Automotive Blindspot Technologies Set to Take Off
Automotive blindspot technologies set to take off, promising safer roads and a more intuitive driving experience. This emerging technology is rapidly evolving, incorporating advanced sensors and sophisticated algorithms to enhance driver awareness and prevent accidents. From radar and camera systems to ultrasonic sensors, the different types of blind spot technologies are rapidly improving in range, accuracy, and reliability.
This detailed exploration dives into the market trends, safety features, technological advancements, and challenges surrounding these crucial automotive innovations. We’ll examine how these systems are changing the landscape of driver-assistance technologies and what the future holds for their continued development and adoption.
Introduction to Automotive Blindspot Technologies
Blind spot detection systems are rapidly evolving from a luxury feature to a crucial safety component in modern vehicles. These systems use various technologies to detect vehicles in the driver’s blind spots, alerting the driver to potential hazards and preventing collisions. Early systems relied on simple visual cues, but advancements have led to sophisticated sensor-based systems that offer enhanced awareness and improved safety.Blind spot detection systems have significantly improved road safety by providing drivers with crucial information about surrounding vehicles.
The initial systems were primarily reactive, merely alerting the driver to a potential hazard. Current advancements involve proactive safety measures, such as automatic braking or lane keeping assistance, integrating blind spot monitoring with other driver-assistance features.
Blind Spot Detection System Types
Different types of sensors are employed in blind spot detection systems, each with its unique characteristics and performance attributes. The core functionalities of these sensors are essential for their respective roles in providing accurate and timely information to the driver.
- Radar sensors use radio waves to detect objects in the vehicle’s blind spot. Their primary function is to measure the distance and speed of surrounding vehicles. This technology provides reliable detection in various weather conditions and can be crucial in situations involving slower-moving vehicles or those partially hidden by obstacles.
- Camera-based systems use visual imagery to identify and track objects. Cameras provide a comprehensive view of the surroundings, enabling them to detect vehicles and other objects, even if obscured by shadows or other conditions that might impact radar performance. Advanced algorithms analyze the visual data to provide accurate and timely warnings to the driver.
- Ultrasonic sensors emit high-frequency sound waves to detect objects. Their function is to provide a relatively short-range detection of objects in the immediate vicinity of the vehicle. These systems are often integrated with other sensor types for a more complete picture of the surrounding environment. They can also detect obstacles in tight spaces where radar and camera sensors might not be optimal.
Comparison of Blind Spot Detection Systems
| Feature | Radar | Camera | Ultrasonic |
|---|---|---|---|
| Range | Good, often extending beyond the immediate blind spot, up to several hundred meters | Good, can be effective up to several hundred meters, dependent on the camera’s resolution and the surrounding lighting | Limited, generally within a few meters of the vehicle |
| Accuracy | Generally high, reliable in various weather conditions and for different types of vehicles, but may struggle with highly reflective or metallic surfaces | High, particularly effective in clear weather and good lighting, but prone to inaccuracies in adverse weather conditions, such as heavy rain or fog, or when the vehicle being detected is partially obscured | Moderate, less precise than radar or camera, more susceptible to false positives |
| Cost | Moderate, often balanced between range, reliability, and cost | Generally moderate to low cost, often a more affordable solution than radar in some cases | Low, often the most cost-effective solution |
| Reliability | High, generally robust in various environmental conditions | High, but can be affected by weather conditions, especially fog or heavy rain | Moderate, reliability can be impacted by weather and certain types of obstacles |
Market Trends and Growth Potential
The automotive industry is undergoing a significant transformation, with blind-spot detection systems rapidly becoming a standard feature rather than a luxury. This shift is driven by a confluence of factors, including rising safety concerns, evolving consumer preferences, and technological advancements. The potential for future innovations in this space is substantial, promising even safer and more intelligent driving experiences.
Key Market Trends
Several key trends are driving the adoption of blind-spot detection technologies. Increased consumer awareness of safety features, fueled by media coverage of accidents and government initiatives, is a primary motivator. Manufacturers are responding to this demand by incorporating these systems into their vehicles, not only to improve safety but also to enhance their brand image and competitive advantage.
Additionally, regulations and safety standards are evolving to mandate the presence of advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), including blind-spot detection, in new vehicles. This regulatory pressure significantly accelerates market adoption.
Projected Market Growth
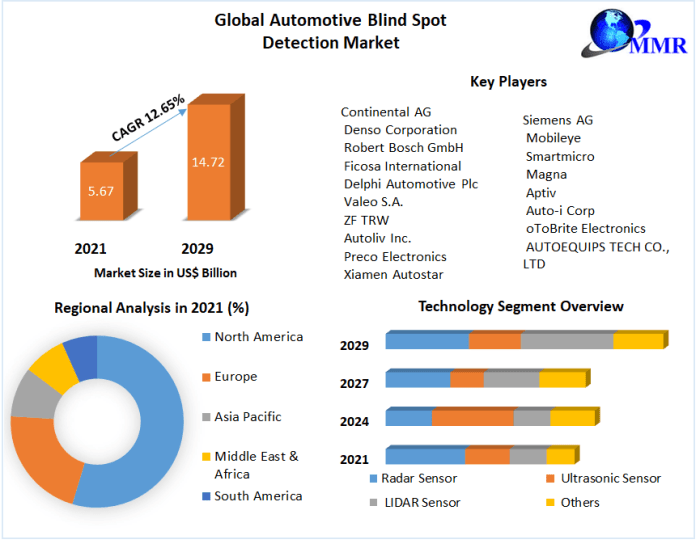
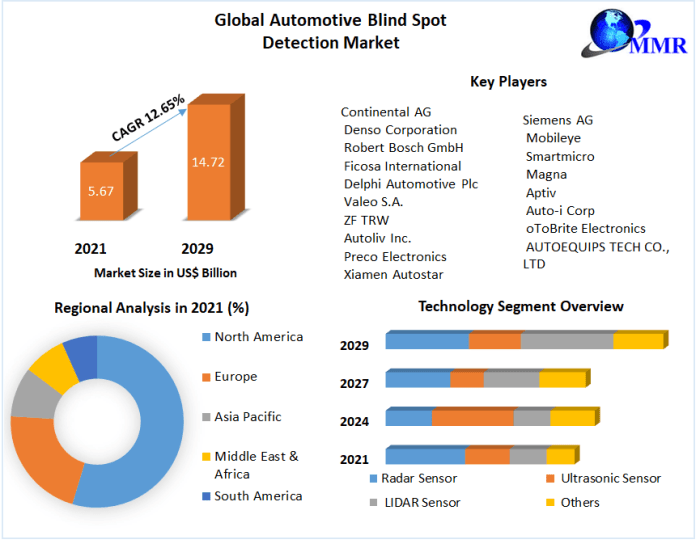
The automotive blind-spot technology market is experiencing robust growth. Data indicates that the market is expected to surpass a certain value by 2028, with a significant compound annual growth rate (CAGR) projected over the next five years. This growth is attributed to the factors mentioned earlier, including rising consumer demand, escalating safety standards, and ongoing technological advancements. The adoption rate of these technologies is increasing at an accelerating pace, particularly in the premium and luxury vehicle segments.
Examples of Current Systems
Several vehicle manufacturers are already incorporating advanced blind-spot detection systems into their models. Examples include radar-based systems, which utilize radio waves to detect objects in the blind spots, and camera-based systems that employ visual sensors to provide a clear view of the surrounding area. These systems often integrate with other ADAS features like lane departure warnings and adaptive cruise control.
Future Innovations
The future of blind-spot technologies promises exciting innovations. The development of more sophisticated sensors, such as those employing lidar technology, is expected to enhance the accuracy and reliability of blind-spot detection. Moreover, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms will likely allow for more proactive and intelligent responses to potential hazards, such as automatically adjusting braking or steering to mitigate collisions.
Projected Market Share (2028)
| Technology | Projected Market Share (2028) |
|---|---|
| Radar | 45% |
| Camera | 35% |
| Ultrasonic | 20% |
This table presents a projection of the market share for different blind-spot technologies by 2028. The dominance of radar is expected due to its robustness in various weather conditions and its ability to detect objects at longer ranges. Camera technology is predicted to gain significant traction due to its ability to provide a clearer visual representation of the surroundings.
Automotive blindspot technologies are poised for a major surge in popularity, promising safer roads for everyone. This exciting development aligns perfectly with Bill Ballmer’s commitment to innovation security, as highlighted in his recent pledge to support ballmer pledges support for innovation security. The increased investment in safety features like these could significantly reduce accidents and improve overall driving experiences.
Ultrasonic sensors, while relatively less expensive, may find application in niche markets or as supplemental technologies.
Safety and Driver Assistance Features

Blind spot monitoring systems are rapidly evolving from a luxury feature to a crucial safety component in modern vehicles. These systems, coupled with other driver assistance technologies, significantly reduce the risk of accidents, particularly those involving lane changes and rear-end collisions. Their increasing prevalence reflects a growing recognition of the critical role they play in preventing potentially life-altering events on the road.Blind spot detection technologies contribute to accident prevention and mitigation by providing drivers with crucial visual and auditory alerts when a vehicle is in their blind spot.
Automotive blindspot technologies are poised for a major surge in popularity, promising safer roads for everyone. This exciting advancement in vehicle safety is closely related to broader internet protocol evolution, like ICANN’s recent steps toward IPv6. ICANN takes first steps toward IPv6 , which will inevitably improve the reliability and efficiency of connected car technology. Ultimately, these interconnected developments in both automotive safety and internet infrastructure are set to reshape the future of driving.
This proactive approach empowers drivers to make informed decisions, avoiding potentially dangerous maneuvers and reducing the likelihood of collisions. The effectiveness of these technologies has been demonstrated through numerous real-world scenarios where timely warnings prevented accidents.
Enhanced Vehicle Safety
Blind spot monitoring systems, in conjunction with other advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), enhance vehicle safety by providing a layered approach to risk mitigation. They complement existing safety features like lane departure warnings and adaptive cruise control, offering a comprehensive suite of safeguards. By actively alerting drivers to potential hazards, these systems contribute to a safer driving environment.
Accident Prevention and Mitigation
Blind spot detection systems play a crucial role in accident prevention and mitigation, particularly in situations where lane changes are involved. By detecting vehicles in the blind spots, these systems allow drivers to react appropriately and avoid collisions. This proactive approach significantly reduces the risk of accidents caused by unawareness of surrounding vehicles. For instance, a timely warning from a blind spot detection system can prevent a collision when a driver attempts a lane change that is obstructed by a vehicle in their blind spot.
Comparison of Safety Features
Different safety features integrated with blind spot detection systems offer various levels of protection. Lane departure warning systems alert drivers if their vehicle is drifting out of its lane, while adaptive cruise control maintains a safe following distance from the vehicle ahead. Blind spot monitoring systems, however, focus specifically on detecting vehicles in the driver’s blind spots, providing a unique layer of protection that addresses a specific hazard.
These systems work synergistically with other ADAS to create a comprehensive safety net.
Role in Lane Changes, Automotive blindspot technologies set to take off
Blind spot monitoring systems directly address the risk of accidents associated with lane changes. By alerting drivers to vehicles positioned in their blind spots, these systems significantly reduce the likelihood of collisions when changing lanes. The warnings empower drivers to make more informed decisions, preventing potentially hazardous lane change maneuvers. Real-world data consistently demonstrates a correlation between blind spot detection systems and a decrease in lane change-related accidents.
Impact on Traffic Fatalities
The integration of blind spot monitoring systems into vehicles is projected to contribute to a reduction in traffic fatalities. By proactively preventing accidents, these systems reduce the number of collisions and injuries, ultimately leading to a safer road environment for all users. Statistics from countries where blind spot detection systems are more prevalent often reveal a lower rate of traffic fatalities compared to areas with less widespread adoption.
This trend highlights the potential of these systems to save lives on the road.
Technological Advancements and Innovations
Blind spot detection systems are rapidly evolving, driven by a relentless pursuit of enhanced safety and driver comfort. This evolution is fueled by innovations in sensor technology, artificial intelligence, and system integration. The future promises even more sophisticated blind spot monitoring, capable of anticipating potential hazards and proactively assisting drivers.
Innovative Blind Spot Technologies Under Development
Several innovative technologies are being explored to improve blind spot detection accuracy and reliability beyond the current capabilities. These include advanced radar systems capable of discerning smaller objects and those that are more difficult to perceive, like motorcycles or bicycles. Furthermore, researchers are exploring the use of cameras with enhanced image processing to improve the identification of obscured or partially visible vehicles.
Some systems are experimenting with combining multiple sensor types for a more comprehensive and reliable detection method.
Latest Advancements in Sensor Technology
The precision and range of sensor technology are significantly impacting blind spot detection systems. Radar technology is advancing, enabling the detection of smaller objects at greater distances. Lidar sensors are also gaining traction due to their ability to provide detailed 3D data of the surrounding environment, offering a more accurate picture of the space around the vehicle. Furthermore, improved signal processing techniques are helping to filter out noise and interference, leading to a more robust and accurate detection process.
Sophisticated sensor fusion is also emerging, combining data from different sensor types to enhance the reliability of blind spot detection.
Role of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are significantly impacting the accuracy and adaptability of blind spot detection systems. AI algorithms can learn to identify patterns in data, helping to recognize subtle cues that might be missed by traditional systems. This includes recognizing various types of vehicles, differentiating between pedestrians and objects, and understanding the dynamic behavior of other drivers on the road.
ML allows the system to adapt to diverse driving conditions, such as varying weather conditions or different road layouts, improving the accuracy and reliability of the system. AI-powered systems can also learn from past experiences to improve the system’s accuracy over time.
Integration of Blind Spot Detection with Other Driver-Assistance Systems
Blind spot detection is increasingly being integrated with other driver-assistance systems. For example, adaptive cruise control systems can integrate blind spot data to prevent lane changes that could lead to collisions. Lane keeping assistance systems can also utilize blind spot information to help the driver stay within their lane and avoid collisions with vehicles in the blind spot.
These integrated systems work together to create a more comprehensive safety net for the driver, proactively preventing potential accidents.
Automotive blindspot technologies are poised for a massive leap forward, promising safer roads for everyone. This surge in innovation mirrors the recent news of Cisco and Fujitsu’s expected dominance in the Japanese router market, demonstrating a parallel trend of technological advancement in diverse sectors. Ultimately, these advancements in both automotive safety and networking infrastructure point towards a future with more sophisticated and interconnected systems, paving the way for even greater progress in automotive blindspot technologies.
Future Advancements and Impact on Driver Safety and Comfort
Future advancements in blind spot detection promise a significant improvement in driver safety and comfort. Systems capable of predicting potential hazards, such as a vehicle unexpectedly changing lanes or a cyclist entering a blind spot, can provide drivers with early warnings and proactive interventions. This proactive approach can significantly reduce the risk of accidents. Enhanced comfort will be a result of the increased driver awareness and reduced stress, leading to a safer and more enjoyable driving experience.
Challenges and Future Considerations
The rapid advancement of automotive blindspot technologies promises a safer driving experience, but widespread adoption faces significant hurdles. Understanding these challenges, alongside economic and regulatory factors, is crucial to accurately predicting the future of this evolving market. The success of blindspot technology hinges not only on technological innovation but also on its seamless integration into the existing infrastructure and consumer acceptance.
Economic Factors Affecting Deployment
The development and deployment of blindspot technologies are significantly influenced by economic factors. High initial investment costs for research, development, and manufacturing can deter both manufacturers and consumers. The cost of incorporating advanced sensor technology, sophisticated algorithms, and robust testing procedures into vehicles is substantial. Furthermore, the cost of maintenance and potential repairs for these systems must also be considered.
The economics of scale and the volume of vehicles equipped with blindspot technology will play a crucial role in reducing the cost of these systems over time. Real-world examples of similar technologies, like adaptive cruise control, illustrate how decreasing costs through increased production and adoption can drive widespread consumer acceptance.
Regulatory Aspects of Implementation
Regulations play a vital role in shaping the implementation of blindspot detection systems. Standardization of testing protocols, safety certifications, and mandated features are crucial for ensuring consistent performance and consumer safety. Regulatory bodies need to consider how blindspot systems interact with other safety features, such as lane departure warnings or automatic emergency braking. Different countries and regions have varying regulations, which can create inconsistencies and complicate the global rollout of these technologies.
Harmonizing regulations across regions will be crucial for fostering global adoption and driving innovation.
Impact of Consumer Acceptance
Consumer acceptance is a critical factor in the future growth of the blindspot technology market. Drivers must trust the accuracy and reliability of these systems, and the user experience must be intuitive and easy to understand. Consumer perception of the value proposition of these technologies, balancing safety benefits with cost, will ultimately determine their adoption. The success of similar driver-assistance features like adaptive cruise control and lane-keeping assist demonstrates that user trust and experience are crucial for widespread market penetration.
Positive experiences and feedback from early adopters can drive wider acceptance and create a demand for such features.
Potential Regulatory Hurdles and Solutions
| Hurdle | Solution |
|---|---|
| Lack of standardized testing protocols for blindspot systems | Development and implementation of globally recognized testing protocols by organizations like the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) or the European Union’s equivalent. |
| Varying regulations across countries and regions | International collaboration and standardization of regulations to create a unified approach to the deployment and use of blindspot detection systems. |
| Integration with existing safety features and systems | Developing clear guidelines and protocols for the seamless integration of blindspot systems with existing vehicle safety features to avoid interference or incompatibility. |
The table above illustrates potential regulatory hurdles and their potential solutions for blind spot technology implementation. Addressing these issues is vital for ensuring the safe and widespread adoption of these life-saving technologies.
Design and Implementation Considerations
Blind spot detection systems are rapidly evolving, becoming increasingly sophisticated and crucial for enhancing vehicle safety. Successfully integrating these systems into existing vehicle architectures requires careful planning, consideration of various design strategies, and rigorous testing procedures. This section delves into the intricacies of designing and implementing blind spot detection systems, emphasizing key considerations and practical examples.The design and implementation of blind spot detection systems encompass a multifaceted approach.
From sensor selection and signal processing to user interface design and integration with existing vehicle systems, every step plays a critical role in the final performance and reliability of the system. A comprehensive understanding of these factors is essential for creating effective and safe blind spot detection systems.
Sensor Selection and Placement
The choice of sensors significantly impacts the accuracy and reliability of blind spot detection. Radar sensors, often preferred for their ability to operate in various weather conditions, offer robust detection capabilities. Camera-based systems, on the other hand, provide a wider field of view, which can improve overall situational awareness. Placement of these sensors is equally important, needing to ensure optimal coverage of the blind spot area while minimizing interference from other vehicle components.
Considerations include the vehicle’s design, mounting constraints, and the need to avoid obstruction by other parts. For example, a vehicle with a prominent rear spoiler might require a more precisely positioned radar sensor to avoid interference.
Integration with Existing Vehicle Systems
Integration with existing vehicle systems is crucial for seamless operation. The blind spot detection system must communicate effectively with other components, such as the braking system and the driver information display. A robust communication protocol ensures timely and accurate information exchange. For instance, a clear communication pathway between the blind spot detection system and the driver’s display allows for immediate visual alerts, improving the driver’s reaction time.
Interfacing with existing systems involves careful consideration of data formats, timing constraints, and potential conflicts.
Design Strategies for Blind Spot Detection
Different design strategies can be employed to incorporate blind spot detection into a vehicle. A modular design, for instance, allows for easier upgrades and adaptations to future technologies. Alternatively, a tightly integrated system can optimize performance by reducing latency and improving overall efficiency. Examples include the use of radar sensors for detecting vehicles in blind spots and cameras for providing a visual confirmation of the detection.
A multi-sensor fusion approach combining data from radar and cameras can further enhance accuracy and reliability.
Evaluation and Testing Procedures
Evaluating the performance of a blind spot detection system is a critical step in the design process. Testing procedures need to cover various scenarios, including different vehicle speeds, weather conditions, and other factors that might influence detection accuracy. Realistic simulations and controlled testing environments are often used to simulate diverse situations. Metrics for evaluating the system’s performance should be well-defined, encompassing aspects like detection accuracy, response time, and false positive rates.
Examples include comparing the system’s performance with established industry standards or benchmarks.
Flowchart for Testing a Blind Spot Detection System
Start | V Define Test Scenarios (e.g., different speeds, weather conditions) | V Prepare Test Environment (e.g., controlled track, test vehicles) | V Calibrate Sensors and Systems | V Execute Test Scenarios | V Analyze Data (e.g., accuracy, response time) | V Evaluate Results Against Specifications | V Iterate and Refine System (if necessary) | V End
This flowchart illustrates the key steps in testing a new blind spot detection system, ensuring comprehensive coverage of diverse scenarios and providing data-driven insights for improvement.
Each step contributes to a more reliable and robust system.
Consumer Perception and Adoption
Blindspot detection systems are rapidly evolving, promising enhanced safety and convenience for drivers. However, successful adoption hinges on consumer perception and trust. Understanding consumer attitudes and the factors driving their decision-making is crucial for manufacturers to effectively market these technologies and achieve widespread adoption. This section delves into the nuances of consumer perception, highlighting key influences and potential strategies for building trust in these innovative systems.
Consumer Attitudes and Perceptions
Consumer attitudes towards blindspot detection systems are generally positive, driven by a desire for increased safety on the road. Studies consistently show that drivers perceive blind spot monitoring as a valuable safety feature, reducing the risk of accidents and enhancing awareness of surrounding vehicles. This positive perception is further fueled by a growing awareness of the potential for accidents caused by blind spots.
The perception of blind spot detection as a proactive safety measure contributes to its appeal to consumers.
Factors Influencing Consumer Adoption
Several factors significantly influence consumer adoption of blind spot detection systems. Price is a primary concern, with affordability playing a crucial role in driving consumer interest and uptake. The perceived value proposition of the technology, including its effectiveness in preventing accidents and enhancing driver confidence, also plays a key role. Additionally, consumer trust in the reliability and safety of the technology is essential.
Furthermore, the availability of comprehensive information about the technology, including clear explanations of its functionality and benefits, is essential for building consumer trust and encouraging adoption. Finally, ease of use and integration with existing vehicle systems are key factors.
Impact of Marketing Strategies
Different marketing strategies have varying impacts on consumer perception. Marketing campaigns focusing on safety benefits and accident prevention tend to resonate strongly with consumers, emphasizing the life-saving potential of the technology. Highlighting the technology’s ability to improve driver confidence and reduce stress associated with driving is also effective. Demonstrating the technology’s ease of use and seamless integration into the vehicle’s existing features can foster positive consumer perception.
Conversely, marketing campaigns that focus solely on the technology’s advanced features without connecting them to tangible benefits for the driver may fail to capture consumer interest.
Potential Benefits from a Consumer Perspective
From a consumer perspective, blind spot detection systems offer several benefits. These benefits include improved safety, enhanced awareness of surrounding vehicles, reduced stress and anxiety associated with lane changes and merging, and improved overall driving confidence. Furthermore, the technology can potentially contribute to a safer driving environment by preventing accidents caused by blind spots. The increased awareness of surrounding vehicles allows for smoother and more confident lane changes, potentially leading to improved traffic flow.
These benefits contribute to a positive user experience, leading to increased adoption.
Building Consumer Trust
Building consumer trust in blind spot detection systems is paramount. Transparency in the technology’s functionality and its limitations is crucial. Demonstrating the technology’s effectiveness through real-world examples, such as case studies and testimonials from satisfied users, can significantly enhance consumer trust. Clear and easily understandable explanations of the technology’s operation, including its limitations and potential error situations, are also critical.
Moreover, partnerships with reputable organizations and institutions known for safety and quality can bolster the technology’s credibility and enhance consumer confidence.
Final Conclusion: Automotive Blindspot Technologies Set To Take Off
In conclusion, automotive blindspot technologies are poised for significant growth, driven by a confluence of factors including safety concerns, evolving consumer preferences, and technological advancements. While challenges remain, the potential benefits for enhancing driver safety and comfort are undeniable. The future of driving is undoubtedly being shaped by these innovations.