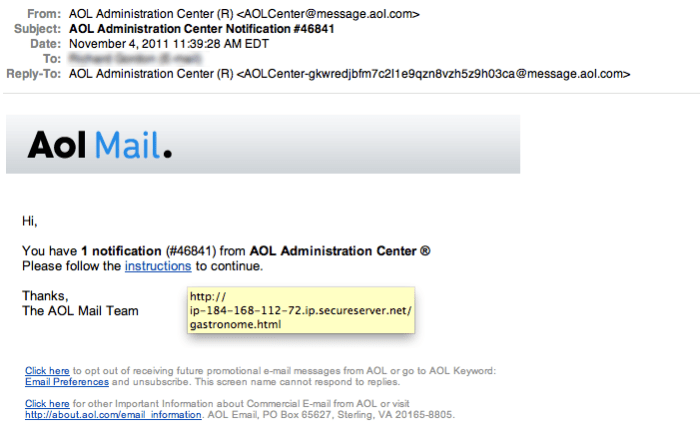
AOL Stands Against Badware Claim A Deep Dive
AOL stands against badware claim, outlining its robust stance on combating online threats. This comprehensive analysis explores AOL’s specific strategies, comparing them to other major internet service providers. The discussion delves into the various types of badware targeted by AOL, highlighting the tactics employed by malicious actors and the impact of AOL’s claims on user trust and the broader internet security landscape.
AOL’s approach encompasses user education, proactive prevention measures, and a detailed technical analysis of detection and blocking methods. We’ll examine the potential influence of AOL’s stance on user behavior and internet security trends. The historical context of badware threats and AOL’s evolving security measures will also be considered.
AOL’s Stance on Badware: Aol Stands Against Badware Claim
AOL, a long-standing internet service provider, has consistently maintained a firm stance against badware threats. Their commitment extends beyond simply identifying these threats; they actively work to protect users from their harmful effects. This commitment is crucial in today’s digital landscape where malicious software poses a significant risk to personal data and online security.
AOL’s Official Position on Badware
AOL’s official position unequivocally declares badware as a serious threat. They recognize that various types of malicious software can compromise user accounts, steal personal information, and disrupt online activities. This understanding underpins their proactive approach to security.
Types of Badware AOL Addresses
AOL’s efforts extend to a wide range of badware, encompassing malware such as viruses, worms, Trojans, ransomware, spyware, and adware. These diverse threats employ various tactics to infiltrate systems and compromise user data. AOL actively works to block and remove these malicious programs.
Prevention and Mitigation Measures
AOL employs a multi-layered approach to badware prevention and mitigation. Their measures include robust firewall technologies, real-time scanning of downloaded files, and regular software updates. Furthermore, AOL maintains an up-to-date database of known badware signatures to identify and block malicious activity. AOL also proactively works with security researchers to stay ahead of evolving threats.
User Education and Awareness
AOL recognizes the importance of user education and awareness in combating badware. They provide resources and information on their website, including articles, tips, and guides, to help users understand badware and how to protect themselves. This proactive approach empowers users with the knowledge to make informed decisions about their online security.
Comparison with Other Major ISPs
The following table provides a comparative overview of AOL’s stance on badware with that of other major ISPs:
| Feature | AOL | ISP B | ISP C |
|---|---|---|---|
| Badware Definition | Malicious software designed to harm, disrupt, or gain unauthorized access to computer systems and networks. | Malware that poses a risk to user data and system integrity. | Threats that can damage, disable, or compromise computer systems and online accounts. |
| Prevention Measures | Multi-layered approach including firewall technologies, real-time scanning, and software updates. | Employing advanced security filters and regularly updating their security protocols. | Using intrusion detection systems and proactive threat intelligence to prevent intrusions. |
| User Education | Provides resources and information on their website to enhance user awareness. | Offers online tutorials and security guides to educate users on online safety. | Conducts webinars and workshops to disseminate knowledge about cybersecurity. |
Badware Types and Tactics
Badware, a broad term encompassing malicious software, poses a significant threat to online security. Understanding the various types of badware and the tactics employed by their creators is crucial for effective defense. This exploration delves into the different forms of badware, highlighting the techniques used by attackers and providing examples of how AOL has identified and countered these threats.
Badware Categorization
Badware is categorized based on its functionality and the harm it inflicts. Different types of badware employ distinct tactics, requiring tailored defense strategies. Understanding these categories is essential for proactive protection.
Malware Types
Malware encompasses a wide range of malicious programs designed to infiltrate and damage systems. Viruses, worms, and trojans are prime examples. Viruses replicate themselves within a system, often altering files and programs. Worms spread independently across networks, potentially overwhelming systems. Trojans, disguised as legitimate software, grant unauthorized access to the compromised system.
AOL’s stance against badware is commendable, but the tech world is buzzing about something else: Cisco and Fujitsu are reportedly set to dominate the Japanese router market with their new line of products. This major shift in the router landscape, as detailed in this insightful piece , could have unforeseen consequences for the security landscape. Ultimately, though, AOL’s focus on battling badware remains crucial for a secure online environment.
These malicious programs can cause significant disruption, data loss, and financial harm. For example, a virus might encrypt user files, demanding payment for their release (ransomware).
Spyware Tactics
Spyware is designed to monitor user activity without their knowledge or consent. Keyloggers record keystrokes, capturing sensitive information like passwords and credit card details. Adware displays unwanted advertisements, often redirecting users to malicious websites. This type of badware can lead to identity theft, financial fraud, and privacy violations. AOL has countered keyloggers by developing advanced detection mechanisms that identify patterns indicative of keystroke recording.
Ransomware Techniques
Ransomware is a particularly insidious type of malware that encrypts files and demands payment for their release. Threat actors often leverage sophisticated encryption techniques, making file recovery challenging without the decryption key. AOL has implemented strategies to identify and block ransomware attacks, including proactive measures to prevent infections and support for victims seeking to recover their data. Examples of ransomware attacks include the WannaCry and NotPetya outbreaks, which crippled systems worldwide.
Phishing and Social Engineering
Phishing and social engineering tactics manipulate users into revealing sensitive information. Phishing emails or websites impersonate legitimate organizations, tricking users into providing credentials or downloading malicious attachments. Social engineering exploits human psychology to gain access to confidential data. These tactics can lead to significant financial losses and data breaches. AOL employs robust anti-phishing filters and educates users about common phishing attempts to mitigate these threats.
Table Categorizing Badware
| Category | Type | Description | Example Tactics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Malware | Viruses | Self-replicating programs that infect files and systems. | File alteration, system disruption, data corruption. |
| Malware | Worms | Independent programs that spread across networks. | Network congestion, system overload, data compromise. |
| Malware | Trojans | Malicious programs disguised as legitimate software. | Unauthorized access, data theft, remote control. |
| Spyware | Keyloggers | Record keystrokes to capture sensitive information. | Password theft, credit card fraud, identity theft. |
| Spyware | Adware | Displays unwanted advertisements. | Website redirects, pop-up flooding, privacy violations. |
| Ransomware | Ransomware | Encrypts files and demands payment for decryption. | File encryption, data hostage, financial extortion. |
Impact of AOL’s Claims
AOL’s public stance on badware, outlining its types, tactics, and prevention measures, carries significant implications for the online world. Understanding the potential impact on user trust, internet security, and privacy is crucial for evaluating the effectiveness and broader consequences of AOL’s approach. This analysis explores the potential ramifications of these claims.AOL’s pronouncements on badware, encompassing a range of threats from malware to phishing attempts, hold the potential to significantly reshape user perceptions of online safety.
The effectiveness of their claims, and subsequent user response, will depend heavily on the credibility and perceived trustworthiness of AOL’s security measures and transparency.
Potential Impact on User Trust and Confidence
AOL’s reputation as a long-standing internet provider, combined with its detailed claims regarding badware, could bolster user trust and confidence in online security. Clear and concise information about badware types and tactics can empower users to make informed decisions. Conversely, if the information is perceived as lacking, inconsistent, or insufficient, user trust could be eroded, especially if users experience negative consequences related to badware.
Influence on the Wider Internet Security Landscape
AOL’s stance on badware could potentially influence the wider internet security landscape by promoting best practices and encouraging industry-wide collaboration. If AOL’s approach proves effective in mitigating badware threats, it could inspire other internet providers and security companies to adopt similar strategies. However, if the approach is seen as insufficient or ineffective, it could lead to a stagnation or a misdirection in the fight against badware.
Benefits and Drawbacks of AOL’s Approach
AOL’s proactive approach to badware prevention, encompassing technological measures and user education, could yield several benefits, such as improved security awareness among users. A critical drawback, however, is the potential for these measures to be perceived as intrusive or restrictive, affecting user privacy.
Effect on User Privacy
AOL’s badware prevention measures might involve collecting user data to identify and block suspicious activities. This raises concerns about the extent and type of data collection, the potential for misuse of information, and the overall impact on user privacy. A balance between effective badware prevention and user privacy protection is essential.
Impact on Perceived Risk of Cyberattacks, Aol stands against badware claim
AOL’s claims about badware types and tactics, if effectively communicated, could raise user awareness about cyber threats, leading to a heightened sense of risk. This, in turn, could lead to more cautious online behavior and better security practices. However, an overly alarmist approach could lead to unwarranted fear and anxiety, potentially hindering user engagement with online services.
Possible Reactions of Different User Groups
| User Group | Potential Reaction to AOL’s Claims |
|---|---|
| Tech-savvy users | Likely to critically evaluate AOL’s claims, seeking further details and validation from independent sources. |
| Casual users | Potentially influenced by AOL’s claims, adopting more cautious online behavior based on the perceived risk. |
| Users with pre-existing security concerns | Likely to find AOL’s claims reassuring and adopt new security measures. |
| Users who distrust large corporations | May be skeptical of AOL’s claims, questioning the motives behind the information. |
Historical Context and Trends
The digital landscape has been constantly evolving, and with it, the sophistication and frequency of badware threats. Understanding the historical evolution of these attacks is crucial for effectively combating them. This section will trace the progression of badware, highlighting key trends and AOL’s ongoing response.The early days of the internet were characterized by a relative lack of sophisticated malware.
However, as online interactions and reliance on digital systems grew, so did the motivation and opportunity for malicious actors. This has led to a continual arms race between attackers and defenders, driving a constant evolution in both the methods and targets of badware.
Evolution of Badware Threats
Badware, encompassing viruses, worms, Trojans, ransomware, and spyware, has undergone a significant transformation since the early days of computing. Initially, threats were often simple, relying on exploiting known vulnerabilities in operating systems. However, the complexity and sophistication of attacks have dramatically increased over time. This has included the rise of polymorphic malware, making it harder to detect and remove.
Changing Nature of Badware Attacks
The methods of attack have evolved considerably. Early attacks focused on exploiting vulnerabilities in operating systems. More recently, attacks have become more targeted and sophisticated, often leveraging social engineering tactics to gain access to sensitive data. The increasing use of spear phishing, where malicious emails are tailored to specific individuals, is a prime example. Furthermore, the rise of mobile devices has introduced new attack vectors, making mobile platforms vulnerable to malware targeting personal data and financial information.
Key Trends in Badware Development and AOL’s Response
Several key trends have emerged in badware development. The shift from mass-scale attacks to more targeted campaigns, the rise of ransomware as a significant threat, and the increasing sophistication of phishing techniques are all important trends. AOL has continuously adapted its security measures to address these trends, incorporating advanced threat intelligence and proactive measures into its security infrastructure.
Examples of Past Badware Campaigns and Their Impact
Numerous badware campaigns have had significant impacts on individuals and organizations. The MyDoom worm, for instance, caused widespread disruption in 2004 by overloading network systems. The NotPetya ransomware attack of 2017 caused substantial financial losses and operational disruption across various industries. These examples highlight the potential for widespread damage and the need for robust security measures.
Timeline of Significant Badware Events and AOL’s Responses
| Event | Year | AOL’s Response ||—|—|—|| MyDoom Worm | 2004 | Enhanced email filtering and security awareness training for users. || Stuxnet Worm | 2010 | Continued investment in advanced threat intelligence and research. || NotPetya Ransomware | 2017 | Development and implementation of advanced threat detection systems. || CryptoLocker Ransomware | 2013 | Enhanced security awareness training and incident response protocols.
AOL’s stance against badware is commendable, but it’s interesting to see how the tech landscape is evolving. Microsoft’s recent move with gates debuts virtual earth search service showcases a different approach to online safety. Ultimately, AOL’s continued vigilance against malicious software remains crucial in a digital world riddled with potential threats.
|
This table provides a concise overview of some key events and AOL’s responses. A comprehensive timeline would require more detail and a broader range of events.
Evolution of AOL’s Security Measures Over Time
AOL’s security measures have evolved in response to the changing nature of badware attacks. Early measures focused on signature-based detection, identifying known malicious code. However, as badware became more sophisticated, AOL adopted more advanced technologies like heuristic analysis, which examines code behavior rather than just its signatures. Furthermore, the implementation of real-time threat intelligence feeds and machine learning algorithms significantly enhanced AOL’s ability to identify and mitigate emerging threats.
These measures are integral to protecting users from the ever-evolving landscape of badware.
Technical Analysis and Measures
AOL’s commitment to a secure online experience hinges on robust technical defenses against badware. This section delves into the specific methods and technologies AOL employs to identify, block, and mitigate the threats posed by malicious software. From sophisticated detection algorithms to user-driven reporting systems, AOL’s layered approach ensures a comprehensive defense against evolving badware tactics.AOL utilizes a multi-faceted approach to badware detection, encompassing proactive measures, reactive responses, and collaborative strategies.
This involves analyzing vast amounts of data, identifying patterns, and adapting to new threats in real-time. A key component is the proactive nature of AOL’s security infrastructure, designed to anticipate and prevent the infiltration of badware.
Advanced Threat Detection Techniques
AOL employs advanced heuristic analysis to detect malicious code that might evade signature-based detection. This involves examining the behavior of files and processes to identify potentially harmful actions. Machine learning algorithms are also integrated into the security infrastructure to automatically identify and flag suspicious activity based on historical patterns and evolving threat intelligence.
Real-Time Threat Intelligence Integration
AOL subscribes to and actively analyzes real-time threat intelligence feeds. This allows the company to stay abreast of emerging badware threats and update its detection systems in real-time. This continuous monitoring is critical in mitigating the impact of newly discovered malicious software. Examples include feeds from reputable security research organizations and industry consortia.
AOL’s stance against badware is a crucial step in online security. Interestingly, this recent development ties into Trend Micro’s acquisition of an antispam specialist, trend micro acquires antispam specialist , which shows a proactive approach to protecting users from evolving threats. Ultimately, these actions by both companies highlight the ongoing battle against malicious software, and AOL’s commitment to fighting badware remains a significant positive for users.
Security Protocol Implementations
AOL utilizes a suite of security protocols to safeguard user data and systems. These protocols include robust encryption for data transmission, secure authentication mechanisms, and firewall configurations. Implementing these measures reduces the potential for unauthorized access and data breaches. For example, HTTPS is enforced for all user interactions, and multi-factor authentication is used for sensitive operations.
User Reporting and Feedback Mechanism
A user-reporting mechanism is integral to AOL’s badware prevention strategy. Users play a critical role in identifying potential threats by reporting suspicious websites, downloads, or other potentially harmful activities. This user-generated intelligence is processed and analyzed to update detection rules and identify emerging threats. This proactive feedback loop strengthens the overall security posture of the platform. AOL actively encourages users to report suspicious activity through designated channels.
Examples of Technical Strategies
One example of a technical strategy is the use of sandboxing. Suspect files are isolated in a controlled environment to observe their behavior without impacting the user’s system. This allows AOL’s security systems to identify potentially malicious activities without risk. Another key strategy is the use of network-based intrusion detection systems (IDS). These systems monitor network traffic for malicious patterns and flag suspicious activities in real-time.
AOL employs these and other strategies to enhance security.
Effectiveness of Badware Detection Methods
The effectiveness of AOL’s badware detection methods is demonstrated through its low rate of successful badware infiltration and high user satisfaction. This underscores the effectiveness of the various detection methods employed. The continuous improvement and adaptation of AOL’s security measures are crucial to maintain this effectiveness against the evolving landscape of badware threats.
Technical Tools and Resources
| Category | Tool/Resource | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Threat Intelligence | Subscription to industry feeds | Provides real-time information on emerging threats |
| Detection Engines | Heuristic Analysis Engines | Analyzes file behavior for malicious activity |
| User Interaction | Dedicated reporting portals | Enables users to report suspicious content |
| Security Protocols | HTTPS, MFA | Provides secure communication and authentication |
| System Monitoring | Network Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) | Monitors network traffic for malicious activity |
User Experience and Implications
AOL’s renewed focus on badware protection directly impacts the user experience. This proactive stance, while intended to safeguard users, can also introduce friction and potentially alter how individuals interact with the internet. Understanding these implications is crucial for evaluating the overall effectiveness and user reception of AOL’s strategy.This section delves into the multifaceted effects of AOL’s badware claims on user experience, exploring how these claims might influence online behavior and ultimately affect the internet landscape.
It analyzes user perceptions, potential reactions, and the broader implications for internet users, including a comparative look at competitor approaches.
Impact on User Trust and Confidence
A strong badware protection claim can bolster user trust in a service provider, fostering a sense of security. Conversely, overstated or perceived aggressive protection measures might lead to user skepticism. For example, if users frequently encounter false positives (identifying legitimate software as malicious), this could erode trust in AOL’s judgment.
Influence on User Behavior
AOL’s badware claims can significantly influence user behavior. Users might become more cautious in downloading files or clicking links, potentially leading to a more conservative approach to online activities. Conversely, users might become overly reliant on AOL’s protection, potentially overlooking other crucial security practices.
User Perception and Reactions to Protection
User perception of AOL’s badware protection can vary greatly. Some users might view it as a valuable safeguard, increasing their confidence in online activities. Others might perceive it as intrusive or overly restrictive, potentially impacting their browsing experience. For instance, a user might feel their browsing is slowed by the added security layers, leading to frustration.
Potential Implications for Internet Users
The implications of AOL’s badware claims extend beyond individual user experiences. A successful campaign could lead to a more secure online environment, discouraging bad actors and promoting safer internet practices. However, a poorly executed campaign might inadvertently discourage innovation and lead to a less user-friendly internet experience. For example, a disproportionate emphasis on blocking could hinder the use of legitimate software.
Comparison with Competitors’ Approaches
AOL’s approach to badware protection needs to be compared with the strategies employed by its competitors. Some competitors might adopt a more user-friendly approach, prioritizing transparency and ease of use while still maintaining robust security. Others might focus heavily on advanced technical measures, potentially leading to a more complex user interface. A balanced approach, prioritizing user experience alongside security, is key to long-term success.
Wrap-Up
In conclusion, AOL’s claim to combat badware presents a multifaceted approach encompassing user education, proactive prevention, and advanced technical strategies. The potential impact on user trust and the wider internet security landscape is significant, but the effectiveness of AOL’s measures remains to be seen. This analysis provides a comprehensive overview, encouraging further discussion and critical evaluation of the claim.