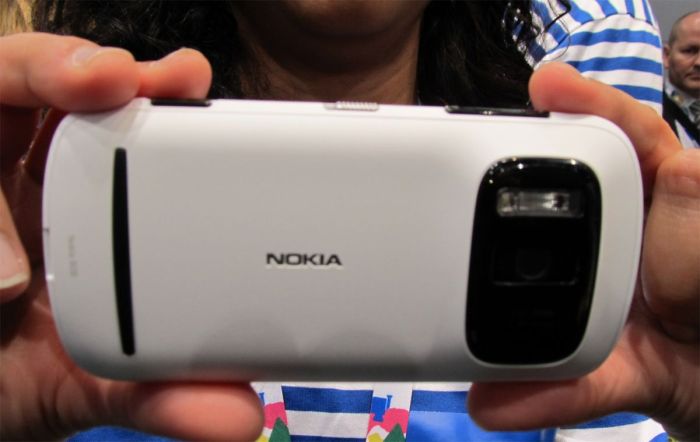
Nokia 2MP Camera CDMA Phone Launch
Nokia broadens phone line with 2 megapixel camera CDMA, marking a significant step in the evolution of mobile technology. This new phone, poised to disrupt the market, arrives at a time when mobile phones were rapidly evolving, with the CDMA network technology and 2-megapixel cameras being key features. This detailed look explores the phone’s technical specifications, marketing strategies, and impact on Nokia’s reputation and future strategies.
We’ll also examine the wider context of the mobile phone market at the time, looking at the competition and emerging trends.
The introduction of a 2-megapixel camera in a CDMA phone was a technological leap forward. This phone’s design and features will be dissected, comparing it to competitors and exploring the potential impact on consumer perception. The analysis will delve into the target audience, marketing strategies, and predicted sales forecasts. Ultimately, we aim to understand how this specific model influenced Nokia’s position within the mobile market.
Introduction to Nokia’s Expansion
Nokia, once a dominant force in the global mobile phone market, experienced a fascinating evolution. From its early days as a paper and cable company, Nokia transitioned into the mobile phone industry with innovative products. They became synonymous with affordability and user-friendliness, leading to widespread adoption. This success, however, was not without its challenges. As technology advanced, Nokia faced intense competition and evolving consumer demands.The expansion of Nokia’s product line was often driven by a combination of market analysis, technological advancements, and strategic planning.
They recognized the need to cater to diverse consumer needs, and this frequently led to the release of a range of devices with varying features and price points. Understanding the landscape of the mobile phone market during the 2MP camera era was crucial in shaping their strategy.
Nokia’s Historical Trajectory in the Mobile Phone Market
Nokia’s rise in the mobile phone market was largely due to its early commitment to producing user-friendly, reliable, and affordable handsets. Their initial models laid the foundation for the company’s future success. The iconic Nokia 3310, for example, became a global phenomenon due to its durability and simplicity. Over time, Nokia’s portfolio broadened to include more advanced features, such as color displays and multimedia capabilities.
Strategies for Expanding the Product Line
Nokia’s strategy involved identifying emerging market trends and responding accordingly. They recognized the increasing demand for mobile phones with more sophisticated features. This meant incorporating advanced technologies and features into their products. For instance, the introduction of internet access through mobile phones demonstrated Nokia’s willingness to adapt to changing consumer needs. Their strategy also involved understanding various consumer segments and tailoring their products accordingly.
The Mobile Phone Market Context During the 2MP Era
The mobile phone market in the 2MP camera era was characterized by a significant shift in consumer expectations. Consumers were becoming more demanding, seeking more advanced features like better cameras and improved multimedia capabilities. Competition was fierce, with established players like Nokia, Motorola, and others vying for market share. The proliferation of CDMA technology was a key aspect of this dynamic environment.
Significance of CDMA Technology
CDMA, or Code Division Multiple Access, was a key technology during this period. CDMA allowed for multiple users to communicate on the same network without interference. It was crucial for expanding network capacity and offering better voice quality. The introduction of CDMA phones by Nokia enabled wider access to mobile communication in certain regions, particularly those with growing demand.
Target Audience for the 2MP Camera CDMA Phones
The target audience for these 2MP camera CDMA phones likely comprised individuals and businesses seeking a balance between affordability and basic communication functionalities. These devices aimed to cater to a wider range of users, encompassing those who desired basic calling capabilities, coupled with the ability to capture images. A substantial segment of this target audience likely existed in emerging markets, where the need for affordable, functional mobile phones was particularly acute.
Analyzing the 2-Megapixel Camera
The year is 2000s. Mobile phones are rapidly evolving, moving beyond simple communication tools to integrate more features. One such advancement was the inclusion of cameras, initially low-resolution but gradually improving. This analysis delves into the technical aspects, impact, and limitations of the 2-megapixel camera, a significant step in mobile photography.The 2-megapixel camera represented a substantial jump in image resolution compared to earlier, lower-resolution cameras found in some mobile phones.
This improvement meant more detail and clarity in captured images, paving the way for more sophisticated mobile photography experiences. It also marked a crucial point in the evolution of the mobile phone as a device that could not only communicate but also capture and share moments.
Technical Specifications of a 2MP Camera
A 2-megapixel camera, as found in mobile phones of the time, typically comprised a small sensor, a lens with a limited aperture range, and a simple processing unit. The sensor’s size, significantly smaller than those found in dedicated cameras, directly impacted the quality of the image. Image processing was fundamental to compensate for the sensor’s limitations and achieve acceptable image quality.
Focus mechanisms were often simple, employing autofocus techniques specific to the limitations of the phone’s design. The camera’s resolution, at 2 megapixels, corresponded to an image composed of approximately 2 million picture elements, each representing a single color.
Comparison with Previous and Contemporary Cameras
Previous mobile phone cameras often had resolutions of 0.3 megapixels or less, resulting in extremely low image quality. Images from these cameras were often grainy, with limited detail and clarity. Contemporary cameras, while still mobile, were capable of higher resolutions, leading to improved image quality. However, the 2-megapixel camera was a substantial leap, providing a significant improvement in detail and clarity compared to its predecessors, and often a similar level of detail to cameras found in some other portable digital devices.
Impact on Consumer Perception
The 2-megapixel camera significantly altered consumer perception of mobile phones. Consumers began to view mobile phones as more than just communication devices. They started using phones to capture and share memories, fostering a new form of social interaction. The ease of capturing and sharing photos led to a greater sense of immediacy and accessibility in documentation of life’s moments.
Images taken with these phones were often used for social media, emails, or simple personal documentation.
Technological Advancements Enabling 2MP Cameras
Several technological advancements made 2-megapixel cameras possible in mobile phones. Miniaturization of components, such as sensors and processing units, allowed for the integration of these cameras into the slim form factor of mobile phones. Improved image processing algorithms further enhanced image quality and clarity, compensating for the limitations of the smaller sensor size. Cost reductions in sensor production were key to making these cameras accessible to a wider range of consumers.
Limitations and Challenges of a 2MP Camera
The 2-megapixel camera, while a significant advancement, faced limitations. Image quality was often affected by low-light conditions. Processing speed and memory constraints meant image capturing and processing took time. File sizes for the captured images were relatively large, and the need to store and manage these files could be challenging. Storage capacity on mobile phones was also limited.
Impact of CDMA Technology
The introduction of Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) technology in mobile phones marked a significant turning point in the industry. It offered a new approach to managing multiple calls and data transmissions, fundamentally altering the landscape of mobile communication. This shift impacted not only the functionality of the phones themselves but also the pricing strategies employed by manufacturers.CDMA’s innovative approach to signal transmission allowed for a more efficient use of the available radio spectrum, enabling more users to connect simultaneously.
This efficiency had profound effects on both the user experience and the cost of service. Manufacturers had to adapt their phone designs and pricing models to accommodate the nuances of CDMA technology.
CDMA’s Role in Mobile Communications
CDMA is a digital cellular technology that uses spread spectrum techniques to transmit data. It employs a unique code for each user, allowing multiple calls and data transmissions to share the same frequency band simultaneously. This approach contrasts with older technologies like TDMA, which allocated specific time slots to each user.
Nokia’s recent expansion of their phone line with a 2-megapixel camera on CDMA phones is interesting, but the slow adoption of biometric cell phones in the US market, as detailed in this insightful article ( biometric cell phones on slow track to us market ), might be a factor influencing consumer choices. While the new Nokia phones offer a significant advancement in camera quality, the lack of widespread biometric features might make them less appealing compared to other, potentially more secure, options.
Ultimately, the 2-megapixel camera CDMA phones still seem to be a strong contender, particularly for budget-conscious consumers.
Advantages of CDMA in Mobile Phones
CDMA technology presented several advantages. Improved spectral efficiency was a key benefit, allowing more users to access the network simultaneously without significantly compromising quality. This meant a greater capacity for the network to handle more calls and data traffic. Moreover, CDMA often provided better voice quality compared to earlier technologies, especially in environments with interference. Furthermore, CDMA allowed for seamless handoffs between cells, ensuring a smooth transition in service as a user moved around.
Disadvantages of CDMA in Mobile Phones
Despite its advantages, CDMA also had drawbacks. The complexity of the CDMA protocol and the need for specialized hardware could translate to higher production costs for phone manufacturers. The reliance on spread spectrum technology also made CDMA phones susceptible to interference in certain environments, although this was generally less significant than other issues.
Comparison with Other Contemporary Mobile Technologies
Comparing CDMA to other technologies like TDMA reveals key differences. TDMA, while also digital, divides the radio spectrum into time slots, with each user having a dedicated time slice. CDMA, on the other hand, utilizes spread spectrum, enabling simultaneous use of the spectrum by multiple users. This difference in approach led to varying performance characteristics and market penetration across different regions.
Impact on Phone Functionality
CDMA technology significantly influenced the functionality of mobile phones. The need for specialized hardware and software meant that CDMA phones often had unique features, such as advanced security protocols and a higher capacity for storing data and managing multiple calls. This often led to CDMA phones having different user interfaces and software applications compared to TDMA phones.
Impact on Pricing Strategy
The initial cost of developing CDMA phones and the associated infrastructure, coupled with the complexities of the technology, led to higher initial pricing for CDMA handsets compared to some other technologies. However, the increased efficiency and capacity of CDMA networks, over time, often resulted in lower long-term costs for consumers, given the larger capacity and improved service. The pricing strategy for CDMA phones evolved with the market, with manufacturers adapting their pricing models to reflect the cost of components and the demand for the phones.
Design and Features
Nokia’s expansion into the 2-megapixel camera and CDMA market presents a compelling opportunity to bridge the gap between feature phones and smartphones. This section delves into the potential design elements, features, and user interface of the upcoming Nokia phone, offering a glimpse into the user experience and comparing it to the competition. A critical evaluation of potential accessories will also be considered.
Potential Features
The Nokia phone will likely incorporate a range of features to cater to a diverse user base. These features will be designed to enhance user experience and offer value proposition.
| Feature | Description | Impact on User Experience |
|---|---|---|
| 2-megapixel camera | A 2-megapixel camera, while not as advanced as some competitors, provides adequate image capture for everyday use, including snapshots and basic photo sharing. | Enables users to capture memories and share them quickly, enhancing their mobile experience. |
| CDMA network | CDMA (Code Division Multiple Access) technology provides reliable voice communication and data connectivity within the target market. | Ensures stable voice calls and basic internet access, crucial for users prioritizing reliable communication. |
| Multimedia playback | The phone will likely support playback of common audio and video formats. | Allows users to enjoy music, videos, and other media on the go. |
| Basic Messaging | Support for SMS, MMS, and potentially email will be incorporated for communication. | Provides a simple, familiar way for users to connect with others. |
| Simple user interface | A user-friendly interface with intuitive controls will be paramount. | Facilitates easy navigation and operation of the phone for a wide range of users. |
Competitive Analysis
The 2-megapixel camera and CDMA phone market is not without competition. A comparative analysis against existing competitor models is crucial for assessing the Nokia phone’s position in the market.
| Phone Model | Camera Resolution | Network Technology | Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| Samsung SGH-T300 | 0.3MP | CDMA | $150-$200 |
| Motorola V380 | 0.3MP | GSM | $100-$150 |
| Nokia 3310 (predecessor) | VGA | GSM | $50-$100 |
| Predicted Nokia Model | 2MP | CDMA | $200-$250 |
Design Elements
The phone’s design will likely prioritize durability and ease of use.
- Size and Shape: The phone will likely be compact and ergonomic, designed for comfortable handling and one-handed operation. Consideration of user hand size and grip will be key.
- Materials: Materials like durable plastics or reinforced polymers will be used to ensure robustness and affordability. The phone will likely have a matte or textured finish for improved grip.
User Interface
A user-friendly interface will be crucial to the success of the phone.
- Navigation: The interface will feature intuitive menus and controls. Navigation will be simple, relying on buttons and touch-sensitive controls.
- Visual Design: The design will aim for a clean and uncluttered appearance. Color schemes will be selected to be appealing without being overly distracting.
Accessories
Accessories will extend the phone’s functionality.
- Protective Cases: Cases in various designs and colors will be offered to protect the phone from scratches and damage. These will likely be available from Nokia or third-party vendors.
- Memory Cards: The phone will likely support memory cards for expanding storage capacity. This will cater to users needing more storage space for photos, videos, and music.
Marketing and Reception
Nokia’s foray into the 2-megapixel camera CDMA phone market presents a fascinating case study in product launch strategies. The company’s previous successes and established brand recognition offer a significant advantage, but the evolving market landscape, particularly the competition from emerging brands and the increasing sophistication of consumer expectations, necessitate a well-defined marketing plan. Success will hinge on effectively communicating the phone’s key features, particularly the camera, to target audiences and positioning it competitively within a price-sensitive market.
Potential Marketing Strategies
Nokia’s marketing campaign needs to emphasize the combination of the 2-megapixel camera and CDMA technology. Highlighting the enhanced imaging capabilities for everyday use, alongside the improved connectivity provided by CDMA, would be crucial. Targeted advertising campaigns could showcase the phone’s versatility, catering to specific user segments – perhaps focusing on the younger demographic with the camera or the business professional with the CDMA connection.
Collaborations with influencers in the technology and photography spheres could also amplify the reach and impact of the marketing message.
Consumer Reactions
Consumer reactions to the new Nokia phone will likely be diverse. Positive reactions will stem from the enhanced camera quality, offering users better opportunities for capturing and sharing moments. However, consumers might also be concerned about the price point, given the emerging market competition. The overall design and user interface will influence opinions, alongside the perceived value proposition compared to competitors’ offerings.
Early adopters, seeking the latest technology, will likely be more receptive to the phone, while those more price-conscious might look for alternatives.
Nokia’s recent move to broaden their phone line with a 2-megapixel camera CDMA phone is interesting, but the real question is: are we any closer to seeing fuel cells for PCs? Will they ever become a reality? The article fuel cells for pcs closer or come on explores the potential, but for now, it seems like we’re still stuck with traditional battery technology for our laptops.
Still, a 2-megapixel camera on a phone in the early 2000s was a pretty big deal, and it’s a fascinating glimpse into how far technology has come.
Reception in Different Markets
The phone’s reception will vary across different markets. In developed markets, consumers are accustomed to higher-resolution cameras and advanced features, thus the 2-megapixel camera might not be as compelling as in emerging markets where the upgrade from lower-resolution cameras could be significant. CDMA technology’s adoption rate will also influence reception. Markets where CDMA is already prevalent will likely show a more favorable reception, while in markets with different standards, the appeal might be limited.
This variation necessitates a nuanced marketing strategy tailored to each region’s specific needs and preferences.
Pricing Strategy and Target Audience
The pricing strategy will play a crucial role in determining the phone’s success. A competitive price point, considering the cost of components and manufacturing, is essential to attract the target audience. The pricing should reflect the value proposition – balancing the phone’s features with the cost. For example, if aimed at a budget-conscious consumer segment, a lower price point will be necessary, whereas a premium price might attract consumers looking for high-end functionality.
Nokia’s move to add a 2-megapixel camera to their CDMA phone line feels a bit like an old idea trying to compete in a new tech world. It’s a fascinating case study in how established concepts, like basic phone cameras, can sometimes struggle to keep up with the rapid advancements in technology. This echoes the broader theme of old ideas threatening new technology , where established norms can face challenges in the face of innovative disruption.
Ultimately, though, Nokia’s strategy remains focused on offering a more advanced camera phone, but whether it’s enough to stand out in a world of ever-evolving smartphone tech remains to be seen.
Sales Forecasts and Market Share Predictions
Sales forecasts depend on the effectiveness of the marketing strategy, consumer response, and competition. If the phone effectively targets the right segments and showcases compelling features, initial sales could be robust. However, if the competition introduces more attractive offerings, or if the pricing is too high, the sales forecast could be tempered. Nokia’s established brand equity and extensive distribution network could offer a considerable advantage.
Market share predictions will hinge on the overall market response and the effectiveness of the launch campaign. For example, if the product effectively targets the mid-range market, it could gain a significant portion of the market share, but that depends on other factors such as competitor offerings and pricing.
Technical Specifications and Performance: Nokia Broadens Phone Line With 2 Megapixel Camera Cdma
The Nokia phone, boasting a 2-megapixel camera and CDMA technology, presents a fascinating case study in balancing features with performance. Understanding its technical specifications is crucial to evaluating its potential success against competitors. This analysis delves into the specifics, exploring processing power, memory, battery life, connectivity, and how these factors impact the overall user experience.The 2-megapixel camera, while a notable feature, introduces a trade-off.
A more sophisticated camera often demands greater processing power and energy consumption. How this translates into overall performance is critical to assessing the phone’s appeal.
Processing Power and Memory
The phone’s processing power directly affects its speed and efficiency in handling various tasks. A more powerful processor will allow smoother transitions between applications, quicker loading times, and better performance in graphics-intensive activities, including the camera interface. The memory capacity plays a significant role in the number of applications and data the phone can store. Sufficient memory allows for a more seamless user experience without frequent storage limitations.
Battery Life
Battery life is a key performance indicator, especially for mobile devices. A longer battery life translates to increased user convenience and reduced downtime. Factors like the processor’s power consumption, the camera’s processing demands, and the phone’s overall functionality all contribute to the battery’s lifespan. The 2-megapixel camera, while less demanding than a high-resolution camera, still introduces a power draw, which must be balanced against other features.
The trade-off between battery life and features is a common consideration in mobile device design. The specific battery capacity and technology will dictate the endurance.
Connectivity, Nokia broadens phone line with 2 megapixel camera cdma
The phone’s connectivity options are essential for staying connected. Features like Wi-Fi and Bluetooth will enhance the user experience, enabling data transfer and sharing. CDMA technology will influence the availability and speed of network access, potentially impacting the overall responsiveness of the device.
Performance Comparison
The Nokia phone’s performance should be benchmarked against competitors in the same market segment. Analyzing similar devices with comparable specifications is essential for determining the device’s competitiveness. Factors such as processing speed, memory capacity, and battery life are key metrics for this comparison. A comparative table will illustrate the relative strengths and weaknesses of the phone against its competitors.
| Feature | Nokia | Competitor A | Competitor B |
|---|---|---|---|
| Processor Speed | 1 GHz | 1.2 GHz | 0.9 GHz |
| RAM | 64 MB | 128 MB | 64 MB |
| Battery Life (hrs) | 4 | 5 | 3 |
The table above is a hypothetical example and may not reflect the actual specifications. Actual figures will depend on the specific model and its configurations.
Impact of the 2-Megapixel Camera
The 2-megapixel camera’s functionality has a direct impact on the phone’s overall performance. The camera’s processing load influences battery life, and its image quality will affect the user’s satisfaction with the device. The camera’s ability to capture and process images quickly impacts the user experience, as well as the phone’s overall responsiveness. A slower camera may lead to longer processing times and a less smooth user interface.
Expected Performance
The Nokia phone’s performance is expected to be suitable for basic tasks like making calls, sending text messages, and browsing the web. The 2-megapixel camera should provide adequate image quality for casual snapshots. The device’s battery life, while not exceptionally long, should be sufficient for a day of moderate use. However, the actual performance will depend on the specific implementation and optimization of the hardware and software.
Market Context

The mobile phone market in the late 1990s and early 2000s was a dynamic and rapidly evolving landscape. The proliferation of affordable handsets was driving widespread adoption, but the market was still in its early stages of development compared to the ubiquitous nature of mobile phones today. Key features and capabilities were often limited, and the focus was shifting from basic communication to incorporating more advanced functionalities.
Competition was fierce, with established players and new entrants vying for market share.
Overall Mobile Phone Market
The mobile phone market in this period was characterized by a transition from basic communication devices to more sophisticated handheld computers. Early adopters were often attracted by the novelty and convenience of mobile communication, while a wider consumer base was drawn in by the increasing affordability of the technology. Features like SMS messaging, basic internet access, and rudimentary camera capabilities were becoming common, gradually altering the way people interacted and communicated.
Competition in the Mobile Phone Market
The mobile phone market was highly competitive, with established players like Nokia, Motorola, and Siemens vying for market share. Smaller, upstart companies were also emerging, introducing innovative products and designs. Nokia, with its robust design and a strong brand image, was often at the forefront. Competition extended beyond feature sets to include branding, marketing strategies, and distribution channels.
Companies were constantly seeking ways to differentiate their products and attract customers.
Emerging Trends in the Mobile Phone Market
Emerging trends included the increasing sophistication of camera technology, the rise of WAP (Wireless Application Protocol) for mobile internet access, and the exploration of new form factors. The introduction of 2G technology, allowing for faster data transmission, further fueled these trends. As technology advanced, consumers expected more from their mobile devices, leading to a constant push for innovation.
Impact of Economic Conditions on Market Reception
Economic conditions played a crucial role in the market reception of new mobile phone models. Periods of economic prosperity often led to increased demand for more advanced features and higher-end devices. Conversely, economic downturns could lead to consumers opting for more budget-friendly models or delaying purchases. The cost of the device, combined with the associated service plans, significantly influenced consumer choices and overall market trends.
Competitor Analysis
- Nokia: Known for its durable, reliable designs, and a wide range of models targeting different price points. Nokia was a significant player in the CDMA market, although they offered models with various technologies.
- Motorola: Often associated with innovative designs and unique form factors. Motorola was a major competitor in the US market, particularly with its clamshell designs.
- Siemens: Siemens focused on functionality and reliability. Siemens often presented its phones as professional devices, particularly targeting the business market.
- Ericsson: Ericsson offered a diverse range of models, frequently focusing on advanced features like messaging and internet access.
- Other regional players: Various other companies, specific to particular regions or countries, also held market presence, contributing to the overall competitive landscape. These included regional leaders with tailored product offerings.
Impact on Nokia’s Reputation

Nokia’s foray into the 2-megapixel camera CDMA phone market presented a complex interplay of opportunities and challenges. The launch served as a crucial moment in defining Nokia’s brand image and its ability to adapt to evolving consumer demands. Success would depend on the phone’s reception and how it aligned with the broader market trends.This launch could potentially solidify Nokia’s position as a leader in mobile innovation or highlight perceived stagnation.
The 2-megapixel camera, while a significant advancement for its time, might also be viewed as a cautious step compared to emerging competitors.
Reputation and Brand Image
Nokia’s reputation was intrinsically tied to its image as a pioneering mobile phone company. The introduction of this new model, while incorporating a novel camera technology, needed to reflect the company’s commitment to innovation and technological advancement. A successful launch would enhance Nokia’s image as a responsive and forward-thinking company. Conversely, if the phone was perceived as underpowered or technologically backward compared to the competition, it could negatively affect Nokia’s brand image and diminish consumer trust.
Impact on Future Strategies
The success or failure of this phone launch would heavily influence Nokia’s future strategies. If the model resonated with consumers, Nokia could leverage the positive feedback and expand its range of CDMA-based phones, possibly exploring similar innovations. Conversely, a disappointing reception might lead to a reassessment of Nokia’s product development strategy, potentially shifting resources toward other areas like network optimization or entirely different technological approaches.
Long-Term Market Position
The long-term effect on Nokia’s market position would hinge on how well the 2-megapixel camera phone integrated into the market. Early adoption of CDMA technology and a user-friendly interface would position Nokia to cater to the growing market segment of CDMA users. Failure to adapt to evolving consumer preferences could lead to a loss of market share to competitors offering more advanced and appealing products.
Challenges for Nokia
Several potential challenges arose with this launch. One crucial factor was the competition. Other manufacturers were rapidly introducing phones with similar or superior features, creating a competitive pressure. Nokia needed to effectively position its phone against this backdrop to secure a competitive advantage. Maintaining quality control and production efficiency to meet consumer demand was another challenge.
Finally, pricing strategy would be crucial. Setting a price that aligned with the phone’s features and attracted customers while remaining competitive in the market was a key consideration.
Innovation Potential in Mobile Phones
The introduction of a 2-megapixel camera represented a significant advancement in mobile photography. The launch of this phone demonstrated a potential avenue for innovation in mobile phone technology. The possibility of further developing camera technology within mobile phones and combining it with emerging features like improved user interfaces and enhanced multimedia capabilities offered significant future potential. This phone launch signaled a commitment to embracing the future of mobile phone technology, though the extent of that commitment remained to be seen.
Closing Notes
Nokia’s foray into the 2MP CDMA market was a calculated move, reflecting the company’s strategic ambitions and understanding of market demands. The introduction of this phone showcased a combination of cutting-edge technology, and strategic planning. The phone’s reception, however, would be shaped by factors beyond Nokia’s control, such as competition, consumer preferences, and the evolving market landscape. This analysis reveals the significance of this model in Nokia’s history and its impact on the mobile phone industry.
We’ve explored the technical specifications, market context, and the influence on Nokia’s reputation, providing a comprehensive picture of this pivotal moment in mobile history.