AMD Takes Turn with Dual-Core Athlon X2
AMD takes turn with dual core Athlon X2, marking a significant shift in the processor landscape. This exploration delves into the historical context, technical specifications, performance evaluation, and market impact of this dual-core marvel. We’ll examine how this processor influenced consumer decisions and the PC market as a whole, ultimately assessing its lasting legacy and modern relevance.
The Athlon X2’s introduction represented a pivotal moment for AMD, pushing the boundaries of processing power and challenging the dominance of Intel. This article will detail its architecture, performance benchmarks, and impact on the personal computer market, offering a comprehensive overview of its journey.
Historical Context of AMD Athlon X2: Amd Takes Turn With Dual Core Athlon X2
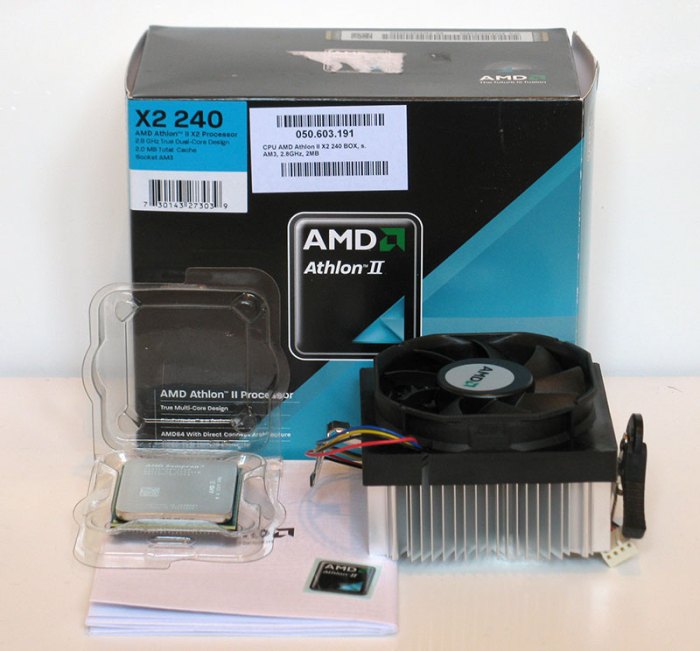

The AMD Athlon X2 processors marked a significant turning point in the personal computer market. They represented AMD’s ambitious effort to compete effectively with Intel’s dominant position in the processor arena, specifically in the dual-core space. This involved not just improving clock speeds, but a fundamental shift in architecture, which had a ripple effect on PC performance and pricing.The Athlon X2 series was a direct response to the growing demand for multi-tasking and more powerful computing capabilities in consumer PCs.
The increasing complexity of software applications and the rising popularity of multimedia tasks pushed the need for faster processing power beyond what single-core processors could provide.
Architectural Advancements Leading to Dual-Core
AMD’s development of the Athlon X2 architecture involved a significant architectural leap from their previous single-core designs. Key advancements focused on integrating two processing cores onto a single chip. This involved intricate design considerations, including optimized memory access, improved instruction pipelining, and sophisticated thread management to leverage the power of multiple cores effectively. Crucially, AMD successfully addressed the challenges of coordinating and managing two processing units simultaneously.
Market Position and Competition
At the time of the Athlon X2’s release, Intel held a dominant position in the processor market. Intel’s Pentium 4 processors, while facing some limitations in multi-tasking, had a strong brand recognition and a significant installed base. AMD’s Athlon X2 aimed to disrupt this dominance by offering a compelling dual-core alternative at a competitive price point. The competition was intense, with AMD’s strategy being centered around delivering a performance-per-dollar proposition that could match or exceed Intel’s offering.
Impact on the Overall PC Market
The introduction of dual-core technology, spearheaded by the Athlon X2, had a profound impact on the overall PC market. Consumers began to experience significantly improved performance for demanding applications, enabling smoother multitasking and more responsive systems. This directly influenced PC sales and further fueled the trend towards more powerful and versatile personal computers. The availability of dual-core processors also spurred innovation in software, encouraging developers to create applications optimized for multi-threaded processing.
Key Competitors
| Processor Name | Cores | Clock Speed | Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| AMD Athlon X2 | 2 | Various (e.g., 2.4 GHz to 3.0 GHz) | Dual-core architecture, AM2 platform |
| Intel Pentium D | 2 | Various (e.g., 2.8 GHz to 3.2 GHz) | Dual-core architecture, FSB based |
| Intel Core Duo | 2 | Various (e.g., 1.83 GHz to 2.66 GHz) | Dual-core architecture, faster cache and integrated memory controller |
| Intel Core 2 Duo | 2 | Various (e.g., 2.0 GHz to 3.0 GHz) | Dual-core architecture, improved performance over Core Duo |
The table above provides a comparative overview of key processors in the dual-core era. Each processor design aimed to offer a balance of performance and features while considering the market’s specific needs. AMD, in particular, sought to position the Athlon X2 as a more cost-effective alternative to Intel’s offerings.
Technical Specifications of the AMD Athlon X2
The AMD Athlon X2 processors marked a significant leap forward in the world of dual-core processors. Building upon the success of previous AMD architectures, the Athlon X2 brought a compelling combination of performance and affordability to the market. This processor line was instrumental in making dual-core technology more accessible to a wider range of users.
AMD’s shift to dual-core Athlon X2 processors was a big deal, but another story, like the one about a web cam worm highlighting the seedy side of the net web cam worm highlights seedy side of net , shows how technology can have both amazing and unsettling applications. Still, the new Athlon X2 chips offered a significant boost in performance for the average consumer, especially compared to older single-core processors.
Core Architecture
The Athlon X2 processors employed a K8 core architecture, a crucial advancement from its predecessors. This architecture featured a superscalar design, enabling the processor to execute multiple instructions simultaneously. The K8 architecture was a significant departure from previous designs, offering improved instruction-level parallelism and a more sophisticated pipeline for higher performance. This architectural shift was vital for handling the increasing complexity of modern software and applications.
Comparison to Predecessors
Compared to single-core Athlon processors, the Athlon X2 offered a substantial performance boost due to its dual-core design. The increase in processing power was not just a doubling, but a significant improvement enabled by the advancements in the K8 architecture. The K8 core was more efficient at handling tasks that benefited from parallel processing, resulting in a notable improvement in application performance compared to its single-core predecessors.
Set Architecture and Performance Impact
The set architecture of the Athlon X2, based on the K8 architecture, played a crucial role in its performance characteristics. This architecture allowed for efficient fetching, decoding, and execution of instructions. The specific design of the pipeline, register file, and caches directly influenced the processor’s speed and efficiency in handling various tasks. A well-optimized set architecture was crucial for the Athlon X2’s success in achieving a balanced performance-to-cost ratio.
Memory and Bus Technologies
The Athlon X2 processors supported various memory technologies, including DDR2 SDRAM. The memory bus, typically a FSB (Front Side Bus), determined the rate at which data could be transferred between the processor and memory. Different Athlon X2 models supported various FSB frequencies, affecting the overall system performance. The choice of memory and bus technologies directly impacted the processor’s ability to access and utilize data efficiently.
Comparison Table
| Processor Name | Clock Speed | Cache Size | TDP |
|---|---|---|---|
| AMD Athlon X2 6400+ | 2.1 GHz | 1 MB L2 Cache | 65W |
| AMD Athlon X2 7750 | 2.8 GHz | 2 MB L2 Cache | 65W |
| Intel Core 2 Duo E6600 | 2.4 GHz | 4 MB L2 Cache | 65W |
| Intel Pentium Dual-Core E2180 | 2.1 GHz | 2 MB L2 Cache | 35W |
Impact on the Consumer Market
The AMD Athlon X2, a dual-core processor, marked a significant turning point in the personal computer market. Its arrival wasn’t just about incremental performance improvements; it represented a fundamental shift in how consumers perceived and utilized their PCs. This shift was largely driven by a compelling combination of affordability, improved multitasking capabilities, and a noticeable jump in the overall user experience.The Athlon X2’s dual-core architecture significantly impacted consumer purchasing decisions.
Previously, the primary consideration for PC upgrades often centered on raw clock speed. However, the Athlon X2 demonstrated that a more sophisticated approach—dual cores working in harmony—could yield substantial performance gains, especially in tasks involving multiple applications or demanding media processing. Consumers began to recognize the value of simultaneous processing, leading to a shift in the way they evaluated and prioritized PC upgrades.
Consumer Reception and Adoption, Amd takes turn with dual core athlon x2
Consumer reception of the AMD Athlon X2 was generally positive. Its ability to handle everyday tasks smoothly and efficiently appealed to a wide range of users, from casual PC users to those performing more demanding tasks. The dual-core technology, previously a feature of more expensive processors, was now accessible to a broader segment of the market, expanding the pool of potential users.
This wider accessibility fueled demand and contributed to a more competitive environment in the PC market.
Influence on Consumer Purchasing Decisions
The Athlon X2’s dual-core architecture fundamentally altered consumer purchasing decisions. Instead of solely focusing on raw clock speed, consumers began evaluating the number of cores and their ability to handle multiple applications concurrently. This shift in priorities demonstrated a growing understanding of the advantages of parallel processing and its impact on user experience. The Athlon X2’s affordability played a crucial role in this change.
It allowed consumers to upgrade their PCs without breaking the bank, making dual-core processing a viable option for a broader range of users.
Impact on PC Component Pricing and Availability
The introduction of the Athlon X2 significantly affected the pricing and availability of PC components. Increased demand for dual-core processors naturally led to a wider range of compatible motherboards and other components being offered. This competition among vendors, fueled by the Athlon X2’s popularity, resulted in more competitive pricing across the entire PC ecosystem. The availability of compatible components also improved, as manufacturers rushed to meet the growing demand.
AMD’s turn with the dual-core Athlon X2 was a significant step forward in processor technology, but the security landscape was also evolving. Microsoft, seemingly oblivious to the ethical implications, continued to enhance its arsenal of tools, including what some would consider spyware, as detailed in this article on microsoft adds spyware weapon to arsenal. Ultimately, these advancements in processor architecture, alongside the questionable practices of tech giants, shaped the digital world we know today, and AMD’s dual-core processors remain a testament to innovation.
Role in the Evolution of the Personal Computer Market
The Athlon X2 played a crucial role in the evolution of the personal computer market. Its affordability and improved performance spurred a shift towards more capable and user-friendly PC systems. The dual-core architecture became a standard feature, impacting not only the CPU market but also influencing the development of other hardware components, software applications, and operating systems. This, in turn, shaped the trajectory of the personal computer market towards greater efficiency and multitasking capabilities.
Pricing Trends of Athlon X2 Processors
| Year | Model | Price (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| 2007 | Athlon X2 6400+ | $150 – $200 |
| 2008 | Athlon X2 7750 | $120 – $170 |
| 2009 | Athlon X2 7750 | $100 – $150 |
| 2010 | Athlon X2 7750 | $80 – $120 |
Note: Pricing data is approximate and may vary depending on retailer and specific configuration.
Evolution and Legacy

The AMD Athlon X2, a dual-core processor, marked a significant step in AMD’s journey to compete with Intel’s dominant position in the CPU market. Its success, while ultimately leading to a transition, left a noticeable impact on the architecture and design philosophy of future AMD processors. This section delves into the successors and replacements, the lasting impact on the AMD product line, and how the Athlon X2 influenced subsequent designs.
Successors and Replacements
The Athlon X2, while a notable achievement, wasn’t the final iteration of AMD’s dual-core strategy. AMD transitioned to newer architectures and core designs, which were necessary to remain competitive in the ever-evolving processor landscape. Its successors, often incorporating improved manufacturing processes and advanced microarchitectures, addressed performance bottlenecks and sought to leverage the growing demands of the computing market.
AMD’s dual-core Athlon X2 processor was a significant step forward, marking a turning point in the CPU landscape. Meanwhile, Intel’s new Itanium processors, powering Unisys and HP servers, new intel itanium inside unisys hp servers , offered a different approach to high-end computing. Ultimately, AMD’s Athlon X2 still represented a major advancement for consumers, pushing the boundaries of affordability and performance in the personal computer market.
Long-Term Impact on the AMD Product Line
The Athlon X2 played a pivotal role in shaping AMD’s future product strategy. It demonstrated AMD’s ability to deliver dual-core processors that were competitive with Intel’s offerings. This success helped to build consumer confidence in AMD’s ability to innovate and create competitive products. The transition from the Athlon X2 to newer architectures highlighted the importance of continuous innovation within the processor market.
Influence on Future Processor Designs
The Athlon X2’s architecture, while eventually superseded, provided valuable lessons in processor design. Its architecture and core design contributed to a better understanding of the requirements and limitations of dual-core processors, which were critical to the success of subsequent models. The architectural improvements and advancements in subsequent models demonstrate the evolution of processor technology and the lessons learned from the Athlon X2’s successes and shortcomings.
Timeline of Key AMD Processor Releases Following the Athlon X2
This timeline showcases a selection of significant AMD processor releases following the Athlon X2, highlighting key features and advancements in architecture. The subsequent processors, though distinct in their names and characteristics, often built upon the architectural lessons learned from the Athlon X2 era.
| Release Date | Processor Name | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| 2008 | AMD Phenom | Quad-core architecture, increased performance compared to dual-core predecessors. |
| 2009 | AMD Phenom II | Further refinements to the Phenom architecture, enhanced performance and power efficiency. |
| 2011 | AMD Bulldozer | New microarchitecture, introduced a modular core design and aimed to improve performance. |
| 2013 | AMD Fusion | Integrated graphics processing units (GPUs) into the CPU, aimed at providing a unified computing experience. |
| 2015 | AMD Ryzen | Revolutionary architecture with a focus on core count and performance per watt, marked a return to high performance. |
Modern Relevance
The AMD Athlon X2, while a significant processor of its time, is now largely obsolete in the modern computing landscape. Its architecture, designed for the mid-2000s, is vastly different from the complex and highly optimized designs of contemporary processors. However, a surprising degree of relevance persists in niche applications and as a fascinating historical artifact.The Athlon X2’s architecture, based on the K8 core, relies on a simpler instruction set compared to modern processors utilizing more advanced microarchitectures.
This difference significantly impacts performance in contemporary applications. Modern processors boast multiple cores, advanced caching strategies, and optimized instruction pipelines that dramatically accelerate processing speeds. The Athlon X2, with its dual-core configuration and relatively limited resources, simply cannot compete.
Use Cases for Legacy Architectures
The Athlon X2, despite its limitations, might still hold a place in certain specialized applications. For example, in environments with stringent power requirements or cost constraints, the Athlon X2’s lower power consumption could be advantageous. Retro gaming enthusiasts might also find it useful for running older games. Another niche use case could be in embedded systems, where a dual-core processor might suffice for the specific workload.
Comparison with Modern Alternatives
Modern processors provide substantial performance gains over the Athlon X2. Their multi-core architecture, advanced cache hierarchies, and sophisticated instruction sets allow for significantly faster processing speeds and greater efficiency in handling complex tasks. For example, a modern dual-core processor from 2010 would likely outperform the Athlon X2 by a substantial margin. This difference in performance extends to other tasks like video editing, content creation, and 3D rendering, where modern processors are far superior.
- Advantages of Athlon X2: Lower power consumption and reduced heat generation, which could be advantageous in certain specific applications. The lower cost of the Athlon X2 might make it attractive for users with tight budgets.
- Disadvantages of Athlon X2: Substantial performance lag compared to modern processors, limited capabilities in running current applications, and potentially incompatible with modern operating systems. Modern systems and applications demand significantly more processing power, memory, and bandwidth, and the Athlon X2 simply lacks the necessary resources.
Upgrading Older PCs
The technical feasibility of upgrading older PCs with an Athlon X2 is highly limited. Modern motherboards are designed with entirely different socket types and require specific compatible components. Upgrading to an Athlon X2 would require compatibility with the motherboard, RAM, and other components of the existing system. Finding a compatible motherboard for the Athlon X2 in an older PC could be challenging.
Moreover, the operating system may not support the Athlon X2 architecture.
| Component | Compatibility |
|---|---|
| Motherboard | Highly dependent on socket type and chipset; compatibility is highly unlikely. |
| RAM | Requires compatibility with the motherboard’s memory controller; compatibility is not guaranteed. |
| Operating System | Potential compatibility issues depending on the operating system version and the Athlon X2’s architecture. |
Last Recap
In conclusion, the AMD Athlon X2’s impact on the PC market, despite its age, remains noteworthy. Its dual-core architecture was a significant advancement for the time, and while it has been superseded by more modern processors, it paved the way for future innovations in multi-core processing. The Athlon X2 serves as a historical marker for AMD’s evolution, offering insights into the technological landscape of the mid-2000s.