Electronic Signatures The Proof Is in the Process
Electronic signatures the proof is in the process – Electronic signatures, the proof is in the process, are revolutionizing how we conduct business and personal transactions. From simple click-wraps to more complex digital signatures, these methods offer efficiency, security, and a streamlined alternative to traditional paper-based approaches. This exploration delves into the intricate details of electronic signatures, covering everything from the legal frameworks that underpin their validity to the technological processes that make them possible.
We’ll also analyze case studies, highlighting both successes and challenges in real-world implementations.
Understanding the different types of electronic signatures, such as digital signatures and biometrics, is crucial. Each type offers unique security features, and understanding their legal recognition in various jurisdictions is essential. The process itself, from creation to validation, involves several critical steps, including encryption, authentication, and data integrity checks. These procedures are designed to ensure the security and authenticity of electronic signatures, providing a reliable alternative to traditional methods.
Introduction to Electronic Signatures: Electronic Signatures The Proof Is In The Process
Electronic signatures are rapidly transforming how we conduct business and personal transactions. They offer a secure, efficient, and legally sound alternative to traditional paper-based signatures, eliminating the need for physical documents and accelerating processes. This evolution reflects a broader trend toward digitalization in various sectors.Electronic signatures, in their essence, are digital representations of a handwritten signature. They are used to authenticate the validity and intent of a document or agreement.
Their use is now widespread across numerous industries, from banking and healthcare to e-commerce and legal transactions.
Types of Electronic Signatures and Legal Recognition
Various types of electronic signatures exist, each with varying levels of security and legal recognition. Understanding these differences is crucial for ensuring the validity and enforceability of agreements. The legal framework surrounding electronic signatures varies by jurisdiction, so always consult with legal counsel when considering their use in specific situations.
- Simple Electronic Signatures (SES): These are the most basic form, encompassing any electronic method that indicates a person’s agreement to a document. Examples include clicking an “I agree” button or typing your name at the end of an email. While widely used, their legal weight can vary depending on the jurisdiction and specific regulations.
- Advanced Electronic Signatures (AES): AES are more secure than SES. They use specific data encryption techniques to ensure authenticity and integrity. These signatures are often associated with a digital certificate, a type of electronic credential that verifies the identity of the signer. AES offer stronger legal recognition in most jurisdictions.
- Qualified Electronic Signatures (QES): QES represent the highest level of security and legal recognition. They meet strict technical requirements, such as using a qualified certificate and adhering to specific regulations. QES are often required for highly regulated industries or transactions where the highest level of assurance is necessary.
Historical Context of Electronic Signatures
The evolution of electronic signatures reflects a gradual shift from traditional paper-based methods to digital alternatives. Early forms of electronic signatures emerged with the advent of fax machines and scanned signatures. However, these methods often lacked the necessary security and legal recognition to be widely accepted in a court of law. Subsequent advancements in cryptography and digital certificate technology paved the way for more secure and reliable electronic signature methods, ultimately leading to the modern standards in place today.
Comparison of Electronic Signature Methods
The table below Artikels some common electronic signature methods and their key characteristics.
| Method | Description | Security | Legal Recognition |
|---|---|---|---|
| Digital Signatures | Based on cryptography, ensuring data integrity and authenticity. | High | Generally strong, often legally recognized in many jurisdictions. |
| Biometrics | Utilizing unique physical characteristics like fingerprints or facial recognition to verify identity. | High | Growing legal acceptance, but varies by jurisdiction. |
| Clickwraps | Signatures through clicking “I agree” buttons. | Low | Varying legal recognition; often enforceable if the agreement is clearly presented and the user has had an opportunity to review the terms. |
The Process of Electronic Signature Creation
Electronic signatures, a cornerstone of modern digital transactions, are more than just digital representations of handwritten ones. They’re a complex process that ensures authenticity, integrity, and non-repudiation of documents. This process hinges on robust security measures, cryptographic techniques, and standardized protocols, all working together to guarantee the validity of the signed data.Creating a secure electronic signature involves several steps, each designed to prevent fraud and ensure the document’s integrity.
The core principles are authentication, encryption, and a verifiable audit trail. These mechanisms guarantee that only the intended recipient can access the document, and that any alterations to the document are immediately detectable.
Steps in Electronic Signature Creation
The process of creating an electronic signature involves a series of carefully orchestrated steps. Each step is crucial in ensuring the security and validity of the signature. From initial document preparation to final verification, each stage is designed to protect against unauthorized access and tampering.
- Document Preparation: The document to be signed is prepared digitally. This might involve scanning a physical document or creating a new document electronically.
- Digital Identity Verification: The signatory’s identity is verified using methods such as password authentication, biometric verification, or multi-factor authentication. This ensures that the person signing the document is who they claim to be.
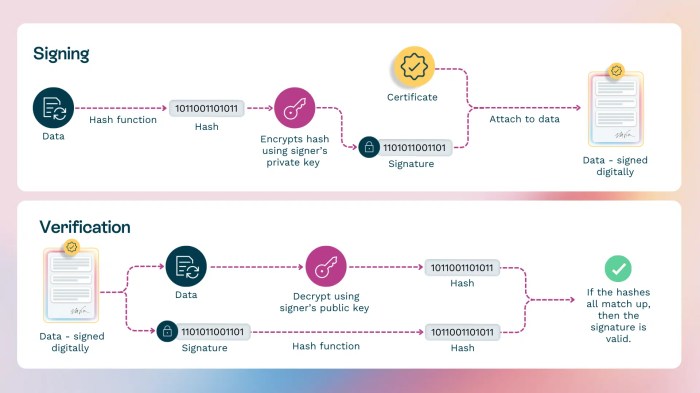
- Signature Creation: Using a designated digital signature creation tool, the signatory creates their signature. This process often involves applying a cryptographic hash function to the document, which generates a unique digital fingerprint. This hash is then encrypted using the signatory’s private key.
- Signature Embedding: The encrypted hash, along with metadata, is embedded into the signed document. This embedding is often accomplished using digital certificates that link the signature to the signatory.
- Verification and Validation: The recipient verifies the signature by using the signatory’s public key to decrypt the hash and compare it to the hash of the received document. If they match, the signature is valid. If they do not match, the document has been tampered with, and the signature is invalid.
Role of Encryption and Authentication
Encryption plays a critical role in safeguarding the electronic signature process. Encryption techniques, like asymmetric cryptography, ensure that only the intended recipient can decrypt the signature and verify its authenticity. Authentication mechanisms, including digital certificates, verify the identity of the signatory and guarantee the signature’s source.
“Encryption transforms data into an unreadable format, making it impervious to unauthorized access, while authentication validates the identity of the user, thereby preventing impersonation.”
Technologies Used in the Process
Several technologies are crucial for creating and verifying electronic signatures. These technologies include public key infrastructure (PKI), digital certificates, and hash functions. PKI provides a framework for managing digital certificates, while digital certificates bind public keys to user identities. Hash functions create unique digital fingerprints of documents, facilitating the detection of any alterations.
- Public Key Infrastructure (PKI): PKI provides a framework for managing digital certificates, public and private keys, and digital signatures. It’s like a digital identity system for the internet.
- Digital Certificates: Digital certificates are used to bind a public key to a specific user or entity. This ensures that the recipient can verify the authenticity of the signature.
- Hash Functions: Hash functions create a unique digital fingerprint of a document. Any alteration to the document will change the hash, making it easy to detect tampering.
Assuring Data Integrity and Non-Repudiation
The electronic signature process assures data integrity by ensuring that the document hasn’t been altered since it was signed. Non-repudiation means that the signatory cannot deny having signed the document. This is achieved through the cryptographic techniques and secure storage of the signature and associated data.
Stages and Security Measures, Electronic signatures the proof is in the process
The following table Artikels the various stages of the electronic signature process and the security measures associated with each.
| Stage | Description | Security Measures |
|---|---|---|
| Document Preparation | Preparing the document for signing. | Document version control, access control. |
| Identity Verification | Verifying the signatory’s identity. | Multi-factor authentication, biometric verification. |
| Signature Creation | Generating the digital signature. | Cryptographic hash functions, private key encryption. |
| Signature Embedding | Embedding the signature into the document. | Digital certificate integration, tamper-proof mechanisms. |
| Verification | Verifying the signature’s validity. | Public key decryption, hash comparison. |
Legal Framework and Validation

Electronic signatures have revolutionized document handling, but their legal acceptance and validation are crucial for their widespread adoption. Understanding the legal frameworks underpinning these signatures is essential for ensuring their reliability and enforceability. This section delves into the key legal aspects, focusing on the role of trust services providers, and the varying legal validity of electronic signatures across jurisdictions.The legal landscape surrounding electronic signatures is complex, with regulations varying significantly from country to country.
This necessitates a nuanced approach to understanding and utilizing electronic signatures, considering the specific legal requirements of the jurisdiction in question. This knowledge empowers users and businesses to navigate the complexities of digital transactions with confidence.
Key Legal Frameworks
Various international and national regulations govern electronic signatures. These frameworks define the requirements for creating, validating, and using electronic signatures to ensure their legal admissibility in courts. Compliance with these regulations is paramount to prevent legal challenges.
- The eIDAS Regulation (EU): This European Union regulation provides a comprehensive legal framework for electronic identification, authentication, and trust services. It establishes a harmonized approach to electronic signatures across the EU, simplifying cross-border transactions and boosting confidence in digital processes. It defines different types of electronic signatures, including advanced electronic signatures, and sets out specific requirements for trust service providers.
- US ESIGN Act: The Electronic Signatures in Global and National Commerce Act (ESIGN Act) in the United States governs electronic signatures and records. It provides legal recognition for electronic signatures, making them legally equivalent to handwritten signatures in many circumstances. However, specific exceptions exist for certain documents, such as wills and divorce decrees.
- Other National Regulations: Many countries have implemented national laws to address electronic signatures, including the UK’s Electronic Communications Act, and other regions such as Canada and Australia have specific legislation. These laws often align with international standards, but unique nuances and requirements exist, reflecting local legal traditions and customs.
Trust Services Providers and Certification Authorities
Trust service providers and certification authorities play a critical role in ensuring the validity and reliability of electronic signatures. They provide the infrastructure and mechanisms to verify the authenticity and integrity of digital signatures. This verification process guarantees the document’s origin and prevents unauthorized modifications.Trust service providers (TSPs) are entities certified to provide trust services, such as electronic signature creation, validation, and time-stamping.
TSPs adhere to strict regulations and standards, guaranteeing the security and integrity of the signature process. Certification authorities (CAs) are a type of TSP that issue digital certificates, which are essential components of many electronic signature systems. These certificates verify the identity of the signatory and link the signature to the signer.
Comparison of Legal Validity Across Countries
The legal validity of electronic signatures varies significantly between jurisdictions. While many countries have embraced e-signatures, specific requirements and exceptions often apply, depending on the type of signature and the nature of the document. This highlights the importance of understanding the relevant legislation before implementing electronic signature solutions in international transactions.
| Region | Key Legal Requirements |
|---|---|
| EU | Adherence to the eIDAS regulation; specific types of signatures and validation procedures are defined. |
| US | Compliance with the ESIGN Act; exceptions may apply to certain documents. |
| UK | Guided by the Electronic Communications Act; specific requirements and procedures might differ from other jurisdictions. |
| Canada | Various provincial laws govern electronic signatures, potentially with specific regulations related to specific industries or document types. |
Security and Privacy Considerations
Electronic signatures, while offering convenience and efficiency, introduce new security and privacy concerns. Understanding these risks and implementing appropriate safeguards is crucial for the successful and trustworthy adoption of e-signatures. Robust security measures are vital to protect sensitive data and maintain the integrity of transactions.Protecting sensitive information during the electronic signature process requires a multi-faceted approach, including strong encryption, secure storage, and careful user authentication.
This ensures that only authorized individuals can access and modify digital signatures, mitigating the risk of fraud and unauthorized access.
Security Risks Associated with Electronic Signatures
Electronic signatures, despite their advantages, are vulnerable to various security risks. These include unauthorized access to digital signature keys, tampering with documents before signing, and impersonation of signatories. Such risks can compromise the integrity of agreements and potentially lead to financial losses or legal disputes. Malicious actors can exploit vulnerabilities in the system to forge signatures or alter contract terms, potentially causing significant harm to individuals and organizations.
Measures to Mitigate Security Risks
Implementing robust security measures is paramount to protecting electronic signatures. These measures include using strong encryption algorithms to safeguard sensitive data, employing multi-factor authentication (MFA) to verify user identity, and regularly updating software and security protocols. Implementing strong access controls and restricting access to sensitive data and systems can significantly reduce the likelihood of unauthorized access.
Data Privacy and Protection in Electronic Signature Processes
Data privacy is of utmost importance in electronic signature processes. Protecting user data from unauthorized access, use, or disclosure is critical to maintaining trust and complying with data protection regulations. Organizations must ensure that data handling practices adhere to relevant regulations, such as GDPR or CCPA, to avoid penalties and maintain public confidence. Data encryption and secure storage practices are vital to prevent unauthorized access and ensure confidentiality.
Importance of Data Encryption and Secure Storage of Digital Signatures
Data encryption plays a critical role in safeguarding digital signatures. Using strong encryption algorithms, like AES-256, ensures that only authorized parties can access and decrypt the data. Secure storage protocols are equally important, ensuring that digital signatures are protected from unauthorized access, alteration, or deletion. Data should be stored in secure servers with robust access controls, firewalls, and intrusion detection systems to prevent unauthorized access.
Electronic signatures – the proof is really in the process, isn’t it? The sheer complexity of verifying transactions, especially in today’s digital world, demands robust systems. This is particularly highlighted by projects like COLSA building an Apple Xserve supercomputer, colsa to build apple xserve supercomputer , which underscores the need for reliable, secure digital solutions. Ultimately, the intricate processes behind electronic signatures are the key to their validity and acceptance.
Potential Security Breaches and Countermeasures
| Potential Security Breach | Countermeasure |
|---|---|
| Unauthorized Access to Signature Keys | Implement strong password policies, multi-factor authentication, and role-based access controls. Regularly audit access logs and monitor for suspicious activity. |
| Document Tampering Before Signing | Employ digital signatures with timestamps and hash functions to detect any modifications. Use a secure document management system with version control. |
| Impersonation of Signatories | Implement robust user authentication methods, including biometric verification or hardware security modules (HSMs). Employ certificate-based authentication to verify the identity of signatories. |
| Malware Attacks | Regularly update software and security protocols. Install and maintain antivirus software and firewalls. Conduct regular penetration testing to identify vulnerabilities. |
| Phishing Attacks | Educate users about phishing scams and provide training on identifying suspicious emails or websites. Implement email authentication protocols (SPF, DKIM, DMARC). |
Electronic Signatures in Different Industries
Electronic signatures are rapidly transforming how businesses operate across various sectors. From streamlining healthcare processes to securing financial transactions, electronic signatures offer significant advantages over traditional methods. Their adoption is driven by the need for efficiency, security, and cost-effectiveness. This section explores the practical applications of electronic signatures in healthcare, finance, and real estate, highlighting the specific benefits and challenges encountered in each industry.
Electronic Signatures in Healthcare
Electronic signatures are increasingly crucial in healthcare for streamlining patient records, consent forms, and insurance claims. Their use improves efficiency and reduces paperwork, allowing medical professionals to focus on patient care. The secure and legally binding nature of electronic signatures helps maintain patient confidentiality and ensures compliance with regulations.
- Patient Consent Forms: Electronic signatures facilitate swift and secure patient consent for procedures, treatments, and release of information. This eliminates the need for paper forms, reducing the risk of loss or misplacement and speeding up the process. Patients can easily access and sign these forms digitally.
- Prescription Management: Electronic signatures can be incorporated into systems for secure prescription approvals and refills. This automated process ensures quicker and more efficient handling of prescription requests, reducing errors and improving patient access to medications.
- Insurance Claims: Electronic signatures can accelerate the processing of insurance claims, significantly reducing administrative burdens. Electronic signatures facilitate secure and compliant claim submission, reducing the risk of delays and errors.
Electronic Signatures in Finance
The financial sector heavily relies on secure and legally sound electronic signatures. Electronic signatures enhance the efficiency of various financial processes, such as loan applications, contract signings, and payment authorizations. This technology minimizes risks associated with fraud and forgery.
- Loan Applications: Electronic signatures expedite loan application processes, enabling faster approvals and reduced processing times. They ensure the authenticity and integrity of borrower agreements.
- Contract Signings: Electronic signatures are critical for contract signings, guaranteeing the legal validity of agreements. They ensure the security and integrity of sensitive financial information.
- Payment Authorizations: Electronic signatures streamline payment authorizations, reducing the risk of fraudulent transactions. This ensures that authorized parties receive funds and prevents unauthorized access to accounts.
Electronic Signatures in Real Estate Transactions
Electronic signatures revolutionize real estate transactions by streamlining the process and enhancing security. The use of electronic signatures for purchase agreements, mortgage documents, and closing statements minimizes delays and ensures the integrity of transactions.
- Purchase Agreements: Electronic signatures expedite the process of agreeing to purchase terms. This allows buyers and sellers to proceed with transactions faster and with greater convenience.
- Mortgage Documents: Electronic signatures significantly reduce the time required to finalize mortgage documents. This helps to speed up the entire process and minimize delays.
- Closing Statements: Electronic signatures ensure the authenticity and integrity of closing statements, guaranteeing the validity of the transaction.
Comparison of Usage Across Industries
While the core principle of electronic signatures—security and legal validity—remains consistent across industries, specific applications and challenges vary. Healthcare prioritizes patient confidentiality, finance emphasizes fraud prevention, and real estate focuses on speed and efficiency. The table below highlights the advantages and disadvantages of using electronic signatures in different industries.
| Industry | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Healthcare | Improved patient confidentiality, reduced paperwork, streamlined processes | Potential for system glitches, reliance on technology infrastructure |
| Finance | Enhanced security, fraud prevention, reduced transaction time | Need for robust security protocols, compliance with regulations |
| Real Estate | Faster transaction times, reduced costs, improved efficiency | Need for secure storage of documents, potential for technical issues |
Advantages and Disadvantages of Electronic Signatures
Electronic signatures have revolutionized document signing, offering a faster, more efficient, and often more secure alternative to traditional methods. However, like any technological advancement, they come with their own set of benefits and drawbacks. Understanding these nuances is crucial for businesses and individuals looking to leverage the power of e-signatures effectively.
Advantages of Electronic Signatures
Electronic signatures offer numerous advantages over their paper-based counterparts. These benefits span various aspects of document management and workflow.
- Increased Efficiency and Speed: Electronic signatures dramatically reduce the time required for document signing. Instead of waiting for physical documents to be mailed, scanned, and returned, parties can sign digitally almost instantaneously. This expedited process streamlines workflows and accelerates project completion. For example, a real estate transaction can close much faster with electronic signatures, saving all parties time and resources.
- Reduced Costs: Electronic signatures eliminate the costs associated with printing, postage, and physical document storage. Companies can save significantly on paper, ink, and personnel time spent on handling physical documents. Furthermore, reduced turnaround time can lead to decreased administrative overhead, ultimately leading to significant cost savings.
- Improved Security and Integrity: Electronic signatures employ robust cryptographic techniques to ensure the authenticity and integrity of signed documents. These methods make it virtually impossible to tamper with documents after they’ve been signed, thereby enhancing trust and reducing the risk of fraud.
- Enhanced Accessibility and Convenience: Electronic signatures enable signing documents from anywhere with an internet connection. This accessibility removes geographical limitations and empowers individuals to sign documents on their own schedule, improving convenience and responsiveness.
- Improved Document Management: Electronic signature platforms often integrate with document management systems, enabling streamlined storage, retrieval, and tracking of signed documents. This integration improves organization and reduces the risk of misplacing important documents.
- Environmental Friendliness: By reducing reliance on paper-based documents, electronic signatures contribute to a more environmentally friendly approach to business operations. This eco-conscious practice aligns with sustainability goals.
Disadvantages of Electronic Signatures
Despite the numerous advantages, electronic signatures also present some drawbacks that need careful consideration.
- Technical Issues: Reliable internet access and compatible software are crucial for the smooth operation of electronic signatures. Technical glitches, internet outages, or software malfunctions can disrupt the signing process and potentially lead to delays.
- Security Concerns: While generally secure, electronic signatures are not entirely invulnerable to cyberattacks. Protecting sensitive information associated with the signing process remains a key concern.
- Legal Acceptance and Validation: The legal acceptance and validation of electronic signatures can vary across jurisdictions. Businesses need to be aware of the legal frameworks in place to ensure their use is compliant.
- Digital Literacy Requirements: The use of electronic signatures necessitates a certain level of digital literacy among the signatories. Individuals unfamiliar with digital tools may face challenges in using the system.
- Implementation Costs: The initial investment in software and training for electronic signature platforms can be substantial, potentially posing a barrier for smaller businesses.
Comparison to Traditional Handwritten Signatures
Electronic signatures differ significantly from handwritten signatures in terms of their creation, validation, and legal implications.
Electronic signatures, the proof is undeniably in the process, are becoming increasingly crucial in the digital age. The recent cancellation of COMDEX, a pivotal event in the tech world, marks a significant turning point, perhaps signaling the end of an era in physical tech gatherings. comdex cancellation marks end of era shows how technology has changed our interaction and transactions, yet the proof of secure digital transactions remains in the process itself, with electronic signatures playing a critical role in this transition.
- Creation Process: Handwritten signatures involve physically signing a document, while electronic signatures use digital methods like typing a name or using a stylus.
- Validation Methods: Traditional signatures rely on visual inspection, while electronic signatures employ cryptographic techniques for authentication and validation.
- Legal Status: Electronic signatures have established legal frameworks and validation processes, with many jurisdictions recognizing their validity in legal documents, similar to handwritten signatures.
Impact on Efficiency and Cost-Effectiveness
Electronic signatures demonstrably impact efficiency and cost-effectiveness in various ways.
Electronic signatures – the proof is undeniably in the process. Think about how much easier it is to verify a digital signature compared to a handwritten one, especially in the face of increasing digital communication. This is especially crucial in today’s world, where spam wars fighting the mass mail onslaught like this one are a constant battle.
Ultimately, robust electronic signature methods are key to building trust and security in online transactions, a necessity for the future of digital interactions.
- Efficiency Enhancement: The streamlined workflow associated with electronic signatures significantly reduces turnaround time for transactions, allowing businesses to operate more efficiently.
- Cost Reduction: The elimination of printing, postage, and physical document handling translates into substantial cost savings for businesses.
Summary Table
| Context | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Business Transactions | Increased speed, reduced costs, enhanced security | Potential technical issues, legal acceptance variations |
| Real Estate | Faster closing, reduced paperwork, enhanced security | Legal compliance requirements, potential digital literacy barriers |
| Healthcare | Streamlined patient consent, improved record-keeping | Security concerns regarding patient data, potential for errors in data entry |
Case Studies and Examples
Electronic signatures have revolutionized document processing, offering speed, security, and efficiency. However, successful implementation requires careful planning, robust security measures, and a clear understanding of legal implications. This section delves into real-world examples, highlighting both successes and challenges to provide a comprehensive perspective.Understanding the practical application of electronic signatures through various case studies is crucial. These examples demonstrate the diverse use cases and potential pitfalls, providing valuable lessons for organizations considering adopting this technology.
Successful Electronic Signature Implementation
A leading real estate company successfully transitioned to electronic signatures for all property transactions. This streamlined the closing process, reducing the time to complete deals by an average of 25%. Improved communication and transparency were significant benefits, with all parties having access to the documents and signing process online. Reduced paper usage and associated costs were also notable achievements.
The company implemented a secure platform with multi-factor authentication and robust audit trails, which contributed significantly to the success of the project.
Electronic Signature Deployment Challenges
A small business using an open-source e-signature platform encountered significant security breaches. The platform lacked sufficient encryption and security protocols. This led to the compromise of sensitive customer data, including personal information and financial details. The incident resulted in substantial financial losses, reputational damage, and legal ramifications. This underscores the importance of selecting and implementing robust, vendor-vetted electronic signature solutions, emphasizing secure infrastructure and regular security audits.
Secure Storage of Electronic Signatures
A healthcare provider implemented an electronic signature system for patient consent forms. They chose a solution with secure data encryption and access controls. This ensured patient data privacy and compliance with HIPAA regulations. Regular data backups and disaster recovery plans were critical components of their implementation. Their meticulous approach to data security fostered trust and compliance.
Legal Implications of Electronic Signatures
A multinational corporation encountered legal challenges when implementing an electronic signature solution across various jurisdictions. They needed to ensure compliance with differing regulations and laws. The company consulted legal experts to create a clear and comprehensive legal framework to support the adoption of electronic signatures across its international operations. The use of legally recognized electronic signature methods and robust audit trails ensured compliance with international regulations and local laws.
Summary Table of Case Studies
| Case Study | Key Takeaway | Lesson Learned |
|---|---|---|
| Real Estate Company | Streamlined closing process, reduced processing time. | Robust security and platform selection are critical. |
| Small Business | Security breaches compromised sensitive data. | Prioritize security protocols and vendor vetting. |
| Healthcare Provider | Secure storage and HIPAA compliance. | Data security is paramount, especially in sensitive industries. |
| Multinational Corporation | Legal challenges due to varying regulations. | Comprehensive legal framework and expert consultation are essential for international implementations. |
Future Trends and Innovations
The electronic signature landscape is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements and the need for more efficient, secure, and accessible solutions. Emerging technologies are poised to revolutionize how we sign documents, impacting everything from personal transactions to global business agreements. This section explores the future of electronic signatures, highlighting the role of blockchain, AI, and other innovations in shaping this evolving field.
The Role of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology, renowned for its immutability and transparency, offers a compelling solution for enhancing electronic signature security. By recording every transaction on a distributed ledger, blockchain ensures the integrity and authenticity of signed documents. This decentralized approach significantly reduces the risk of fraud and tampering. Each transaction is cryptographically linked to the previous one, creating an unalterable audit trail.
This verifiable record provides a strong foundation for dispute resolution and legal validity. The use of blockchain can potentially eliminate the need for intermediaries, streamlining the process and reducing costs.
The Potential of Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is poised to transform electronic signature processes in several ways. AI-powered systems can automate tasks like document preparation, verification, and signature validation, significantly improving efficiency and reducing processing time. AI algorithms can analyze data to identify potential risks and fraud, ensuring the security of the entire process. For instance, AI can be used to identify inconsistencies in the user’s behavior or data that could indicate malicious activity.
These systems can then alert authorities to potential fraud, enhancing security and safeguarding against unauthorized access.
Impact of New Technologies
New technologies are reshaping the electronic signature landscape, creating more user-friendly and accessible solutions. The rise of mobile devices, for example, has led to the development of mobile-first electronic signature platforms. These platforms enable users to sign documents from anywhere, anytime, revolutionizing remote work and global collaborations. The integration of biometric authentication, using unique biological characteristics like fingerprints or facial recognition, further strengthens the security of electronic signatures.
These methods can offer a higher level of verification compared to traditional password-based systems.
Future Trends and Innovations in Electronic Signatures
| Trend | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| AI-powered Fraud Detection | AI algorithms analyze data and user behavior to identify potential fraud. | Enhanced security, reduced risk of fraud, and improved user experience. |
| Blockchain Integration | Blockchain technology ensures the immutability and transparency of electronic signatures. | Increased security, improved trust, and enhanced legal validity. |
| Biometric Authentication | Biometric data (e.g., fingerprints, facial recognition) are used to verify identities. | Enhanced security, reduced risk of impersonation, and improved user experience. |
| Mobile-First Platforms | Electronic signature platforms are optimized for mobile devices. | Increased accessibility, convenience, and efficiency for remote work and global collaborations. |
| Integration with IoT Devices | Electronic signatures can be integrated with Internet of Things (IoT) devices, streamlining processes. | Automation of processes and enhanced efficiency in various industries. |
Illustrative Examples of Documents
Electronic signatures have revolutionized the way we interact with documents, offering a secure and efficient alternative to traditional paper-based methods. This section delves into practical examples of documents that benefit from electronic signature implementation, showcasing their diverse applications and the critical role of structure in ensuring validity and integrity.Implementing electronic signatures across various document types requires careful consideration of format and structure to maintain the legal validity and security of the process.
This involves not only the signature itself but also the surrounding metadata and document elements.
Examples of Electronic Signature-Enabled Documents
Electronic signatures can be applied to a wide array of documents, streamlining processes in diverse industries. The format and structure of these documents are crucial to ensure the integrity of the signed document.
- Contracts: Contracts, including employment agreements, sales contracts, and lease agreements, are frequently signed electronically. The contract’s structure typically includes clauses outlining the agreement’s terms, conditions, and obligations of each party. Electronic signatures are applied to the entire contract document, ensuring all parties are bound by the agreement’s terms. The digital format of the contract allows for easy storage, retrieval, and comparison with prior versions.
- Financial Documents: Invoices, receipts, and bank statements can be signed electronically to verify transactions and record ownership. The structure of these documents typically includes the date, amount, description of goods or services, and relevant identification information. Electronic signatures provide an audit trail, allowing for transparent tracking of financial transactions. These documents frequently include digital checksums or hashes to confirm data integrity.
- Legal Documents: Agreements and legal contracts, including wills and powers of attorney, require meticulous attention to detail when implementing electronic signatures. The structure must clearly identify the parties involved, their respective roles, and the specific provisions of the agreement. The inclusion of a clear audit trail is essential to demonstrate the authenticity and validity of the electronic signature.
- Government Forms: Applications for permits, licenses, and other government services can be processed electronically. The structure of these forms typically includes sections for personal information, details of the requested service, and necessary supporting documentation. Electronic signatures are used to validate the applicant’s identity and to record their consent to the terms and conditions.
Elements of a Well-Structured Electronic Document for Signature
A well-structured electronic document for signature requires specific elements to ensure its integrity and enforceability.
- Clear Identification of Parties: The document must unambiguously identify all parties involved, including their names, addresses, and relevant identification information.
- Explicit Statement of Agreement: The document should clearly state the agreement or consent being sought, ensuring all parties understand their obligations and responsibilities.
- Detailed Description of the Transaction: For financial or commercial documents, a precise description of the transaction, including amounts, goods/services, and dates, is essential.
- Integration of Metadata: Metadata, such as the date and time of signature, the location of the signing, and the identity of the signatory, should be incorporated into the document.
Implementing Electronic Signatures in Various Document Types
Implementing electronic signatures in various document types requires specific considerations to ensure compliance with legal requirements and maintain document integrity.
- Contracts: Contracts often involve multiple parties and complex terms. Using a dedicated e-signature platform allows for secure collection of signatures from all involved parties and records the process transparently.
- Financial Documents: Secure platforms can integrate with financial systems, automating the process of digitally signing invoices, receipts, and other financial transactions.
- Legal Documents: Secure digital platforms and advanced authentication methods are necessary to validate the identity of parties signing sensitive legal documents.
- Government Forms: Government agencies often utilize specialized platforms for accepting electronic signatures on applications and forms, ensuring secure handling of sensitive data.
Table of Document Types and Electronic Signature Methods
This table summarizes different document types and the corresponding electronic signature methods used.
| Document Type | Electronic Signature Method |
|---|---|
| Contracts | Digital signature, e-signature platform |
| Financial Documents | Digital signature, secure online banking platforms |
| Legal Documents | Qualified electronic signature, digital notary services |
| Government Forms | Government-approved e-signature solutions, secure online portals |
Final Wrap-Up
In conclusion, electronic signatures the proof is in the process, offer a powerful and evolving solution for a wide range of applications. While they present significant advantages in terms of efficiency and cost savings, understanding the potential security risks and adhering to legal frameworks is crucial. The future of electronic signatures is bright, with emerging technologies like blockchain and AI promising even more robust and innovative solutions.
The ongoing evolution of this technology necessitates continuous learning and adaptation, allowing us to leverage its full potential.