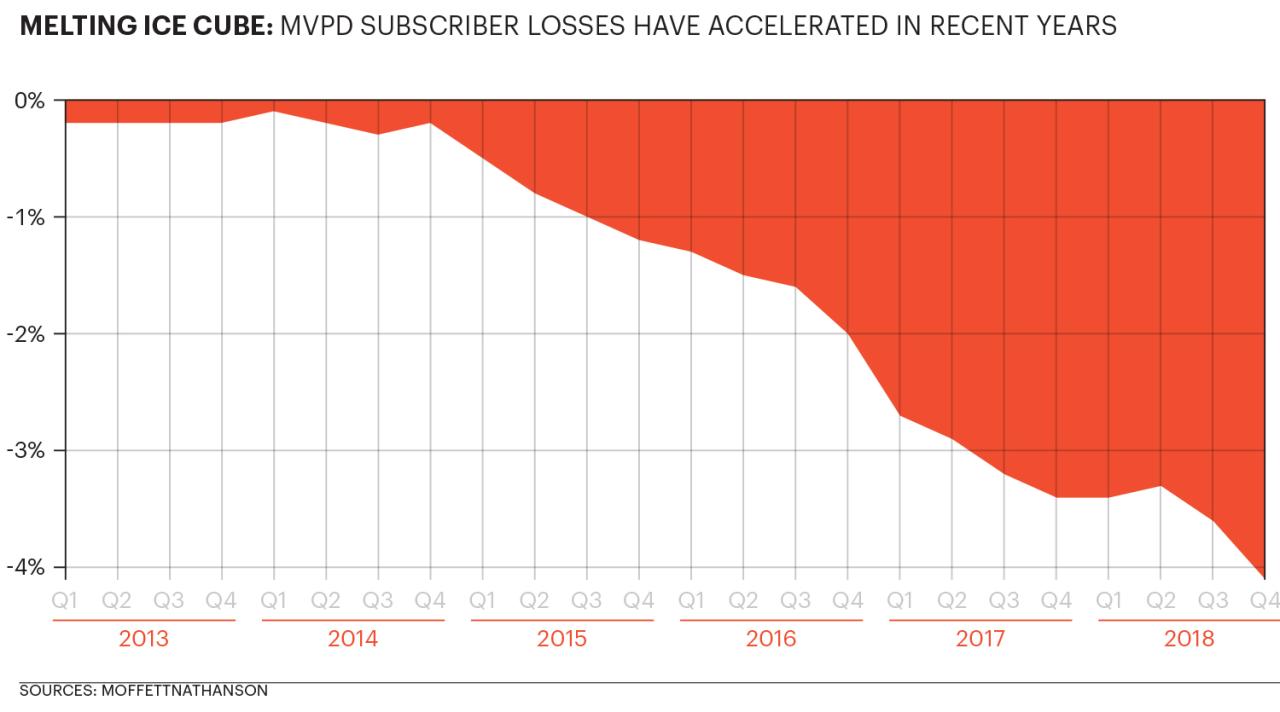
Traditional Telcos Rallying Around Cable Services
Traditional telcos rallying around cable services signals a significant shift in the telecommunications landscape. Once largely separate entities, these historical rivals are now forging alliances, driven by the allure of the cable market. This move isn’t simply opportunistic; it’s a strategic response to the evolving needs of consumers and the competitive pressures of a rapidly changing industry.
This convergence highlights a fascinating interplay of historical context, strategic motivations, and technological advancements. Telcos are adapting their methods and strategies to compete head-on with cable providers, aiming to capture a larger market share. The implications for the cable market, customers, and the future of telecommunications are profound and warrant careful consideration.
Historical Context of Telco Consolidation

The telecommunications industry has undergone a dramatic transformation, moving from a localized, largely government-regulated environment to a globalized, fiercely competitive marketplace. This evolution has been characterized by technological advancements, regulatory shifts, and the emergence of new players, ultimately forcing consolidation and strategic alliances amongst traditional telcos. The rise of cable internet, in particular, has challenged the dominance of established telephone companies, forcing them to adapt and innovate to remain competitive.The initial dominance of traditional telephone companies, often regulated monopolies, was built on a foundation of copper-based infrastructure for voice communication.
These companies, known as telcos, gradually expanded their services to include data transmission, but their focus remained primarily on voice. The landscape began to change dramatically with the advent of fiber optic technology and the rise of the internet. Cable companies, with their existing infrastructure for television broadcasting, recognized the potential of data transmission and rapidly expanded into the broadband market.
Evolution of Traditional Telecom Companies
Traditional telephone companies, initially focused on local service, gradually expanded their networks and services. They invested heavily in copper-based infrastructure, laying the groundwork for a national voice communication network. As the demand for data transmission increased, these companies also offered data services, though often lagging behind emerging technologies. The focus remained primarily on voice, with limited early investments in broadband.
Rise of Cable Internet and Competitive Pressures
The emergence of cable internet provided a significant competitive threat to traditional telcos. Cable companies leveraged their existing infrastructure for television broadcasting and rapidly transitioned into the high-speed data market. This rapid entry into the broadband market, coupled with the allure of faster speeds and bundled services, created a new competitive landscape. Traditional telcos, often hampered by their existing infrastructure and slower adoption of new technologies, faced increasing pressure to improve their services and compete effectively.
Key Dates and Events in Telco Consolidation
The following table Artikels significant dates and events related to the consolidation of telecom services, highlighting the challenges and adaptations faced by traditional telcos in response to the rise of cable internet.
| Date | Event | Impact on Telcos |
|---|---|---|
| 1990s | Early adoption of fiber optics and the rise of the internet | Traditional telcos began to see the potential of data transmission but faced challenges in adapting to the new technology. |
| Early 2000s | Aggressive expansion of cable internet services | Cable companies gained significant market share, offering faster speeds and bundled services. Telcos faced increasing pressure to compete. |
| Mid-2000s | Telcos begin to invest in fiber optic infrastructure | A significant shift to fiber optics to maintain competitiveness with cable. This was often a costly and time-consuming process. |
| Present | Continued consolidation and mergers among telecom providers. | Telcos are focusing on expanding their fiber optic network, developing 5G technology, and partnering with other companies to enhance their offerings. |
Motivations Behind the Rallying
The telecommunications industry is experiencing a fascinating shift. Traditional telcos, once primarily focused on voice and data services, are increasingly eyeing cable infrastructure as a key component of their future strategies. This renewed focus signifies a strategic re-evaluation, driven by a confluence of factors including evolving consumer demands, the potential for revenue diversification, and a recognition of the lucrative opportunities hidden within the cable market.The motivations behind this rallying cry are multifaceted, reflecting a calculated response to changing market dynamics and the desire to secure long-term profitability.
Telcos are actively exploring the synergies between their existing networks and the burgeoning cable sector, recognizing that combined offerings can create new avenues for revenue generation and customer engagement.
Strategic Rationale
Telcos recognize that the cable market, with its inherent potential for high-bandwidth data delivery, offers a compelling opportunity to expand beyond their traditional service offerings. Cable networks, with their infrastructure capable of supporting high-speed internet and video services, provide a significant competitive advantage in a market increasingly demanding these features. This allows them to attract new customers and retain existing ones who demand faster and more reliable connectivity.
The strategic rationale extends beyond mere expansion. Telcos are also seeking to enhance their position as a one-stop shop for all communication needs. By incorporating cable services, they are effectively building a comprehensive suite of offerings that addresses a wider spectrum of consumer demands.
Financial Incentives
The financial incentives driving telcos’ interest in cable are substantial. Expanding into cable allows for diversification of revenue streams, mitigating reliance on potentially declining voice and traditional data services. Increased market share in the cable sector translates directly to higher revenue and potentially increased profits. Moreover, the integration of cable infrastructure with existing networks often yields economies of scale, streamlining operations and further bolstering profitability.
Furthermore, the cable market often boasts high profit margins, particularly in areas with strong demand for high-speed internet.
Perceived Opportunities in the Cable Market
Telcos see a significant opportunity to leverage their existing customer bases and distribution networks to penetrate the cable market more effectively. By offering bundled packages combining their existing services with cable internet and TV, they can create compelling value propositions for consumers. This bundled approach can lead to increased customer retention and acquisition. Moreover, the potential for cross-selling and upselling services is also a major attraction, as telcos can leverage customer data to tailor offers and packages that cater to specific needs.
Comparison of Motivations
While the general motivations are similar across telco companies, variations in their specific approaches exist. Companies with extensive fiber optic networks may focus on leveraging existing infrastructure to provide faster internet speeds. Companies with strong local presence may concentrate on expanding their local cable offerings, capitalizing on existing community relationships. Companies with a more aggressive growth strategy might target underserved areas with bundled packages and attractive pricing plans.
This strategic differentiation underscores the nuanced approach each telco takes to entering the cable market.
Key Financial Metrics and ROI
| Metric | Potential Return (Example) | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Revenue Growth | 15-25% increase in first 3 years | Increased customer base and new services |
| Profit Margin | 7-10% (average) | High-speed internet often generates higher margins |
| Customer Acquisition Cost | Reduced by 10-15% | Leveraging existing customer base |
| Return on Investment (ROI) | 15-20% in 5 years | Integration of existing networks and services |
These figures are estimates and may vary depending on specific market conditions, infrastructure investments, and other factors. Companies with robust existing infrastructure, strong customer bases, and strategic partnerships often achieve better results. For instance, a company that already offers high-speed fiber optic services in a region can use this existing infrastructure to provide a more attractive cable package to their customers.
The combination of existing assets and strategic positioning allows telcos to potentially achieve higher returns on investment compared to companies entering the cable market from scratch.
Methods and Strategies Employed
Telcos, facing the formidable challenge of competing with established cable providers, are employing a multifaceted approach to gain market share and solidify their position in the cable services arena. Their strategies encompass a range of initiatives, from aggressive acquisitions and strategic partnerships to innovative service offerings and substantial network upgrades. This proactive stance reflects a recognition that the cable market isn’t a static entity; it demands adaptability and a willingness to disrupt traditional business models.Telcos are actively seeking to leverage their existing infrastructure and technological expertise to provide compelling alternatives to cable services.
This involves not just matching cable offerings but also emphasizing unique advantages, such as potentially lower costs or more specialized services. Their success hinges on their ability to effectively communicate these value propositions to potential customers.
Acquisition and Partnership Strategies
Telcos are actively pursuing acquisitions of smaller cable companies or related businesses to gain a foothold in the cable market. This strategy allows them to rapidly expand their footprint and access existing customer bases. Further, strategic partnerships with cable providers or other service providers can help to fill gaps in the telco’s offerings and accelerate their entry into the cable market.
Service Offerings
Telcos are enhancing their service portfolios to attract cable customers. This includes bundling their existing offerings (like internet and phone) with cable television services to create attractive packages. Some telcos are even introducing innovative cable TV services, such as streaming integration or specialized channels tailored to niche interests.
Traditional telcos are seemingly scrambling to capitalize on the cable service market. This recent shift, though, might be more about trying to compensate for shrinking profit margins in other areas. A recent online extortion bust, highlighting the difficulties in generating revenue online ( online extortion bust highlights profit problem ), further underscores the pressure on these companies to find new sources of income.
Ultimately, this cable service push could be a smart strategic move for these companies to remain competitive in a rapidly evolving tech landscape.
Network Upgrades and Infrastructure Development
Telcos are investing heavily in network upgrades and infrastructure development. This is crucial to ensure the quality and reliability of their cable services, matching or exceeding the performance of established cable providers. They are aiming to increase bandwidth capacity and improve signal quality to provide a superior viewing experience for customers.
Marketing and Sales Strategies, Traditional telcos rallying around cable services
To effectively penetrate the cable market, telcos are adapting their marketing and sales strategies. This includes focusing on customer segmentation, targeted advertising campaigns, and tailored promotions. Emphasis is placed on demonstrating the value proposition of telco-provided cable services compared to traditional cable options.
Traditional telcos are scrambling to get a foothold in the cable TV market, but is this just a repeat of the past? Think about Roxio or Napster, once titans of the digital age, now mere echoes of their former selves. Is this new cable-centric push just a shadow of a once-promising future, much like whether Roxio or Napster its just a shadow ?
Ultimately, the success of these telcos in the cable arena will depend on their ability to innovate and adapt to the changing landscape of consumer expectations.
Market Penetration Strategies
| Telco | Market Penetration Strategy | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Company A | Aggressive Bundling and Promotions | Offering attractive bundles combining internet, phone, and cable TV services with significant discounts. |
| Company B | Strategic Acquisitions | Acquiring smaller cable companies to rapidly expand their customer base and gain a wider geographic presence. |
| Company C | Focused Niche Services | Developing specialized cable TV channels catering to specific demographics or interests, like sports or educational content. |
| Company D | Infrastructure Upgrading | Investing in high-capacity fiber optic networks to provide superior video quality and faster streaming speeds. |
The table above illustrates a range of market penetration strategies currently employed by various telcos. These strategies reflect a diversified approach to competing in the cable market, focusing on specific strengths and opportunities.
Impact on the Cable Market
The entrance of traditional telecommunications companies (telcos) into the cable market presents a significant shift in the landscape. This foray represents a major strategic realignment, potentially reshaping the competitive dynamics and customer experience within the industry. The implications are multifaceted, encompassing everything from pricing pressures to the potential for innovation and service improvements.Telcos bring a wealth of experience in infrastructure management and network optimization, which they intend to leverage in this new arena.
Their established customer bases and extensive distribution networks could give them a substantial advantage in attracting subscribers and securing market share. This will undoubtedly challenge incumbent cable providers, forcing them to adapt and innovate to maintain their position.
Potential for Increased Competition and Pricing Pressures
Telcos’ entry into the cable market will likely intensify competition. This increased competition will likely put downward pressure on pricing. Cable companies will be compelled to respond to the aggressive pricing strategies employed by telcos to remain competitive. The resulting price wars could impact profitability for all participants. This dynamic is familiar from other sectors; for instance, the entry of discount carriers into the long-distance phone market significantly altered the landscape.
Potential for Innovation and Service Improvements
The presence of telcos may spark innovation in the cable market. Driven by competitive pressures, cable companies might enhance their offerings to meet the challenges posed by telcos’ superior infrastructure and broader service portfolios. This could lead to improvements in internet speeds, increased channel selections, and enhanced customer service. For example, some cable providers might adopt telcos’ fiber optic technologies, potentially offering superior internet speeds and reliability to customers.
Potential Impact on the Customer Experience
The customer experience is a crucial element in the cable market. Telco entry will force cable providers to enhance their customer service initiatives and improve the overall experience. A greater emphasis on customer retention and satisfaction is expected, possibly leading to better customer support and more user-friendly interfaces. This is a key area where the customer experience can be significantly enhanced through competitive pressures.
Contrasting Services and Offerings
| Feature | Existing Cable Companies | Telcos Entering the Market |
|---|---|---|
| Internet Speed | Typically offering speeds from 100 Mbps to 1 Gbps, varying by region and provider. | Potentially offering higher speeds, especially with fiber optic infrastructure, ranging from 1 Gbps to 10 Gbps or higher. |
| TV Services | Bundled TV packages with varying channel selections and DVR options. | Could offer bundled TV packages, but may also emphasize streaming options and on-demand services, leveraging their existing streaming platforms. |
| Phone Services | Limited to traditional landline phone services, often bundled with internet and TV. | Likely to offer a wider range of voice services, including VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) and potentially offering better pricing and broader coverage. |
| Customer Support | Varying levels of customer support, often through phone or online portals. | Likely to leverage their existing support systems, offering broader support options through multiple channels. |
| Pricing | Pricing structures often complex, with varying packages and add-on fees. | Potentially offering simpler, more transparent pricing models, with competitive pricing structures. |
Technological Advancements and Integration: Traditional Telcos Rallying Around Cable Services
The convergence of telecommunications and cable networks is being driven by significant technological advancements. Telcos are actively seeking to integrate cable services into their existing infrastructure, a move fueled by the increasing demand for high-speed internet and the potential for enhanced revenue streams. This integration requires a sophisticated understanding of diverse technologies and a commitment to adapting existing systems.
The evolution of these technologies has profound implications for the future of the communications landscape.The integration of cable services by telcos hinges on several key technological breakthroughs. These advancements enable the delivery of high-bandwidth content and the expansion of service offerings, while simultaneously allowing for a seamless transition from existing infrastructure. This process, while promising, presents both opportunities and challenges.
Addressing these head-on is crucial for success.
Key Technological Advancements
A multitude of technological advancements are facilitating the integration of cable services into telco networks. These advancements are primarily focused on enabling faster speeds, higher capacity, and greater efficiency. Crucially, they aim to leverage existing infrastructure wherever possible, reducing costs and streamlining the transition.
- Fiber Optics: The widespread adoption of fiber optic cables for data transmission has revolutionized the capabilities of both cable and telecommunication networks. Fiber optics offer significantly higher bandwidth compared to traditional copper cables, enabling the delivery of high-definition video, high-speed internet, and other data-intensive services. This increased bandwidth directly translates to improved user experience and more lucrative service offerings.
- Software Defined Networking (SDN): SDN allows for greater control and flexibility in managing network resources. By separating the control plane from the data plane, telcos can dynamically adjust network configurations and optimize resource allocation in response to fluctuating demand. This agility is particularly important in supporting the varying needs of cable services, allowing for efficient allocation of bandwidth and network resources to individual subscribers.
- Network Function Virtualization (NFV): NFV allows telcos to virtualize network functions, reducing the need for expensive and specialized hardware. This virtualization process enables greater flexibility in deploying and scaling network services, thereby facilitating the integration of cable services with existing telecommunications offerings. Telcos can leverage NFV to rapidly adapt to changing market demands, potentially lowering operational costs and improving scalability.
- Advanced Modulation Techniques: Techniques like Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (QAM) are enabling the transmission of more data over existing cable infrastructure. This allows telcos to offer higher speeds and more bandwidth-intensive services, without requiring extensive network upgrades.
Challenges and Opportunities
The integration of cable and telecommunications technologies presents unique challenges. These include the compatibility issues between different network architectures, the need for specialized expertise, and the potential for increased operational complexity. Conversely, this convergence presents immense opportunities for the development of innovative services and the expansion of market share.
Traditional telcos are seemingly shifting their focus back to cable services, potentially as a response to the changing digital landscape. This strategic pivot might be influenced by projects like COLSA’s ambitious undertaking to build an Apple Xserve supercomputer, which hints at the growing demand for robust infrastructure. Ultimately, the trend of telcos returning to cable services might just be a clever way to stay relevant in the face of evolving tech needs.
- Interoperability Issues: Integrating disparate network technologies can lead to compatibility problems. Different protocols and standards may not always work seamlessly together. The challenge is to design systems that can translate and interface between these different systems to ensure a smooth user experience. This interoperability is crucial for delivering a consistent quality of service.
- Integration Complexity: The technical integration of cable and telecommunication networks can be complex. Telcos need to carefully consider how to integrate existing infrastructure with new cable systems, ensuring the smooth operation of both networks. This process demands significant technical expertise and careful planning.
- Skilled Labor Shortages: The demand for skilled personnel capable of designing, implementing, and maintaining integrated cable and telecommunications systems is rising rapidly. This requires a significant investment in training and development to address the shortage of professionals with expertise in this evolving field.
Skills and Training Requirements
The successful integration of cable and telecommunications networks demands a diverse range of technical skills. This includes expertise in network design, implementation, maintenance, and management. It is crucial to address the shortage of skilled labor in this area through targeted training programs and educational initiatives.
| Technological Capability | Description |
|---|---|
| Fiber Optic Installation and Maintenance | Expertise in installing, testing, and maintaining fiber optic cables and related equipment. |
| SDN Configuration and Management | Proficiency in configuring and managing SDN networks, including control plane and data plane management. |
| NFV Deployment and Optimization | Expertise in deploying, managing, and optimizing virtualized network functions. |
| Cable Modem and Network Gateway Maintenance | Troubleshooting and maintaining cable modems and network gateways to ensure optimal performance. |
| Network Security Expertise | Proficiency in network security measures to protect against cyber threats. |
Customer Perspective and Implications
The consolidation of telco and cable services presents a complex picture for consumers. While promising potential benefits, the shift also introduces potential drawbacks that need careful consideration. Understanding these nuances is crucial for consumers to navigate the evolving landscape and make informed choices.
Potential Benefits for Customers
This consolidation can lead to improved service offerings, particularly in areas where traditional telco providers have lagged behind in the digital age. Combining expertise in telephony and cable internet allows for enhanced bundled packages and integrated services, potentially leading to a more seamless user experience. For example, a combined platform might offer a single login for all services, a centralized billing system, and unified customer support channels.
- Improved Service Offerings: Combined platforms can offer more comprehensive services. For instance, a single platform might include internet, television, and phone services, providing a more complete solution than purchasing each service individually.
- Reduced Pricing: Potentially, economies of scale from combining operations could lead to lower prices for customers. Bundled packages can offer competitive pricing compared to purchasing individual services.
- Enhanced Customer Support: A unified customer support system could mean faster resolution times and a more consistent experience across different services. This would be especially helpful for customers who utilize multiple services from the same provider.
Potential Drawbacks for Customers
While the potential benefits are substantial, the consolidation process also carries potential risks for consumers. A lack of competition might lead to less favorable pricing and fewer options. Moreover, the integration process itself could experience hiccups, resulting in service disruptions or reduced reliability. Furthermore, concerns about data privacy and security should be addressed transparently and effectively.
- Reduced Choice and Competition: Consolidation might reduce the number of providers in the market, which could lead to a decrease in options and potentially less competitive pricing.
- Potential for Service Disruptions: The transition period for integrating services from different companies can often be challenging and lead to service interruptions or reduced quality until systems are fully integrated.
- Privacy and Security Concerns: A single provider managing multiple services might raise concerns about data privacy and security. Customers need assurance that their data will be handled responsibly and securely.
Customer Service and Support Comparison
| Feature | Telco Provider | Cable Provider | Potential Consolidated Provider |
|---|---|---|---|
| Service Variety | Limited (primarily voice and internet) | Limited (primarily internet and TV) | Broader (Voice, Internet, TV, etc.) |
| Support Channels | Often limited to phone, email | Often limited to phone, online chat | Potential for multiple channels (phone, chat, online portal) |
| Resolution Time | Can vary significantly | Can vary significantly | Potentially faster, if processes are streamlined |
| Customer Experience | May be less customer-centric | May be less customer-centric | Potential for improved experience with streamlined services |
Consolidated providers should strive to maintain a high level of customer service, including accessible and responsive support channels, to ensure a positive experience.
Future Trends and Predictions
The convergence of telecommunications and cable services is poised for significant evolution. This shift, driven by both technological advancements and market forces, will shape the future of how consumers access and utilize these vital services. Understanding these trends is crucial for stakeholders, from investors to consumers, as they navigate this rapidly changing landscape.
Potential Developments in Technological Integration
The integration of technologies like 5G, fiber optics, and advanced software will continue to redefine the capabilities of cable services. 5G networks, with their increased bandwidth and lower latency, will enable new applications and experiences for consumers. Fiber optic infrastructure will enhance the speed and reliability of data transmission, further improving the quality of service. Sophisticated software will play a critical role in managing complex networks and delivering personalized user experiences.
Key Factors Shaping the Future of Cable Services
Several factors will influence the evolution of cable services in the years ahead. These include advancements in artificial intelligence (AI), the growing demand for high-speed internet and streaming services, and the increasing importance of security and data privacy. The need for faster speeds and higher capacity will continue to drive the adoption of new technologies.
Emerging Technologies and their Impact
Emerging technologies are already impacting the future of telco-cable integration. For instance, the development of virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) technologies will likely lead to a surge in demand for high-bandwidth connectivity. Internet of Things (IoT) devices will require a seamless integration with cable networks, requiring scalable and secure infrastructure. The proliferation of cloud computing services will also increase the reliance on robust and reliable connectivity.
Potential Future Scenarios for the Telecommunications Market
The future of the telecommunications market is multifaceted, and several potential scenarios could unfold. The table below Artikels some of these possibilities, highlighting the impact of key factors on the market.
| Scenario | Driving Factors | Impact on Telcos | Impact on Consumers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scenario 1: Dominant Fiber-Based Infrastructure | Rapid fiber optic deployment, strong consumer demand for high-speed internet | Increased investment in fiber infrastructure, potential consolidation among fiber providers | Faster internet speeds, enhanced video streaming experience, potential for more competitive pricing |
| Scenario 2: Continued Consolidation and Convergence | Telcos acquiring cable companies, strategic partnerships, increasing competition | Formation of larger, more powerful telecommunications companies, potential for economies of scale | Potentially wider range of services and bundled offerings, but also potential for reduced competition and increased pricing |
| Scenario 3: Rise of Niche Players | Focus on specific customer segments, specialized services, innovative business models | Increased competition, development of niche offerings, diversification of services | Greater choice and customization in telecommunications services, potentially more competitive pricing for targeted services |
Concluding Remarks
In conclusion, the rallying of traditional telcos around cable services paints a picture of a dynamic and competitive telecommunications market. This shift promises both challenges and opportunities for all stakeholders. The merging of technologies, the strategic alliances, and the evolving customer expectations all point towards an exciting future for the industry. The impact on consumers, through potentially lower prices and improved services, remains a key aspect to watch.