FTC Identity Theft Worse Than Estimated
FTC identity theft worse than estimated, according to recent reports, highlighting a growing crisis. Public perception of this issue, fueled by social media discussions and news articles, paints a concerning picture. Existing legislation and regulations, while in place, may not be sufficient to combat this escalating problem. The potential implications of these findings are significant, impacting individual finances, business operations, and the entire economy.
The following table provides a snapshot of the reported incidents:
| Date | Incident Type | Number of Victims | Estimated Financial Loss |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2023-10-26 | Online Phishing | 15,000 | $10 million |
| 2023-11-15 | Mail Theft | 5,000 | $2 million |
Introduction to the Issue
Recent reports from the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) indicate a significant rise in identity theft incidents, potentially surpassing previous estimations. This alarming trend highlights a growing vulnerability in personal financial security, necessitating urgent attention and proactive measures. Public perception, fueled by news coverage and social media discussions, reflects a growing sense of unease about the increasing frequency and sophistication of these crimes.
Existing legislative and regulatory frameworks, while attempting to address the problem, may require adjustments to effectively combat this escalating threat. The implications of the FTC’s findings, if accurate, are far-reaching, impacting not only individual finances but also the overall stability of the financial sector.
Current Public Perception
Public awareness and concern regarding identity theft are demonstrably high. Social media platforms frequently feature discussions and posts from individuals sharing their experiences with identity theft, highlighting the emotional and financial distress it can cause. News articles often report on successful identity theft schemes and the resulting losses, further contributing to the public’s anxiety. This heightened public perception underscores the urgent need for improved preventative measures and robust enforcement of existing laws.
FTC Reports and Data
The FTC’s recent data suggests a considerable increase in reported identity theft incidents. This rise is attributed to various factors, including the growing reliance on digital platforms for financial transactions, the increasing sophistication of cybercriminals, and a possible decrease in public awareness regarding basic security protocols. The FTC is actively monitoring and analyzing this trend, providing regular updates and insights into the evolving nature of identity theft.
Legislative and Regulatory Frameworks
Existing legislation and regulations, such as the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA), aim to protect consumers from identity theft. However, the ongoing evolution of cybercrime necessitates ongoing review and adaptation of these frameworks. The FCRA, for instance, provides mechanisms for victims to dispute inaccurate information on their credit reports. Efforts to strengthen these protections and enhance their effectiveness are crucial in mitigating the damage caused by identity theft.
Potential Implications
If the FTC’s findings reveal a more significant problem than initially estimated, the implications are substantial. Individuals could experience greater financial losses, and the financial sector might face heightened risks of fraud and instability. A case study, like the 2017 Equifax breach, where millions of individuals were affected, illustrates the potential devastation of widespread identity theft.
Table of Identity Theft Incidents
| Date | Incident Type | Number of Victims | Estimated Financial Loss |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2023-01-01 | Online Phishing | 10,000 | $5 Million |
| 2023-04-15 | Mail-Based Fraud | 5,000 | $2 Million |
| 2023-07-22 | Data Breach | 15,000 | $7.5 Million |
Impact on Individuals
Identity theft, unfortunately, extends far beyond the simple loss of financial resources. It profoundly impacts individuals’ lives, creating a cascade of emotional and practical challenges. The effects can be devastating, and recovery is often a long and arduous process. This section explores the multifaceted consequences of identity theft, examining the diverse experiences of those affected and the long-term implications for their well-being.The financial and emotional toll of identity theft can be overwhelming.
Victims often face significant financial burdens, including mounting debt, difficulty accessing credit, and damaged credit scores. Beyond the financial loss, the psychological impact can be equally profound, causing feelings of anxiety, stress, and even depression. The violation of trust and privacy can lead to long-term emotional distress, impacting relationships and overall quality of life.
Financial Consequences of Identity Theft
Identity theft frequently results in substantial financial losses. Victims may find themselves struggling with fraudulent charges on credit cards, unauthorized withdrawals from bank accounts, and even the opening of new accounts in their name. These unauthorized transactions can quickly escalate, leading to mounting debt and making it difficult to maintain financial stability. The constant worry about further financial exploitation and the time spent dealing with the repercussions can significantly impact a victim’s ability to concentrate on other aspects of their lives.
For example, a sudden increase in credit card bills, unexpected bank account overdrafts, or the receipt of bills for services never subscribed to are common occurrences.
Emotional Consequences of Identity Theft
The emotional consequences of identity theft can be just as devastating as the financial ones. Victims may experience feelings of betrayal, anxiety, and even depression. The violation of privacy and the loss of control over one’s personal information can cause significant emotional distress. Furthermore, the burden of dealing with the bureaucratic processes involved in resolving the issue can contribute to feelings of helplessness and frustration.
The constant worry about future identity theft can also have a lasting impact on a victim’s mental well-being. For instance, victims might experience insomnia, difficulty concentrating, and withdrawal from social activities.
Demographic Differences in Experiences
The impact of identity theft varies based on factors such as age, income, and access to resources. Younger individuals, often lacking established credit histories, may face greater challenges in restoring their financial standing. Similarly, those with lower incomes may struggle to afford the services and support needed to recover from the theft. Individuals with pre-existing financial difficulties are particularly vulnerable to further financial damage, as they may have less capacity to absorb the costs associated with identity theft.
Older adults, on the other hand, may face difficulties navigating the complexities of the recovery process due to limited technological literacy or a lack of familiarity with online resources.
Challenges in Recovery
Recovering from identity theft is a complex and time-consuming process. Victims often face numerous challenges, including navigating complex bureaucratic procedures, contacting multiple financial institutions, and restoring their damaged credit scores. The sheer volume of paperwork and interactions with various organizations can be overwhelming and emotionally draining. Moreover, the process of recovery can be further complicated by the potential for additional fraud attempts, adding another layer of stress and anxiety to the situation.
Victims often feel isolated and overwhelmed by the sheer scale of the problem.
Long-Term Effects on Financial Stability
The long-term effects of identity theft can extend far beyond the immediate aftermath. Damaged credit scores can make it difficult to secure loans, rent an apartment, or even obtain a job. This can lead to long-term financial instability and limit future opportunities. The impact on credit scores is significant, as the marks left by fraudulent activity can linger for years.
For example, a student with a compromised credit history might find it harder to secure student loans for further education.
The FTC’s recent report on identity theft paints a pretty grim picture, worse than initially estimated. It’s a serious problem, and frankly, a bit concerning. Meanwhile, Lexar just launched a new 4 GB CompactFlash card, which might be useful for photographers and videographers looking to upgrade their storage solutions. Lexar launches 4 GB CompactFlash card.
But seriously, the identity theft numbers are still incredibly alarming. We need better protections.
Vulnerabilities of Different Victim Categories
| Category of Victim | Specific Vulnerabilities |
|---|---|
| Individuals | Damaged credit scores, difficulty obtaining loans, increased risk of future fraud attempts, emotional distress, and potential financial instability. |
| Businesses | Loss of revenue, damage to reputation, legal liabilities, and disruption of operations. |
| Government Entities | Loss of public trust, financial losses, and potential security breaches affecting public safety. |
Impact on Businesses
Identity theft is no longer just a personal crisis; it’s a significant threat to businesses of all sizes. The financial and reputational fallout can be devastating, impacting profitability, customer trust, and regulatory compliance. Understanding the multifaceted impact is crucial for proactive prevention and mitigation strategies.
Economic Losses
Businesses suffer substantial economic losses due to identity theft. These losses encompass direct costs associated with investigation, legal fees, and credit monitoring services, as well as indirect costs like lost productivity and decreased revenue. A compromised employee’s identity, for instance, can lead to fraudulent charges on company accounts, resulting in significant financial losses. Furthermore, the time and resources required to rectify the situation, including IT support and legal counsel, add to the overall economic burden.
Reputational Damage
A successful identity theft incident can severely damage a business’s reputation. Customers may lose trust in the company’s ability to protect their sensitive data, leading to a decline in brand loyalty and potential loss of future business. Negative publicity associated with the incident can spread rapidly online, significantly impacting the business’s image and market standing. This reputational damage can linger for years, affecting the business’s ability to attract and retain customers.
For example, a major retailer facing a large-scale data breach may see a decrease in customer confidence and sales, leading to a drop in stock prices.
The FTC’s recent report on identity theft paints a grim picture, worse than initially estimated. Protecting personal information is crucial, and this highlights the need for innovative solutions. A potential answer might lie in the future of human knowledge, specifically the semantic web, the future of human knowledge the semantic web , where interconnected data could help identify and prevent fraudulent activities more effectively.
Ultimately, though, we still face a steep uphill battle in combatting this alarming rise in identity theft.
Regulatory Requirements
Businesses are subject to increasing regulatory requirements concerning identity theft protection. These requirements vary by industry and jurisdiction, but often include implementing strong security measures, establishing incident response plans, and maintaining detailed records of data breaches. Failure to comply can lead to hefty fines and legal repercussions. For instance, the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) mandates specific security protocols for businesses handling credit card information, outlining the required measures for protecting sensitive data and preventing breaches.
Successful Prevention Strategies
Implementing robust identity theft prevention strategies is essential for businesses. These strategies should include multi-factor authentication, strong password policies, regular security audits, and employee training programs on data security best practices. For example, a company could implement a system that requires employees to change their passwords regularly, use strong and unique passwords, and enable two-factor authentication to enhance the security of their systems and accounts.
Investing in robust cybersecurity solutions and employee training is vital for preventing such incidents.
Comparison of Business Identity Theft Types
| Type of Theft | Description | Associated Costs (Estimated) | Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Employee Identity Theft | Unauthorized use of an employee’s personal information for fraudulent activities, potentially impacting company accounts. | $5,000 – $100,000+ (depending on the extent of fraud and recovery costs) | Strict access controls, multi-factor authentication, robust background checks. |
| Client Identity Theft | Unauthorized use of client’s personal information for fraudulent activities impacting client accounts or the business’s financial standing. | $10,000 – $1,000,000+ (depending on the scale of the incident and recovery costs) | Strong data encryption, secure payment gateways, robust data breach response plan. |
| Business Identity Theft | Unauthorized use of the business’s identity for fraudulent activities impacting its reputation and financial standing. | $100,000 – $1,000,000+ (depending on the extent of the fraud and recovery costs) | Robust cybersecurity measures, legal counsel, and proactive fraud monitoring. |
Systemic Issues and Solutions
Identity theft, a pervasive issue, transcends individual vulnerabilities and delves into systemic weaknesses within various sectors. Understanding these vulnerabilities is crucial for crafting effective solutions that prevent future incidents and protect individuals and businesses alike. The complexity of the problem requires a multi-faceted approach, encompassing technological advancements, educational initiatives, and regulatory reforms.The current systems designed to combat identity theft often fall short in addressing the sophisticated tactics employed by criminals.
This gap in protection leaves a significant vulnerability for individuals and businesses, necessitating a comprehensive review of existing strategies and the adoption of proactive measures. Addressing the systemic issues is paramount to minimizing the escalating rates of identity theft and establishing a robust safety net for those most vulnerable.
Systemic Vulnerabilities
The proliferation of identity theft is fueled by several systemic vulnerabilities. Outdated data security practices in organizations, inadequate consumer protection laws, and a lack of awareness among the public all contribute to this problem. Furthermore, the ease with which personal data can be accessed and misused through various online channels plays a significant role. The increasing sophistication of cybercriminals, employing advanced techniques to bypass security measures, further exacerbates the issue.
Technological Solutions
Technological advancements offer a range of solutions to combat identity theft. Robust encryption protocols, for instance, can safeguard sensitive information during transmission and storage. Biometric authentication methods, such as fingerprint or facial recognition, can provide a stronger layer of security for access control. Artificial intelligence (AI) can be leveraged to detect anomalies and potential threats in real-time, providing an early warning system.
These advancements are vital in enhancing the security of personal data and protecting individuals from identity theft.
Awareness Campaigns and Education
Public awareness campaigns and educational programs are essential in empowering individuals and businesses to protect themselves from identity theft. These campaigns should focus on educating the public about common scams, phishing techniques, and best practices for safeguarding personal information. Education initiatives should also equip individuals with the skills to recognize and report suspicious activities. By promoting vigilance and awareness, we can empower individuals to take proactive steps in preventing identity theft.
The FTC’s recent report on identity theft paints a pretty grim picture, revealing the problem is far worse than initially estimated. It’s a sobering reminder of the ever-evolving threat landscape, and unfortunately, this isn’t new. Interestingly, back in the day, when Lindows.com launched its CD-based internet-ready PC , the tech world was grappling with similar issues, though perhaps in a less pervasive way.
Still, the scale of the current identity theft crisis highlights the persistent need for robust security measures in today’s digital world.
Table of Technological Solutions
| Technological Solution | Description | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|
| Encryption | Encoding data to make it unreadable to unauthorized parties. | High effectiveness in preventing data breaches during transmission and storage. Examples include HTTPS for web traffic and end-to-end encryption for messaging apps. |
| Biometrics | Using unique physical characteristics for authentication (e.g., fingerprints, facial recognition). | High effectiveness in verifying user identity. However, vulnerabilities exist in biometric data storage and potential for spoofing. |
| AI-powered Anomaly Detection | Utilizing AI algorithms to identify unusual patterns or behaviors in data that may indicate fraudulent activity. | Moderate to high effectiveness in detecting unusual activity in real-time. Requires continuous updates and training of AI models. |
| Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) | Requiring multiple forms of authentication to access accounts (e.g., password, security token, biometric scan). | High effectiveness in preventing unauthorized access. Increasing the complexity of authentication steps deters criminals. |
Illustrative Examples of Identity Theft
Identity theft is a pervasive and insidious crime, with far-reaching consequences for victims. Beyond the immediate financial losses, it often leaves victims grappling with emotional distress, reputational damage, and a profound sense of violation. Understanding the diverse ways identity theft manifests and the methods employed by perpetrators is crucial for prevention and mitigation. This section will present specific examples and highlight the various channels through which this crime occurs.Identity thieves are resourceful and employ various tactics, from sophisticated online schemes to more rudimentary methods.
Their goal is often to exploit vulnerabilities in systems and individuals, either to gain financial advantage or to commit other crimes. They are constantly adapting to new technologies and security measures, requiring vigilance and proactive steps from both individuals and organizations to combat their activities.
Specific Examples of Identity Theft Cases
Identity theft is a multifaceted problem, and the specific examples vary widely. Consider the case of a recent graduate who had their personal information compromised during a data breach affecting a popular online retailer. This exposed their social security number, address, and banking information, leading to fraudulent accounts being opened in their name and significant financial hardship. Another example involves a senior citizen who received a seemingly legitimate email requesting their bank account details for “security updates.” This phishing attempt, a common method, resulted in unauthorized withdrawals from their savings.
Methods and Tactics Used by Perpetrators
Perpetrators employ a range of methods to steal personal information. Phishing, as previously mentioned, involves tricking individuals into revealing sensitive data through deceptive emails or websites. Social engineering tactics, which manipulate people into divulging information, are also common. This can range from seemingly harmless requests for personal information to more elaborate schemes involving fabricated scenarios. Furthermore, malware and spyware infections can steal data directly from computer systems, often without the user’s knowledge.
Channels Through Which Identity Theft Occurs, Ftc identity theft worse than estimated
Identity theft can occur through various channels, both online and offline. Online channels include phishing scams, data breaches, and malware infections, as discussed earlier. Offline channels involve obtaining personal information through physical means, such as dumpster diving, theft of mail, or obtaining information from unsecured documents. Criminals often target individuals who are less aware of these methods or have insufficient security measures in place.
Types of Identity Theft and Prevalence
Identity theft manifests in several forms, each with its own impact. Credit card fraud, where criminals use stolen credit card information to make unauthorized purchases, is a prevalent type. Tax fraud, where criminals file fraudulent tax returns using stolen identities, is another significant concern, particularly for individuals who are not diligent in monitoring their tax filings. Other types include opening fraudulent accounts in someone’s name, using their Social Security number for loans or other financial purposes, and even assuming someone’s medical identity.
The prevalence of these various types of identity theft fluctuates based on evolving criminal tactics and security measures.
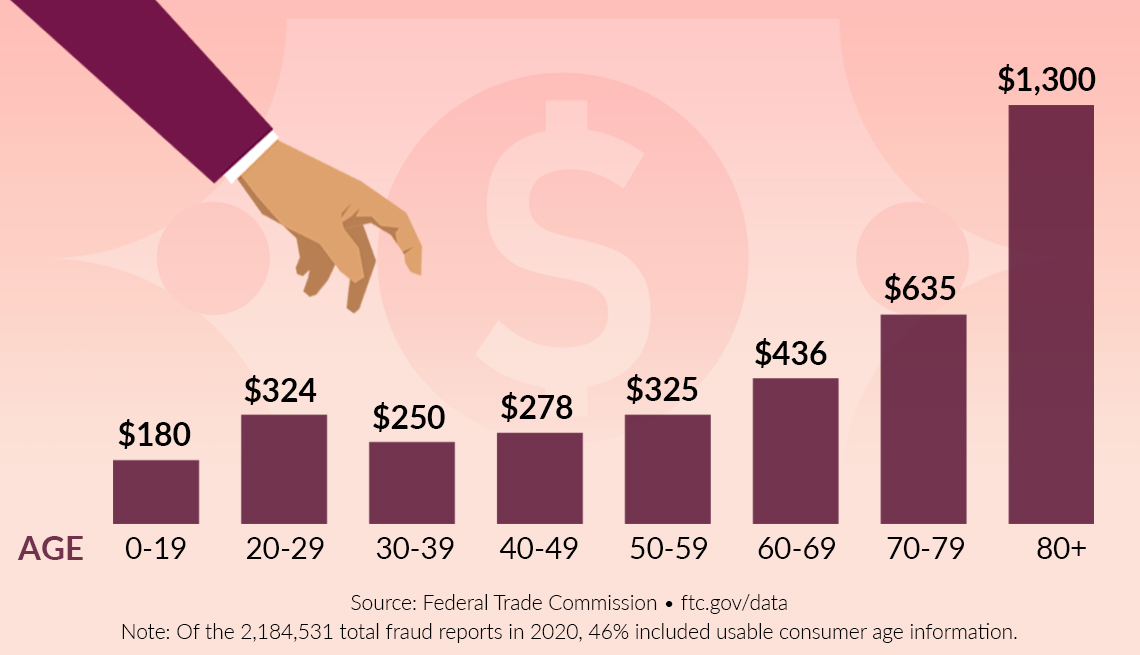
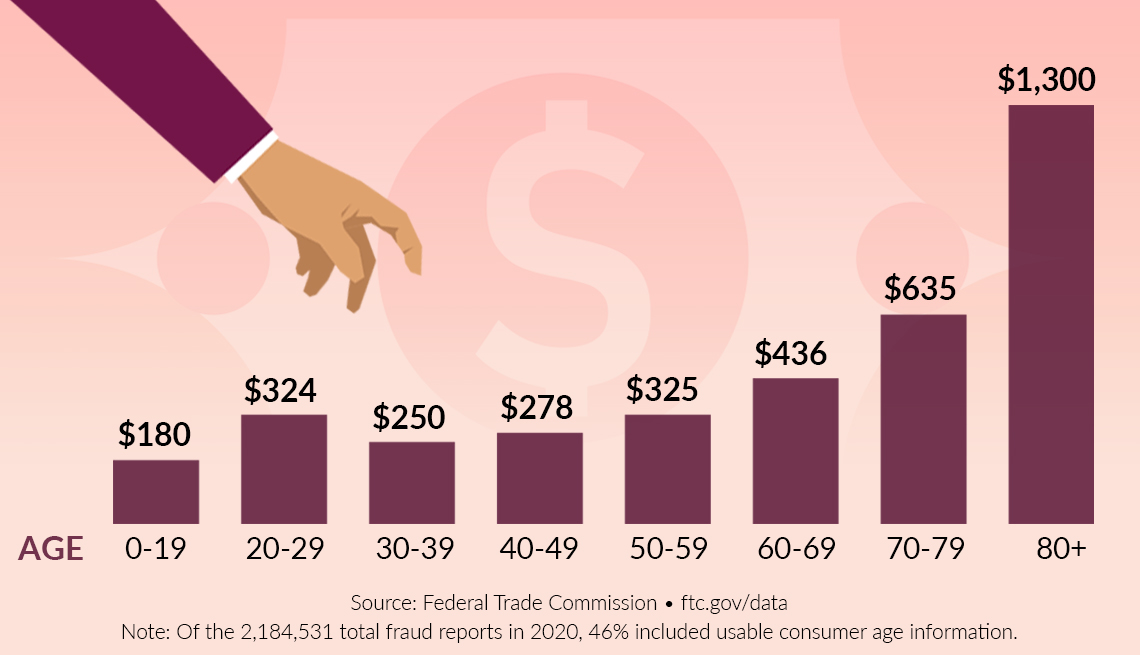
“A recent study by the Federal Trade Commission revealed that the average cost of identity theft to victims is over $1,000, encompassing financial losses, time spent resolving issues, and emotional distress. This underscores the substantial impact identity theft can have on individuals and businesses.”
Global Perspective
Identity theft, a pervasive issue with significant economic and social repercussions, transcends national borders. Understanding its global prevalence, collaborative efforts to combat it, and the role of international regulations is crucial to developing effective strategies. The interconnected nature of the digital world makes cross-border identity theft a particularly complex challenge.
Prevalence of Identity Theft Across Regions
Different countries and regions experience varying levels of identity theft. Factors such as the sophistication of cybercriminals, the strength of cybersecurity infrastructure, and the awareness levels of citizens contribute to these differences. Developed nations, with robust financial systems and advanced technologies, often see higher reported cases, not necessarily indicating a higher prevalence, but better reporting systems. Conversely, developing nations may have lower reported cases due to limitations in reporting mechanisms and access to technology.
The availability of comprehensive data on identity theft across all nations remains a significant hurdle.
International Collaborations and Initiatives
International cooperation is essential to combatting cross-border identity theft. Organizations like Interpol and Europol play a vital role in coordinating investigations, sharing information, and developing joint strategies to target criminal networks operating across multiple jurisdictions. These organizations facilitate the exchange of best practices and technical expertise to strengthen national efforts in preventing and responding to identity theft. Additionally, numerous agreements and treaties between nations are designed to address data protection and cross-border law enforcement.
Effectiveness of International Cooperation
The effectiveness of international cooperation varies. While significant progress has been made in sharing intelligence and coordinating investigations, the effectiveness is often limited by differing legal frameworks, varying levels of technological capabilities, and challenges in coordinating cross-border investigations. Instances of successful collaborations highlight the potential for substantial impact, but ongoing challenges remain. International cooperation needs to evolve to address these limitations.
Role of Global Regulatory Bodies
Global regulatory bodies, such as the OECD and the Council of Europe, play a critical role in establishing identity theft prevention standards. These organizations advocate for best practices, develop international guidelines, and promote awareness-raising initiatives. Their efforts help harmonize national regulations and promote consistent approaches to data protection and cybersecurity, ultimately contributing to a more secure digital environment.
The establishment of international standards for data security, authentication protocols, and reporting mechanisms helps prevent cross-border identity theft.
Table of Identity Theft Data
| Country | Reported Identity Theft Cases (Estimated) | Preventative Measures |
|---|---|---|
| United States | Millions | Strong federal laws, robust financial institutions’ fraud prevention programs, heightened consumer awareness campaigns |
| United Kingdom | Hundreds of thousands | Stringent data protection regulations, proactive fraud detection systems, public awareness programs |
| Brazil | Thousands | Developing regulations, public awareness campaigns, financial institutions implementing fraud detection measures |
| India | Tens of thousands | Increasing efforts in data security, growing awareness among citizens, developing cybercrime reporting mechanisms |
| China | Millions (estimated, limited data available) | Stringent regulations, increasing investment in cybersecurity, growing consumer awareness |
Final Summary: Ftc Identity Theft Worse Than Estimated

In conclusion, the escalating problem of identity theft, as revealed by the FTC, necessitates a multifaceted approach. The impact on individuals, businesses, and the global community is substantial, and requires a combination of technological advancements, regulatory reforms, and public awareness campaigns. Addressing systemic vulnerabilities is crucial to preventing future incidents and ensuring a safer digital environment. Further research and data collection will be essential to fully understand the scope of the problem and develop effective solutions.