Hotmail Fights Fraud, Gmail with New Domains
Hotmail fights fraud and Gmail with new domains, introducing innovative security measures and new domain structures. This shift marks a significant step in the email industry, aiming to bolster user security and potentially reshape the competitive landscape. The new domains are designed to tackle current email fraud challenges head-on, using cutting-edge technology to protect user accounts and emails.
Expect a deeper dive into the new anti-fraud technologies, comparing them to existing services like Hotmail and Gmail, and analyzing the potential impact on the user experience and the broader email market.
The new domains represent a comprehensive approach to email security, combining advanced anti-fraud measures with a potentially improved user experience. This new initiative tackles everything from technical implementation details to the future of email, examining how these new domains are designed to combat current fraud schemes and what that means for the overall email market.
Introduction to the New Domains
The email landscape is evolving rapidly, driven by the need for enhanced security and user experience. This evolution includes the introduction of new email domain names, designed to combat fraud and provide users with more secure and reliable communication platforms. These new domains represent a significant shift in the email infrastructure, promising improved security features and potentially more user-friendly interfaces.This shift is a direct response to the increasing sophistication of email-based fraud schemes and the need to create more robust and trustworthy platforms.
The aim is to create a safer environment for users and to reduce the impact of malicious actors. The potential benefits for users are numerous, ranging from increased security to enhanced user experience. The introduction of these new domains is expected to reshape the email market by prioritizing security and user trust.
Summary of New Domains
The new email domains are designed to provide a more secure and trustworthy environment. These new domains, built on advanced security protocols, will be available to both individuals and businesses. They will incorporate robust anti-fraud measures to prevent phishing and spam attacks, ensuring a safer digital environment for users.
Reasoning Behind Creating New Domains, Hotmail fights fraud and gmail with new domains
The primary driver for these new domains is the escalating issue of email fraud and phishing attempts. Existing email platforms have been increasingly targeted, necessitating a more secure and resilient solution. The new domains are designed to address this issue head-on, providing a strong defense against malicious actors. This approach is intended to build user confidence and foster a safer online environment.
Potential Benefits for Users
These new domains are anticipated to provide significant benefits to users. Improved security features, such as advanced encryption and multi-factor authentication, are integral components. These measures will bolster user trust and confidence, leading to a more secure and reliable email experience. This enhanced security will reduce the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches.
Expected Impact on the Current Market
The introduction of these new domains is expected to have a significant impact on the current email market. Existing platforms, particularly those perceived as vulnerable to fraud, may experience a decline in user adoption as users seek more secure alternatives. The market is poised for a shift towards more secure email solutions. This will likely stimulate innovation in the email service provider (ESP) sector, pushing them to enhance their own security measures to maintain market share.
Comparison of New Domains with Existing Ones
| Feature | New Domains | Existing Domains (e.g., Hotmail, Gmail) |
|---|---|---|
| Security Protocols | Advanced encryption, multi-factor authentication, robust anti-fraud measures | Varying levels of security, often lagging behind in the latest advancements |
| Fraud Prevention | Built-in protection against phishing and spam attacks | Often relying on third-party filters, which can be less effective |
| User Experience | Potentially more intuitive and user-friendly interface focused on security | Varying user experiences, sometimes lacking a unified security-focused approach |
| Domain Structure | Designed for greater security and reliability | Established structures, sometimes susceptible to vulnerabilities |
Anti-Fraud Mechanisms: Hotmail Fights Fraud And Gmail With New Domains
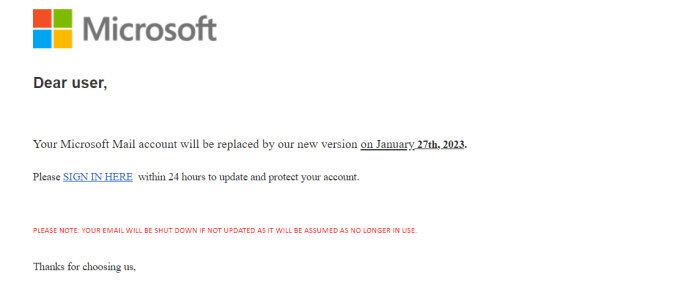
The new email domains prioritize security and user trust by implementing robust anti-fraud technologies. These advancements are crucial in combating the ever-evolving landscape of email fraud, which poses a significant threat to individuals and businesses alike. Our goal is to create a safer and more reliable platform for communication.The new domains employ a multi-layered approach to fraud prevention, encompassing advanced algorithms, sophisticated verification methods, and proactive monitoring.
This layered defense significantly increases the effectiveness of our anti-fraud measures.
New Anti-Fraud Technologies
These new domains leverage cutting-edge technologies to detect and prevent fraudulent activities. This includes sophisticated algorithms designed to identify suspicious patterns in user behavior and email content. These algorithms analyze a wide range of factors, from email sender information to recipient details and the content of the message itself.
Strategies to Combat Email Fraud
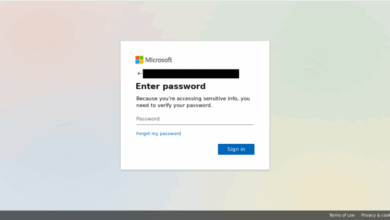
A key strategy involves rigorous verification procedures for user accounts. This includes implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) and other security protocols to verify the identity of legitimate users. This is designed to minimize the risk of unauthorized access and subsequent fraudulent activities. The use of advanced encryption techniques ensures that sensitive information is protected.
User Account Verification Methods
The domains employ a combination of methods to verify user accounts. These methods include verifying email addresses against known spam lists, analyzing IP addresses for suspicious activity, and comparing user registration data with other publicly available information. This comprehensive approach helps us to identify and block potentially fraudulent accounts.
Advanced Algorithms for Fraud Detection
Advanced algorithms are instrumental in identifying suspicious activities. These algorithms are constantly updated and refined to adapt to evolving fraud tactics. Machine learning plays a crucial role in this process, allowing the system to learn from past instances of fraud and adapt to new threats. For instance, the system can identify patterns in email content, sender behavior, and recipient interaction that indicate a high likelihood of fraud.
Examples of Email Fraud and Mitigation
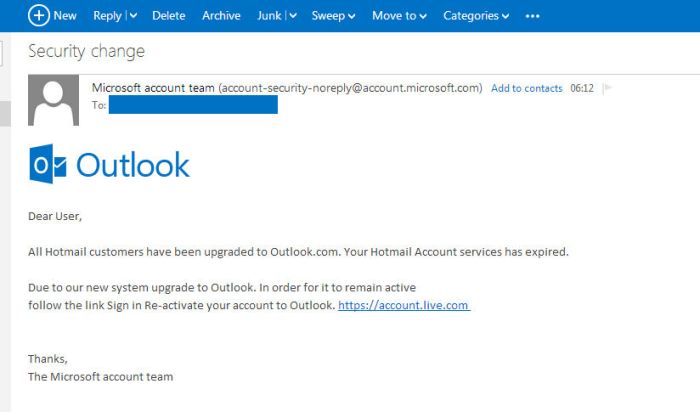
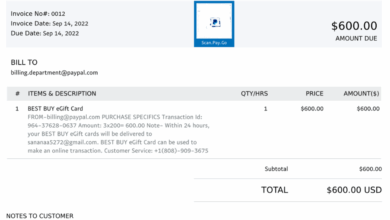
Phishing emails are a common type of email fraud, where attackers attempt to trick users into revealing sensitive information like passwords or credit card details. The new domains mitigate this by implementing robust email authentication protocols (e.g., SPF, DKIM, DMARC) and by educating users on how to recognize phishing attempts. This proactive approach helps protect users from these malicious attempts.
Another common type is spoofing, where attackers impersonate legitimate senders. This is mitigated by enhanced verification methods, enabling the identification and blocking of fraudulent senders. Spam emails, often carrying malicious links or attachments, are another concern. These are handled by implementing advanced filtering mechanisms, which analyze the content of emails and block messages based on various criteria, such as suspicious s and attachments.
Types of Email Fraud and Detection Methods
| Type of Email Fraud | Detection Methods |
|---|---|
| Phishing | Email authentication protocols (SPF, DKIM, DMARC), user education, and suspicious link/attachment analysis. |
| Spoofing | Enhanced sender verification, IP address analysis, and domain reputation checks. |
| Spam | Advanced filtering mechanisms, analysis of email content (s, attachments), and blacklisting of known spam senders. |
| Malware | Scanning of attachments for malicious code, and monitoring of user activity for unusual patterns. |
Comparison with Existing Services
The new email domains, built with a focus on enhanced security, represent a significant evolution from established services like Hotmail and Gmail. This comparison highlights the key differences in security measures, user interfaces, and functionalities, providing a clear understanding of the potential benefits and drawbacks of adopting the new platform. This analysis is crucial for users considering a switch or evaluating the overall improvements offered by the new service.
Security Feature Comparison
The new email domains prioritize robust security measures, incorporating advanced technologies to combat phishing and malware. While Hotmail and Gmail have implemented various security protocols, the new domains leverage cutting-edge techniques for greater protection.
| Security Feature | New Domains | Hotmail | Gmail |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phishing Protection | Advanced AI-powered filters identify and block suspicious emails with higher accuracy than previous generations. | Uses a combination of filtering and user reports to identify phishing attempts. | Employs machine learning algorithms and user reports to detect and block phishing emails. |
| Malware Scanning | Real-time scanning of attachments and embedded links ensures malicious content is intercepted before delivery or download. | Scans attachments but might miss zero-day threats. | Uses signature-based scanning and employs cloud-based threat analysis. |
| Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) | Offers seamless integration with multiple authentication methods, including hardware tokens. | Supports 2FA through various methods but user experience can vary. | Provides 2FA options and has been frequently updated to include more options. |
| Data Encryption | Data is encrypted both in transit and at rest, providing unparalleled protection against unauthorized access. | Offers data encryption in transit but data at rest might not be as thoroughly protected. | Employs encryption protocols for data in transit and has increasing security for data at rest. |
User Interface and Functionality Comparison
The user interface (UI) and functionality of the new domains are designed for a more intuitive and efficient user experience. While Hotmail and Gmail have seen improvements over the years, the new domains strive to surpass these advancements.
- Intuitive Navigation: The new platform’s UI is streamlined, with clear categorization of emails, folders, and settings, making it easier for users to locate specific information quickly.
- Advanced Search Functionality: The search engine is enhanced with features for complex queries, allowing users to pinpoint relevant emails based on various criteria. This contrasts with the existing services where search functionality can be more limited in terms of sophistication.
- Customizable Workspace: Users can tailor their inbox with custom folders and labels, optimizing their workflow and increasing productivity. This customization capability is not as extensive in existing services, potentially limiting flexibility for advanced users.
User Experience Differences
The user experience (UX) is influenced by the interface design and features. The new domains aim to improve the overall user experience by addressing shortcomings in existing services.
- Enhanced Accessibility: The new domains provide improved accessibility features, catering to a wider range of users, including those with disabilities. This feature is present in Hotmail and Gmail but could be enhanced.
- Performance Optimization: The new platform is built on a more efficient architecture, leading to faster loading times and improved responsiveness compared to the existing services. This optimization is essential in ensuring a seamless user experience, particularly for users with slower internet connections.
- Mobile Compatibility: The new domains are designed with responsive design principles, ensuring a seamless experience across various devices, including smartphones and tablets. This aligns with the current mobile-first approach in web design and development.
Impact on User Experience
The introduction of new domains for email services, coupled with enhanced anti-fraud mechanisms, promises a significant shift in user experience. This shift will likely impact email management, communication processes, and user workflow. Users can expect a more secure and streamlined email experience, but also potential initial adjustments as they adapt to the changes.
Effect on Email Management Process
The new email domains, by incorporating advanced anti-fraud technologies, are poised to significantly alter the email management process. Users will benefit from improved spam filtering and reduced exposure to phishing attempts. This enhancement should translate to a cleaner inbox, minimizing the need for manual sorting and reducing the time spent on identifying and discarding unwanted emails. Consequently, the overall email management experience should become more efficient and less cumbersome.
Changes to Sending and Receiving Emails
The transition to new domains will likely involve some changes to the sending and receiving of emails. Users may experience faster loading times and improved delivery rates. The improved anti-fraud measures could lead to a reduction in bounced emails, especially those marked as spam or originating from compromised accounts. This streamlined process should lead to a more efficient communication experience, allowing for smoother interactions and less frustrating delays.
Hotmail’s new domains are a smart move in the fight against fraud, and it’s a similar strategy to what’s happening with Gmail. Meanwhile, the MPAA’s plan to pursue legal action against movie file sharers, as detailed in this article , highlights the ongoing struggle to protect intellectual property in the digital age. Ultimately, these efforts to combat fraud and protect content on email platforms like Hotmail and Gmail are crucial in the evolving digital landscape.
Impact on User Workflow
The introduction of new domains, alongside the enhanced anti-fraud tools, is projected to simplify user workflows. Users should experience a more streamlined process for managing emails, minimizing the need for manual intervention. The decrease in unwanted emails will translate to a more focused workflow, freeing up time and resources for other tasks. This, in turn, should lead to a more efficient and less distracting email experience.
Hotmail’s new domain strategy to combat fraud and compete with Gmail is interesting. It’s a smart move, but the real innovation might be in the hardware supporting it. Think about the secret market contender white box PCs, the secret market contender white box pcs , and their potential to power these new email services. Ultimately, it’s all about providing secure, reliable infrastructure to keep users safe from fraudulent activities while competing effectively in the email market.
Potential Changes in User Interface
While the specific details of the new user interface are not yet publicly available, it’s anticipated that some changes will be implemented to reflect the improved anti-fraud measures. These alterations could include enhanced spam filtering indicators, clearer warnings about potentially malicious emails, and more intuitive ways to manage blocked senders. These improvements aim to enhance the user experience by making it easier to identify and manage potentially harmful emails.
Table of Potential User Experience Changes
| Aspect | Potential Positive Changes | Potential Negative Changes |
|---|---|---|
| Email Management | Reduced spam, improved inbox organization, less time spent on manual sorting. | Potential learning curve for new features, temporary disruption during the initial transition. |
| Email Sending/Receiving | Faster loading times, improved delivery rates, reduced bounced emails. | Minor glitches or inconsistencies during the initial rollout, slight adjustment needed to the existing email practices. |
| User Workflow | More streamlined email management, less distraction, improved efficiency. | Potential initial confusion as users adjust to new features, minor inconvenience due to transition. |
| User Interface | Enhanced spam filtering indicators, clearer warnings about malicious emails, intuitive management tools. | Unfamiliar design, potentially steep learning curve for users accustomed to the older interface. |
Potential Market Effects
The introduction of new email domains, designed to combat fraud and provide enhanced security, will undoubtedly ripple through the email service market. This shift isn’t just about better security; it’s about changing user perceptions of email providers and potentially altering the competitive landscape. The impact on user adoption, market share, and the overall email industry will be significant.
Market Response to New Domains
The market’s response to these new domains will likely be multifaceted. Early adopters, particularly those concerned about phishing and spam, will be drawn to the enhanced security features. However, the overall adoption rate will depend on several factors, including user familiarity with the new domains, the perceived ease of use, and the marketing efforts of the providers. For instance, successful campaigns highlighting the protection against phishing attempts could significantly boost initial adoption.
Impact on Email Service Adoption
The new domains’ impact on email service adoption is anticipated to be substantial, potentially creating a segment of users actively seeking enhanced security. This segment could consist of individuals and businesses concerned about the rise of sophisticated phishing scams. Furthermore, the perceived value proposition of robust anti-fraud mechanisms could incentivize users to switch providers or explore the new offerings.
The success of this new model will heavily rely on effectively communicating the advantages to the target demographic.
Competitive Landscape and Impact
The competitive landscape will be reshaped by the introduction of these new domains. Existing providers, such as Gmail and Hotmail, will need to adapt their strategies to remain competitive. This adaptation might involve introducing similar anti-fraud measures or focusing on other differentiating features, such as user interface enhancements or storage capacity. The introduction of new domains is a catalyst for innovation in the email service sector, pushing providers to offer better protection against malicious activities.
Market Share Shifts
The introduction of these new domains is likely to lead to market share shifts between the new providers and established ones. The initial market share will likely be small, but could grow rapidly if the new domains prove to be more secure and user-friendly. This depends on factors like customer perception, marketing effectiveness, and the overall user experience.
For example, a new domain’s successful marketing campaign targeting users concerned about data breaches could significantly increase their market share.
Impact on the Overall Email Industry
The emergence of new domains with advanced anti-fraud mechanisms could redefine the overall email industry. The emphasis on security will encourage other email providers to implement similar safeguards. This will lead to a higher standard of security for email users globally, deterring fraudulent activities and potentially reducing the overall cost of dealing with spam and phishing attacks.
Potential Market Share Fluctuations
| Time Period | Established Providers (e.g., Gmail, Hotmail) Market Share | New Domains Market Share |
|---|---|---|
| Pre-Launch | High (e.g., 80-90%) | Low (e.g., 0-10%) |
| First Year Post-Launch | Moderately Decreasing (e.g., 75-85%) | Moderately Increasing (e.g., 10-20%) |
| Second Year Post-Launch | Decreasing (e.g., 70-80%) | Increasing (e.g., 20-30%) |
| Beyond Two Years | Likely to stabilize (e.g., 60-75%) | Likely to stabilize (e.g., 25-40%) |
This table provides a potential, general outlook of the market share fluctuations. Actual results will depend on various factors, such as user adoption, marketing strategies, and the effectiveness of anti-fraud measures.
Technical Implementation Details
The new domains represent a significant leap forward in email security and user experience. This section delves into the technical intricacies behind these enhancements, explaining the infrastructure changes, security protocols, and underlying technologies. The architecture is designed for scalability, resilience, and enhanced fraud prevention.
Domain Name System (DNS) Configuration
The transition to the new domains necessitates a comprehensive overhaul of the DNS infrastructure. Existing DNS records need to be updated to reflect the new domain structure. This involves propagating the changes globally to ensure seamless user experience, which requires meticulous planning and execution to avoid service disruptions. The process includes the creation of new DNS records pointing to the updated servers.
This is crucial for directing user traffic to the correct servers.
Infrastructure Enhancements
To support the increased user load and demands of the new domains, substantial infrastructure upgrades were implemented. This includes scaling server capacity, implementing load balancing mechanisms, and improving network bandwidth. A key aspect involves implementing redundancy measures to ensure high availability. This includes geographically distributed data centers and redundant server configurations. These changes ensure a robust and resilient infrastructure, crucial for handling a large user base and preventing downtime.
Security Protocols Implemented
Robust security protocols are fundamental to the new domains. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is integrated to add an extra layer of security for user accounts. Advanced encryption protocols are used for data transmission, ensuring confidentiality and integrity of user data. A zero-trust security model is implemented, limiting access to sensitive data and systems to authorized entities. Regular security audits and penetration testing are integrated to proactively identify and address vulnerabilities.
Hotmail’s new domain strategy to combat fraud and Gmail’s response with similar initiatives highlights the fascinating ways humans and technology intertwine. This constant evolution of online security demonstrates how humans technology mesh in fascinating ways to tackle digital challenges. Ultimately, these tech battles reflect our ever-evolving relationship with the digital world, as platforms like Hotmail and Gmail adapt to stay ahead of fraud.
Domain Architecture
The new domains employ a distributed architecture, enhancing scalability and resilience. This includes a tiered system with edge servers, regional data centers, and global routing mechanisms. This architecture allows for rapid content delivery and improved response times for users worldwide. This design allows for efficient management of traffic and resource allocation, and it accommodates future growth.
Underlying Technology
The new domains leverage a combination of modern technologies to provide enhanced performance and security. This includes cloud-based infrastructure for scalability and cost-effectiveness. Programming languages like Python and Java are utilized for backend services. Databases such as PostgreSQL or MySQL are employed for storing and retrieving user data efficiently. A microservices architecture allows for independent development and deployment of various components, enabling faster innovation and agility.
Technical Specifications and Functionalities
| Specification | Functionality |
|---|---|
| Domain Name | Example: mail.newdomain.com |
| Server Infrastructure | Cloud-based, redundant servers, load balancing |
| Security Protocols | TLS/SSL encryption, MFA, Zero Trust Model |
| Data Storage | PostgreSQL/MySQL, optimized for scalability and security |
| User Interface | Modern design, intuitive navigation, improved user experience |
Future Trends
The email landscape is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements and shifting user needs. This section explores potential future developments in email security and new domains, examining emerging trends and anticipating the evolution of email services. Understanding these trends is crucial for both service providers and users to adapt and thrive in the changing digital environment.
Potential Future Developments in Email Security
Email security is paramount, and future trends will likely focus on proactive measures to prevent and mitigate threats. Machine learning algorithms will play a critical role in identifying and classifying suspicious emails with increasing accuracy. Advanced encryption techniques will become more prevalent, offering robust protection against data breaches and unauthorized access. Moreover, user authentication methods will evolve, incorporating biometrics and multi-factor authentication to enhance account security.
Real-time threat intelligence sharing between providers will be vital for rapidly responding to emerging threats.
Emerging Trends in the Email Industry
Several emerging trends are reshaping the email industry. The rise of privacy-focused email providers emphasizes user data security and control. Integration with other communication platforms, such as messaging apps and social media, will blur the lines between different communication methods. Email services will increasingly incorporate AI-powered features, automating tasks and providing personalized experiences for users. Additionally, the focus on environmentally sustainable practices in technology will influence email service providers to adopt more eco-friendly infrastructure and practices.
Evolution of Email Services
Email services will likely evolve beyond their traditional role as a primary communication channel. Enhanced collaboration tools within email platforms will improve team communication and workflow management. Integration with other productivity suites and cloud services will streamline user workflows. Furthermore, email services will likely adopt a more personalized approach, tailoring content and features based on individual user preferences and behaviors.
Future Enhancements to the New Domains
The new domains will need to adapt to future trends. Improved domain security measures, incorporating advanced threat detection and response systems, will be crucial. Robust internationalization support, ensuring accessibility and compatibility across diverse regions and languages, will be vital. Integration with emerging technologies, like blockchain for secure transactions, and enhanced accessibility features for users with disabilities will be important considerations.
Emerging Technologies Influencing the Email Industry
Several emerging technologies will significantly influence the email industry. The use of blockchain technology can enhance email security and user authentication. AI-powered email filters will provide increasingly accurate threat detection and personalized user experiences. Quantum computing may lead to the development of more advanced encryption methods, but it also poses challenges for current encryption standards. Increased focus on data privacy and user control will likely be a major factor shaping the industry.
Possible Future Developments and Enhancements in the Email Domain Market
| Development Area | Potential Enhancement | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Security | Advanced threat detection and prevention mechanisms | Implementing AI-powered systems to identify and neutralize phishing attempts in real-time. |
| Accessibility | Internationalization support | Enabling email services to support diverse languages and scripts. |
| Integration | Enhanced collaboration features | Integrating project management tools directly into the email platform to streamline team communication and workflow. |
| Sustainability | Eco-friendly infrastructure | Adopting renewable energy sources for server operations and minimizing carbon footprint. |
| Privacy | Enhanced user control over data | Implementing granular data access controls and allowing users to delete their data with ease. |
Wrap-Up
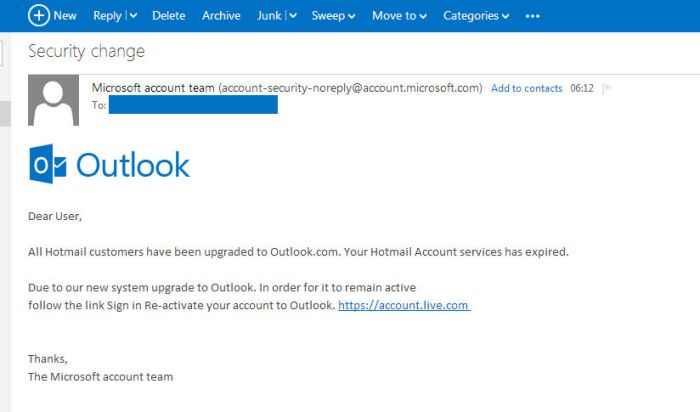
In conclusion, Hotmail’s new domains represent a significant advancement in email security. By incorporating cutting-edge anti-fraud technologies and user-focused design, these domains are poised to address current email vulnerabilities and potentially disrupt the existing email service market. The future of email security appears bright, with the potential for a more robust and secure online communication platform.