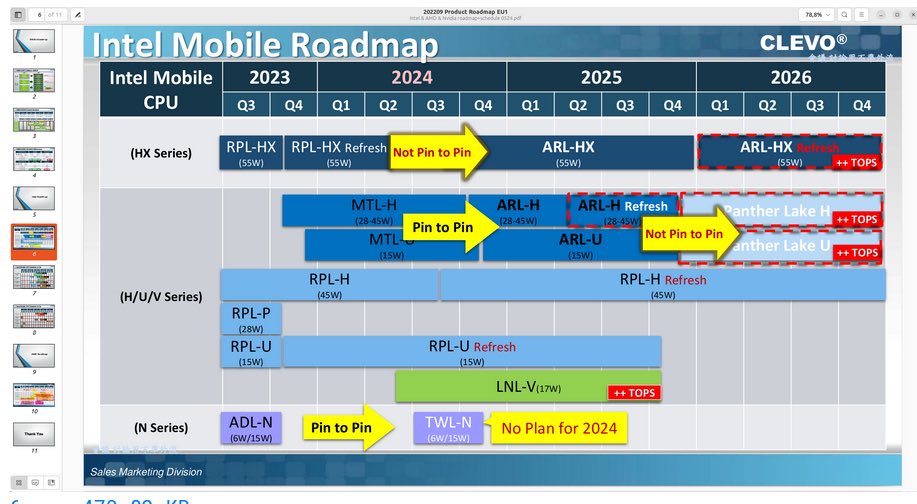
Intel Lays Out Future Product Roadmap
Intel lays out future product roadmap, painting a vivid picture of the tech giant’s upcoming innovations. This detailed roadmap covers everything from CPUs and GPUs to AI, providing a fascinating look at Intel’s strategic direction and projected release timelines for major products. We’ll dive deep into the specifics, examining key product categories, technological advancements, market positioning, and the potential impact across various industries.
The document offers a comprehensive overview, comparing Intel’s roadmap to its competitors. Tables highlight key specifications, performance benchmarks, and potential applications of new products. It also speculates on potential new product categories, analyzing their possible benefits and drawbacks, and how they’ll integrate with existing systems. This gives a comprehensive understanding of the strategic vision behind Intel’s future.
Overview of Intel’s Roadmap: Intel Lays Out Future Product Roadmap
Intel’s recent announcements paint a picture of a company navigating a complex technological landscape. They’ve Artikeld a multi-pronged approach, aiming to maintain competitiveness in the face of rapid advancements from rivals like AMD and Nvidia. This roadmap, while ambitious, acknowledges the challenges of innovation and the need for strategic investments.Intel’s strategy revolves around a commitment to diverse technologies, recognizing the increasing importance of not just CPUs but also GPUs and AI-focused solutions.
The timeline presented suggests a phased rollout, with early focus on foundational technologies to build a solid base for future advancements.
Key Areas of Focus
Intel is concentrating its efforts on several key areas: CPUs, GPUs, and AI. These segments are interconnected, and advancements in one often contribute to improvements in others. This integrated approach suggests a long-term strategy to leverage advancements in one area to boost the entire portfolio.
- Central Processing Units (CPUs): Intel is emphasizing enhanced performance and efficiency in their CPUs. Improvements in architecture and manufacturing processes are central to this strategy. They’re aiming to close the performance gap with competitors and retain market share in this crucial segment.
- Graphics Processing Units (GPUs): Intel is actively developing advanced GPU technologies, including specialized chips for AI and high-performance computing. The growing demand for powerful GPUs in various applications (gaming, data centers, scientific simulations) is driving this investment. This effort reflects a proactive response to the rising dominance of dedicated GPU providers.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI is a key strategic priority for Intel. Their roadmap includes dedicated hardware and software solutions for AI workloads. The development of custom AI chips and optimized software stacks highlights Intel’s commitment to this evolving field. This strategic initiative aims to leverage AI for improved data processing, optimization, and automation across their product portfolio.
Timeline of Major Product Releases
Intel’s roadmap details projected release dates for several significant product lines. These dates provide a glimpse into their planned rollout strategy and the expected availability of their advanced technologies. The timeline anticipates a phased release, allowing for testing, refinement, and adaptation based on market feedback.
- 2024: Initial releases of new CPU architectures are expected, focusing on improving performance and efficiency. These initial releases are crucial for setting the stage for future enhancements.
- 2025: A major push in GPU development is anticipated. These new GPUs are designed to address emerging AI and high-performance computing needs. The timeline reflects a planned increase in GPU-based product offerings.
- 2026-2027: Further expansion into AI-focused hardware and software solutions is anticipated. This stage likely involves the launch of specialized AI processors and enhanced software libraries.
Comparison with Competitors’ Roadmaps
The following table provides a comparative overview of Intel’s roadmap with those of key competitors. This comparison reveals the competitive landscape and Intel’s strategic positioning.
| Feature | Intel | AMD | Nvidia |
|---|---|---|---|
| CPU Performance | Focus on efficiency and performance improvements | Strong focus on high-end performance | N/A (primarily GPU focus) |
| GPU Performance | Expanding GPU offerings for diverse applications | Strong competition in the GPU market | Leading provider of GPUs |
| AI Specialization | Developing dedicated AI hardware and software | Growing AI capabilities in their product portfolio | Strong AI capabilities, focusing on hardware and software solutions |
| Projected Release Dates | Phased rollout, focusing on specific segments | Focus on aggressive timelines | Focus on high-end GPU releases and supporting software |
Specific Product Categories
Intel’s future roadmap encompasses a diverse range of product categories, each designed to meet evolving technological demands. This exploration delves into the anticipated features, functionalities, and innovations within these categories, providing a glimpse into Intel’s vision for the future of computing. From CPUs to GPUs, and beyond, this analysis compares current offerings with the planned future advancements, emphasizing the significant leaps forward.
Intel’s latest product roadmap is pretty exciting, highlighting some serious advancements. But while we’re buzzing about the future of chips, it’s worth noting that Napster is also making a comeback, partnering with Penn State to bring its services back to the campus. Napster returns to campus with penn state partnership. This could potentially open up interesting new opportunities for students and faculty, and ultimately, could impact the future of the tech industry.
All in all, it’s a pretty cool time to be in the tech world and see how these innovations intertwine.
Central Processing Units (CPUs)
Intel’s CPUs are the heart of computing, and future offerings aim to further enhance performance and efficiency. Current CPUs already excel in multitasking and handling demanding applications. The anticipated future generation will leverage innovative architectures and advanced manufacturing processes, such as Intel 4, to boost clock speeds and core counts. This will enable faster processing and improved performance in demanding tasks like gaming, video editing, and scientific simulations.
- Enhanced Instruction Sets: Future CPUs will likely include enhanced instruction sets, enabling more efficient handling of specific tasks. For example, specialized instructions for AI workloads or machine learning tasks are likely to be integrated, offering tailored performance improvements in specific domains.
- Improved Cache Mechanisms: Optimization of cache mechanisms is crucial for minimizing latency and maximizing performance. Future designs are anticipated to improve cache sizes and access speeds, further accelerating data retrieval and processing.
- Advanced Packaging: Advancements in packaging technology, such as chiplets and 3D stacking, will be key to enhancing CPU performance and efficiency. Such innovations will allow for increased integration density, leading to higher core counts and improved inter-component communication. This will improve the thermal performance and power efficiency of future CPUs.
Graphics Processing Units (GPUs)
Intel’s GPUs are gaining traction in diverse applications, from gaming to professional visualization. Current GPUs provide a solid foundation, but future generations are projected to further expand their capabilities and performance. Key improvements are expected in areas such as AI acceleration and ray tracing capabilities.
- AI Acceleration: Future GPUs will likely incorporate specialized hardware accelerators to handle AI workloads more efficiently. This will enable faster training and inference times, facilitating advancements in fields such as machine learning and deep learning.
- Ray Tracing Capabilities: Significant advancements in ray tracing capabilities will enhance realism and visual fidelity in gaming and other applications. Future GPUs will support more sophisticated ray tracing algorithms, pushing the boundaries of visual fidelity in real-time rendering.
- Unified Memory Architecture: Future GPUs will likely feature a unified memory architecture, enabling faster and more efficient communication between the CPU and GPU. This will lead to better performance in applications that require close collaboration between the two components.
Other Product Categories
- Networking: Future networking solutions from Intel are expected to support high-bandwidth and low-latency connections, enabling faster data transfer rates and improved network performance. The use of advanced technologies, such as optical transceivers, is likely to contribute to this improvement.
- Storage: Intel’s storage solutions will likely focus on faster data access times and greater storage capacities. Advancements in SSD technologies will improve performance and reliability.
Comparison Table: Key Specifications and Performance Benchmarks
| Product Category | Current Generation | Future Generation (Estimated) | Key Advancements |
|---|---|---|---|
| CPUs | Alder Lake | Raptor Lake | Increased core count, enhanced architecture, improved cache mechanisms |
| GPUs | Arc A770 | Arc A780 (projected) | Enhanced ray tracing, AI acceleration, unified memory architecture |
| Networking | Ethernet 2.5G/10G | Ethernet 20/40/100G | Higher bandwidth, lower latency, advanced optical transceivers |
| Storage | PCIe 4.0 SSDs | PCIe 5.0 SSDs (projected) | Faster data access, increased capacity, improved reliability |
Technological Advancements
Intel’s roadmap is driven by a relentless pursuit of innovation in microarchitecture, materials science, and manufacturing processes. These advancements are critical to maintaining leadership in the computing industry, enabling faster, more efficient, and more powerful devices for consumers and businesses alike. The company is heavily invested in research and development to stay ahead of the curve and meet the evolving demands of the market.These advancements are not simply incremental improvements; they represent fundamental shifts in how computers operate.
From new transistor designs to innovative packaging techniques, each step forward promises significant gains in performance and energy efficiency. However, these breakthroughs also introduce challenges that require careful planning and execution. Intel’s strategy involves addressing these obstacles proactively to ensure a smooth transition and maximize the benefits of these cutting-edge technologies.
New Architectures
Intel’s roadmap includes significant investments in new microarchitectures designed to enhance performance and efficiency. These architectures often feature novel instruction sets, optimized cache hierarchies, and improved branch prediction mechanisms. These advancements are essential for achieving higher clock speeds and reducing power consumption without sacrificing performance. For example, the company’s recent focus on incorporating AI acceleration into its CPU architectures is a key element of this trend.
Material Science Innovations
Advancements in material science are crucial to shrinking transistor sizes and improving device performance. The transition from silicon to more advanced materials, such as germanium and gallium arsenide, is being explored, potentially offering significant gains in transistor density and speed. Research into novel materials and their integration into existing processes is crucial for maintaining Moore’s Law-like progress in the long term.
Furthermore, improved dielectric materials will help reduce leakage currents and enhance transistor switching speed.
Process Improvements
Intel is committed to refining its manufacturing processes, enabling smaller and faster transistors. Extreme ultraviolet (EUV) lithography is a key component in achieving these advancements. EUV allows for the creation of intricate transistor patterns with finer details, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in terms of transistor density. This translates to higher performance and greater energy efficiency in modern processors.
The company is also working on 3D chip stacking and packaging, further increasing the density and performance of its chips.
Challenges and Mitigation Strategies
While these advancements promise substantial benefits, they also introduce challenges. The transition to new materials and manufacturing processes can be complex and costly. For instance, scaling EUV lithography and maintaining consistent quality across large production runs poses significant technical hurdles. Intel is proactively addressing these challenges through strategic partnerships, investments in research and development, and continuous process optimization.
Additionally, the company is working to develop robust testing methodologies to ensure the reliability and quality of these advanced components.
Market Positioning and Competition
Intel’s future roadmap hinges on its ability to effectively compete in a dynamic market landscape. The company faces significant challenges, particularly from rivals like AMD and Nvidia, who are aggressively pursuing new technologies and market segments. Intel’s success will depend on its ability to adapt, innovate, and maintain its competitive edge in the face of these challenges.
Intel’s Market Position
Intel has historically dominated the CPU market, but its recent performance has been less impressive. AMD has chipped away at Intel’s dominance with innovative architectures and competitive pricing. Nvidia, while primarily known for GPUs, has also made inroads into the CPU market with its high-performance computing offerings. This evolving landscape necessitates a strategic response from Intel.
Competitive Landscape and Market Trends
The market for processors is becoming increasingly diversified. High-performance computing (HPC), mobile devices, and the burgeoning field of AI are all driving demand for specialized processors. The increasing prevalence of cloud computing and edge computing further complicates the market landscape, requiring processors that are efficient, powerful, and adaptable to various needs. This necessitates a nuanced approach to product development and marketing.
Intel’s latest product roadmap looks promising, with a focus on innovative chips. However, it’s important to remember that while technological advancements are exciting, we shouldn’t forget the ongoing need for cybersecurity awareness, especially given the prevalence of hoaxes like the Bin Laden virus hoax identified targeted. This targeted hoax serves as a reminder of the importance of verifying information and staying vigilant in today’s digital landscape.
Intel’s roadmap, despite these concerns, still seems like a forward-thinking strategy.
Comparison with AMD and Nvidia
AMD has successfully challenged Intel’s dominance in the CPU market, particularly in the high-performance segment. Nvidia, while primarily known for GPUs, is increasingly targeting the CPU market with its HPC offerings. These competitors are leveraging advances in chip architecture and manufacturing processes to gain market share. Intel’s response must be multifaceted, addressing both cost and performance.
Addressing Perceived Weaknesses, Intel lays out future product roadmap
Intel is actively addressing perceived weaknesses by focusing on innovative chip architectures, particularly in areas like specialized processors for AI and HPC. The company is also investing in new manufacturing processes to improve performance and reduce costs. Intel is further seeking strategic partnerships to complement its existing offerings and explore new market segments.
Strengths and Weaknesses Compared to Competitors
| Feature | Intel | AMD | Nvidia |
|---|---|---|---|
| CPU Performance (General-Purpose) | Historically strong, but facing challenges | Strong gains in recent years, particularly in high-performance segments | Competitive but not a primary focus |
| CPU Performance (Specialized) | Developing specialized processors, but lagging in certain areas | Developing specialized processors for specific needs | Strong specialized processors for AI and HPC |
| GPU Performance | Limited compared to Nvidia | Limited compared to Nvidia | Dominant |
| Manufacturing Process | Historically strong, but facing catch-up | Improving manufacturing processes, competing with Intel | Strong manufacturing partnerships |
| Pricing Strategy | Can be high, especially in some segments | Competitive pricing, particularly in certain segments | Pricing varies based on product segment |
This table highlights the key areas where Intel needs to improve to remain competitive. A thorough analysis of each category is critical to success.
Intel’s latest product roadmap reveals exciting plans, with a significant emphasis on the future of connectivity. They’re clearly focusing on boosting performance in areas like broadband wireless chips, like those detailed in this insightful article intel to focus on broadband wireless chips. This shift suggests a strong commitment to the evolving needs of the tech world, and it’s a key element of their overall strategy moving forward.
Potential Impact and Implications

Intel’s forthcoming roadmap promises a significant shift in the computing landscape. From advancements in chip architecture to the integration of new technologies, the implications for various industries, including consumer electronics, data centers, and beyond, are substantial. The potential for enhanced performance, energy efficiency, and innovative applications is vast, creating both opportunities and challenges for stakeholders.
Impact on Consumer Technology
Consumer electronics will see a noticeable upgrade with Intel’s new processors. Faster speeds and improved graphics capabilities will translate into more responsive and visually stunning devices. This will drive demand for new laptops, desktops, and potentially even more powerful gaming consoles. Expect to see a faster pace of innovation in areas like virtual reality and augmented reality experiences, as the hardware becomes more capable of supporting these demanding applications.
Impact on Data Centers
Intel’s roadmap anticipates significant improvements in data center infrastructure. Increased processing power and energy efficiency will enable more complex data analytics and machine learning tasks. This translates to faster, more reliable cloud services and more powerful artificial intelligence systems. Data centers can leverage these advancements to enhance their scalability and responsiveness, facilitating the growth of data-intensive industries.
Impact on Other Sectors
Beyond consumer electronics and data centers, Intel’s advancements will ripple through other industries. The enhanced processing capabilities will be beneficial to scientific research, enabling more complex simulations and data analysis. Similarly, the automation of industrial processes can benefit from the increased computing power, leading to improved efficiency and productivity. Furthermore, the potential for more robust and reliable Internet of Things (IoT) devices will open new avenues for innovation across various sectors.
Expected Changes in the Hardware Landscape
Intel’s roadmap foresees a transition towards more compact and efficient hardware. The integration of new materials and designs will lead to a reduction in size and power consumption of computing devices. This trend is already evident in the shrinking size of smartphones and laptops, and Intel’s advancements will further accelerate this miniaturization trend. Expect greater portability and enhanced battery life in various devices.
Potential Applications of Intel’s Upcoming Products
| Product Category | Potential Applications |
|---|---|
| High-performance processors | Advanced gaming, scientific simulations, data analysis, artificial intelligence training |
| Efficient processors | Portable devices, embedded systems, Internet of Things (IoT) devices, energy-conscious data centers |
| Specialized processors | AI-specific workloads, machine learning, high-performance computing |
| Advanced graphics processing units (GPUs) | Virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), high-definition gaming, and video editing |
Illustrative Examples of New Products
Intel’s future roadmap hints at exciting possibilities, pushing the boundaries of computing beyond what we currently experience. This section delves into potential new product categories, showcasing key features and applications, and assessing their potential impact. We’ll examine how these innovations could integrate with existing systems and reshape various sectors.
Potential New Product Categories
Intel’s future endeavors may encompass specialized hardware tailored for emerging markets. Consider a new category of neuromorphic computing chips, designed for complex pattern recognition and deep learning. These chips would be distinctly different from traditional CPUs and GPUs, offering optimized performance for AI applications. Another possibility involves developing quantum-resistant cryptography processors. These would be crucial for protecting sensitive data in an era of increasing cyber threats.
Finally, the development of highly-efficient, AI-assisted embedded systems for smart homes and industrial automation is also a potential focus.
Key Features and Specifications of Hypothetical Products
- Neuromorphic Computing Chips: These chips would feature a massively parallel architecture, mimicking the structure and function of the human brain. Key specifications would include high-density neural networks, low-power consumption, and optimized algorithms for deep learning tasks, potentially exceeding the processing speed of current GPUs for complex pattern recognition and predictive modeling. These chips would likely come in specialized packages, optimized for high-density connectivity, to facilitate seamless integration with existing AI frameworks.
- Quantum-Resistant Cryptography Processors: These processors would employ advanced cryptographic algorithms resistant to attacks from quantum computers. Their specifications would include hardware acceleration for complex cryptographic operations, ensuring secure communication and data protection in future scenarios. This would be essential for protecting sensitive data, especially in financial institutions, healthcare systems, and national security sectors. These processors would have specialized instruction sets and support various encryption standards, including post-quantum cryptographic algorithms.
- AI-Assisted Embedded Systems: These embedded systems would feature low-power consumption, highly integrated hardware, and embedded AI algorithms for real-time decision-making. They would likely include sensors for data acquisition, dedicated processing units, and communication protocols for efficient data exchange. Key specifications would include flexible software frameworks for customizing AI models and low latency for rapid responses.
Benefits and Drawbacks of New Product Categories
| Product Category | Potential Benefits | Potential Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|
| Neuromorphic Computing Chips | Enhanced AI capabilities, faster pattern recognition, lower energy consumption for complex tasks | Higher development costs, potential market saturation, dependence on specialized software and algorithms |
| Quantum-Resistant Cryptography Processors | Enhanced data security, protection against future quantum computing threats, secure communication channels | High development costs, potential compatibility issues with existing systems, need for widespread adoption of new protocols |
| AI-Assisted Embedded Systems | Improved automation, enhanced efficiency, real-time decision-making in various sectors | Potential for job displacement in certain industries, security vulnerabilities in connected devices, high cost of development and implementation |
Integration with Existing Systems
“Seamless integration is crucial for the adoption of new technologies.”
These new products will integrate with existing systems through standardized interfaces and APIs. Neuromorphic chips could be connected to existing servers via high-speed networks, leveraging existing AI frameworks. Quantum-resistant processors would utilize existing communication protocols and encryption standards, ensuring compatibility. AI-assisted embedded systems would interface with IoT networks, providing a seamless flow of data and control.
Potential Applications and Use Cases
- Neuromorphic Computing Chips: Real-world applications could include autonomous driving systems, medical image analysis, and fraud detection. Imagine self-driving cars reacting to unpredictable situations with speed and accuracy, or medical diagnosis systems identifying anomalies in patient scans with unprecedented speed and efficiency.
- Quantum-Resistant Cryptography Processors: These would be vital for secure transactions in e-commerce, protecting financial data, and safeguarding sensitive government information. Consider the ability to maintain the integrity of online banking transactions and prevent fraudulent activities.
- AI-Assisted Embedded Systems: These could be used in smart homes, optimizing energy consumption and security. Imagine a smart home automatically adjusting lighting and temperature based on occupancy and weather conditions, while also monitoring for potential security threats in real-time. Industrial automation systems could use these for predictive maintenance and optimization of production processes.
Summary
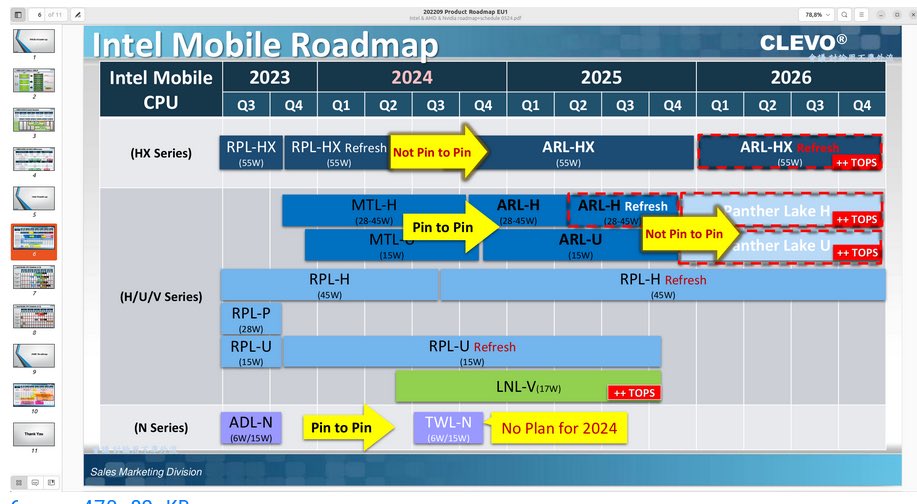
Intel’s future product roadmap promises exciting advancements, particularly in areas like AI. The competitive landscape is also highlighted, showcasing Intel’s strategies and positioning against competitors like AMD and Nvidia. The potential impact on various industries, from consumer technology to data centers, is significant. While challenges are anticipated, Intel’s plan to overcome these limitations provides a strong outlook for the future of computing.
Overall, the roadmap suggests a clear vision and a proactive approach to the ever-evolving tech market.