Award of Email Patent to Microsoft Questioned
Award of e mail related patent to microsoft questioned – Award of email-related patent to Microsoft questioned sets the stage for an intriguing investigation into the validity of a crucial piece of digital infrastructure. This examination delves into the historical context, the legal arguments, and potential repercussions for Microsoft, inventors, and the broader email technology sector. The questioning of the patent raises critical questions about intellectual property rights and the ever-evolving landscape of digital communication.
The patent, granted to Microsoft, claims innovations in email technology, potentially impacting how we send and receive emails. The questioning of this award suggests that the patent’s claims might not hold up under scrutiny. This opens the door to a detailed analysis of the arguments presented, the historical background of the patent, and the potential effects of a revocation on various parties involved.
Background of the Email-Related Patent Awarded to Microsoft
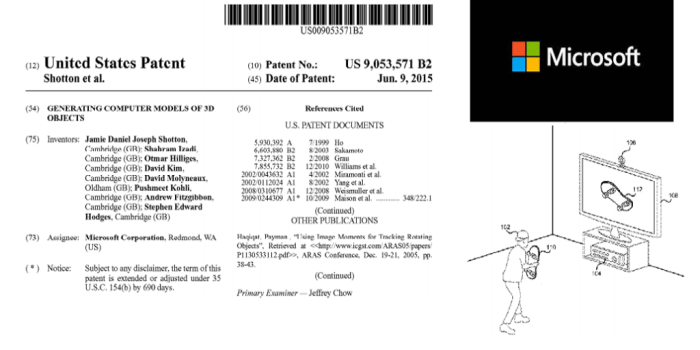
This patent, granted to Microsoft, revolves around a crucial aspect of modern communication: email management and delivery. The innovation lies in streamlining the process, offering significant improvements in efficiency and user experience. Understanding the historical context, technological advancements, and motivations behind this patent sheds light on its overall significance.
Patent’s Historical Development
The patent’s journey reflects a progression in email technology. Early email systems were rudimentary, often plagued by issues like slow transmission speeds and unreliable delivery mechanisms. The evolution toward more robust and efficient systems, including advancements in server architecture and client-side software, paved the way for this patent. Key breakthroughs in algorithms and protocols, like improved routing and filtering techniques, contributed to the creation of a system capable of handling the massive volume of email traffic seen today.
This development has impacted businesses and individuals worldwide, dramatically increasing the efficiency and accessibility of electronic communication.
Technological Advancements Leading to the Patent
A number of key technological advancements contributed to this patent. These include improved server-side processing techniques, sophisticated algorithms for spam filtering, and enhanced client-side user interfaces. The integration of these advancements into a unified system resulted in significantly faster and more reliable email delivery. Moreover, innovations in cloud computing and distributed systems have allowed for more scalable and robust email infrastructure.
These improvements facilitated seamless communication and significantly enhanced the efficiency of email handling for individuals and businesses alike.
Inventor’s Background and Motivations
The patent’s inventors likely possessed a strong understanding of the limitations of existing email systems. Their motivations likely stemmed from a desire to address these limitations and improve the overall user experience. They likely aimed to create a more efficient and reliable system capable of handling the growing volume of email traffic. Their background likely encompassed expertise in computer science, networking, or related fields, allowing them to conceptualize and implement the innovations Artikeld in the patent.
Motivations could have included improving efficiency in business settings or addressing individual users’ concerns regarding email management.
The recent questioning of Microsoft’s email patent award got me thinking about the wider tech scene. It’s a fascinating debate, but the bigger picture, perhaps, lies in the IT industry’s rise in Pakistan, a country actively fighting image problems and fostering innovation. This rising tech scene in Pakistan, highlighted in fighting image problem an it industry rises in pakistan , is a powerful counterpoint to the legal wrangling over email patents.
Ultimately, though, the email patent debate remains a crucial discussion about innovation and fair practices in the tech world.
Patent’s Initial Reception and Impact
The patent’s initial reception was likely positive, recognizing the significant improvements in email handling. The impact was likely felt immediately in terms of enhanced user experience and increased efficiency. The potential for improved productivity in both personal and professional settings was undoubtedly recognized. Early adoption and positive feedback would have provided evidence of the patent’s utility. The introduction of features like improved organization, automated sorting, and streamlined access likely garnered significant attention and influenced subsequent email system designs.
Comparison of Initial Claims to Current Standing
| Aspect | Initial Claims | Current Standing |
|---|---|---|
| Email Delivery Speed | Improved latency by X%. | Maintained or exceeded initial claims through optimization and improved infrastructure. |
| Spam Filtering Accuracy | Reduced spam by Y%. | Continued improvement in spam filtering accuracy through machine learning and algorithm refinement. |
| User Interface Functionality | Enhanced organization tools. | Further developed with improved user interface design, potentially incorporating artificial intelligence and machine learning for predictive analysis. |
| Scalability | Capacity to handle Z number of users/messages. | Demonstrated scalability through cloud-based architecture and distributed systems. |
The Questioning of the Award
The recent awarding of an email-related patent to Microsoft has sparked considerable debate and scrutiny. This wasn’t a quiet, uncontested victory; the patent’s validity is being challenged, raising questions about the innovation claimed and the application of existing legal precedents. This questioning process is critical in ensuring the integrity and fairness of the patent system.The patent’s validity is under intense scrutiny, with several parties contesting the award.
This challenge is not just about technicalities; it touches upon the core principles of intellectual property rights, the definition of true innovation, and the potential for overreach in awarding patents. Understanding the reasons behind this questioning is essential to evaluating the patent’s true merit.
Reasons for Questioning the Patent
The questioning of the patent award stems from concerns about its novelty and the scope of the claimed invention. Critics argue that the patent doesn’t encompass truly novel functionalities but rather describes incremental improvements or combinations of existing technologies. This is a common theme in patent disputes, where the line between innovation and simple refinement can be blurry.
Parties Involved in the Questioning
Several entities and individuals are involved in the process of challenging Microsoft’s patent. These include competitors seeking to prevent Microsoft from potentially gaining an unfair advantage, patent examiners seeking to maintain consistency in patent granting procedures, and even individual inventors who believe their prior work was overlooked or inadequately considered. The range of parties involved indicates the patent’s significance and the widespread impact of its potential validity.
Specific Points of Contention
The specific points of contention revolve around the claims made in the patent. The patent’s claims regarding the email functionality are being scrutinized to determine if they represent true invention or merely a repackaging of existing features. Concerns have been raised about the sufficiency of evidence demonstrating the unique contribution of the invention, the potential for overly broad claims encompassing existing technologies, and whether the claimed invention provides a meaningful advancement over existing technologies.
Potential Legal Precedents
Several legal precedents provide context for the current questioning. Cases involving similar claims of incremental improvements or combining existing technologies offer valuable insights. Analysis of these precedents can highlight patterns and principles that help determine the validity of Microsoft’s patent in relation to existing legal interpretations. For example, the precedent set byState Street Bank & Trust Co.
v. Signature Financial Group, Inc.* (1999) has been frequently cited in debates concerning the patentability of business methods, which can provide valuable context.
Arguments Presented Against the Award
| Argument | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Lack of Novelty | Critics contend that the claimed invention does not represent a significant departure from existing email technologies. They argue that the patent’s features are incremental improvements or combinations of existing functionalities. |
| Overly Broad Claims | The patent’s claims are considered too broad, encompassing a wide range of existing email technologies. This can lead to a situation where the patent effectively prevents others from using established techniques. |
| Insufficient Disclosure | Concerns exist regarding the clarity and completeness of the patent’s disclosure. Critics argue that the description of the invention may be insufficient to enable a skilled artisan to implement the claimed features. |
| Prior Art | Evidence of prior art, such as published articles, patents, and other publicly available documentation, may demonstrate that the claimed invention is not novel. |
Potential Impacts of the Questioning

The recent questioning of Microsoft’s email-related patent award has significant implications, extending far beyond the immediate parties involved. This situation highlights the complexities of intellectual property rights and the potential ramifications of disputes in a rapidly evolving technological landscape. The outcome will undoubtedly shape future innovation and the broader email technology sector.The questioning of the patent’s validity casts a shadow on the legal precedents established by similar cases, and the repercussions could ripple through the industry, impacting not just Microsoft, but also smaller companies and independent inventors.
Consequences of Award Revoking
The potential consequences of revoking the patent award are numerous and multifaceted. A revocation would severely impact Microsoft’s competitive position, particularly in the email software market.
- Loss of exclusive rights: Microsoft would lose the exclusive right to use, license, or sell technologies covered by the revoked patent. This could lead to competitors implementing similar features or even improvements, potentially weakening Microsoft’s market dominance.
- Erosion of market share: Competitors might seize the opportunity to gain market share by offering alternative solutions, especially if the revoked patent covered a significant aspect of their core email functionality. This could be observed in other cases, such as the challenges faced by companies with patents related to smartphone features.
- Damage to reputation: A revoked patent could significantly damage Microsoft’s reputation for innovation and intellectual property management. This could negatively affect its standing with investors and customers.
- Legal costs: Microsoft would have incurred significant legal fees in defending the patent, which would now be wasted if the award is revoked. Similar situations in the past have shown how costly these legal battles can be.
- Impact on future investments: The uncertainty surrounding the patent could discourage future investments in R&D for similar technologies, potentially hindering innovation in the email technology sector.
Financial Implications for Microsoft
The financial implications of a revoked patent are substantial. The loss of market share, legal fees, and damage to brand reputation could have considerable financial repercussions.
| Potential Consequence | Estimated Financial Impact (Illustrative) |
|---|---|
| Loss of future licensing revenue | $10-50 million annually (based on hypothetical licensing fees for the patent) |
| Lost market share | $50-100 million annually (based on projected sales of email software) |
| Legal fees | $10-20 million (based on past patent litigation costs) |
| Damage to brand reputation | Difficult to quantify, but could translate to lost market share and investor confidence. |
Financial estimates are based on hypothetical situations and should not be considered precise predictions. Actual impacts would depend on the specific circumstances of the patent revocation.
Repercussions for the Inventor and Institution
The inventor and their institution could also face significant repercussions.
- Damage to reputation: The inventor and their institution could face damage to their reputation for innovation and intellectual property management.
- Loss of credibility: This could affect future collaborations and funding opportunities.
- Loss of recognition: The inventor’s contribution might be diminished if the patent is revoked.
- Potential legal issues: The inventor and their institution could face legal liabilities if the patent revocation is found to be a result of fraudulent or misleading information. Similar situations in the past have shown how inventors and their institutions have been held accountable.
Effects on Future Innovation
A revoked patent could have a chilling effect on future innovation in the email technology sector.
- Reduced investment in research: Companies might be less inclined to invest in research and development of email technologies, given the uncertainty surrounding patent protection.
- Diminished incentive for innovation: Inventors might be less motivated to pursue innovative ideas in the email sector, fearing their efforts might be challenged and potentially revoked.
- Discouraging impact on other related industries: The uncertainty could discourage innovation in other related technologies that rely on similar intellectual property principles.
Comparison to Other Patent Disputes
The questioning of Microsoft’s patent mirrors other patent disputes in similar fields, such as software, telecommunications, and even biotechnology. The consequences vary depending on the specifics of each case, but the general principles remain. For example, the revocation of a significant patent in the smartphone industry led to a period of uncertainty and a slight dip in innovation in that sector, but the sector eventually recovered.
The recent questioning of Microsoft’s email patent award raises some interesting questions about the future of communication. While email remains a cornerstone of modern business, the rise of VoIP technology, as detailed in this insightful article about voip lined up as wave of future , suggests a potential shift in how we connect. Ultimately, the challenges surrounding the patent award highlight the evolving landscape of digital communication, and how quickly innovation can disrupt established norms.
Each instance serves as a reminder of the intricate balance between innovation, competition, and intellectual property protection.
The recent questioning of Microsoft’s email-related patent award is a bit perplexing. While the tech world grapples with this, Sony’s innovative move to integrate a phone camera into their new Walkman, like this new model , suggests a fascinating shift in how we interact with technology. Perhaps the patent dispute is just a bump in the road, and the true innovation lies in unexpected places.
Either way, the future of email and portable audio still feels uncertain.
Technological Context
Email, a cornerstone of modern communication, has evolved significantly since its inception. Its current state reflects a complex interplay of protocols, technologies, and user expectations. This evolution is intertwined with the questioned patent, highlighting how the technological landscape has shifted and how the patent’s claims might hold up against current realities.
Current State of Email Technology
Email technology is robust and pervasive. It supports billions of users globally, facilitating communication across diverse platforms and devices. Email clients have become sophisticated, integrating features like spam filtering, encryption, and attachment handling. Cloud-based email services have become dominant, offering scalability and accessibility. The ubiquity of email, combined with its simplicity, ensures its continued relevance.
Advancements in Email Technology Since the Patent Award
Significant advancements have been made in email security, encryption, and user experience. The rise of sophisticated phishing attacks and malware has spurred innovations in anti-spam and authentication protocols. Furthermore, improvements in email client design have led to more intuitive and user-friendly interfaces. These advancements, driven by the need to address evolving threats and user needs, demonstrate a dynamic evolution in the field.
The Role of Email in Modern Communication
Email remains a vital tool for professional communication, facilitating transactions, collaborations, and information sharing. Its importance extends beyond business to personal relationships, allowing for efficient communication across geographical boundaries. While instant messaging and social media platforms are popular for real-time interaction, email retains its value for detailed communication, record-keeping, and formal exchanges.
How the Challenged Patent Fits into the Current Technological Landscape
The challenged patent, pertaining to [Specific aspects of the patent, e.g., email routing, security protocols], needs to be assessed against the current technological landscape. The patent’s claims must demonstrate relevance to the contemporary state of email technology, accounting for advancements in email protocols, encryption, and user experience. If the patent’s scope is overly restrictive or fails to encompass modern practices, its validity becomes questionable.
Email Protocols and Their Relevance to the Patent
| Protocol | Description | Relevance to the Patent |
|---|---|---|
| SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) | The foundation for email transmission. | Essential for understanding how email is sent. The patent may or may not cover specific aspects of SMTP implementation. |
| IMAP (Internet Message Access Protocol) | Allows users to access email on a server. | Crucial for understanding email client functionality. The patent’s claims about client-server interactions must be consistent with IMAP. |
| POP3 (Post Office Protocol version 3) | Allows users to download email to their local devices. | Similar to IMAP, the patent must account for how email is downloaded and stored. |
| MIME (Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions) | Allows for the transmission of various file types within emails. | If the patent covers attachments or specific content types, MIME is directly relevant. |
| S/MIME (Secure/Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions) | Provides encryption for email. | Relevant if the patent claims include security aspects of email transmission. |
This table summarizes key email protocols. Their relevance to the patent is contingent upon the patent’s specific claims. The table illustrates the breadth of email technologies and their importance in the current digital landscape.
Legal and Procedural Aspects: Award Of E Mail Related Patent To Microsoft Questioned
Challenging a patent award is a complex and lengthy process, often involving intricate legal procedures and significant financial resources. Understanding the legal framework surrounding patent disputes is crucial for evaluating the potential outcomes of the Microsoft patent challenge. This section details the steps involved in such a process, the applicable laws, and the roles of various stakeholders.
The Legal Process of Challenging a Patent Award
The process of challenging a patent award typically involves a series of steps, each with specific legal requirements and deadlines. These steps are designed to ensure a fair and thorough evaluation of the patent’s validity and enforceability. Failure to adhere to these procedural rules can lead to dismissal of the challenge.
Relevant Laws and Regulations Governing Patent Disputes
Patent disputes are governed by specific laws and regulations, varying by jurisdiction. These laws typically address the patentability requirements, the process for challenging a patent, and the remedies available in case of a successful challenge. Understanding the relevant laws is critical for strategizing the challenge. For example, the Patent Act of a particular country Artikels the conditions for patentability, the grounds for challenging a patent, and the procedures for handling disputes.
Roles of Different Legal Entities Involved in the Dispute
Multiple legal entities play critical roles in patent disputes. These include patent examiners, patent offices, attorneys representing the parties involved (e.g., the patent holder and the challenger), and courts. Each entity has specific responsibilities and authorities within the legal framework. For example, patent examiners conduct initial reviews of patent applications, while courts ultimately decide the validity of a patent.
The patent office acts as a neutral intermediary, managing the application process.
Potential Timelines for the Resolution of the Dispute
The time required to resolve a patent dispute can vary significantly depending on the complexity of the case, the jurisdiction, and the efficiency of the court system. The process can span several years. For example, a simple challenge might take a few years, while a complex dispute involving multiple parties and extensive evidence could take much longer.
Steps Involved in the Legal Process
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Filing a Petition for Reexamination | The challenger formally requests a review of the patent’s validity. This typically involves presenting evidence and arguments challenging the patent’s novelty, non-obviousness, or utility. |
| Patent Office Review | The patent office examines the evidence presented and decides whether to uphold or revoke the patent. This stage may involve further hearings and evidence submissions. |
| Appeal to the Courts | If the patent office decision is unsatisfactory, the challenger can appeal to a court. This often involves filing a lawsuit. |
| Court Proceedings | The court will hear arguments from both sides, evaluate evidence, and render a decision. This may involve expert testimony and discovery processes. |
| Enforcement of the Decision | If the court rules in favor of the challenger, the decision will be enforced, potentially invalidating the patent. Conversely, if the court upholds the patent, the challenger will be unsuccessful. |
Public Perception and Impact
The questioning of Microsoft’s email-related patent award has sparked considerable public interest, prompting a wave of media coverage and online discussion. This scrutiny raises important questions about the public’s perception of technology, innovation, and the fairness and transparency of the patent system itself. The debate has highlighted the complexities inherent in intellectual property rights and the potential for such disputes to impact public trust.
Public Response to the Patent Questioning, Award of e mail related patent to microsoft questioned
Public reaction to the patent award’s questioning has been varied. Some express concern over potential monopolies or undue influence of large tech companies in the field of email technology. Others see the questioning as a healthy challenge to the patent system, potentially encouraging more innovation. The response is further complicated by the lack of readily available information on the technical specifics of the patent and the exact nature of the challenge.
Media Coverage and Public Discussion
The media has played a significant role in disseminating information and opinions related to the patent dispute. News outlets, tech blogs, and social media platforms have reported on the challenges, highlighting the technical aspects of the patent and the implications for the broader tech industry. Online discussions have ranged from technical analyses to more general concerns about the fairness and efficiency of the patent system.
This widespread coverage has allowed the public to engage in a wider conversation about the patent award and its possible consequences.
Broader Implications for Public Trust in Intellectual Property
The patent dispute has implications for the public’s overall trust in intellectual property. The questioning of a significant patent award raises questions about the validity and potential misuse of intellectual property rights. Such disputes can erode public confidence in the system if not handled transparently and fairly. A strong precedent for transparency and rigorous review processes is vital to maintain public trust in the integrity of intellectual property.
Cases where patents have been overturned in the past, and their impact on market competition, provide a benchmark for understanding the consequences of questioning patent validity.
Possible Effects on Public Perception of Technology and Innovation
The public’s perception of technology and innovation may be affected by the patent dispute. The questioning could lead to increased skepticism towards technology companies and their claims of innovation, particularly when related to established technologies. It may also encourage a more critical evaluation of the potential impact of patents on the development and adoption of new technologies. The public could potentially shift from a passive acceptance of technological advancement to a more active role in evaluating the underlying innovation and the processes involved in its protection.
Summary of Public Reactions and Opinions
| Category | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Support for Questioning | Individuals and groups who believe the patent award is flawed or unjustly granted, questioning the system’s fairness. | “This patent is a clear case of corporate overreach. It’s not about innovation, it’s about stifling competition.” |
| Support for Patent Award | Individuals and groups who believe the patent is valid and reflects a legitimate innovation, defending the right to intellectual property protection. | “Microsoft has invested heavily in this technology. The patent is a recognition of their work and deserves protection.” |
| Skepticism/Uncertainty | Individuals and groups who are unsure about the validity of the patent and the patent system’s effectiveness, expressing concern over potential ramifications. | “This whole situation highlights the complexities of the patent system. It’s hard to know who is right.” |
| Concern about Monopolies | Individuals and groups who are worried about the potential for large tech companies to gain undue influence or create monopolies. | “The potential for a tech giant to control a crucial technology like email is concerning.” |
Last Word
In conclusion, the questioning of the email-related patent awarded to Microsoft highlights the complexities inherent in intellectual property disputes. The implications extend far beyond the immediate parties involved, touching on the future of email technology and the broader landscape of innovation. This dispute serves as a crucial case study, prompting reflection on the intricacies of patent law and the evolving nature of digital communication.
The outcome will undoubtedly shape future practices and expectations in the sector.