Ten Steps to Email Security A Comprehensive Guide
Ten steps to e mail security – Ten steps to email security is your essential guide to navigating the complex digital landscape of today’s email interactions. We’ll explore fundamental security principles, practical authentication protocols, and effective filtering strategies. This comprehensive overview will also cover encryption techniques, secure user practices, and the crucial aspects of implementing robust policies and utilizing advanced tools.
From the basics of email security to the intricacies of incident response, this article equips you with the knowledge and actionable steps needed to protect your email communications and sensitive data. Let’s delve into the ten steps to fortify your email defenses.
Email Security Fundamentals
Email security is no longer a luxury but a necessity in today’s interconnected world. With the rise of cyber threats and the increasing reliance on digital communication, safeguarding email accounts and the sensitive information they contain is paramount. Protecting your email from malicious attacks is vital to maintaining your personal and professional reputation, and preventing financial and reputational damage.
Defining Email Security
Email security encompasses the measures and technologies employed to protect email accounts and their contents from unauthorized access, misuse, and malicious attacks. It involves preventing phishing attempts, spam, malware delivery, and other forms of cyber threats targeting email communications. Comprehensive email security solutions go beyond simply blocking spam; they actively identify and mitigate threats to prevent data breaches and ensure the integrity of email communications.
Importance of Email Security in Today’s Digital Landscape
In the modern digital age, email remains a critical communication tool for both personal and professional interactions. The reliance on email for everything from business transactions to personal correspondence makes email security a critical aspect of maintaining privacy and data integrity. Compromised email accounts can lead to identity theft, financial losses, and reputational damage. The potential consequences of a security breach are far-reaching and significant, necessitating a proactive approach to email security.
Common Email Security Threats
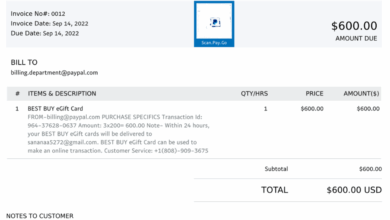
Various threats pose risks to email security. Phishing attacks, which involve deceptive emails aiming to trick recipients into revealing sensitive information, are a prevalent concern. Spam emails, often used for malicious purposes like malware distribution or financial fraud, inundate inboxes. Malware, disguised as legitimate attachments or links, can infect systems with viruses, spyware, and ransomware. Social engineering, which manipulates users into divulging confidential information, also poses a significant threat.
Thinking about ten steps to email security? It’s crucial, especially with the rapid advancements in computing power. IBM’s upcoming project to build the world’s fastest Linux supercomputer, IBM to build the world’s fastest Linux supercomputer , highlights the need for robust email security measures. After all, a more powerful system means more potential for cyberattacks. Protecting our email systems is paramount in this evolving digital landscape.
So, let’s delve back into those ten steps to email security.
All these threats underscore the need for robust email security measures.
The Role of Strong Passwords in Email Security
Strong passwords are the first line of defense against unauthorized access. Weak or easily guessable passwords make email accounts vulnerable to hacking. Employing strong, unique passwords for each account is crucial to protect against unauthorized access. This involves using a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols, creating passwords that are difficult to decipher. Password managers can help generate and securely store complex passwords, further enhancing email security.
Comparison of Email Security Software
| Software Type | Description | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anti-Spam Filters | Filter out unsolicited emails (spam) and potentially harmful messages. | Reduces the volume of spam, improving inbox organization. | May occasionally misclassify legitimate emails as spam, requiring manual review. |
| Anti-Phishing Tools | Identify and block phishing emails attempting to deceive users into revealing sensitive information. | Reduces the risk of phishing attacks, protecting personal and financial data. | May not catch all sophisticated phishing attempts, requiring user vigilance. |
| Email Encryption Software | Securely encrypt emails to prevent unauthorized access during transmission. | Protects sensitive information transmitted via email. | May require additional configuration and setup on both sender and recipient ends. |
| Email Security Suites | Integrate various security features into a single platform. | Comprehensive security coverage in a single package. | Can be complex to set up and manage, requiring technical expertise. |
This table provides a basic comparison of different email security software types, highlighting their functionalities, benefits, and potential drawbacks. Choosing the right software depends on specific needs and technical capabilities.
Email Authentication Protocols
Email security is a multifaceted challenge, and a critical component is ensuring the authenticity of incoming messages. Email authentication protocols are designed to verify the sender’s identity and prevent malicious actors from impersonating legitimate organizations or individuals. This crucial step helps safeguard against phishing attacks, spam, and other forms of email-borne threats.Email authentication protocols play a vital role in establishing trust in the digital realm.
By verifying the origin of emails, these protocols minimize the risk of fraudulent communications and maintain the integrity of online interactions. Understanding how these protocols work and their limitations is essential for organizations and individuals alike.
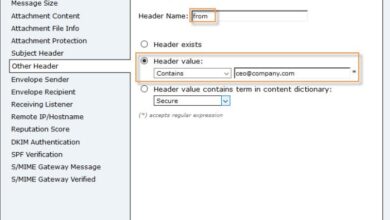
SPF (Sender Policy Framework)
SPF records define the authorized mail servers that are permitted to send email on behalf of a specific domain. This is crucial for preventing email spoofing, where an attacker sends emails from a forged sender address. A properly configured SPF record ensures that emails claiming to originate from a particular domain are indeed sent from a legitimate server.
Thinking about ten steps to email security? It’s crucial in today’s digital landscape, especially as we move towards more sophisticated lighting technologies like those explored in the fascinating article on ever present LEDs and the future of light. Protecting your data from cyber threats is paramount, and these steps will help. Strong passwords, regular updates, and secure email practices are key.
Keeping up with the latest security measures is essential, no matter how advanced our tech becomes.
DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail)
DKIM adds a digital signature to emails. This signature is cryptographically linked to the sender’s domain, providing an additional layer of authentication. DKIM helps to verify that the email content hasn’t been tampered with during transit. This critical step strengthens the trust in the message’s origin and integrity.
DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance)
DMARC acts as a policy framework that combines SPF and DKIM. It dictates how receiving mail servers should handle emails that fail authentication checks. DMARC policies can be configured to either reject, quarantine, or simply report emails that fail authentication, further mitigating the risk of spoofing. This policy framework ensures consistent and comprehensive protection against email fraud.
Successful and Failed Implementations
Many organizations have successfully implemented these protocols, leading to a significant reduction in phishing attempts and spam. However, inadequate configuration or lack of implementation can result in failed authentication and subsequent security breaches. A real-world example of a successful implementation involves a major e-commerce company that saw a drastic decrease in phishing attempts after implementing robust SPF, DKIM, and DMARC policies.
Conversely, a less secure example is a smaller company that did not implement DMARC, resulting in a noticeable increase in spam emails and phishing attacks.
Implementation Complexity
| Protocol | Implementation Complexity | Description |
|---|---|---|
| SPF | Low | Relatively easy to set up and maintain, often integrated into DNS records. |
| DKIM | Medium | Requires some technical understanding of email and cryptography. |
| DMARC | High | Requires careful configuration and ongoing monitoring to ensure proper reporting and handling of authentication failures. |
Effectiveness Comparison
SPF provides a basic level of sender authentication. DKIM adds a stronger layer by verifying the message content. DMARC, by combining SPF and DKIM, and providing reporting mechanisms, offers the most comprehensive protection. While each protocol plays a crucial role, a holistic approach integrating all three provides the most robust defense against email spoofing and improves the overall security posture of an organization.
Email Filtering and Spam Prevention

Protecting your inbox from unwanted messages is crucial in today’s digital landscape. Spam, phishing attempts, and malicious content can compromise your security and productivity. Robust email filtering is essential to maintaining a secure and efficient communication environment. Effective spam prevention techniques go beyond simply blocking messages; they involve a multi-layered approach to identify and filter various threats.Spam filters act as the first line of defense against unwanted email.
They employ sophisticated algorithms to distinguish legitimate messages from spam, helping users focus on important communications. Understanding how these filters work and how to best utilize them is vital for safeguarding your email accounts.
Email Filtering Techniques
Email filtering utilizes various techniques to categorize incoming messages. These methods range from simple matching to complex machine learning algorithms. Filtering techniques work together to identify and block unwanted emails.
- Blacklisting: This method involves maintaining a list of known spam senders. Messages originating from these addresses are automatically blocked.
- Whitelisting: Conversely, whitelisting allows only messages from approved senders to reach your inbox. This approach offers a higher degree of security by limiting unwanted messages.
- Content Filtering: Analyzing the content of an email, including subject lines, body text, and attachments, helps identify potentially malicious or unwanted messages. This technique often employs sophisticated algorithms that scan for s, phrases, and patterns associated with spam.
- Bayesian Filtering: This approach uses statistical analysis to learn from the user’s email history. It analyzes the characteristics of emails the user has marked as spam or not spam to predict future messages. The more data it processes, the more accurate its spam detection becomes.
- Reputation-Based Filtering: This method relies on the reputation of email servers and senders. Emails from servers known to send spam or phishing messages are flagged or blocked.
Role of Spam Filters in Email Security
Spam filters are crucial components of email security. They act as a barrier against various threats, including phishing attempts, malware distribution, and unwanted advertisements. Their role extends beyond simple spam blocking.
- Phishing Prevention: Spam filters can often detect phishing emails by identifying suspicious links, sender addresses, and content. This helps protect users from malicious attempts to steal sensitive information.
- Malware Mitigation: Spam filters often identify and block emails containing malicious attachments or links that could infect a user’s computer with malware.
- Protecting Against Identity Theft: By blocking phishing attempts and suspicious emails, spam filters can prevent potential identity theft, safeguarding user accounts and personal information.
Identifying and Reporting Suspicious Emails
Recognizing suspicious emails is vital for preventing security breaches. Look for red flags like unusual sender addresses, generic greetings, urgent requests for personal information, and suspicious links.
- Unusual Sender Addresses: Pay close attention to the sender’s email address. If it seems unfamiliar or unexpected, be cautious.
- Generic Greetings: Emails that use generic greetings like “Dear Customer” or “Dear User” rather than your name often indicate a spam or phishing attempt.
- Urgent Requests: Emails demanding immediate action or containing urgent requests for personal information should be treated with extreme caution.
- Suspicious Links: Hover your mouse over links before clicking. Look for unusual or suspicious URLs. If the link doesn’t match the context of the email, it’s likely a phishing attempt.
Spam Filter Algorithm Comparison
Different algorithms have varying strengths and weaknesses. Choosing the right algorithm depends on the specific needs and resources of the user.
| Algorithm | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|
| Bayesian Filtering | High accuracy, adaptable to user behavior | Reliance on user training data, may miss novel spam |
| Rule-Based Filtering | Simple to implement, effective for known spam | Less adaptable to new types of spam, relies on pre-defined rules |
| Machine Learning-Based Filtering | High accuracy, adaptable to new threats | Requires significant computational resources, complex to implement |
Best Practices for Setting Up a Robust Spam Filter
Implementing robust spam filtering involves a multi-faceted approach. Users should configure their spam filters and follow best practices.
- Regularly update your spam filter: New spam techniques emerge constantly. Keeping your filter updated with the latest definitions and rules is crucial for effective protection.
- Configure your spam filter settings: Adjust your spam filter settings to match your needs and preferences. This can involve setting thresholds for different types of messages.
- Enable email authentication protocols: Implementing SPF, DKIM, and DMARC helps verify the authenticity of emails, reducing the risk of spoofing and phishing.
- Report suspicious emails: Reporting suspicious emails helps the spam filter learn and improve its accuracy over time.
Email Encryption Techniques
Email encryption is a crucial component of email security, safeguarding the confidentiality and integrity of sensitive information transmitted through electronic mail. By converting readable text into an unreadable format, encryption effectively prevents unauthorized access and ensures that only intended recipients can decipher the message. This layer of protection is vital in today’s digital landscape, where sensitive data like financial transactions, personal information, and confidential business communications are frequently exchanged via email.Encryption transforms plain text into cipher text, an unintelligible format.
This transformation is achieved using cryptographic algorithms, which are mathematical formulas that operate on the data. Decryption, the reverse process, converts cipher text back to its original readable format. This process is essential for protecting sensitive information during transit and at rest.
Understanding the Mechanics of Encryption
Email encryption works by applying cryptographic algorithms to the email content. These algorithms use a secret key or a pair of keys (public and private) to encrypt and decrypt the data. The security of the encryption relies heavily on the strength of the algorithm and the security of the key. A strong algorithm, combined with a well-protected key, makes it extremely difficult for unauthorized parties to decipher the encrypted message.
End-to-End Encryption in Email
End-to-end encryption (E2EE) ensures that only the sender and the recipient can read the email content. No intermediary, including the email service provider, can access the unencrypted message. This level of security is particularly important for sensitive communications. E2EE is a crucial feature in modern messaging applications and email platforms designed for enhanced security.
Examples of Encryption Protocols
Various protocols are used for email encryption, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Here are a few prominent examples:
- S/MIME (Secure/Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions): S/MIME is a widely adopted protocol for encrypting email messages. It leverages public key cryptography to encrypt email content and digitally sign it. S/MIME is often integrated into email clients and servers, making it relatively user-friendly, though it may require configuring the email system for optimal usage.
- PGP (Pretty Good Privacy): PGP is a widely used open-source encryption method for email. It utilizes public-key cryptography to encrypt and digitally sign email messages, ensuring both confidentiality and integrity. PGP’s flexibility and wide adoption make it a powerful tool for secure communication. It is often preferred for its robustness and adaptability to various platforms.
Comparing Encryption Method Security
Different encryption methods offer varying levels of security. The security strength is often determined by the algorithm’s complexity, the key size, and the implementation’s robustness. A comparison of common methods can help to understand their respective capabilities:
| Method | Security Strength | Ease of Use |
|---|---|---|
| S/MIME | Generally strong, widely deployed | Moderate, often integrated into email clients |
| PGP | Very strong, highly customizable | Steeper learning curve, often requires more technical configuration |
A strong encryption method, like PGP, often involves more technical setup and configuration but provides a higher degree of protection compared to simpler methods like S/MIME. The choice of encryption method depends on the sensitivity of the data being exchanged and the technical expertise of the users involved.
Secure Email Practices for Users
Email security isn’t just about sophisticated technology; it’s critically about the conscious actions of individual users. This section focuses on the practical steps everyday users can take to significantly enhance their email security posture. Understanding and applying these best practices can drastically reduce the risk of falling victim to phishing attacks and other email-borne threats.By adopting proactive security habits, users can protect themselves and their organizations from email-related vulnerabilities.
This includes recognizing phishing attempts, correctly handling suspicious emails, creating strong passwords, and avoiding common mistakes. A strong user security culture is an essential component of a robust email security strategy.
Recognizing Phishing Attempts
Phishing attempts are designed to trick users into revealing sensitive information, like passwords or credit card details. These attacks often use deceptive emails that mimic legitimate organizations. Critically evaluating the sender, subject line, and email content is paramount. Look for poor grammar, misspellings, and urgent tones. Be wary of links within emails, and always verify the website address before clicking on it.
Genuine organizations rarely use generic greetings like “Dear Customer.”
Handling Suspicious Emails
Suspicious emails should never be opened or interacted with. Do not click on links, download attachments, or reply to the message. Instead, immediately report the suspicious email to your organization’s IT department or the appropriate authorities. This proactive approach prevents potential malware infections and data breaches.
Creating Strong Email Passwords
Strong passwords are essential to prevent unauthorized access to email accounts. Use a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. Avoid using easily guessable information like birthdates or names. Consider using a password manager to generate and store complex passwords securely.
Common Email Security Mistakes and Remedies
- Using the same password for multiple accounts: This is a critical security vulnerability. Use a unique and strong password for each account to limit the impact of a breach. A password manager can help.
- Not enabling two-factor authentication (2FA): 2FA adds an extra layer of security, requiring a second verification method (e.g., code from a phone app) beyond the password. Activating 2FA significantly strengthens your account protection.
- Opening suspicious attachments: Attachments can contain malicious software. Never open an attachment from an unknown sender, or one that seems suspicious. Verify the sender’s identity before opening attachments.
- Ignoring security updates: Regularly updating email clients and operating systems patches security vulnerabilities. Staying current with security updates is vital for preventing exploitation.
- Not regularly changing passwords: Regular password changes help maintain a strong security posture. Periodically changing passwords reduces the risk associated with compromised passwords.
Implementing Email Security Policies: Ten Steps To E Mail Security
Email security isn’t just about technology; it’s a multifaceted approach requiring clear policies, vigilant incident response, comprehensive training, and dedicated IT staff. Effective email security policies form the bedrock of a strong defense against cyber threats, reducing the risk of data breaches and reputational damage. A well-defined policy will guide all users, enabling them to recognize and report suspicious activities, ensuring the organization’s email system remains a secure and reliable channel of communication.Implementing a robust email security policy requires careful consideration of various aspects.
From defining clear procedures for handling security incidents to establishing mandatory training programs for employees, every step plays a critical role in creating a culture of email security awareness. This multifaceted approach ensures that everyone understands their role in maintaining the integrity and confidentiality of the organization’s communication channels.
Designing a Comprehensive Email Security Policy
A comprehensive email security policy serves as a crucial document outlining acceptable email practices, procedures for handling sensitive information, and reporting mechanisms for security incidents. It should cover various aspects such as acceptable use guidelines, restrictions on sending or receiving certain types of emails, and the handling of attachments. The policy should be easily accessible to all employees and regularly reviewed to adapt to emerging threats and best practices.
A well-structured policy clarifies expectations and empowers employees to make informed decisions regarding email security.
Procedures for Reporting Security Incidents
Establishing clear procedures for reporting security incidents is critical to timely response and mitigation. A dedicated reporting channel, such as a designated email address or a secure online portal, should be readily available to employees. The procedures should also Artikel escalation protocols for escalating significant incidents to the relevant IT staff or security team. A clear communication plan ensures swift action to contain potential damage and prevent further breaches.
The policy should explicitly detail the type of information to include in a report, including details about the incident, affected systems, and any potential damage.
Importance of Employee Training on Email Security
Employee training is fundamental to fostering a culture of email security awareness. Regular training programs should cover topics such as identifying phishing attempts, recognizing suspicious emails, and adhering to email security policies. Training should be interactive and include practical exercises to reinforce the learned concepts. This empowers employees to become active participants in maintaining email security, recognizing and avoiding potential threats.
Role of IT Staff in Maintaining Email Security
IT staff play a crucial role in maintaining email security. They are responsible for implementing and maintaining email security systems, including firewalls, antivirus software, and spam filters. Proactive monitoring of email systems and timely patching of vulnerabilities are essential to prevent unauthorized access and data breaches. IT staff should also actively investigate and resolve any reported security incidents promptly and effectively.
Methods for Enforcing the Email Security Policy
Enforcement mechanisms are crucial to ensure compliance with the email security policy. These mechanisms can include regular audits of email traffic to identify potential security breaches, monitoring for suspicious activity, and the implementation of penalties for non-compliance. Clear communication of consequences for violating the policy helps reinforce the importance of email security best practices. Implementing these enforcement methods ensures the policy’s effectiveness and maintains a secure email environment.
Email Security Tools and Technologies
Email security is a multifaceted endeavor, and robust tools are essential for organizations and individuals to protect sensitive information. Beyond the fundamental practices we’ve already discussed, leveraging the right email security tools can significantly bolster your defenses against threats. These tools can automate tasks, detect suspicious activity, and provide a layered approach to email protection, ensuring a more secure digital environment.
Various Email Security Tools Available
A wide array of email security tools are available, catering to diverse needs and budgets. These tools provide a range of functionalities, from basic spam filtering to advanced threat detection and incident response. Some common types include:
- Spam Filters: These tools analyze incoming emails to identify and block spam messages, protecting inboxes from unwanted content and potentially malicious attacks. Effective spam filters can reduce the volume of unwanted emails, saving time and resources.
- Anti-virus and Anti-malware Solutions: These solutions scan emails for viruses, malware, and other malicious code, preventing infections and data breaches. These tools are crucial for safeguarding against sophisticated threats that might bypass other security measures.
- Email Authentication Tools: Tools like SPF (Sender Policy Framework), DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail), and DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance) authenticate the sender of emails, helping to prevent spoofing and phishing attempts. This crucial step ensures that emails are truly from the claimed sender.
- Email Encryption Tools: These tools encrypt emails to protect sensitive data during transit, ensuring confidentiality and integrity. Many solutions offer different encryption levels and methods, depending on the sensitivity of the information.
- Advanced Threat Detection and Response (EDR) Systems: These solutions provide more sophisticated threat hunting capabilities, proactively identifying and responding to advanced threats that bypass basic email security measures. These tools often integrate with other security systems for a comprehensive defense.
How These Tools Enhance Email Security
Email security tools work in conjunction with other security measures to create a layered approach. By automating tasks, like spam filtering, these tools can free up personnel for other important duties. Sophisticated solutions can identify and block threats that may not be apparent through basic methods, enhancing the overall security posture. They often use a combination of techniques like heuristics, signature-based detection, and behavioral analysis to identify malicious emails.
Email Security Solutions for Different Needs
The right email security solution depends on the specific needs of the organization or individual. Smaller businesses might benefit from a basic spam filter and antivirus solution, while larger organizations may require more advanced tools like threat detection and incident response systems. Here are some examples:
- Basic Email Security: A combination of spam filtering, antivirus, and anti-malware solutions is often sufficient for smaller organizations or individuals with minimal sensitive data.
- Advanced Email Security: For larger organizations handling sensitive information, advanced tools like email encryption, threat detection, and incident response systems are crucial to mitigate sophisticated attacks.
- Specialized Email Security: Some organizations might require specific solutions tailored to their industry or regulatory compliance needs, such as HIPAA compliance for healthcare or PCI DSS compliance for financial institutions.
Comparing Email Security Tools
The table below provides a basic comparison of features and pricing for various email security tools. Note that pricing and features can vary significantly depending on the specific vendor and the level of service required.
| Tool Category | Features | Pricing | Suitable for |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basic Spam Filter | Basic spam filtering, antivirus | Affordable | Small businesses, individuals |
| Advanced Email Security Suite | Spam filtering, antivirus, encryption, threat detection | Moderate to high | Large organizations, sensitive data |
| Specialized Email Security | Industry-specific compliance features | Variable | Healthcare, financial institutions |
Importance of Regular Updates and Maintenance
Regular updates and maintenance are critical for email security tools. Security threats are constantly evolving, and new vulnerabilities are discovered regularly. Tools need to be updated to address these vulnerabilities and maintain their effectiveness. Maintenance procedures should include tasks like software updates, configuration checks, and regular scanning for threats. Failure to maintain these tools can create vulnerabilities and expose systems to threats.
Incident Response and Recovery
Email security breaches are a significant concern for organizations of all sizes. A well-defined incident response plan is crucial for minimizing damage and restoring operations quickly. Proactive measures, including regular security audits and employee training, are vital for preventing breaches, but having a robust response plan is equally critical for mitigating the impact of a successful attack.
Importance of an Incident Response Plan
A comprehensive incident response plan Artikels procedures for detecting, containing, eradicating, recovering, and learning from a security breach. This structured approach ensures a coordinated and efficient response, minimizing downtime and the potential for further damage. The plan should be regularly reviewed and updated to reflect evolving threats and security best practices.
Steps to Take in Case of a Suspected Breach, Ten steps to e mail security
Immediate action is critical when a suspected email security breach occurs. A well-defined incident response plan will guide the process. Key steps include:
- Immediate Containment: Immediately isolate the affected systems or accounts to prevent further compromise. This might involve disabling compromised email accounts, quarantining infected devices, or blocking malicious IP addresses.
- Notification and Reporting: Notify relevant stakeholders, including IT personnel, management, and potentially legal counsel. Accurate and timely reporting is essential for regulatory compliance and minimizing reputational damage. This involves a clear communication strategy.
- Investigation and Analysis: Thoroughly investigate the breach to determine the scope, extent, and methods of the attack. This involves analyzing logs, identifying compromised data, and tracing the source of the intrusion.
- Damage Control and Recovery: Implement measures to mitigate the damage caused by the breach. This may include restoring data from backups, resetting passwords, and implementing enhanced security measures. A data recovery plan is essential for this phase.
Examples of Successful Incident Responses
Many organizations have successfully navigated email security breaches by following a well-structured response plan. One notable example is a large financial institution that, upon detecting a phishing campaign targeting employees, immediately isolated the affected accounts, notified employees about the attack, and implemented enhanced email security protocols. This proactive response prevented widespread compromise and financial loss. Another example involves a healthcare provider that, after a ransomware attack, followed a documented recovery plan to restore critical data from backups, minimizing disruption to patient care.
Post-Breach Recovery Checklist
A post-breach recovery checklist is an invaluable tool for ensuring a systematic and thorough approach to restoration. A checklist ensures critical steps are not overlooked.
- Data Recovery: Verify the integrity of data backups and restore any compromised data. This requires a well-tested data backup and recovery plan.
- System Remediation: Patch vulnerabilities, install security updates, and enhance security configurations on all affected systems.
- User Account Management: Reset passwords, disable compromised accounts, and implement multi-factor authentication for enhanced security.
- Security Awareness Training: Reinforce security awareness training for employees to prevent future attacks.
- Incident Review: Conduct a thorough post-incident review to identify weaknesses and improve future security measures. Document lessons learned and implement changes to the security plan.
Importance of Data Backup
Data backups are essential for restoring data in the event of a security breach. A comprehensive backup strategy ensures the recovery of critical email data, preventing significant business disruptions. Regular backups, stored in a secure off-site location, are critical for recovery. Using various backup methods, including cloud-based solutions, strengthens the backup strategy.
Security Awareness Training

Email security is only as strong as the weakest link – your employees. Robust security measures are rendered ineffective if employees lack the knowledge to identify and avoid common email threats. A dedicated security awareness training program is crucial for bolstering overall email security posture.Effective security awareness training empowers employees to recognize phishing attempts, suspicious attachments, and other email-borne threats, thus minimizing the risk of data breaches and financial losses.
This proactive approach equips individuals with the tools to safeguard sensitive information and corporate assets.
Importance of Employee Security Awareness Training
Security awareness training equips employees with the knowledge and skills to identify and avoid common email threats. This training fosters a culture of security vigilance, reducing the likelihood of successful attacks. A well-trained workforce serves as a critical first line of defense against phishing, malware, and other cyber threats.
Training Module Focusing on Common Email Threats
A comprehensive training module should cover various email threats. It should include interactive scenarios, real-world examples, and clear explanations of how to spot malicious emails.
- Phishing: This involves fraudulent emails designed to trick recipients into revealing sensitive information, like usernames, passwords, or credit card details. The training module should provide examples of phishing emails, highlighting the telltale signs of phishing attempts, such as suspicious sender addresses, poor grammar, and urgent requests for personal information.
- Malware: Malicious software, often disguised as legitimate attachments or links, can compromise systems and steal data. The training should emphasize how to recognize suspicious attachments and the importance of not opening unknown files or clicking on unfamiliar links. A crucial aspect of this training is teaching employees how to report suspicious emails and attachments.
- Spear Phishing: This is a more targeted form of phishing that leverages specific information about the recipient to increase the likelihood of success. The module should emphasize how personal information can be used to craft more convincing phishing attempts, and how to recognize subtle clues that something is amiss.
- Social Engineering: This involves manipulating individuals into performing actions that compromise security. The training should provide examples of how social engineering techniques can be used in email communications, including impersonation and emotional manipulation. It should teach employees to verify information independently and avoid acting on urgent requests without verification.
Interactive Training Materials for Email Security
Interactive training materials are highly effective for engaging employees and reinforcing security awareness. Simulations of phishing attempts, quizzes, and interactive exercises are ideal tools for keeping learners engaged and demonstrating the real-world impact of security breaches.
Frequency of Security Awareness Training
Regular security awareness training is essential to maintain a high level of employee vigilance. Training should be delivered periodically, ideally on a quarterly basis, to reinforce knowledge and address new threats. Ongoing training is vital, not just initial instruction.
Resources for Ongoing Email Security Education
Ongoing email security education is critical for maintaining a robust security posture. Regularly updating employee knowledge with current threats and best practices is crucial. There are many resources available for this purpose, both internal and external.
While ten steps to email security are crucial, it’s also interesting to consider the less obvious aspects of digital threats. For example, understanding the potential benefits of computer viruses, as explored in this fascinating article about whats good about computer viruses , can actually enhance your email security strategy. Ultimately, a well-rounded understanding of the digital landscape is key to effective email security practices.
- Company Intranet: Internal portals should house security guidelines, FAQs, and links to resources.
- Security Newsletters: Regular email updates can alert employees to emerging threats and provide actionable advice.
- External Security Websites: Numerous reputable websites offer email security tips and best practices.
- Security Blogs and Articles: Regularly reviewing security blogs and articles can provide valuable insights into the latest trends and threats.
Staying Updated on Email Security Trends
Staying ahead of evolving email threats requires a proactive approach to cybersecurity. Email security is a dynamic landscape, constantly changing with new vulnerabilities and attack vectors. This proactive approach involves continuous learning and adaptation to the latest threats and best practices.Email security is no longer a static set of rules; it’s a dynamic process demanding constant vigilance and adaptation.
Cybercriminals are always innovating, creating new methods to exploit vulnerabilities. Staying updated on the latest trends and best practices is crucial for safeguarding sensitive information and maintaining a robust security posture.
Importance of Staying Updated
Constant vigilance and adaptation are critical to a robust email security posture. Failure to stay informed can leave organizations vulnerable to emerging threats. Email security best practices are not static; they evolve as new attack methods are developed. Organizations that prioritize continuous learning and adaptation can proactively address evolving threats and mitigate risks.
Role of Cybersecurity News Sources
Reliable cybersecurity news sources play a vital role in keeping abreast of the latest email security trends. These sources often provide early warnings about emerging threats, detailed analyses of attack vectors, and insights into the latest security best practices. Subscribing to newsletters, following reputable security analysts on social media, and reading security blogs can help organizations stay informed.
Resources for Researching Email Security Best Practices
Numerous resources offer valuable insights into email security best practices. Government agencies, such as the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA), provide comprehensive guidance and resources. Industry organizations, like the SANS Institute, offer detailed training materials and certifications. Specialized security blogs and websites often publish articles on the latest email security trends and techniques.
Adapting to Evolving Threats
Email security threats are constantly evolving. New malware variants, phishing techniques, and social engineering tactics emerge regularly. Organizations need to adapt their security measures to counter these threats. This adaptability requires a flexible security posture, continuous monitoring of email traffic, and proactive implementation of the latest security tools and protocols.
Timeline of Major Developments in Email Security (Past 5 Years)
- 2018-2019: Increased sophistication of phishing campaigns, with targeted attacks becoming more prevalent. The rise of social engineering techniques, exploiting human psychology, was a significant development. Email-borne ransomware attacks also increased in frequency and impact.
- 2020-2021: The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the shift to remote work, creating new attack vectors. Phishing attacks targeting remote workers increased dramatically. The rise of cloud-based email services brought new security challenges. Increased use of AI-powered tools to detect and block sophisticated phishing campaigns was observed.
- 2022-2023: The prevalence of AI-generated phishing emails increased, presenting a significant new threat. More sophisticated spear-phishing attacks targeted specific individuals and organizations. The rise of “deepfakes” as a tool in social engineering campaigns was a notable development.
Final Wrap-Up
In conclusion, email security is an ongoing process, requiring continuous vigilance and adaptation. By understanding and applying the ten steps Artikeld in this guide, you can significantly reduce your vulnerability to threats and safeguard your digital interactions. Remember, proactive measures are key to ensuring secure email practices in today’s interconnected world.