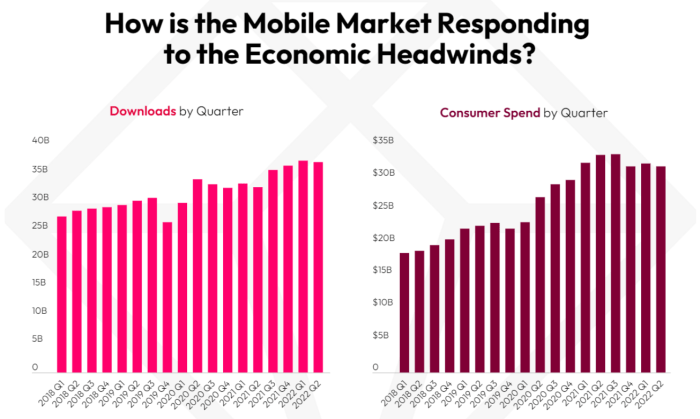
Software Shift in Mobile A Market Revolution
Software shift in the mobile device market is reshaping how we interact with technology. From the early days of mobile apps to today’s sophisticated AI-powered experiences, the evolution has been dramatic. This shift isn’t just about faster processors and bigger screens; it’s about fundamental changes in software design, user expectations, and the very industries that rely on mobile technology.
This exploration dives deep into the history, emerging technologies, and industry impacts of this revolution.
The rise of mobile-first software has transformed industries like finance, healthcare, and retail, creating new opportunities and challenges. This evolution is driven by innovations in cloud computing, AI, and AR/VR, changing the way apps function and interact with users. Understanding these shifts is crucial for businesses seeking to thrive in the modern mobile landscape.
The Rise of Mobile-First Software
The mobile revolution has fundamentally reshaped the software landscape. Once relegated to simple games and basic communication tools, mobile applications are now integral to nearly every facet of modern life. This evolution wasn’t instantaneous; it was a gradual shift driven by technological advancements, changing user expectations, and the emergence of powerful mobile operating systems. The transition from desktop-centric software to mobile-first design principles has significantly impacted software architecture and user experience, creating a new era of application development.This shift wasn’t just about building software for smaller screens; it was a paradigm shift in how we interact with technology and how software is designed to meet those interactions.
The increasing prevalence of smartphones and tablets fundamentally altered user expectations, demanding responsive, intuitive, and engaging experiences. Mobile-first design became crucial to capture and retain users in this competitive environment.
Historical Overview of Mobile Software Development
Early mobile software was largely limited by processing power and screen size. Simple games and communication apps dominated the early years. The rise of the smartphone, with its increased processing power and touch-screen interfaces, paved the way for more complex applications. Key milestones included the introduction of the App Store and Google Play, which fostered a vibrant ecosystem of app developers and users.
The proliferation of smartphones led to a significant increase in mobile data usage, creating new opportunities and challenges for developers.
Shift from Desktop-Centric to Mobile-Centric Software
User expectations shifted dramatically. Users became accustomed to seamless, responsive interactions, demanding immediate access to information and services from their mobile devices. The shift from desktop software, with its emphasis on complex interfaces and extensive functionalities, necessitated a focus on simplicity, efficiency, and a user-friendly experience. Mobile apps needed to be intuitive and easily navigable on smaller screens, leading to the adoption of touch-friendly interfaces and responsive design principles.
This emphasis on user experience (UX) and user interface (UI) became paramount in mobile app development.
The mobile device market is undergoing a massive software shift, with new features and functionalities constantly emerging. This rapid evolution, however, necessitates robust security measures. Fortunately, the recent recommendations from the NCSP task force, ncsp task force makes security recommendations , offer crucial guidelines for developers to build more secure mobile applications. Ultimately, these recommendations are essential to the ongoing software shift, ensuring the continued growth and stability of the mobile device ecosystem.
Impact of Mobile-First Design Principles
Mobile-first design principles significantly altered software architecture. Prioritizing a mobile-first approach often involved optimizing existing desktop applications for mobile platforms, but frequently led to the creation of entirely new applications tailored for the mobile environment. This required developers to consider smaller screen sizes, touch interactions, and limited processing power. The focus on lightweight code, efficient data handling, and optimized performance became critical.
A strong emphasis on responsiveness and adaptability across various screen sizes and orientations was crucial.
Comparison of iOS and Android
iOS and Android, the dominant mobile operating systems, each have unique characteristics that influence software development. iOS, with its tightly controlled ecosystem, generally promotes a consistent user experience. Android, with its open-source nature, provides developers with greater flexibility but can lead to greater fragmentation in terms of device compatibility. These differences affect how developers approach application design, testing, and deployment.
Understanding the nuances of each platform is vital for successful application development.
| Feature | iOS | Android |
|---|---|---|
| Operating System | Proprietary | Open-source |
| Device Ecosystem | More controlled and homogenous | Wider range of devices and configurations |
| Development Tools | Often more integrated with platform | Often more diverse tools available |
Evolution of Mobile Software Development Tools and Frameworks
Development tools and frameworks have evolved to support the mobile-first approach. Early tools were limited, requiring significant effort to adapt desktop code for mobile platforms. The emergence of frameworks like React Native and Flutter significantly improved cross-platform development, allowing developers to write code once and deploy to multiple platforms. These tools have streamlined development processes, reduced development time, and lowered costs.
They have become essential in the modern mobile development landscape.
Emerging Technologies Driving the Shift
The mobile device market is undergoing a profound transformation, driven by a confluence of powerful emerging technologies. These innovations are fundamentally altering the way we interact with mobile software, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible and creating a richer, more dynamic user experience. The capabilities of mobile applications are expanding exponentially, offering unprecedented functionality and accessibility.This evolution is fueled by advancements in cloud computing, artificial intelligence, and augmented/virtual reality.
These technologies are not merely enhancing existing mobile applications; they are creating entirely new categories of apps and redefining the user experience. The seamless integration of these technologies is reshaping the mobile landscape, leading to a more sophisticated and intuitive interaction with digital tools.
Cloud Computing in Mobile Software
Cloud computing plays a pivotal role in enabling the scalability and responsiveness of modern mobile applications. The cloud acts as a powerful infrastructure, providing the resources needed for applications to handle increasing user demands and data volumes. This infrastructure allows for efficient storage, processing, and delivery of data, critical for delivering a high-quality user experience.Mobile applications can leverage cloud services to offload computationally intensive tasks, freeing up device resources and improving performance.
This allows developers to create applications that are both feature-rich and lightweight. Furthermore, the cloud facilitates seamless data synchronization across multiple devices, ensuring that users can access their data consistently regardless of the device they are using.
Artificial Intelligence in Mobile Applications
Artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming mobile applications, leading to more personalized and intelligent user experiences. AI algorithms can analyze user behavior, preferences, and context to deliver tailored recommendations, suggestions, and content. This personalized approach enhances user engagement and satisfaction.Examples of AI integration include personalized news feeds, tailored product recommendations, and intelligent assistants that anticipate user needs. AI-powered chatbots can handle customer service inquiries, provide real-time support, and enhance overall user interaction within applications.
These advancements are leading to a more intuitive and helpful mobile experience.
Augmented and Virtual Reality in Mobile Apps
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) are transforming the way we interact with mobile applications, creating immersive and interactive experiences. AR overlays digital information onto the real world, enriching user interaction with their surroundings. VR creates entirely simulated environments, allowing for new forms of entertainment, education, and training.Mobile AR applications are increasingly being used for gaming, navigation, and even retail experiences.
For example, users can visualize furniture in their homes before purchasing, or explore historical sites in a realistic 3D environment. VR applications offer a new dimension for entertainment, education, and professional training. Immersive experiences are becoming more readily available through the power of mobile devices.
Cloud vs. Local Software Performance and Security
Cloud-based mobile software offers significant advantages in terms of scalability and responsiveness compared to traditional, locally installed software. Cloud services are designed to handle fluctuating demands, ensuring applications remain accessible and responsive even during peak usage periods. This scalability is particularly important for applications that handle large volumes of data or user interactions.Security considerations are paramount in both cloud-based and locally installed software.
Cloud providers often have robust security measures in place, including data encryption and access controls. However, security remains a critical factor for both types of software, requiring careful consideration of user data protection and application vulnerabilities. The choice between cloud and local software often depends on specific application requirements, user data sensitivity, and the resources available to the development team.
Impact on Different Industries
The mobile-first software shift is revolutionizing how businesses operate across various sectors. This transformation is driven by the increasing adoption of smartphones and tablets, which have become ubiquitous in daily life. Mobile apps are no longer just a convenience; they are essential tools for streamlining operations, improving customer engagement, and fostering innovation.
Impact on Finance
Mobile banking applications are transforming financial services by providing 24/7 access to accounts, facilitating secure transactions, and offering personalized financial management tools. Customers can now manage their finances from anywhere, anytime. Examples include mobile check deposit, bill payment, and real-time account balance monitoring. These features enhance efficiency and convenience for both consumers and financial institutions.
Impact on Healthcare
The rise of mobile health (mHealth) applications is reshaping healthcare delivery. Telemedicine platforms enable remote consultations, medication management, and health tracking, making healthcare more accessible and convenient. Patient portals provide secure access to medical records, facilitating communication between patients and healthcare providers. Examples include remote patient monitoring systems, electronic health records (EHR) apps, and telehealth consultations. This shift improves patient engagement and reduces the burden on physical healthcare facilities.
Impact on Retail
Mobile commerce (m-commerce) is significantly impacting the retail industry. Mobile apps allow customers to browse products, make purchases, track orders, and receive personalized recommendations. Businesses can use location-based services to provide targeted promotions and in-store experiences. Examples include mobile point-of-sale (POS) systems, online ordering and delivery platforms, and interactive product catalogs. This integration of mobile technology into retail operations fosters customer loyalty and enhances sales efficiency.
Impact on Education
Mobile learning applications are transforming the education landscape. Students can access educational resources, participate in online courses, and connect with teachers and peers through mobile devices. Educational institutions can utilize mobile platforms for administrative tasks, communication, and resource sharing. Examples include interactive learning apps, online tutoring platforms, and mobile-based learning management systems. This integration fosters a more dynamic and personalized learning experience for students.
The mobile device market is experiencing a significant software shift, with new players constantly emerging and pushing the boundaries of what’s possible. Recent developments, like Microsoft settling with the last states in the antitrust trial ( microsoft settles with last states in antitrust trial ), could potentially influence the competitive landscape and further accelerate this transition. Ultimately, this dynamic environment will likely lead to even more innovative and user-friendly mobile experiences for consumers in the future.
Competitive Advantages
Businesses adopting mobile-first software strategies gain significant competitive advantages. These advantages include improved customer experience, enhanced operational efficiency, and increased market reach. By leveraging mobile technology, companies can streamline processes, personalize interactions, and provide customers with greater convenience. This ultimately translates into increased customer satisfaction, loyalty, and profitability.
Impact Comparison Across Industries
| Industry | Impact on Business Processes | Competitive Advantages |
|---|---|---|
| Finance | 24/7 access, secure transactions, personalized financial management | Enhanced customer experience, increased accessibility, streamlined operations |
| Healthcare | Remote consultations, medication management, health tracking | Improved patient engagement, reduced healthcare facility burden, enhanced accessibility |
| Retail | Mobile commerce, personalized recommendations, location-based services | Increased customer loyalty, enhanced sales efficiency, streamlined operations |
| Education | Access to educational resources, online courses, student-teacher interaction | Personalized learning experiences, increased accessibility, dynamic learning environment |
Features and Functionalities of Mobile Apps
- Finance: Mobile banking apps typically include account access, transaction history, bill payment, mobile check deposit, and investment tracking. These functionalities enhance financial management and security for users.
- Healthcare: mHealth apps often feature remote patient monitoring, appointment scheduling, medication reminders, health record access, and telehealth consultations. These features facilitate convenient and efficient healthcare interactions.
- Retail: Retail apps commonly include product browsing, online shopping, order tracking, loyalty programs, and location-based promotions. These functionalities create a seamless and engaging shopping experience for customers.
- Education: Educational apps often provide access to course materials, interactive exercises, online discussions, and communication tools. These functionalities enhance learning and engagement for students.
User Experience and Interface Design
The mobile-first shift has dramatically reshaped how users interact with software. This evolution necessitates a deep understanding of user experience (UX) and user interface (UI) design principles to create engaging and intuitive mobile applications. Successful mobile apps prioritize seamless interactions, intuitive navigation, and visually appealing aesthetics. This emphasis on user-centric design is key to driving user engagement and ultimately, success in the mobile market.The current landscape is characterized by a relentless pursuit of simpler, more efficient, and aesthetically pleasing mobile interfaces.
Users expect applications to load quickly, adapt to various screen sizes and orientations, and offer personalized experiences. The demand for accessible designs for diverse users with varying abilities is also growing. This underscores the critical need for robust UX/UI considerations in mobile software development.
Evolving UX/UI Trends
Mobile UX/UI trends are constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements and user expectations. Visual appeal and intuitive navigation are paramount. Flat design, with its clean lines and minimal imagery, is gaining popularity for its accessibility and ease of use on various devices. The use of animations and micro-interactions is becoming more prevalent, enhancing the perceived responsiveness and engagement with the app.
A growing trend is the use of dynamic content and personalized experiences to cater to individual user preferences and needs.
Importance of Responsiveness and Accessibility
Responsiveness is critical for mobile app design. Apps must adapt seamlessly to different screen sizes, orientations, and devices, ensuring a consistent and enjoyable user experience across the spectrum of mobile platforms. Accessibility is equally vital. Mobile applications should be designed with users with disabilities in mind, incorporating features like adjustable text sizes, screen readers, and alternative input methods.
These features ensure inclusivity and broaden the user base.
Innovative UI/UX Designs in Popular Apps
Many popular mobile applications exemplify innovative UI/UX design principles. For example, apps like Instagram leverage intuitive swiping gestures for navigation and image sharing, showcasing how effective UI design can simplify complex tasks. Similarly, apps like Uber utilize a streamlined interface for booking rides and tracking their progress, reflecting the importance of efficient and informative design elements. These examples demonstrate how well-designed interfaces can improve the overall user experience and foster greater user engagement.
Guidelines for Creating Intuitive and User-Friendly Mobile Interfaces
Creating intuitive and user-friendly mobile interfaces requires adherence to specific guidelines. Prioritize clear and concise information architecture, ensuring that users can easily find what they need. Use consistent design elements, such as typography, color palettes, and imagery, to create a cohesive and recognizable brand identity. Provide clear and informative feedback mechanisms, allowing users to understand the app’s responses to their actions.
Testing with real users is essential to identify usability issues and refine the design accordingly.
Role of Mobile-First Design Principles, Software shift in the mobile device market
Mobile-first design principles are crucial for optimizing user engagement. These principles prioritize the mobile experience, ensuring that the app is designed with a mobile user in mind first. This often leads to a more streamlined and efficient design, resulting in improved user experience. Furthermore, the design adapts to different screen sizes and resolutions, which improves the overall user experience across various devices.
This approach reduces development time and resources by focusing on the core functionality from the start.
Security and Privacy Considerations
Mobile software, while revolutionizing various industries, introduces unique security challenges. The ubiquity of mobile devices and the sensitive data they often handle necessitates robust security measures to protect user privacy and prevent malicious activity. The shift towards mobile-first necessitates a profound understanding of these considerations.The sheer volume of data transmitted and stored on mobile devices, combined with the potential for physical loss or theft, creates a significant vulnerability.
Furthermore, the increasing reliance on mobile applications for financial transactions and personal information necessitates meticulous attention to security protocols.
Unique Security Challenges of Mobile Software
Mobile devices face unique security challenges compared to desktop systems. These include the potential for malware infection through compromised applications, vulnerabilities in operating systems, and the inherent risk of physical access to the device. The limited processing power and memory of some mobile devices can also make them more susceptible to resource-intensive attacks. Furthermore, the diversity of mobile operating systems and devices adds complexity to developing universal security solutions.
The mobile device market is constantly shifting, with new software features and operating systems emerging regularly. However, this rapid evolution also presents security challenges. A recent vulnerability discovered in popular browsers, like the one detailed in vulnerability pops up in popular browsers , highlights the need for robust security measures alongside the software shift. This constant need for updates and security patches further underscores the importance of ongoing development and testing in the mobile software ecosystem.
Importance of Data Privacy in Mobile Applications
Data privacy is paramount in mobile applications. User data, ranging from personal information to financial details, must be handled with utmost care. Compliance with data protection regulations like GDPR and CCPA is crucial. Transparency about data collection practices and user consent mechanisms are essential to build trust and ensure ethical use of data.
Role of Encryption and Authentication in Securing Mobile Data
Encryption plays a vital role in safeguarding mobile data. Strong encryption algorithms, like AES, protect sensitive information during transmission and storage. Robust authentication methods, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA) and biometrics, are essential to verify user identity and prevent unauthorized access. This approach helps mitigate the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access to user accounts.
Mobile Operating Systems and Software Developer Security Measures
Mobile operating systems (OS) like iOS and Android have implemented various security measures. These include sandboxing applications, code signing, and regular security updates. Software developers also have a crucial role to play. They must adhere to security best practices, perform thorough code reviews, and address vulnerabilities promptly. Security audits and penetration testing are vital steps in ensuring robust protection.
Comparison of Security Practices in Different Mobile Platforms
Different mobile platforms, such as iOS and Android, employ varying security approaches. iOS, with its tighter control over the app ecosystem, generally offers a higher level of security. Android, with its broader open-source nature, has more avenues for potential vulnerabilities. However, Android also benefits from a larger developer community, potentially leading to faster identification and patching of vulnerabilities.
Both platforms continuously update their security measures to address evolving threats. Table below highlights key security differences.
| Feature | iOS | Android |
|---|---|---|
| App Store vetting | Rigorous vetting process | More diverse app ecosystem, potentially more vulnerabilities |
| Security updates | Frequent and comprehensive updates | Updates depend on the device manufacturer and carrier |
| Security features | Built-in encryption and security protocols | Often relies on user configuration and app-level security |
Future Trends and Predictions
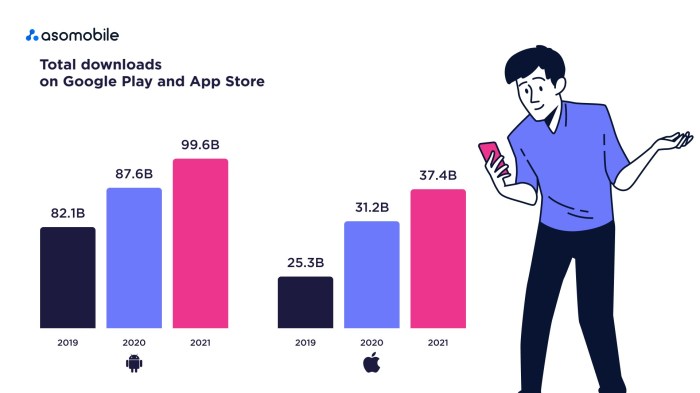
The mobile software landscape is constantly evolving, driven by advancements in technology and shifting user expectations. Predicting the future is inherently challenging, but analyzing current trends and emerging technologies allows for informed speculation about the direction of mobile software development. This section will explore potential future directions, the impact of emerging technologies, and showcase emerging trends in mobile software, including AR/VR applications.
We will also examine hypothetical future applications in various sectors and present a detailed description of a specific niche mobile application.
Future Direction of Mobile Software Development
Mobile software development is moving towards greater personalization and contextual awareness. Applications will increasingly leverage machine learning and AI to adapt to individual user needs and preferences in real-time. This includes anticipating user actions and proactively offering relevant information or services. The rise of personalized experiences is already evident in various platforms, demonstrating the increasing importance of tailoring user interfaces to individual preferences and behaviors.
Impact of Emerging Technologies on the Mobile Software Market
Emerging technologies like 5G, edge computing, and the Internet of Things (IoT) will significantly impact the mobile software market. 5G’s enhanced speed and reliability will enable new types of applications and experiences, including real-time data streaming and interactive experiences. Edge computing will bring processing power closer to the user, reducing latency and improving responsiveness in mobile applications. IoT integration will open doors for smart home applications, connected devices, and a more seamless integration of physical and digital worlds.
Emerging Trends in Mobile Software Development
Augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) are transforming the mobile software landscape. AR applications overlay digital information onto the real world, enhancing user interaction and providing novel ways to engage with the environment. VR applications immerse users in virtual worlds, offering opportunities for entertainment, education, and training. The increasing accessibility and affordability of AR/VR technologies are driving their integration into mobile platforms.
The growing popularity of gaming and entertainment applications leveraging AR/VR technologies, such as Pokémon Go and various VR experiences, exemplify the trend.
Potential Future Applications of Mobile Software in Different Sectors
| Sector | Potential Applications |
|---|---|
| Healthcare | Remote patient monitoring, personalized medicine apps, virtual consultations, AI-powered diagnostics, telehealth platforms, and interactive medical training simulations. |
| Entertainment | Immersive storytelling experiences, interactive gaming environments, AR/VR-enhanced concerts and events, personalized music recommendations, and social networking platforms with enhanced interactive features. |
| Education | Interactive learning platforms, personalized tutoring systems, AR/VR-enhanced field trips, virtual labs and experiments, and global collaboration tools. |
Hypothetical Future Mobile Application: Personalized Wellness Companion
This application focuses on personalized well-being through AI-driven insights and adaptive routines. The application would track user activity, sleep patterns, dietary habits, and emotional states using various sensors and user input. Advanced algorithms would analyze this data to provide personalized recommendations for exercise, nutrition, and stress management techniques. The application would integrate with wearable devices and smart home appliances to create a holistic wellness ecosystem.
For instance, the application could adjust lighting and temperature settings based on the user’s mood and activity level. The app would also incorporate gamified elements to motivate users and encourage consistent engagement. The app’s interface would be highly customizable, allowing users to tailor the experience to their specific needs and preferences.
Final Wrap-Up: Software Shift In The Mobile Device Market
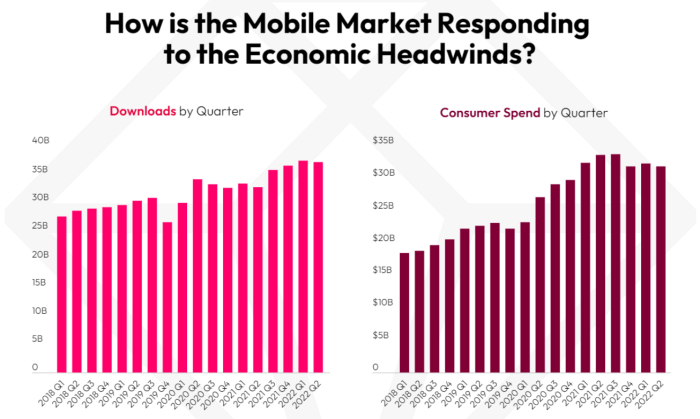
In conclusion, the software shift in the mobile device market is a dynamic and ongoing process. The convergence of technology, user expectations, and industry needs is pushing the boundaries of what’s possible. From the foundational changes in software development to the future trends shaping the market, this revolution is transforming how we live, work, and interact. The future of mobile software promises even more innovation and integration across various sectors.