Digital Divide Separates Rural Urban Internet Users
Digital divide separates rural urban internet users, highlighting a critical gap in access, affordability, and skills between rural and urban populations. This disparity impacts education, employment, and overall societal progress. The varying levels of internet infrastructure, from speed and reliability to availability, create a stark contrast between rural and urban areas, influencing opportunities and quality of life.
This article delves into the multifaceted nature of the digital divide, examining the factors contributing to this disparity. From infrastructure limitations and economic disparities to digital skills gaps, we’ll explore the intricate web of challenges and opportunities in bridging this crucial divide. We’ll analyze the impact on education, employment, and entrepreneurship, highlighting the importance of closing this gap for equitable societal advancement.
Defining the Digital Divide: Digital Divide Separates Rural Urban Internet Users
The digital divide, a persistent societal chasm, separates individuals and communities based on their access to and ability to utilize information and communication technologies (ICTs). This disparity is particularly stark when examining the rural-urban divide, where access to reliable internet and digital skills often lag behind urban counterparts. This difference in access and use has profound implications for education, economic opportunities, and social inclusion.The digital divide manifests in various dimensions, each with unique implications for rural and urban populations.
These dimensions, including access, affordability, digital skills, and usage patterns, highlight the complexities of bridging this gap.
Access to Internet Infrastructure
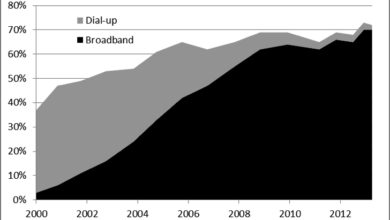
The fundamental aspect of the digital divide is access to reliable internet infrastructure. Urban areas generally boast a denser network of broadband providers and more readily available high-speed connections. Conversely, rural areas often face limitations in infrastructure, including a lack of fiber optic cables and limited coverage from internet service providers. This leads to slower speeds, higher latency, and spotty connectivity in rural areas, severely hindering access to online resources and services.
Affordability of Digital Technologies
The cost of internet access and digital devices significantly impacts access to the digital world. High internet subscription fees and the cost of purchasing computers or smartphones can create a financial barrier, especially for low-income households. In urban areas, the prevalence of affordable internet options and readily available devices can ease this burden. In rural areas, limited choices and higher costs frequently limit access to these vital tools, further exacerbating the digital divide.
Digital Skills and Literacy, Digital divide separates rural urban internet users
Beyond access and affordability, the digital divide extends to digital literacy and skills. Urban populations often have more opportunities for formal and informal digital training, fostering a higher level of digital proficiency. Conversely, rural communities may lack the same educational resources, workshops, or mentors, hindering the development of essential digital skills. This disparity in digital literacy directly impacts the ability to effectively utilize the internet for educational, professional, and personal pursuits.
Usage Patterns and Applications
The utilization of digital technologies varies considerably between rural and urban populations. Urban areas tend to utilize digital technologies for a wider range of applications, including e-commerce, online education, remote work, and social media interactions. In contrast, rural areas may see limited usage due to factors like reduced access, lower digital skills, and fewer readily available online resources.
This disparity in usage patterns further contributes to the overall digital divide.
Key Contributing Factors
Several factors contribute to the rural-urban digital divide. Infrastructure limitations, including the lack of broadband infrastructure in rural areas, are a major contributing factor. Economic disparities, where rural communities often have lower incomes and fewer job opportunities, can restrict access to digital technologies and services. Furthermore, educational opportunities often differ, with urban areas offering more robust digital literacy programs and resources.
These factors interact and compound to create the persistent rural-urban digital divide.
Social and Economic Implications
The digital divide has significant social and economic consequences. Limited access to online resources and services can hinder educational attainment, limit economic opportunities, and exacerbate existing inequalities. Rural communities often experience difficulties in accessing healthcare, government services, and educational opportunities, while urban areas often have easier access to a wider range of online resources. This disparity can result in a widening gap in social and economic well-being.
Access to Internet Infrastructure
The digital divide isn’t just about having a device; it’s deeply rooted in the availability and quality of internet infrastructure. This crucial element significantly impacts access and usage, especially in rural communities. Understanding the varying levels of internet infrastructure across urban and rural areas is vital to bridging the gap.The disparity in internet access extends beyond simply having a connection.
Factors like speed, reliability, and the availability of diverse technologies play a pivotal role in the digital experience. Rural areas often face challenges in establishing robust infrastructure, leading to significant differences in internet access compared to their urban counterparts. This disparity can affect educational opportunities, economic prospects, and overall societal well-being.
Internet Speed and Reliability
Rural areas frequently experience slower internet speeds compared to urban areas. This difference is often attributed to a lack of fiber optic cables and the prevalence of less capable technologies like satellite or older wireless connections. Reliability is another significant concern. Interruptions and slower speeds are more common in rural areas due to factors such as limited infrastructure maintenance and fewer redundant network pathways.
This variability makes consistent online activities like video conferencing or online learning more challenging.
Availability of Internet Access
Internet access is not uniformly distributed. In many rural areas, the percentage of households with reliable internet access is significantly lower than in urban centers. This lack of access directly affects educational attainment, job opportunities, and overall economic development. For instance, remote medical facilities in rural areas often struggle with transmitting medical images or accessing real-time patient data due to unreliable connections.
Successful Rural Internet Infrastructure Projects
Several initiatives have successfully addressed the digital divide in rural areas. One prominent example involves the deployment of fiber optic networks in underserved communities. This approach offers significantly higher speeds and more reliable connections than traditional technologies. Projects like these have demonstrated that dedicated investment in rural infrastructure can significantly improve access to the internet. Furthermore, community-based initiatives often work with local governments and private companies to install and maintain infrastructure, ensuring long-term sustainability.
Comparison of Access Technologies
Different internet access technologies have varying strengths and weaknesses, particularly when comparing rural and urban environments. Fiber optic cables, while offering the fastest speeds, are typically more expensive to install and maintain, making them less common in rural areas. Satellite internet provides a solution for remote locations, but it can be slower and less reliable, often affected by weather conditions.
Wireless technologies, such as 4G and 5G, offer increasing speed and reliability but are often limited by coverage in sparsely populated areas. The choice of technology depends on the specific needs and economic viability of the rural community.
Internet Infrastructure Comparison Table
| Feature | Rural | Urban |
|---|---|---|
| Internet Speed (avg. Mbps) | 10-50 Mbps | 100-500 Mbps |
| Reliability (downtime %) | 5-10% | 1-3% |
| Availability (percentage of households) | 50-80% | 95-100% |
| Access Technology | Satellite, DSL, Wireless | Fiber Optic, Cable, Wireless |
Economic Factors and Affordability
The digital divide isn’t just about access to internet infrastructure; it’s also deeply intertwined with economic realities. Cost plays a crucial role in determining who can truly participate in the digital economy, particularly in rural areas. The price of internet services varies significantly between urban and rural locations, creating a barrier to entry for those outside major population centers.The cost of internet services is a significant factor influencing digital inclusion.
Rural areas often face higher costs for comparable internet speeds and packages compared to urban areas. This is largely due to the lower population density and the resulting challenges in infrastructure deployment and maintenance. Consequently, affordability becomes a key issue for rural households and businesses.
Internet Subscription Prices and Bundles
Different internet subscription plans and bundles are available for both rural and urban residents, reflecting varying needs and usage patterns. Urban areas generally have a wider range of options with competitive pricing, often driven by higher population density and increased competition among providers. Rural areas frequently have fewer choices and often higher prices for similar bandwidth. This limited choice can limit options for users seeking specific data packages or speeds.
The digital divide continues to widen, with rural internet access lagging far behind urban areas. While advancements like the new Panasonic Blu-ray/DVD recorder panasonic debuts blu ray dvd recorder might offer entertainment options, they don’t address the fundamental issue of unequal internet access. This disparity in connectivity ultimately hinders rural communities’ economic and educational opportunities, perpetuating the digital divide.
The pricing structures themselves can vary considerably.
Impact on Rural Households and Businesses
High internet costs disproportionately affect rural households and businesses. Limited access to affordable internet can hinder educational opportunities for students, restrict remote work possibilities for employees, and limit the ability of businesses to expand their operations or access new markets. Without reliable and affordable internet access, rural businesses often struggle to compete with their urban counterparts, who can leverage the digital tools for improved efficiency and productivity.
This creates a cycle of disadvantage, perpetuating the digital divide.
Government Policies and Initiatives
Numerous government policies and initiatives are designed to address internet affordability in rural areas. These policies aim to bridge the gap in access and affordability, often focusing on subsidies, infrastructure development, and encouraging competition among providers. Examples include tax credits, funding for rural internet infrastructure, and support for community-based internet access projects. The specific policies and their effectiveness vary significantly from region to region.
Pricing Models of Internet Providers
| Provider | Rural Plan | Urban Plan |
|---|---|---|
| Company A | $50/month (10 Mbps) | $40/month (20 Mbps) |
| Company B | $65/month (20 Mbps) | $50/month (30 Mbps) |
| Company C | $70/month (25 Mbps) with limited promotional offers | $45/month (25 Mbps) with multiple bundle options |
The table above provides a snapshot of potential pricing models. Actual prices and plans may vary based on location, provider, and specific service requirements. Note that the table does not reflect all providers and pricing options available.
Digital Skills and Literacy
The digital divide extends beyond access to internet infrastructure; it profoundly impacts digital skills and literacy. Understanding the varying levels of digital proficiency between rural and urban populations is crucial to bridging the gap and fostering equitable opportunities in the digital age. This disparity in skills directly influences economic participation and social inclusion, making digital literacy a critical component of overall societal progress.The digital age demands a level of technical competency that is not uniformly distributed.
This lack of consistent digital skills can have far-reaching consequences, limiting access to opportunities and perpetuating existing inequalities. Digital literacy encompasses a range of abilities, from basic computer use to complex data analysis and digital problem-solving. These skills are essential for navigating the modern world and participating fully in the economy and society.
Digital Skills Levels in Rural and Urban Areas
Rural populations often exhibit lower levels of digital literacy compared to their urban counterparts. This difference stems from a combination of factors, including limited access to digital resources, fewer opportunities for training, and a smaller pool of digital professionals in rural areas. Urban environments, on the other hand, typically offer greater access to technology, more readily available training programs, and higher concentrations of digital specialists.
The digital divide, unfortunately, continues to widen the gap between rural and urban internet access. This disparity often leaves rural communities underserved, while urban areas enjoy robust connectivity. It’s a complex issue, and recent developments in tech like the strategies behind Microsoft, Apple, and HP’s market moves, as seen in microsoft apple and the hp gambit , highlight the need for equitable access across the board.
Ultimately, bridging this gap is crucial for fostering a truly digital future for everyone.
The result is a significant disparity in the practical application of digital skills between these populations.
Impact of Digital Literacy on Economic Opportunities and Social Inclusion
Digital literacy is directly linked to economic advancement and social inclusion. Individuals with strong digital skills can access remote work opportunities, engage in e-commerce, and participate in online learning platforms, fostering entrepreneurship and personal growth. Conversely, individuals lacking these skills face limitations in accessing these opportunities, potentially hindering their economic and social advancement. This disparity can lead to a widening economic gap between rural and urban communities.
Differences in Access to Digital Skills Training and Education
Rural communities often experience significant limitations in accessing quality digital skills training compared to urban areas. This can stem from a lack of dedicated training centers, fewer qualified instructors, and limited funding for digital literacy programs. Urban centers, in contrast, typically have more readily available training resources, more instructors, and greater funding for programs designed to enhance digital literacy.
This uneven distribution of resources directly affects the ability of rural residents to develop the digital skills necessary for modern employment.
Strategies to Bridge the Gap in Digital Skills
Several strategies can help bridge the digital skills gap between rural and urban populations. These include:
- Developing targeted digital literacy programs in rural areas, focusing on specific skill sets relevant to local industries.
- Partnering with local businesses and community organizations to offer affordable and accessible training programs.
- Deploying mobile digital literacy hubs in underserved rural communities to provide hands-on training and access to technology.
- Encouraging the development of digital literacy programs that integrate with existing educational curricula.
- Promoting digital literacy initiatives that empower individuals to share their skills and knowledge within their communities.
Digital Literacy Programs in Rural and Urban Areas
This table showcases examples of digital literacy programs available in rural and urban areas. Note that specific program details and target audiences may vary.
| Program | Location | Target Audience |
|---|---|---|
| Program A (Rural Community Tech Hub) | Rural | Individuals seeking employment in agriculture, small business owners, and youth |
| Program B (Urban Digital Skills Bootcamp) | Urban | Recent graduates, unemployed individuals, and those seeking career advancement |
| Program C (Online Digital Literacy Course) | Both | Individuals with varying levels of digital experience who seek to improve their digital skills |
Impact on Education and Employment
The digital divide significantly impacts educational opportunities and employment prospects for rural communities. Limited access to high-speed internet restricts access to online learning resources, hindering academic progress and career advancement. This disparity in internet access creates a crucial barrier to economic development, impacting both individual and societal growth.Rural communities often face unique challenges in bridging this gap. From the cost of internet service to the lack of reliable infrastructure, these hurdles create a significant obstacle to progress.
The digital divide, unfortunately, continues to separate rural and urban internet users. This disparity is often amplified by issues like limited infrastructure and affordability. For example, Google’s China filtering, as highlighted in the article googles china filtering draws fire , showcases how complex geopolitical factors and internet censorship can exacerbate these existing problems. Ultimately, bridging this gap requires a multifaceted approach to ensure equitable access for everyone.
Addressing these issues is essential for fostering equitable opportunities in education and employment.
Rural Educational Opportunities
The lack of robust internet connectivity in rural areas severely restricts access to online educational resources. Students in these regions often lack access to interactive learning platforms, virtual libraries, and online tutoring services, which are increasingly prevalent in urban areas. This disparity in access can lead to significant academic gaps, impacting their future educational and career paths. Rural schools may struggle to afford or maintain the technology necessary to provide comprehensive online learning experiences, potentially exacerbating the existing inequalities.
Internet’s Role in Rural Entrepreneurship
The internet plays a pivotal role in supporting rural entrepreneurship and job creation. Online platforms provide access to global markets, enabling rural businesses to reach a wider customer base. E-commerce allows small businesses to compete with larger corporations, fostering innovation and economic growth. This access can be particularly beneficial for rural entrepreneurs who may lack traditional retail spaces or face geographical limitations.
Challenges Faced by Rural Businesses in Online Markets
Rural businesses encounter numerous challenges in accessing online markets. Limited internet bandwidth and unreliable connectivity can hinder efficient online transactions and communication. Furthermore, the lack of digital literacy among some rural entrepreneurs can be a significant hurdle to utilizing online platforms effectively. The absence of reliable digital infrastructure can pose challenges in processing online payments and maintaining secure online transactions.
The need for reliable and affordable internet access is crucial for rural businesses to thrive in the digital age.
Leveraging the Internet to Overcome Rural Challenges
Numerous rural businesses have effectively leveraged the internet to overcome various challenges. For instance, farmers can use online platforms to connect with buyers, sell produce directly to consumers, and access market information, enabling them to increase their revenue streams. Similarly, craft artisans can use online marketplaces to reach a broader audience and sell their products globally. These examples demonstrate the potential of the internet to foster economic growth in rural communities.
Remote Learning and Online Education Opportunities
The internet has revolutionized remote learning and online education opportunities. Online courses, webinars, and virtual classrooms allow individuals in rural areas to access educational resources previously unavailable. This expands access to higher education and professional development, fostering personal and professional growth. Online learning platforms offer flexibility and accessibility, making education more accessible to those in remote locations. However, challenges such as unreliable internet connectivity, limited digital literacy, and lack of technical support must be addressed to ensure effective implementation.
Policy and Solutions

Bridging the digital divide requires a multifaceted approach encompassing government policies, private sector initiatives, and community involvement. Existing policies, while often well-intentioned, frequently fall short in reaching remote and underserved populations. This section explores existing policies, identifies gaps, and proposes innovative solutions to effectively address the digital divide in rural areas, highlighting the crucial role of all stakeholders.Effective policies must consider the specific needs and challenges faced by rural communities, such as limited infrastructure, economic constraints, and a lack of digital literacy programs.
Innovative solutions must be adaptable and scalable, ensuring equitable access to technology and digital resources for everyone.
Existing Policies and Initiatives
Many governments worldwide have implemented policies and initiatives to address the digital divide. These range from subsidies for internet access to the provision of digital literacy training. However, the effectiveness of these policies often varies depending on factors like community size, geographical location, and local needs. Understanding these complexities is crucial for designing effective solutions.
Gaps and Limitations in Existing Policies
A significant gap in existing policies often lies in the lack of tailored solutions for rural areas. Many policies are designed with urban contexts in mind, neglecting the unique challenges faced by rural communities. This can include insufficient funding for infrastructure development in remote areas, a lack of awareness about the specific digital needs of rural populations, and a shortage of qualified instructors for digital literacy programs.
These limitations can hinder the effectiveness of existing policies.
Innovative Solutions to Address the Digital Divide in Rural Areas
Innovative solutions must address the specific needs of rural communities. This includes expanding broadband access through community-based initiatives like community fiber networks or deploying satellite internet solutions to reach remote locations. Providing digital literacy programs in local languages and using mobile technology to deliver training are also important aspects of this approach. Further, establishing partnerships with local businesses and community organizations to offer internet access and training can create sustainable solutions.
Examples of Successful Initiatives Bridging the Digital Divide
Several rural communities have successfully implemented programs to bridge the digital divide. One example involves a rural school district partnering with a local telecommunications company to install high-speed internet access throughout the district. This not only enhanced educational opportunities but also opened up new economic prospects for the community. Another initiative focused on providing free computer labs and digital literacy workshops in underserved rural areas, fostering digital skills among residents.
Role of Stakeholders in Closing the Digital Divide
Closing the digital divide requires a collaborative effort from various stakeholders. Governments can play a crucial role by allocating resources to infrastructure development and digital literacy programs. The private sector can contribute by offering affordable internet access and promoting digital literacy initiatives. Community organizations can facilitate the implementation of local programs and provide ongoing support to rural communities.
This collaborative approach ensures that solutions are tailored to the specific needs of each community.
Summary of Policy Initiatives and Their Impact
| Policy | Description | Impact (Rural) | Impact (Urban) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Policy A (Example: Community Fiber Network Subsidy) | Subsidies for rural communities to install and maintain high-speed internet access via community-owned fiber optic networks. | Improved broadband access, increased economic opportunities, enhanced educational opportunities. | Improved access to broadband, potential for increased competition among providers. |
| Policy B (Example: Mobile Digital Literacy Program) | Mobile training units equipped with technology and digital literacy instructors, visiting remote rural areas to provide workshops. | Increased digital literacy and skills, enhanced access to information, support for remote communities. | Potential for upskilling initiatives and increased digital literacy for urban residents. |
Concluding Remarks

In conclusion, the digital divide separating rural and urban internet users is a complex issue requiring multifaceted solutions. Addressing the infrastructure gap, improving affordability, and fostering digital literacy are crucial steps. Government policies, private sector initiatives, and community involvement are all vital components of bridging this divide and ensuring equitable access to the digital world for all. Ultimately, closing this divide is not just about technology; it’s about creating a more inclusive and prosperous society for everyone.