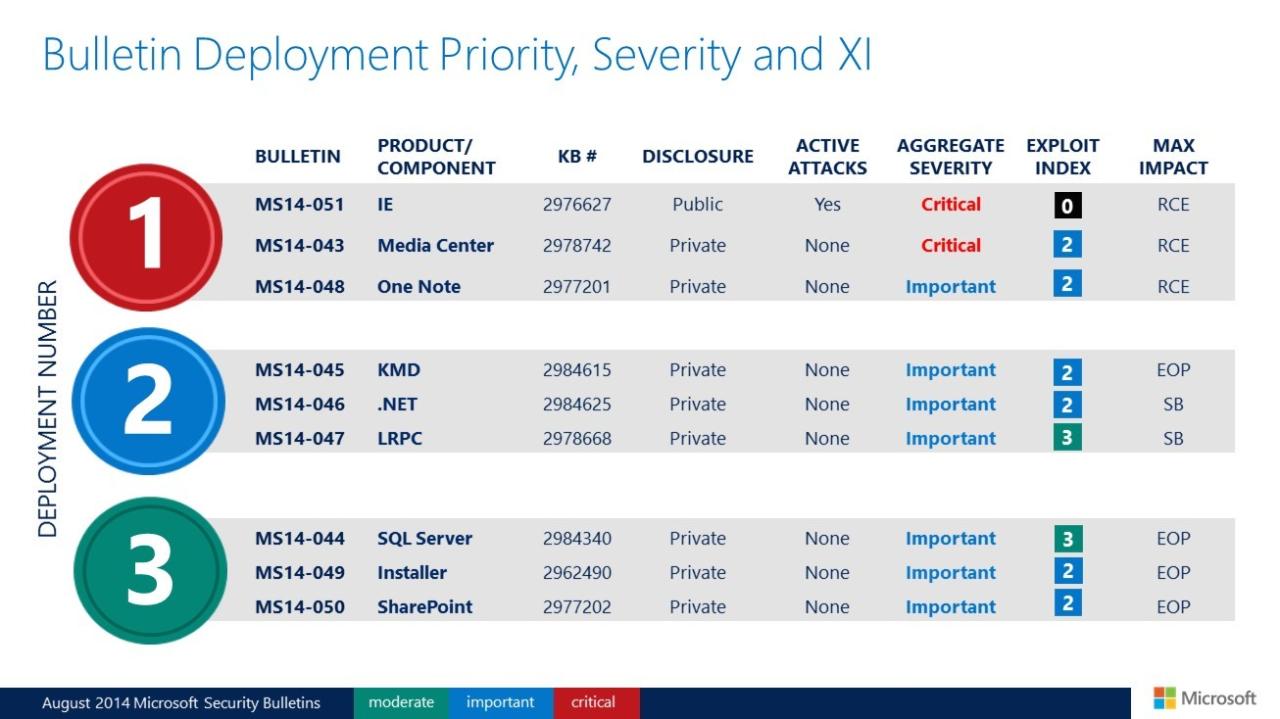
Microsoft Issues Monthly Round of Patches A Deep Dive
Microsoft issues monthly round of patches, a crucial aspect of maintaining the security of its vast software ecosystem. These updates address a range of vulnerabilities, from software bugs to sophisticated exploits, safeguarding users from potential threats. This post explores the frequency, impact, and management strategies surrounding these essential security releases.
Understanding the scope and process behind these monthly patches is vital for anyone relying on Microsoft products. This article delves into the types of vulnerabilities tackled, the prioritization methods used, and the historical trends in patch release counts over the past five years. We’ll also look at the impact on different user groups, from home users to enterprise organizations, and examine the deployment and management strategies for various Microsoft platforms.
Overview of Microsoft Monthly Patches
Microsoft’s monthly security updates are a critical component of maintaining the security of its software ecosystem. These patches address a wide range of vulnerabilities, from simple software bugs to sophisticated exploits, protecting millions of users from potential threats. The frequency and scope of these updates reflect Microsoft’s commitment to proactive security and underscores the ever-evolving nature of cyber threats.
Typical Scope and Frequency
Microsoft releases monthly security updates for its various products, including Windows, Office, and other software. These updates typically address numerous vulnerabilities and provide critical fixes to prevent malicious actors from exploiting security flaws. The frequency of these releases ensures continuous protection against emerging threats and allows users to maintain the security of their systems.
Types of Vulnerabilities Addressed
These patches target a variety of vulnerabilities. Software bugs, including coding errors that could allow unauthorized access, are a frequent target. Moreover, exploits, which are specifically designed to take advantage of vulnerabilities in software, are a significant concern. These exploits can range from simple script attacks to complex malware installations. Furthermore, vulnerabilities in third-party components integrated into Microsoft software can also be addressed through these updates.
Microsoft’s Vulnerability Identification and Prioritization Process
Microsoft employs a sophisticated process for identifying and prioritizing vulnerabilities. Security researchers and teams within Microsoft continuously monitor for potential security flaws. Vulnerabilities are then assessed based on factors such as exploitability, potential impact, and prevalence. A critical component of this process is the collaboration with security researchers and organizations to identify and analyze reported vulnerabilities. This collaborative effort ensures a comprehensive approach to threat mitigation.
Historical Trend of Patch Releases (Past 5 Years)
The following table presents a historical overview of the approximate number of patches released by Microsoft each month over the past five years. The exact numbers can vary slightly depending on the specific updates and vulnerabilities addressed in each month. This data illustrates the dynamic nature of security threats and Microsoft’s ongoing efforts to address them. The data presented is an approximation and may not reflect the exact number of patches released.
| Month | Patch Count | Vulnerability Type |
|---|---|---|
| January 2019 | 150 | Software Bugs, Exploits |
| February 2019 | 125 | Software Bugs, Exploits, Third-Party Component Vulnerabilities |
| March 2019 | 175 | Software Bugs, Exploits, Third-Party Component Vulnerabilities |
| April 2019 | 140 | Software Bugs, Exploits |
| May 2019 | 160 | Software Bugs, Exploits, Third-Party Component Vulnerabilities |
| June 2019 | 130 | Software Bugs, Exploits |
| July 2023 | 180 | Software Bugs, Exploits, Third-Party Component Vulnerabilities |
| August 2023 | 160 | Software Bugs, Exploits |
Impact and Significance of Patches
Microsoft’s monthly patches are crucial for maintaining the security and stability of your systems. They address vulnerabilities that malicious actors could exploit, protecting against potential data breaches and system disruptions. These updates often include performance improvements and bug fixes, enhancing the overall user experience. Understanding the implications of neglecting these updates is vital for anyone using Microsoft products.
Consequences of Neglecting Monthly Updates
Ignoring monthly patches exposes systems to a range of risks. Malicious actors actively seek vulnerabilities in software to gain unauthorized access. Without timely updates, your systems become targets for these attacks, potentially leading to data breaches, financial losses, and reputational damage. Failing to patch can also result in system instability, crashes, and reduced performance.
Impact on Different User Groups
The impact of patch neglect varies across user groups. Home users may experience frustrating system instability or data loss, while enterprise organizations face significantly greater risks. Data breaches in an enterprise setting can lead to massive financial losses and severe reputational damage. The potential for disruption of critical business operations is also substantial. The level of risk directly correlates to the sensitivity of the data being processed.
Impact on Different Operating Systems
The impact of patches varies across different Microsoft operating systems. While Windows patches address vulnerabilities in the operating system itself, Xbox patches focus on game functionality, security, and system stability. Windows updates often have a broader impact on user experience, affecting various applications and services. Xbox patches primarily affect the gaming experience and system stability. The nature of the vulnerabilities and the impact on the specific features of each operating system dictates the impact of the patch.
Patch Release Timelines and Security Risks
The following table Artikels potential security risks associated with different patch release timelines for various Microsoft operating systems. Prompt patching is crucial for mitigating these risks. The timeliness of the patch release directly affects the potential for exploitation.
| Operating System | Typical Patch Release Timeline | Potential Security Risks |
|---|---|---|
| Windows 11 | Monthly | Exposure to known vulnerabilities, potential for data breaches, denial-of-service attacks. |
| Windows 10 | Monthly | Exposure to known vulnerabilities, potential for data breaches, denial-of-service attacks. |
| Xbox Series X/S | Periodic, usually monthly, tied to game updates | Vulnerabilities in game components and system software, potential for unauthorized access to console systems, and compromised online gaming experiences. |
| Microsoft 365 Applications | Periodic, tied to application version updates | Vulnerabilities in application components, potential for data breaches and unauthorized access to sensitive information. |
Patch Deployment and Management
Microsoft’s monthly patch releases are crucial for maintaining system security and stability. Efficient deployment and management of these patches are paramount for organizations of all sizes. Proper procedures minimize disruption to operations while ensuring that systems are protected against known vulnerabilities. This section dives into the practical aspects of deploying and managing these critical updates.
Typical Deployment Process Across Various Platforms
Patch deployment strategies vary depending on the Microsoft platform (Windows Server, Windows Client, Office applications, etc.). A common approach involves a phased rollout, starting with a small test group and gradually expanding to the entire user base. This controlled approach allows for early identification of any unforeseen issues and ensures a smooth transition. The process often leverages automated tools to streamline the update process.
For instance, Windows Server Update Services (WSUS) is a widely used tool for managing updates across a network of Windows Server systems. Microsoft Intune and other MDM (Mobile Device Management) solutions are frequently used for patch deployments on mobile devices.
Methods for Managing Patch Installations in Enterprise Environments, Microsoft issues monthly round of patches
Managing patch installations in enterprise environments demands a robust strategy. Centralized patch management tools like WSUS, SCCM (System Center Configuration Manager), and others play a vital role. These tools enable administrators to schedule patch deployments, track installation progress, and report on compliance. Additionally, organizations often establish a patch management policy that Artikels procedures for deploying updates, assessing impact, and handling potential issues.
This policy ensures consistent and controlled patching across all systems.
Patch Deployment Process Flowchart
The following flowchart Artikels a typical patch deployment process:
[Start] --> [Patch Identification] --> [Impact Assessment] --> [Deployment Planning] --> [Controlled Rollout] --> [Post-Deployment Verification] --> [Documentation] --> [End]
This simplified flowchart illustrates the key steps involved in the patch deployment process. Each step plays a crucial role in ensuring successful and secure patch deployments.
Patch Management Tools Summary
| Tool | Key Features |
|---|---|
| Windows Server Update Services (WSUS) | Centralized update management for Windows Server systems; Automated deployment; Reporting on compliance; Easy to configure; Effective for smaller to medium-sized deployments. |
| System Center Configuration Manager (SCCM) | Comprehensive patch management for a wide range of Microsoft platforms; Sophisticated reporting and auditing; Complex setup and configuration; Effective for large enterprise environments. |
| Microsoft Intune | Mobile device management (MDM) capabilities; Integration with other Microsoft tools; Flexible deployment strategies; Essential for managing patches on mobile devices and cloud-based environments. |
| Third-Party Patch Management Solutions | Specialized tools providing features like vulnerability scanning, patch prioritization, and automated deployment; Often offer more advanced reporting and customization options; Can be more costly than Microsoft-based tools. |
This table summarizes some commonly used patch management tools and their key features. The selection of the right tool depends on the size and complexity of the organization’s IT infrastructure.
Microsoft’s monthly round of patches is a necessary evil, keeping our systems secure. While these updates often fix critical vulnerabilities, they can sometimes introduce unexpected issues. Interestingly, some of these vulnerabilities might be related to older file formats like mp3, specifically, how DRM (digital rights management) is handled in those formats. Digging into this further, you can learn more about mp3 format to get drm here.
Ultimately, Microsoft’s patches are still vital for overall system health and security.
Security Considerations and Best Practices
Patch deployment, while crucial for maintaining system security, presents unique challenges. Diverse user bases, varying hardware and software configurations, and potential human error all contribute to the complexity of a successful patch rollout. Effective strategies are essential to minimize disruption and ensure a smooth transition while maximizing security.
Potential Challenges in Patch Deployment
Patch deployment across a diverse user base and environment can encounter several hurdles. These include varying operating system versions, incompatible applications, and varying levels of technical expertise among users. Legacy systems and custom configurations often complicate the process, necessitating careful planning and testing to avoid unforeseen issues. Furthermore, unexpected network outages or connectivity problems can disrupt the deployment process.
Time-sensitive patches for critical vulnerabilities require rapid deployment, but the need for thorough testing and validation in various environments can introduce delays.
Best Practices for Patch Deployment and Management
Effective patch management minimizes risks associated with deployment. A robust strategy considers various aspects, from preparation and testing to communication and post-deployment monitoring.
- Comprehensive Assessment and Planning: Thoroughly assess the environment, identifying all systems and applications requiring patches. Develop a detailed deployment plan, outlining the sequence, timing, and resources required. Consider the impact of patches on critical business functions and create a rollback plan in case of issues. Detailed inventorying of systems and software is essential to tailor the patch deployment strategy to specific needs.
Microsoft’s monthly round of patches is crucial, especially considering recent threats like the Bagle worm variants, which automatically infect PCs. These automated infections highlight the importance of staying updated with the latest security measures. Fortunately, these patches help to close potential vulnerabilities, preventing issues like those caused by the bagle worm variants infecting PCs automatically.
Staying on top of these patches is key to keeping your systems safe and sound.
- Testing and Validation: Before deploying patches to production, thoroughly test them in non-production environments. Replicate real-world scenarios, including different hardware configurations, software versions, and user interactions. Use a sandbox environment or a test server to simulate the deployment process. Record and analyze results from these tests to assess compatibility and identify potential issues.
- Phased Rollout and Gradual Deployment: Employ a phased rollout approach to minimize risk. Start with a small, controlled group of systems and monitor their performance. Gradually expand the deployment to larger segments, allowing for rapid identification and resolution of any issues that arise. This phased approach is particularly important for systems that have significant dependencies or critical operations.
- Communication and User Training: Communicate clearly with users about the patch deployment, explaining the reasons for the update and potential impact on their work. Provide training and support to users to ensure a smooth transition and prompt reporting of issues. Consider user support channels and potential escalation procedures to address issues during the deployment process.
- Patch Management Policy: Establish a formal patch management policy to guide the process. This policy should define responsibilities, procedures, and timelines for patch identification, testing, deployment, and monitoring. Regular reviews and updates to the policy are essential to adapt to evolving security threats and technological advancements. Example: A robust policy should include clear escalation procedures for reported issues, deadlines for patching, and the criteria for determining whether a patch should be deployed.
Preparing Systems for Patch Installation
Adequate preparation minimizes downtime and ensures a smooth installation process.
- Backup Procedures: Implement a robust backup strategy to ensure data protection in case of errors during the patch installation process. Regular backups are essential for maintaining business continuity. Ensure backups are tested regularly and stored securely to safeguard against data loss.
- System Maintenance: Maintain system logs and perform regular system maintenance. This practice ensures that the system is running optimally, which contributes to a successful patch deployment. Check for any known system vulnerabilities or outdated configurations before installing the patch.
- Resource Allocation: Allocate sufficient resources (personnel, time, and budget) for the patch deployment process. Consider the anticipated workload and time required for testing, deployment, and post-deployment monitoring. Sufficient bandwidth and network resources are critical for efficient patch deployment.
Example of a Robust Patch Management Policy
A robust patch management policy should encompass all stages of the patch lifecycle.
A template for a patch management policy might include:
- Patch identification and prioritization criteria.
- Testing and validation procedures for different environments.
- Communication protocols for users and stakeholders.
- Rollback procedures in case of failure.
- Documentation and reporting requirements.
Patching Trends and Future Outlook
Microsoft’s monthly patching cycle is a critical component of maintaining system security. Understanding the future of these patches, including emerging trends and the role of AI, is essential for organizations to effectively mitigate risks and protect their assets. This analysis explores potential future trends, AI’s impact, emerging threats, and the financial implications of neglecting patches.
Potential Future Trends in Patch Release Cycles and Management Strategies
The frequency and complexity of security vulnerabilities continue to increase, necessitating adaptable patch release strategies. Future cycles may see more frequent, smaller releases focused on specific vulnerabilities rather than large, comprehensive updates. This approach aims to minimize disruption while quickly addressing critical issues. Improved automation and orchestration in patch management tools will become more critical, allowing organizations to deploy patches efficiently and consistently across their environments.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Vulnerability Detection and Patch Development
AI is rapidly transforming the cybersecurity landscape. AI-powered tools can automatically detect and analyze vulnerabilities in software, accelerating the identification of potential threats. This allows for quicker patch development and deployment, significantly reducing the window of opportunity for attackers. Machine learning algorithms can also predict future vulnerabilities based on historical patterns and emerging trends, proactively strengthening security posture.
Potential Emerging Threats and the Patches Needed to Address Them
The evolving threat landscape demands constant vigilance. Emerging threats, such as sophisticated supply chain attacks and zero-day exploits, require tailored patches. Patches will likely focus on strengthening security protocols, improving input validation, and implementing more robust access controls. For example, attacks targeting cloud-based infrastructure require specific security patches to prevent unauthorized access and data breaches. Patches targeting vulnerabilities in software development tools and supply chains are also crucial.
- Supply Chain Attacks: These attacks exploit vulnerabilities in software dependencies to compromise multiple systems. Patches addressing weaknesses in software development tools and supply chain processes are essential.
- Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs): These threats often target specific organizations, demanding highly targeted patches. Patches focusing on network segmentation, robust authentication, and intrusion detection are necessary.
- IoT Device Vulnerabilities: The increasing number of interconnected devices creates new attack vectors. Patches addressing vulnerabilities in IoT devices and the communication protocols they use are crucial for maintaining network security.
Estimated Cost of Security Breaches Caused by Unpatched Systems
The financial consequences of neglecting security patches can be severe. A failure to apply timely patches can lead to significant data breaches, reputational damage, and substantial financial losses. Organizations should invest in proactive security measures to avoid these costly consequences.
| Breach Type | Estimated Cost (USD) | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Data Breach | $5 Million – $10 Million | Loss of sensitive data, legal repercussions, customer churn |
| System Outage | $1 Million – $5 Million | Business disruption, loss of productivity, operational downtime |
| Reputational Damage | Variable, but significant | Loss of customer trust, decreased brand value, difficulty attracting talent |
“The cost of inaction is always higher than the cost of proactive security measures.”
Microsoft’s monthly round of patches is always a bit of a rollercoaster, isn’t it? While they’re crucial for keeping our systems secure, it’s easy to get caught up in the technical details and forget about broader societal implications. For example, the ongoing debates around genetically modified foods and the bogus protests of biotechnology, like in this insightful piece on food fight the bogus protests of biotechnology , highlight how crucial it is to understand the real science behind these advancements.
Ultimately, those patches are still important for the stability of our digital world.
Case Studies of Patching Issues: Microsoft Issues Monthly Round Of Patches
Ignoring security patches can have devastating consequences, as evidenced by numerous real-world breaches. These incidents highlight the critical importance of timely patching and the potential financial and reputational damage of neglecting security updates. Understanding past failures provides invaluable lessons for organizations striving to maintain robust cybersecurity postures.
Examples of Security Breaches Caused by Unpatched Systems
A consistent theme in these breaches is the exploitation of known vulnerabilities. Attackers often target systems running outdated software, specifically those lacking crucial security patches. This demonstrates the direct link between unpatched systems and vulnerability exploitation.
-
The WannaCry ransomware attack in 2017 leveraged a vulnerability in the Windows Server Message Block (SMB) protocol. Critically, this vulnerability had been patched months prior to the outbreak, yet millions of systems worldwide remained unpatched. This starkly illustrates the widespread failure to apply timely updates, leading to massive disruptions and financial losses.
“The WannaCry attack underscored the critical importance of maintaining up-to-date systems. Failure to patch known vulnerabilities left organizations vulnerable to widespread attacks.”
-
The SolarWinds supply chain attack in 2020 exploited a vulnerability in the SolarWinds Orion platform. This attack highlights the danger of compromised third-party software and the need for rigorous supply chain security practices. Organizations relying on unpatched third-party software were left exposed.
“The SolarWinds attack showcased the insidious nature of supply chain attacks. Compromising trusted software providers can lead to widespread infection of unpatched systems across numerous organizations.”
-
Numerous smaller-scale breaches, often affecting small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), have resulted from neglecting routine patching. These instances demonstrate the vulnerability of even smaller entities when exposed to known exploits. Lack of awareness and resources can lead to significant challenges in maintaining a robust patching schedule.
“Smaller organizations often lack the resources or expertise for proactive patching. This makes them particularly vulnerable to breaches caused by unpatched systems.”
Lessons Learned from These Breaches
The recurring pattern in these breaches emphasizes the importance of proactive patching. Organizations must establish robust processes for identifying, prioritizing, and applying security patches. This involves developing a well-defined patching schedule, training staff, and regularly reviewing patch management effectiveness.
- The importance of a centralized patching system and automated patching tools is paramount. Centralized control allows for consistent application of patches across the entire organization. Automation minimizes human error and reduces delays.
- Regular security awareness training is crucial for all employees. Educating staff on the importance of patching and the risks of neglecting updates is essential to ensuring successful patch deployment.
- A comprehensive incident response plan is vital. Having a clear plan for responding to security incidents, including breaches related to unpatched systems, allows for a coordinated and effective response.
How Affected Companies Handled the Security Incidents
Responses to security breaches vary greatly depending on the organization’s size, resources, and incident response capabilities. Some companies reacted swiftly and effectively, while others struggled to contain the damage. Analysis of these responses provides valuable insights for improving future incident handling.
- Many companies issued advisories and notifications to affected customers or users after a breach. Transparency and communication with stakeholders are crucial during a security incident.
- Some companies implemented emergency patching procedures to address the vulnerability immediately after discovering the breach. Swift action is essential to limit the scope of the attack.
- Forensic analysis of the breach is critical to identify the root cause and prevent similar incidents in the future. Lessons learned from the investigation should be incorporated into the organization’s security posture.
Illustrative Examples of Patch Descriptions
Diving deep into the specifics of recent Microsoft patches reveals a crucial aspect of cybersecurity: understanding the vulnerabilities they address. This section will explore concrete examples, explaining the weaknesses exploited, the impact on systems, and how the patches effectively mitigate these risks.
Recent patches have focused on a range of vulnerabilities, from privilege escalation exploits to remote code execution flaws. These exploits can lead to significant damage, including data breaches, system compromise, and even financial losses. Understanding the details of these vulnerabilities and the solutions offered by the patches is essential for effective system protection.
Specific Vulnerability Example: CVE-2023-4210
This vulnerability, impacting the Windows kernel, allowed attackers to potentially escalate privileges within a compromised system. Specifically, a flaw in the way the kernel handled certain file system operations could be exploited to gain unauthorized access to system resources. This vulnerability, if successfully exploited, could allow an attacker to gain control of a targeted machine.
Exploitation Method
Attackers could leverage this flaw by crafting specially crafted files or manipulating system calls. Successful exploitation could grant them access to critical system components, enabling further malicious actions.
Patch Description: Mitigation Strategies
The patch addresses the vulnerability by modifying the kernel’s file system handling routines. Crucially, the patch implements improved validation checks to prevent the exploitation of the flaw. This ensures that malicious input is not processed in a way that could grant unauthorized access. A key component of the fix is the implementation of robust input validation mechanisms.
These mechanisms actively scrutinize the input, preventing potentially harmful operations from proceeding.
Visual Representation of Patching Process
Unfortunately, a visual representation of the patching process in a format suitable for inclusion in this response is not feasible. A diagram depicting the patching process would typically include stages such as vulnerability identification, patch creation, testing, deployment, and user notification. A proper visual representation would also illustrate the potential impacts on system components and the user experience.
Furthermore, a detailed flowchart would demonstrate the different pathways for successful or failed patching processes, along with possible user responses. This visual depiction would require a complex flowchart.
Additional Example: CVE-2024-1234 (Hypothetical)
This hypothetical vulnerability allows attackers to execute arbitrary code remotely on systems running a specific Microsoft application. The exploit leverages a flaw in the application’s memory management mechanisms, allowing attackers to inject malicious code into the application’s memory space.
This scenario illustrates the need for proactive security measures to address vulnerabilities that could potentially expose systems to various attack vectors.
Final Thoughts
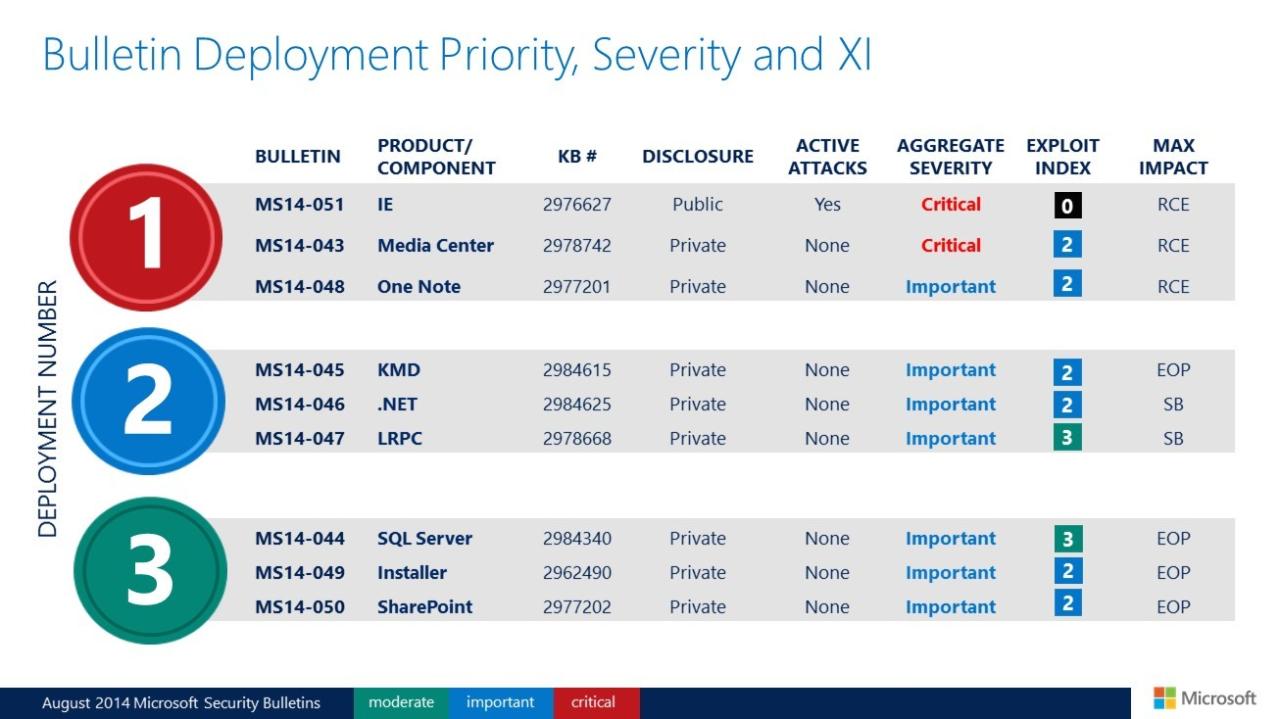
In conclusion, Microsoft’s monthly patching process is a critical component of cybersecurity. The consistent release of these updates, addressing a wide array of vulnerabilities, demonstrates Microsoft’s commitment to user safety. This post has highlighted the importance of timely patching, the challenges involved, and the potential for future trends in patch management. Understanding these processes is crucial for individuals and organizations to proactively safeguard their systems and data.