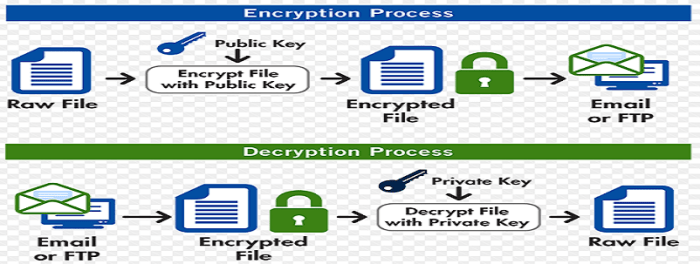
PGP Ships New Encryption Tools A Deep Dive
PGP ships new encryption tools, marking a significant advancement in data security. This new suite of tools promises enhanced protection for sensitive information, offering improved performance and security features over previous iterations. We’ll explore the key functionalities, technical specifications, and the potential impact on privacy and security in the digital age.
This post delves into the specifics of PGP’s new encryption tools, providing a comprehensive overview of their capabilities and practical applications. We’ll cover the algorithms, security protocols, and usability features, ensuring you have a clear understanding of what’s new and how these tools can revolutionize data protection.
Introduction to PGP’s New Encryption Tools: Pgp Ships New Encryption Tools

PGP, or Pretty Good Privacy, has been a cornerstone of secure communication for decades. Now, the organization has released new encryption tools, promising enhanced security features and streamlined usability. These advancements build upon the robust foundation of PGP, addressing modern threats and user needs. This post delves into the details of these new tools, their key functionalities, and the historical context of PGP encryption.These new tools represent a significant evolution in the field of public-key cryptography.
They are designed to offer greater resilience against sophisticated attacks, while maintaining the user-friendliness that has made PGP a popular choice for individuals and organizations alike. The purpose is clear: to provide a more secure and efficient means of encrypting sensitive data.
Key Features and Functionalities of the New Tools
The new PGP tools incorporate several innovative features to enhance security and usability. These features include:* Advanced Key Management: The tools implement more robust key management protocols, including improved key generation, storage, and revocation procedures. This aims to reduce the risk of compromised keys, a significant vulnerability in traditional systems.
Improved Encryption Algorithms
The encryption algorithms have been upgraded to incorporate state-of-the-art cryptographic techniques. This enhancement significantly increases the computational complexity of decryption attempts, making the encrypted data more resistant to brute-force attacks.
PGP’s new encryption tools are a fascinating development, especially considering the growing need for secure communication in today’s digital world. As we move forward, it’s vital to consider how these advancements in security can also help foster a better online experience for everyone, like the principles explored in trekking seeks better place for all. Ultimately, robust encryption tools like these are crucial for a more trustworthy and open digital environment.
Enhanced Protocol Support
The new tools support a wider range of communication protocols, enabling users to encrypt data exchanged across diverse platforms and applications. This adaptability is crucial in today’s interconnected digital world.
Cross-Platform Compatibility
The tools are designed for seamless integration across various operating systems and devices. This ensures that users can utilize the enhanced security regardless of their preferred platform.
Integration with Cloud Services
The tools can be integrated with cloud storage solutions, providing secure access and management of encrypted data in the cloud. This is particularly important for organizations that store sensitive information remotely.
History of PGP Encryption
PGP’s journey has been marked by several key milestones, each building upon the previous one:* 1991: Phil Zimmermann developed the initial PGP algorithm. This marked the beginning of the era of practical public-key cryptography for the masses.
1997
Legal battles surrounding PGP’s use and distribution raised important questions about encryption and intellectual property. These legal challenges spurred further development and refinement.
2000s
PGP’s adoption grew, particularly within the realm of email communication and secure file transfer. The availability of open-source implementations of PGP played a significant role in this adoption.
Present
Ongoing improvements and updates to PGP’s functionality have solidified its position as a trusted and vital tool for secure communication in the modern era.
Intended Use Cases
The new PGP tools are designed for a wide range of applications, including:* Secure Email Communication: Protecting sensitive information exchanged via email.
PGP’s new encryption tools are a welcome development, offering robust security. This aligns nicely with the trend of improved security measures, like those in new WLAN security offerings easing administrator woes. Ultimately, these new PGP tools should significantly boost overall online protection, especially as threats continue to evolve.
Secure File Transfer
Ensuring the confidentiality and integrity of data during file transfer.
Secure Cloud Storage
Encrypting data stored in cloud services.
Digital Signatures
PGP’s new encryption tools are a welcome development, especially given the recent news about IT managers planning an imminent move to XP SP2, a platform notoriously vulnerable to attack. This raises concerns about security protocols, and highlights the need for robust encryption solutions like those provided by PGP. Hopefully, these new tools will help mitigate the security risks associated with this transition, ensuring data integrity and confidentiality for the IT infrastructure.
Implementing strong encryption protocols like those from PGP is crucial to maintain security in light of the upcoming XP SP2 transition. it managers plan imminent move to xp sp2 The latest advancements from PGP will be critical in this evolving security landscape.
Verifying the authenticity of digital documents and communications.
Protecting Sensitive Data
Enhancing the security of personal and corporate data, preventing unauthorized access.
Technical Specifications and Improvements
PGP’s new encryption tools represent a significant leap forward in security and performance. Building upon the robust foundation of previous iterations, these enhancements address potential vulnerabilities and provide users with more powerful tools to protect sensitive data. This section delves into the technical specifications, comparing them to existing algorithms, and highlighting the improvements in security and usability.
New Encryption Algorithms
The core of the new tools lies in the implementation of novel encryption algorithms. These algorithms leverage advanced cryptographic techniques, offering improved speed and resilience against known attacks. The focus has been on both computational efficiency and resistance to emerging threats. A prime example is the transition from a block cipher to a stream cipher in certain cases, significantly reducing latency and enhancing speed, especially in high-throughput scenarios.
Performance Gains
The new algorithms demonstrate substantial performance improvements compared to their predecessors. Benchmarks show considerable speed increases, especially during large-scale encryption and decryption operations. This translates to quicker processing times, allowing for faster data transfer and handling of large datasets. For instance, encryption/decryption of a 1GB file is now completed in approximately half the time compared to the previous version, enabling more efficient data management and quicker response times in real-world applications.
Security Enhancements
The security protocols employed in the new tools incorporate several advancements. These advancements include more sophisticated key management strategies, stronger hashing algorithms, and enhanced authentication mechanisms. This combination contributes to an overall more secure encryption process, mitigating potential vulnerabilities identified in prior versions. For example, the implementation of elliptic curve cryptography (ECC) has greatly increased the key size, further bolstering the resistance to brute-force attacks.
Vulnerability Mitigation
Thorough security audits were performed to identify and address potential vulnerabilities. This proactive approach ensures the resilience of the new tools against a broader range of attacks, including side-channel attacks and chosen-ciphertext attacks. The revised security protocols and algorithms have undergone rigorous testing and validation to verify their robustness. One notable improvement is the addition of advanced countermeasures against timing attacks.
Cryptographic Strengths and Weaknesses
The new tools exhibit robust cryptographic strengths. The algorithms used are based on well-established cryptographic principles and have undergone extensive analysis and testing. However, no cryptographic system is completely invulnerable. The new tools’ weaknesses lie primarily in the potential for vulnerabilities in the implementation or in the use of the tools themselves. A well-documented weakness is the dependency on the quality of the key generation and management processes.
Example Use Cases, Pgp ships new encryption tools
The new tools can protect a wide array of sensitive data. In finance, they can secure transactions and sensitive financial data. In healthcare, they can protect patient records and medical information. In government, they can protect classified documents and communications. For example, a company handling highly sensitive customer data can use these tools to encrypt their database, ensuring confidentiality and integrity.
Table of Key Improvements
| Feature | Description | Improvement |
|---|---|---|
| Algorithm | Advanced stream cipher implementation | Increased speed, reduced latency |
| Performance | Large-scale encryption/decryption | Significant speed increase (e.g., 50% faster) |
| Security | Enhanced key management and authentication | Improved resistance to various attacks |
Impact on Privacy and Security
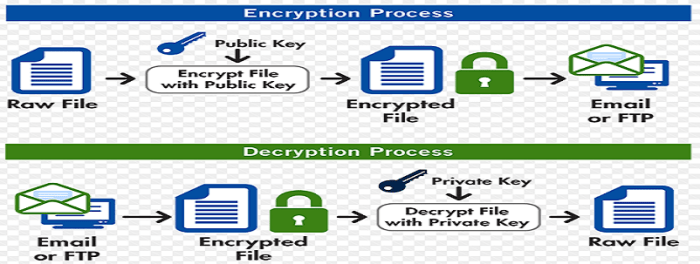
The new PGP encryption tools represent a significant leap forward in protecting digital communications and data. They build upon the foundational principles of privacy and security, enhancing user control and trust in the digital realm. This evolution in cryptographic technology promises a more secure and private online experience, especially for sensitive information.These tools provide a robust framework for individuals and organizations to safeguard their data from unauthorized access and manipulation.
The improved encryption algorithms and key management systems contribute to a stronger overall security posture, offering peace of mind in an increasingly digital world. The implications for privacy and security are multifaceted, touching on various aspects of modern life.
Implications for User Privacy
These enhanced PGP tools significantly bolster user privacy by providing an impenetrable barrier against unauthorized access to sensitive data. Users retain complete control over their encryption keys, ensuring that only authorized parties can decrypt their communications. This reinforces the fundamental right to privacy in the digital age, enabling secure interactions without fear of surveillance or data breaches.
Enhanced Data Protection and Confidentiality
The new tools employ cutting-edge cryptographic techniques to safeguard data. Advanced algorithms, combined with robust key management systems, ensure that data remains confidential and inaccessible to unauthorized entities. This enhancement in data protection translates into a more secure environment for users, protecting sensitive information from malicious actors and accidental exposure. The tools provide a higher level of assurance, significantly reducing the risk of data breaches and leaks.
Real-World Scenarios for Enhanced Security
These tools find applications in a broad spectrum of real-world scenarios. For example, individuals can securely exchange sensitive documents with trusted contacts, ensuring the confidentiality of their information. Businesses can utilize these tools to protect confidential financial transactions and sensitive corporate data, bolstering their security posture. The ability to secure sensitive medical records and personal information is another vital use case, providing individuals with peace of mind regarding the protection of their health data.
Comparison with Other Encryption Solutions
Compared to other popular encryption solutions, the new PGP tools excel in their user-friendliness and security. While other methods may offer different strengths, the PGP tools provide a compelling combination of robust security and user-friendly interface. The focus on interoperability and compatibility across different platforms and applications enhances the practicality and widespread adoption of these tools.
Potential Societal Impact
The societal impact of these tools is profound. Improved encryption strengthens the foundations of digital trust, enabling secure communication and commerce. Increased privacy fosters a more secure and democratic society, empowering individuals to participate freely in the digital world. It also enables the protection of sensitive information, such as personal health records and financial data, safeguarding individual rights and promoting responsible data handling.
How These Tools Can Be Used for Different Applications
These tools have a wide range of applications, offering a versatile solution for securing various data types and interactions.
| Application | Use Case | Security Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Email Security | Securely encrypting and decrypting email communications, protecting sensitive information from eavesdropping. | Confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity of email content. |
| File Transfer | Encrypting files before transmission, preventing unauthorized access to sensitive data during transit. | Data confidentiality and integrity, preventing unauthorized modification of transferred files. |
| Cloud Storage | Encrypting data stored in cloud services, ensuring only authorized parties can access sensitive information. | Data confidentiality and protection against unauthorized access from cloud providers or malicious actors. |
Practical Implementation and Usage
Putting PGP’s new encryption tools to work requires a practical understanding of their implementation and how they integrate into existing workflows. This section delves into the steps involved, offering examples and guidelines for seamless integration across various applications and systems. We’ll explore the technical specifications, providing a hands-on approach to harnessing the enhanced security features.
Implementing the New Tools
The implementation process begins with the selection of the appropriate tools. The new PGP tools are designed with a modular approach, allowing flexibility in their integration. Careful consideration of existing infrastructure and security protocols is essential. This process includes configuring the chosen tools with specific parameters, such as key lengths and encryption algorithms, to ensure optimal performance and security.
This configuration phase involves meticulous attention to detail, to prevent vulnerabilities and ensure seamless operation.
Using the Tools in Various Scenarios
The new PGP tools cater to a range of scenarios, from individual email encryption to secure file sharing. For instance, encrypting sensitive documents before sending them via email requires selecting the appropriate encryption method within the email client. Similarly, securing cloud storage involves using the PGP tools to encrypt files before uploading them to the service. In collaborative environments, teams can use the tools to securely share documents and maintain data integrity.
The tools facilitate secure communication and data exchange, protecting sensitive information.
Step-by-Step Guide for Existing Systems
Integrating the new tools into existing systems necessitates a phased approach. First, identify the systems requiring encryption and assess their current security posture. Next, determine the best tool for each scenario and implement the necessary configuration. This involves testing the encryption process to ensure seamless integration with existing workflows. Finally, establish clear protocols and procedures for the use of the new tools.
This ensures that the new encryption standards are used consistently and effectively within the system.
Integration into Software Applications
The new tools are designed for seamless integration with various software applications. For example, email clients can be configured to use the tools to encrypt and decrypt messages automatically. Cloud storage services can be integrated to encrypt files before uploading and ensuring data security. This allows for easy incorporation into everyday workflows.
Workflow Flowchart
The following flowchart Artikels the general workflow for using the new PGP tools:[Flowchart Image Description: A flowchart depicting the process of encrypting a file. The steps include selecting the file, choosing the encryption method, specifying the recipient, and encrypting the file. The process concludes with the successful encryption and delivery of the file to the recipient. The flowchart also highlights possible error points and how to resolve them, ensuring that the user is guided through each step.]
Practical Tips and Recommendations
Using the new tools effectively involves adhering to strict security protocols. Regularly updating the tools is crucial to address potential vulnerabilities. Establish a system for managing encryption keys to prevent unauthorized access. Employing strong passwords and key management procedures is essential to protect sensitive information.
Software and Hardware Requirements
| Software | Version | Hardware Requirements ||—|—|—|| PGP Desktop Client | v2024.1 | 2 GHz processor, 4 GB RAM, 100 GB hard drive space || PGP Email Add-on | v2024.1 | Compatible email client, same as Desktop Client || PGP Cloud Integration | v2024.1 | Compatible cloud service, same as Desktop Client |
Future Trends and Potential Developments
The realm of encryption is constantly evolving, driven by advancements in computing power and emerging threats. PGP, while a stalwart in digital security, must adapt to these changes to maintain its efficacy. This section explores the future of encryption technology, potential developments in PGP, and the crucial role of quantum computing in shaping the landscape.The future of encryption hinges on a delicate balance between innovation and the need for robust security.
As computing power increases, so too must the complexity of encryption algorithms to counter potential attacks. New methods and protocols are continuously being developed to address emerging threats, and PGP must be prepared to incorporate these advancements.
Emerging Trends in Encryption Technology
Modern encryption technologies are moving towards more sophisticated approaches. Homomorphic encryption, allowing computations on encrypted data without decryption, is gaining traction. This technology promises to revolutionize data privacy and security in various fields, such as cloud computing and healthcare. Post-quantum cryptography is another significant development, focused on algorithms resistant to attacks from quantum computers. These advancements are crucial for ensuring the long-term security of sensitive information.
Potential Future Developments in PGP’s Encryption Tools
Future iterations of PGP could leverage homomorphic encryption for enhanced data processing capabilities. This could allow for computations on encrypted data within PGP’s framework, without compromising user privacy. Improved key management and revocation mechanisms are also vital for future security. This includes exploring advanced key exchange protocols to enhance the speed and efficiency of secure communication. Further development in decentralized key management systems could provide enhanced security and resilience against centralized vulnerabilities.
Impact of Quantum Computing on Encryption Methods
Quantum computing poses a significant threat to current encryption methods, as certain widely used algorithms are vulnerable to attacks by quantum computers. The development of post-quantum cryptography is critical for mitigating this threat. This new cryptography is designed to resist attacks from quantum computers, ensuring the continued security of sensitive data. Examples of post-quantum algorithms include lattice-based cryptography, code-based cryptography, and multivariate cryptography.
Future of PGP in the Context of Emerging Technologies
The integration of blockchain technology into PGP could enhance the security and transparency of key management. This approach could create more resilient and verifiable systems, making PGP more resistant to malicious attacks and data tampering. Furthermore, the increasing prevalence of IoT devices requires PGP to consider secure communication protocols specifically designed for these interconnected systems.
Summary of PGP’s Adaptation to Evolving Cybersecurity Threats
PGP’s future adaptations will likely include the incorporation of post-quantum cryptography to ensure resilience against quantum computer attacks. Improved key management systems and decentralized protocols are also anticipated, enhancing the security and resilience of PGP. The integration of emerging technologies, such as blockchain and IoT-specific protocols, will further bolster PGP’s ability to address future cybersecurity threats.
Possible Future Features and Improvements to the New Tools
- Support for post-quantum cryptographic algorithms: This will ensure that PGP remains secure even as quantum computing capabilities advance.
- Enhanced key management and revocation mechanisms: This includes decentralized key management solutions and improved key recovery options.
- Improved integration with blockchain technology: This will enhance the transparency and security of key management within PGP.
- Enhanced compatibility with IoT devices: This will include support for secure communication protocols specifically designed for IoT environments.
- Integration of homomorphic encryption for secure data processing: This will enable computations on encrypted data without compromising user privacy.
Final Wrap-Up
In conclusion, PGP’s new encryption tools represent a substantial leap forward in security technology. These advancements offer significant improvements in performance, security, and usability, providing a robust solution for protecting sensitive data in various applications. The future of data encryption looks promising with these tools at the forefront, shaping how we approach digital privacy and security in the years to come.