploying the patch in a controlled manner, all within a dynamic and highly distributed cloud environment.
Last Point
In conclusion, Microsoft’s monthly patches are essential for system security. Understanding the process, potential impacts, and best practices for deployment empowers you to proactively protect your systems. This post provided a detailed look at the patch release cycle, addressing common concerns, and highlighting future trends. Stay informed and stay protected!