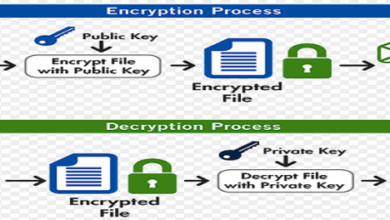
Financial Institutions Unwitting ID Thief Accomplices
Financial institutions unwitting accomplices of id thieves sets the stage for a critical examination of how seemingly secure systems can be exploited. This investigation delves into the vulnerabilities within financial institutions, revealing how they can inadvertently facilitate identity theft. We’ll explore various contributing factors, from inadequate security measures to a lack of employee training, and examine the devastating consequences for both individuals and the institutions themselves.
From weak passwords and insecure systems to outdated technology and insufficient regulatory oversight, the landscape of identity theft is fraught with peril. We’ll dissect the common pitfalls and highlight the crucial role of proactive security measures, robust employee training, and vigilant regulatory compliance in preventing these crimes.
Defining the Problem
Financial institutions, while crucial for a functioning economy, can inadvertently become unwitting accomplices in identity theft. This happens when lax security practices or insufficient oversight allow fraudulent activities to flourish. Understanding how this occurs is critical to strengthening security measures and protecting consumers.The concept of unwitting accomplices in identity theft involves financial institutions unknowingly facilitating the theft of an individual’s identity.
Financial institutions are sometimes unwitting accomplices to identity theft, failing to adequately protect customer data. This unfortunately leaves many vulnerable to fraud. While exploring ways to improve security, I’ve been impressed by the capabilities of 3D modeling software, like the sharp ships 3D notebook , which could potentially offer new solutions to enhance data encryption and verification processes.
This ultimately strengthens the fight against identity thieves and helps prevent future fraud cases.
This can manifest in various forms, from failing to detect fraudulent transactions to inadequately verifying customer identities. The resulting harm to consumers can be significant, encompassing financial losses, damage to credit rating, and emotional distress.
Unintentional Facilitation of Identity Theft
Financial institutions can unintentionally facilitate identity theft through several channels. Insufficient background checks, inadequate fraud detection systems, and weak authentication procedures are all contributing factors. Furthermore, the failure to promptly investigate suspicious activities can allow criminals to exploit vulnerabilities and cause substantial harm.
Examples of Implicated Financial Institutions
Numerous instances highlight financial institutions’ involvement in identity theft cases. For example, a bank might fail to scrutinize a suspicious wire transfer request, leading to a significant loss for the account holder. Similarly, a credit card company might not adequately verify a new account application, resulting in the fraudulent use of the card. These situations demonstrate the potential for financial institutions to unintentionally become part of the problem.
Financial institutions are sometimes unwitting accomplices to identity theft, failing to adequately protect customer data. This is a serious issue, and while the FBI’s new anti-piracy seal for publishers, like the one detailed in fbi rolls out antipiracy seal for publishers , aims to combat a different kind of fraud, it highlights the larger problem of safeguarding sensitive information.
Ultimately, financial institutions need to step up their game to prevent these kinds of crimes.
Types of Identity Theft Enabled by Financial Institutions
Financial institutions can unintentionally enable various forms of identity theft. These range from unauthorized account access and fraudulent transactions to the creation of false identities for criminal activities. These acts can have far-reaching consequences, impacting the victim’s financial stability, creditworthiness, and overall well-being.
Responsibilities and Rights in Identity Theft Prevention
The responsibilities of financial institutions in preventing identity theft are substantial. They must implement robust security measures, train employees on fraud detection techniques, and promptly investigate suspicious activities. Conversely, consumers have a right to expect their financial institutions to safeguard their information and take reasonable steps to prevent fraudulent activities. A balance between these responsibilities and rights is critical to fostering a secure financial environment.
Common Pitfalls and Vulnerabilities in Financial Institutions
| Pitfall | Vulnerability | Impact | Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inadequate security measures | Weak passwords, insecure systems | Unauthorized access, data breaches | Strong authentication, data encryption |
| Lack of fraud detection | Failure to monitor unusual transactions | Significant financial losses for consumers | Advanced fraud detection systems, real-time monitoring |
| Insufficient customer verification | Inadequate checks on new account applications | Creation of fraudulent accounts | Enhanced Know Your Customer (KYC) procedures |
| Slow response to suspicious activity | Delays in investigating unusual transactions | Increased opportunity for criminals | Immediate response protocols, dedicated fraud teams |
Root Causes and Contributing Factors
Financial institutions, despite their best intentions, can inadvertently become accomplices in identity theft. This unfortunate reality highlights a complex web of vulnerabilities, often stemming from a confluence of factors that extend beyond simple negligence. Understanding these root causes is crucial to developing robust preventative measures and fostering a more secure financial landscape.Many financial institutions face challenges in safeguarding customer data, with insufficient resources, outdated technology, and inadequate training frequently playing significant roles.
The sheer volume of transactions and the constant evolution of fraudulent techniques make maintaining a vigilant security posture an ongoing struggle.
Primary Reasons for Unwitting Accomplices
Financial institutions may unwittingly facilitate identity theft due to a variety of factors. These include insufficient internal controls, lack of employee training, and reliance on outdated technologies. A robust security framework necessitates addressing these vulnerabilities proactively.
- Inadequate Internal Controls: Weaknesses in internal controls can create opportunities for fraudsters to exploit loopholes and bypass security measures. This may manifest in insufficient authentication protocols, weak access controls, or inadequate monitoring of suspicious activities. For instance, a lack of real-time monitoring of account activity can allow fraudulent transactions to go undetected for extended periods.
- Lack of Employee Training and Awareness: Employees are the first line of defense against fraud. Insufficient training on identifying red flags, recognizing phishing attempts, and reporting suspicious activities can lead to a significant increase in identity theft incidents. A lack of comprehensive training programs can leave employees ill-equipped to handle potentially fraudulent situations. A recent study highlighted that employees lacking proper training were 2.5 times more likely to fall victim to phishing scams compared to those with adequate training.
- Technological Limitations or Outdated Systems: Legacy systems and outdated technologies often lack the robust security features necessary to counter modern identity theft tactics. These systems may be vulnerable to hacking or data breaches, making them a prime target for fraudsters. For example, a financial institution relying on outdated software may be susceptible to known exploits that are readily available to malicious actors.
This can lead to significant data breaches and expose sensitive customer information.
Role of Inadequate Regulations and Oversight
Regulations and oversight play a pivotal role in shaping the security posture of financial institutions. Weak or absent regulations can create an environment where fraudsters operate with impunity. A lack of clear guidelines and enforcement mechanisms can hinder the ability of institutions to adopt effective security measures.
- Lack of Stringent Regulations: Inadequate regulations often fail to address the evolving nature of identity theft tactics, leaving institutions vulnerable to emerging threats. This can lead to a lack of standardization in security practices across the industry, creating inconsistencies in the level of protection offered to customers.
- Insufficient Oversight: Weak oversight can allow institutions to operate with lax security protocols without facing significant consequences. This can result in a culture of complacency, where the importance of security is not adequately prioritized.
Significance of Industry Best Practices and Compliance Standards, Financial institutions unwitting accomplices of id thieves
Adherence to industry best practices and compliance standards is crucial for preventing identity theft. These standards provide a framework for implementing robust security measures and ensuring consistent levels of protection for customers.
- Importance of Best Practices: Best practices provide a roadmap for implementing security controls, mitigating risks, and adapting to emerging threats. These practices are vital in maintaining a robust security posture.
- Compliance Standards: Compliance with relevant regulations and standards is crucial for demonstrating a commitment to security. Compliance frameworks such as PCI DSS provide a structured approach to enhancing security and protecting customer data.
Comparative Analysis of Security Awareness Improvement Approaches
The following table compares various approaches to enhancing security awareness within financial institutions.
| Approach | Description | Effectiveness | Implementation Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|
| Employee Training Programs | Comprehensive training on recognizing and reporting suspicious activities. | High potential for improvement in employee awareness and reporting rates. | Requires significant investment in time and resources. |
| Security Awareness Campaigns | Regular communication and educational materials to raise awareness. | Helpful for general awareness but may not always translate to practical application. | Maintaining engagement and consistent messaging can be difficult. |
| Simulated Phishing Exercises | Testing employee responses to phishing attempts. | Effective in identifying vulnerabilities and reinforcing training. | Can cause discomfort among employees and require careful implementation to avoid negative perceptions. |
Consequences and Impacts
The fallout from identity theft extends far beyond the immediate financial loss. It creates a cascade of negative consequences for victims, financial institutions, and society as a whole. Understanding these impacts is crucial to addressing the problem effectively and developing preventative measures. Financial institutions, in particular, face significant risks if they fail to adequately protect customer data.
Financial Consequences for Institutions
Financial institutions bear significant financial burdens due to identity theft. These costs encompass the direct expenses of investigating and resolving fraudulent activity, as well as the indirect costs of lost revenue and damaged reputation. Lawsuits and regulatory penalties further increase the financial strain. For example, a bank that experiences a large-scale data breach might face millions of dollars in remediation costs, legal fees, and potential fines.
Moreover, the loss of customer trust can lead to a decline in deposits and account holders.
Reputational Damage for Institutions
A financial institution’s reputation is a critical asset. Identity theft incidents severely damage this reputation, leading to a loss of public trust and potential customer defections. Negative publicity from such incidents can persist for years, making it challenging to rebuild public confidence. For example, news coverage of a significant data breach at a major bank will likely tarnish its image, making it harder to attract new customers and retain existing ones.
Emotional Toll on Victims
Identity theft is more than just a financial loss; it significantly impacts the emotional well-being of victims. The constant stress of dealing with fraudulent activity, the frustration of restoring their financial lives, and the feeling of violation can be overwhelming. Victims often experience anxiety, depression, and feelings of powerlessness. Furthermore, the emotional toll extends to family members and loved ones.
The stress of dealing with fraudulent bills and calls, the uncertainty of future financial stability, and the need to navigate complex legal procedures can be emotionally draining for the entire family.
Financial institutions are sometimes unwitting accomplices to identity theft, failing to implement robust security measures. This echoes the seemingly endless, and ultimately pointless, tech wars of the past, like the MSN vs AOL battle that never was, a fascinating look at the history of online services. Ultimately, both highlight a fundamental disconnect between the potential for innovation and the realities of security, with financial institutions still struggling to keep pace with evolving threats.
Legal Implications for Institutions
Failure to implement adequate data security measures can result in severe legal repercussions for financial institutions. Regulations like the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA) and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) Artikel specific requirements for safeguarding customer data. Non-compliance can lead to substantial fines, lawsuits, and even criminal charges. Moreover, financial institutions may face legal action from individual victims of identity theft who claim negligence in protecting their personal information.
The legal framework surrounding identity theft and data breaches is continuously evolving, demanding ongoing vigilance from financial institutions.
Societal Impact of Widespread Identity Theft
Widespread identity theft has profound societal consequences. It undermines public trust in financial institutions and the overall economy. The costs associated with identity theft, both financial and emotional, are significant, impacting individuals and families across the country. Moreover, it can lead to a decline in economic activity and a decrease in overall societal well-being.
Examples of Successful Lawsuits Against Financial Institutions
Numerous lawsuits have been filed against financial institutions over identity theft incidents. These cases often allege negligence in data security practices, resulting in significant financial losses for victims. Examples include instances where banks failed to implement robust security measures, leading to unauthorized access to customer accounts and resulting in substantial losses for the victims. Such examples highlight the potential legal and financial ramifications for institutions that fail to prioritize customer data security.
Table Summarizing Damages and Costs
| Type of Damage | Description | Financial Impact (Approximate) | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Direct Financial Losses | Costs associated with fraudulent transactions, account recovery, and credit repair. | Thousands to millions of dollars, depending on the scale of the breach. | Unauthorized withdrawals, fraudulent purchases, and collection of debt. |
| Indirect Financial Losses | Lost revenue, damaged reputation, and increased operational costs. | Potentially substantial, depending on the reputational damage and the loss of customer trust. | Reduced customer deposits, increased customer service costs, and the need for security system upgrades. |
| Legal Costs | Expenses associated with lawsuits, settlements, and regulatory penalties. | Vary greatly depending on the severity of the breach and the outcome of legal proceedings. | Legal fees, expert witness costs, and potential fines. |
| Emotional Distress | Anxiety, depression, and feelings of powerlessness experienced by victims. | Difficult to quantify but significant in terms of long-term impact on victims’ well-being. | Difficulty sleeping, loss of appetite, and persistent feelings of insecurity. |
Mitigation Strategies and Prevention: Financial Institutions Unwitting Accomplices Of Id Thieves

Financial institutions are increasingly recognizing the critical need to proactively combat identity theft and reduce their role as unwitting accomplices. This necessitates a multi-faceted approach encompassing robust security measures, comprehensive employee training, stringent regulatory compliance, and a constant vigilance against evolving threats. A focus on prevention, rather than simply reacting to incidents, is paramount.Effective mitigation strategies require a shift in mindset, moving beyond reactive measures to a proactive, preventative posture.
This includes implementing advanced technologies, enhancing communication with customers, and fostering a culture of security awareness throughout the organization. A proactive approach not only minimizes the risk of becoming a victim of identity theft but also strengthens the institution’s overall reputation for security and trustworthiness.
Enhancing Security Measures Within Financial Institutions
Implementing robust security measures is fundamental to mitigating the risk of identity theft. These measures should extend beyond basic security protocols to incorporate advanced techniques that anticipate and counter sophisticated attacks. Security measures should be designed with a layered approach, making it difficult for attackers to breach multiple lines of defense. This includes using multi-factor authentication, strong encryption for sensitive data, and regular security audits.
- Implementing Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide multiple forms of verification, such as a password, a code from a mobile device, or a biometric scan, before accessing sensitive accounts. This makes it significantly harder for attackers to gain access, even if they have compromised one factor.
- Employing Strong Encryption: Encryption protects sensitive data by converting it into an unreadable format. This is crucial for safeguarding customer information during transmission and storage. Advanced encryption standards, such as AES-256, should be used to ensure maximum protection.
- Conducting Regular Security Audits: Regular audits identify vulnerabilities in systems and processes, allowing for proactive remediation before attackers exploit them. These audits should encompass both internal controls and external threats.
Improved Employee Training and Awareness Programs
Employee training plays a critical role in preventing identity theft. By equipping employees with the knowledge and skills to recognize and respond to potential threats, financial institutions can significantly reduce the risk of becoming unwitting accomplices. This training should be ongoing and cover topics such as phishing scams, social engineering tactics, and data security best practices.
- Regular Security Awareness Training: Ongoing training programs are crucial for maintaining employee awareness of emerging threats. This should include simulated phishing exercises and real-world case studies to enhance their understanding and preparedness.
- Emphasis on Recognizing Phishing Attempts: Training should focus on recognizing phishing emails, text messages, and phone calls. Examples of common phishing tactics and how to identify them should be covered in detail.
- Implementing Reporting Mechanisms: Establish clear and accessible reporting mechanisms for employees to report suspicious activities or potential security breaches. This fosters a culture of transparency and encourages proactive reporting.
Implementing and Enforcing Stricter Regulatory Compliance Standards
Stricter regulatory compliance standards are essential to minimize financial institutions’ susceptibility to identity theft. Adherence to these standards not only safeguards customer data but also positions the institution as a responsible and secure entity. Financial institutions must regularly review and update their compliance procedures to address evolving regulatory requirements.
- Staying Current with Regulations: Financial institutions must stay abreast of any updates or new regulations related to data security and identity theft prevention. This includes actively monitoring regulatory bodies for changes and updates.
- Internal Audits of Compliance Procedures: Regularly conduct internal audits to ensure compliance with regulatory requirements. These audits should encompass all relevant policies and procedures, including those related to data security, customer identification, and transaction monitoring.
- Maintaining Robust Documentation: Maintain detailed documentation of all compliance procedures, security measures, and training programs. This documentation serves as evidence of compliance and aids in incident investigations.
Staying Abreast of Emerging Threats and Vulnerabilities
The threat landscape is constantly evolving. Financial institutions must actively monitor emerging threats and vulnerabilities to stay ahead of attackers. This proactive approach involves utilizing threat intelligence, attending industry conferences, and participating in information sharing platforms.
- Utilizing Threat Intelligence: Subscribe to and utilize threat intelligence services to stay updated on the latest attacks, vulnerabilities, and tactics used by cybercriminals. This provides valuable insights for strengthening security protocols.
- Participating in Industry Forums: Attending industry conferences and participating in online forums provides opportunities to learn from peers, share best practices, and gain insights into emerging threats.
- Active Monitoring of Security News: Financial institutions should actively monitor reputable security news sources to identify emerging vulnerabilities and threats.
Utilizing Advanced Technologies to Strengthen Security Protocols
Advanced technologies offer significant opportunities to enhance security protocols. These include AI-powered fraud detection systems, behavioral biometrics, and blockchain technology. Implementing these technologies can significantly improve the accuracy and efficiency of security measures.
- Leveraging AI for Fraud Detection: Artificial intelligence can analyze large datasets to identify suspicious patterns and behaviors, significantly improving the accuracy of fraud detection systems. This can identify anomalies that might be missed by traditional methods.
- Utilizing Behavioral Biometrics: Behavioral biometrics analyzes patterns in user behavior, such as typing speed and mouse movements, to authenticate users. This adds an extra layer of security by making it harder for attackers to impersonate users.
- Implementing Blockchain Technology: Blockchain technology can enhance the security of transactions and records by providing a transparent and immutable ledger. This can help to prevent fraudulent activities and enhance the reliability of data.
Improving Communication and Transparency with Customers Regarding Security
Transparency and open communication with customers regarding security are vital. Customers need to understand the measures taken to protect their data and be informed about potential threats. Regular security updates and clear communication can build trust and foster a culture of security awareness.
- Providing Regular Security Updates: Financial institutions should communicate regularly with customers about security measures and any potential threats. This can be done through emails, newsletters, or dedicated security portals.
- Clearly Explaining Security Policies: Clear and concise explanations of security policies and procedures help customers understand the steps taken to protect their data. Simple and accessible language should be used.
- Responding Promptly to Customer Concerns: Prompt and professional responses to customer inquiries and concerns regarding security issues demonstrate a commitment to customer service and build trust.
Actionable Steps for Financial Institutions
Financial institutions can take a range of actionable steps to minimize their role as unwitting accomplices in identity theft. These steps should be integrated into the daily operations of the institution.
- Implement a comprehensive security awareness training program for all employees: This program should include regular updates and practical exercises to keep employees informed about evolving threats.
- Strengthen security protocols to meet or exceed industry best practices: This includes implementing multi-factor authentication, data encryption, and robust access controls.
- Conduct regular security audits and vulnerability assessments: Proactive identification of weaknesses is crucial for mitigating potential risks.
Illustrative Cases
Financial institutions, while striving to provide secure services, sometimes become unwitting accomplices in identity theft. This often occurs due to vulnerabilities in their systems and processes, or through inadequate security measures. Understanding past cases provides crucial insights into the vulnerabilities and highlights the need for proactive measures to prevent such incidents.Examining real-world instances of financial institutions being implicated in identity theft demonstrates the complexities and costs involved.
Each case illustrates a specific flaw in the institution’s procedures or technology, revealing areas for improvement and strengthening security protocols. By learning from these errors, institutions can proactively safeguard their customers’ sensitive data and mitigate the risks of future incidents.
Case Study 1: The Phishing Campaign
A major bank experienced a significant data breach when a phishing campaign targeted its customers. Phishing emails, expertly crafted to mimic legitimate bank communications, tricked users into revealing their login credentials. The bank’s security protocols were insufficient to detect the sophisticated nature of the phishing attack. The result was a massive data leak, leading to identity theft for hundreds of customers.
The key issue here was a lack of robust anti-phishing measures. The bank failed to adequately train customers on identifying phishing attempts and also lacked a strong system to automatically flag suspicious login attempts.
Case Study 2: The Data Breach
A significant data breach exposed sensitive customer information, including social security numbers and account details, at a credit union. The breach was a result of a vulnerability in the credit union’s database management system. This vulnerability allowed hackers to gain unauthorized access to the system, compromising a substantial number of accounts. The key issues were insufficient system security and inadequate penetration testing.
The credit union had failed to conduct regular penetration tests to identify potential weaknesses in their system.
Case Study 3: The Shared Account Compromise
A small brokerage firm suffered significant losses due to a compromised shared account. A disgruntled former employee gained unauthorized access to the system and transferred funds from several client accounts into his own. The key issue was inadequate access controls and weak password policies. The firm failed to implement strong authentication measures and limit access privileges based on roles.
Furthermore, the firm lacked effective monitoring of account activity.
Case Study 4: The Weak Authentication System
A large investment firm experienced an increase in fraudulent transactions due to a weak authentication system. Hackers exploited vulnerabilities in the authentication process to gain unauthorized access to client accounts. The firm’s authentication system did not incorporate multi-factor authentication, making it easy for attackers to bypass security measures. The key issue here was a failure to implement multi-factor authentication and other robust security protocols.
Summary Table
| Case Study | Key Issues | Outcomes | Lessons Learned |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phishing Campaign | Insufficient anti-phishing measures, lack of customer training | Massive data leak, identity theft for hundreds of customers | Invest in robust anti-phishing measures and comprehensive customer training programs. |
| Data Breach | Vulnerability in database management system, inadequate penetration testing | Exposure of sensitive customer information, compromised accounts | Regular penetration testing and robust database security are crucial. |
| Shared Account Compromise | Inadequate access controls, weak password policies, lack of monitoring | Significant financial losses for clients, damage to reputation | Implement strong access controls, enforce strong password policies, and implement effective monitoring systems. |
| Weak Authentication System | Lack of multi-factor authentication, inadequate security protocols | Increase in fraudulent transactions, unauthorized access to client accounts | Implement multi-factor authentication and other robust security protocols to strengthen authentication systems. |
Best Practices and Recommendations
Financial institutions, despite their robust systems, remain vulnerable to identity theft. Proactive measures, coupled with a security-conscious culture, are paramount in mitigating risks and protecting customers. This section Artikels best practices and recommendations to strengthen defenses against identity theft.Effective strategies employed by other institutions can provide valuable insights. Many institutions are now implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) systems, requiring more than one form of verification to access accounts.
This significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access. Implementing stringent data encryption policies and employing robust access controls are also crucial for safeguarding sensitive information.
Effective Strategies Used by Other Institutions
Financial institutions can leverage successful strategies from their peers to enhance their own security posture. For instance, some institutions utilize advanced fraud detection systems that analyze vast datasets in real-time to identify suspicious transactions. These systems can flag unusual patterns, anomalies, or potentially fraudulent activities, enabling swift intervention.
- Strong Password Policies: Enforcing complex password requirements and regular password changes significantly reduces the risk of brute-force attacks. This includes requiring a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols, along with enforcing password expiration periods.
- Regular Security Awareness Training: Educating employees on the latest identity theft tactics and best practices is essential. Training programs should cover phishing scams, social engineering techniques, and other common threats. Simulations of phishing attacks can help employees recognize and avoid these tactics.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Implementing MFA for all online and mobile banking transactions enhances security by requiring multiple verification steps beyond just a username and password. This significantly increases the barrier to unauthorized access.
Proactive Risk Assessments
Regular risk assessments are crucial for identifying potential vulnerabilities and weaknesses in the institution’s security posture. These assessments should cover all operational processes, systems, and data flows. They should consider internal and external threats, including emerging threats and evolving attack vectors.
- Regular Security Audits: Conducting regular security audits of systems and processes can uncover vulnerabilities and weaknesses before they are exploited. Audits should assess the effectiveness of controls, procedures, and policies to ensure compliance with industry standards and regulations.
- Vulnerability Scanning and Penetration Testing: Employing vulnerability scanning and penetration testing tools can proactively identify potential weaknesses in systems. These tests simulate real-world attacks to assess the effectiveness of security measures. Results from these assessments should be used to prioritize remediation efforts.
Fraud Detection Systems and Monitoring
Robust fraud detection systems and proactive monitoring are vital for identifying and preventing fraudulent activities. These systems should be designed to detect unusual patterns, anomalies, and potentially fraudulent activities in real-time. The data should be analyzed to identify and prevent attacks.
- Real-time Transaction Monitoring: Implementing real-time transaction monitoring systems is essential for identifying and blocking suspicious transactions immediately. These systems should flag unusual patterns, high-risk transactions, or transactions exceeding predefined thresholds.
- Data Analytics and Machine Learning: Leveraging data analytics and machine learning techniques can significantly improve fraud detection capabilities. Algorithms can be trained to identify patterns and anomalies that may indicate fraudulent activity.
Security-Conscious Culture
Fostering a security-conscious culture within financial institutions is critical. Employees should understand their role in preventing identity theft and be empowered to report suspicious activities.
- Employee Training Programs: Regular training programs should equip employees with the knowledge and skills to identify and report suspicious activities. This includes recognizing phishing attempts, social engineering tactics, and other threats.
- Incentivizing Reporting: Creating a culture that encourages employees to report suspicious activities without fear of retribution is essential. Rewards or recognition for identifying and preventing fraud can motivate employees to participate in security initiatives.
Collaboration with Law Enforcement
Collaboration between financial institutions and law enforcement agencies is crucial for effective identity theft prevention and investigation. Information sharing and joint efforts are essential for successful outcomes.
- Information Sharing Protocols: Establishing clear information sharing protocols with law enforcement agencies is essential for effective coordination and cooperation. This includes establishing procedures for reporting suspected fraud and providing necessary data.
- Joint Task Forces: Forming joint task forces with law enforcement agencies can facilitate information sharing and coordinated efforts to combat identity theft. This can lead to quicker identification and prosecution of perpetrators.
Resources for Financial Institutions
A wide array of resources can assist financial institutions in strengthening their identity theft prevention efforts. These resources provide valuable information and guidance.
- Industry Best Practices and Standards: Referencing industry best practices and standards for identity theft prevention can provide guidance on implementing effective security measures. Regulatory compliance and industry standards are crucial for ensuring the institution’s security posture aligns with best practices.
- Government Agencies and Regulatory Bodies: Consult government agencies and regulatory bodies for resources and guidance on identity theft prevention. These agencies often provide helpful resources and guidelines. Referencing their recommendations can enhance the institution’s security protocols.
Outcome Summary

In conclusion, financial institutions unwitting accomplices of id thieves highlights a critical issue demanding immediate attention. By understanding the vulnerabilities and contributing factors, institutions can implement proactive measures to bolster security, protect customer data, and minimize their role in identity theft. Ultimately, this discussion underscores the importance of continuous vigilance, proactive risk assessments, and a culture of security awareness within the financial sector.