Are Consumer-Grade Firewalls Really Secure?
Are consumer grade firewalls really secure – Are consumer-grade firewalls really secure? This question delves into the effectiveness of these commonly used security tools. We’ll examine their features, security practices, potential vulnerabilities, and compare them to other security solutions. Understanding these factors is crucial for consumers seeking to protect their digital assets.
Consumer-grade firewalls are a fundamental layer of defense against online threats. They sit between your devices and the internet, monitoring and controlling network traffic. However, their effectiveness varies depending on the specific implementation and the user’s understanding of security best practices. This exploration aims to clarify the strengths and weaknesses of these firewalls.
Defining “Consumer-Grade Firewall”: Are Consumer Grade Firewalls Really Secure
Consumer-grade firewalls are security systems designed to protect individual computers, home networks, or small businesses. They differ significantly from enterprise-grade firewalls, which are far more complex and powerful, addressing the needs of large organizations with extensive network infrastructures. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for choosing the right security solution for your needs.These firewalls act as gatekeepers, controlling network traffic and filtering out potentially harmful connections.
They play a critical role in preventing unauthorized access and protecting sensitive data from cyber threats. The effectiveness of a consumer-grade firewall hinges on its ability to recognize and block malicious activity, while allowing legitimate traffic to flow freely.
What Constitutes a Consumer-Grade Firewall?
Consumer-grade firewalls are fundamentally different from enterprise-grade firewalls in their complexity and functionalities. They typically prioritize ease of use and affordability over advanced features, catering to the needs of individual users and small-scale networks. These firewalls offer a basic level of protection against common online threats.
Common Features and Functionalities
Consumer-grade firewalls often include features such as port filtering, stateful inspection, and basic intrusion prevention. Port filtering allows or blocks traffic based on the destination port number, while stateful inspection analyzes the context of network connections. These mechanisms help to identify and block malicious traffic based on patterns and behaviors. Basic intrusion prevention systems can detect and block known malicious attacks.
Hardware and Software Components
The hardware components of a consumer-grade firewall can range from a dedicated network appliance to a software application running on a standard computer. The software component is usually a firewall application that sits on the user’s computer or a router. Hardware-based firewalls are often integrated into routers, providing a single device for both routing and security.
Types of Consumer-Grade Firewalls
Consumer-grade firewalls come in two primary forms: software-based and hardware-based. Software-based firewalls are installed as applications on personal computers, while hardware-based firewalls are standalone devices often integrated into routers. This diversity in implementation reflects the various needs and preferences of users.
Comparison of Firewall Types
| Feature | Software-Based | Hardware-Based |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Generally lower, often free or inexpensive | Can range from low to moderate, often integrated into a router’s price |
| Performance | Performance can be affected by the computer’s resources | Generally higher performance as dedicated hardware |
| Features | Limited to the features of the specific software | Often includes features like VPN support and QoS |
| Setup | Relatively easy to install and configure | May require more technical knowledge to configure |
Assessing Security Features
Consumer-grade firewalls, while offering a crucial first line of defense against online threats, often have limitations in their security features compared to enterprise-grade solutions. Understanding these features and their effectiveness is key to gauging their real-world security capabilities. A deeper dive into the specific security protocols and algorithms employed, along with an analysis of their strengths and weaknesses, will shed light on the true picture of their protective power.The security features of consumer-grade firewalls are designed to protect against a wide range of cyber threats.
However, the sophistication of these threats is constantly evolving, which means the limitations of these features are also worth considering. The effectiveness of these features depends not only on the specific implementation but also on the user’s configuration and awareness.
Firewall Rules
Firewall rules are fundamental to consumer-grade firewalls. They act as gatekeepers, controlling network traffic based on predefined criteria such as source IP address, destination port, and protocol. This control prevents unauthorized access to a user’s network and limits the potential entry points for malicious actors. For instance, a firewall rule can be set to block all incoming traffic from a known malicious IP address.
Intrusion Detection
Consumer-grade firewalls often incorporate intrusion detection systems (IDS). These systems monitor network traffic for suspicious patterns indicative of malicious activity, such as attempts to exploit known vulnerabilities or unusual traffic spikes. While effective in detecting some threats, the effectiveness of IDS varies greatly. IDSs often rely on signature-based detection, which can be less effective against zero-day attacks (attacks exploiting vulnerabilities not yet documented).
Some more advanced systems use anomaly-based detection, which looks for deviations from normal network behavior.
Anti-virus
Anti-virus protection is another common security feature. These programs scan files and applications for known malware signatures. The effectiveness of anti-virus depends on the real-time updates to its database of known malware signatures. Real-time scanning and automatic updates are critical to staying ahead of evolving threats. The limitations of anti-virus software include its inability to detect all types of malware, particularly those that are polymorphic or use advanced obfuscation techniques.
For example, if a new type of ransomware is released, it might take a few days for the anti-virus software to add it to its database, leaving users vulnerable during that time.
| Feature | Description | Effectiveness Against Common Threats |
|---|---|---|
| Firewall Rules | Controls network traffic based on predefined criteria. | Effective against basic attacks like port scans and denial-of-service attacks, but less effective against sophisticated attacks targeting specific vulnerabilities. |
| Intrusion Detection | Monitors network traffic for suspicious patterns. | Moderate effectiveness against known threats; less effective against zero-day exploits and advanced persistent threats. |
| Anti-virus | Scans files and applications for known malware signatures. | Relatively effective against known malware but less effective against zero-day exploits and advanced malware. |
Evaluating Security Practices

Consumer-grade firewalls, while often a valuable first line of defense, aren’t foolproof. Their effectiveness hinges significantly on how users configure and interact with them. This section delves into the critical security practices surrounding these firewalls, highlighting both best and worst-case scenarios.Proper configuration and user vigilance are paramount to maximizing the security benefits of consumer-grade firewalls. Neglecting these aspects can create vulnerabilities that malicious actors can exploit.
Understanding these practices is crucial for maintaining a secure online environment.
Importance of Proper Firewall Configuration, Are consumer grade firewalls really secure
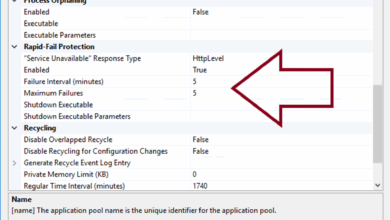
Proper firewall configuration is essential for effective security. Incorrect settings can inadvertently expose your network to threats. A poorly configured firewall might allow unauthorized access or block legitimate traffic, disrupting internet services. Careful consideration of rules and settings is vital.
- Default Rules: Many consumer firewalls utilize default rules. These rules, while convenient, may not always align with your specific needs. Carefully reviewing and adjusting these default settings is critical to ensure they don’t create unnecessary security holes.
- Port Forwarding: This feature allows specific network traffic to be routed to a particular device. While useful for accessing services like gaming servers or file sharing, it requires careful consideration of which ports to open. Only open ports that are strictly necessary to prevent unauthorized access.
- Application Rules: Most consumer firewalls allow you to specify rules for applications. Reviewing and setting rules for programs you use is essential. For instance, if you only need a program to access the internet, you don’t need to allow the program to receive connections from the internet. Allow only necessary network access.
Impact of User Behavior on Firewall Security
User behavior significantly influences firewall effectiveness. A user’s actions can bypass security measures and create vulnerabilities. For example, clicking on suspicious links or downloading untrusted files can compromise the system.
- Suspicious Links and Downloads: Users should exercise caution when clicking links or downloading files. Unverified downloads can introduce malware, viruses, and other malicious software that can disable or bypass security protocols. Always exercise extreme caution when visiting unverified websites or downloading files from untrusted sources.
- Weak Passwords: Weak or easily guessed passwords can allow unauthorized access to your network. Use strong, unique passwords for your firewall and any accounts connected to your network.
- Ignoring Security Alerts: Firewall alerts should never be ignored. These alerts often indicate potential threats. Failing to respond to these alerts can lead to a security breach. Promptly address all security alerts to prevent potential threats.
Good and Bad Firewall Configuration Practices
Following good firewall configuration practices is crucial for optimal security. Conversely, poor practices can leave your system vulnerable.
- Good Practices: Implementing strong passwords for the firewall and network accounts, regularly updating the firewall software, and configuring the firewall to block known malicious IP addresses are examples of good practices. Regularly reviewing and updating firewall settings based on your needs can further enhance security.
- Bad Practices: Leaving default settings in place without review, opening unnecessary ports, and failing to update the firewall software are examples of bad practices. Failing to adjust firewall rules based on new applications and services introduced to the network can lead to security vulnerabilities.
Importance of Regular Updates
Regular updates and security patches are critical for maintaining a firewall’s effectiveness. Security vulnerabilities are frequently discovered and patched by firewall vendors. Failure to apply these updates leaves your system exposed to known exploits.
Regular updates are essential for a secure network.
Factors Reducing Security Effectiveness
Several factors can diminish the effectiveness of security practices.
- Outdated Software: Outdated firewall software often lacks crucial security patches and features, making it vulnerable to attacks. Maintaining the latest version of the firewall software is vital to ensure you have the most recent security protections.
- Lack of Awareness: Insufficient awareness about security best practices among users can lead to poor security decisions, potentially compromising the firewall’s effectiveness.
- Complex Networks: Complex network setups can introduce vulnerabilities that are difficult to identify and address. Carefully managing network complexity is vital for effective security.
Comparing with Alternative Security Measures

Consumer-grade firewalls are just one piece of the security puzzle. A comprehensive approach requires understanding the strengths and weaknesses of various security tools. This comparison will examine consumer-grade firewalls alongside other common security measures like antivirus software, anti-malware programs, and intrusion detection systems, highlighting their individual roles and how they complement each other. A multi-layered approach is often more effective than relying solely on a single tool.A robust security posture is not a single product but a strategy.
While a consumer-grade firewall acts as a first line of defense, other tools are vital in protecting against various threats. This discussion will help you understand the strengths and weaknesses of each tool and build a more comprehensive security plan.
Alternative Security Measures
Consumer-grade firewalls primarily monitor and control network traffic. They are good at blocking known malicious connections but are less effective against sophisticated threats or attacks targeting vulnerabilities within the system. Other security measures provide complementary protection. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of these measures is crucial for building a comprehensive defense.
Comparison of Security Solutions
The table below provides a comparative analysis of consumer-grade firewalls, antivirus software, anti-malware programs, and intrusion detection systems.
| Feature | Consumer-Grade Firewall | Antivirus Software | Intrusion Detection System (IDS) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cost | Typically low, often bundled with internet service or free options | Low to moderate, ranging from free to premium versions | Moderate to high, depending on the complexity and features |
| Ease of Use | Generally easy to configure, often requiring minimal technical expertise | Relatively easy to install and use, with user-friendly interfaces | Can be more complex to set up and configure, requiring some technical understanding |
| Performance | Can impact network performance if not properly configured, potentially slowing down internet access | Minimal impact on performance, especially with optimized software | Can have a noticeable impact on system resources, especially during high-traffic periods. |
| Features | Basic traffic filtering, port blocking, and some intrusion prevention | Scanning for malware, viruses, spyware, and other threats, quarantine and removal | Monitoring network traffic for malicious patterns, alerting administrators of potential intrusions |
Complementary Security
A consumer-grade firewall provides a fundamental level of network security, preventing unauthorized access. However, it doesn’t address threats already inside the network. Antivirus software and anti-malware programs are essential for detecting and removing malicious software, while intrusion detection systems (IDS) proactively monitor network traffic for suspicious activity. A multi-layered approach is crucial to mitigate risks effectively.
Analyzing Vulnerabilities and Risks
Consumer-grade firewalls, while offering a basic layer of protection, are often vulnerable to various attacks. Understanding these vulnerabilities and the potential risks is crucial for users to make informed decisions about their security posture. This section delves into the weaknesses of these firewalls and the potential consequences of their exploitation.Consumer-grade firewalls, designed for ease of use and affordability, often prioritize simplicity over advanced security features.
This simplification, while beneficial for novice users, can leave them exposed to threats that more sophisticated security solutions can mitigate.
So, are consumer-grade firewalls truly secure? It’s a complex question, especially when considering the ever-evolving threat landscape. While they offer a basic layer of protection, the sophistication of modern attacks often surpasses the capabilities of these basic tools. For a deeper dive into how tech trends like those behind MacroMedia’s Flash evolve, check out this insightful article on beyond the fad MacroMedia’s Flash matures.
Ultimately, a consumer firewall alone likely isn’t enough for robust protection against targeted attacks.
Potential Vulnerabilities in Consumer Firewalls
Consumer-grade firewalls frequently lack advanced filtering capabilities. Their rule sets are typically simpler and less comprehensive than those found in enterprise-grade firewalls. This limitation can allow unauthorized connections and malicious traffic to bypass the firewall. Moreover, older or poorly maintained software versions in these firewalls might contain known vulnerabilities that attackers can exploit. Furthermore, the limited processing power and memory of consumer-grade firewalls can make them susceptible to denial-of-service (DoS) attacks.
Potential Risks Associated with Consumer Firewalls
The risks associated with using consumer-grade firewalls stem directly from their limitations. A weak firewall can expose user devices to malware infections. Unauthorized access to personal data, including financial information and sensitive documents, is a major concern. Unprotected devices on the network are vulnerable to exploitation. Furthermore, compromised systems can be used as launching pads for attacks on other networks.
Exploitation Techniques for Attackers
Attackers leverage various techniques to exploit vulnerabilities in consumer-grade firewalls. One common approach is to exploit known vulnerabilities in the firewall software itself. Another method involves exploiting weaknesses in the operating system of the user’s computer, often by targeting known vulnerabilities that are not patched. Moreover, attackers may use social engineering tactics to trick users into disabling security features or providing them with access to their networks.
Impact on User Data and Privacy
The impact of a compromised consumer-grade firewall on user data and privacy can be significant. Attackers can steal sensitive personal information, financial details, and confidential documents. This information can be used for identity theft, financial fraud, or blackmail. Furthermore, a compromised system can be used as part of a larger botnet, enabling further malicious activities. The loss of privacy can have long-lasting repercussions for individuals.
So, are consumer-grade firewalls truly secure? It’s a tricky question, really. While they might offer a basic layer of protection, the VoIP industry’s guerilla-style effort to supplant traditional telcos ( voips guerilla effort to supplant traditional telcos ) highlights the ever-evolving threat landscape. Ultimately, a robust security strategy needs more than just a firewall, especially with the increasing sophistication of online attacks.
Consumer-grade firewalls are simply not enough in today’s digital world.
Real-World Examples of Compromised Consumer Firewalls
Numerous incidents illustrate the vulnerabilities of consumer-grade firewalls. For instance, a widely publicized incident involved a popular consumer firewall that was found to have a critical vulnerability allowing remote code execution. This vulnerability was exploited by hackers to gain control of user devices. Another example demonstrates how poorly configured consumer firewalls can lead to unauthorized access to home networks.
These incidents highlight the need for users to be vigilant about the security of their home networks.
Security Best Practices for Consumers
Consumer-grade firewalls, while a crucial first line of defense, aren’t foolproof. Maximizing their effectiveness requires proactive steps from the user. This section details essential practices to bolster security beyond the firewall’s basic functions. Understanding these strategies will empower consumers to create a more secure digital environment.
Strong Passwords and Account Security
Robust passwords are paramount to protecting online accounts. Weak passwords are easily compromised, opening doors to unauthorized access. Employing strong passwords significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized logins and data breaches. This proactive approach ensures the security of personal information and prevents potential identity theft.
- Use a password manager: Password managers generate and store complex, unique passwords for each online account. This automates the process and significantly reduces the risk of using the same password across multiple sites, a common vulnerability. A dedicated password manager ensures the safety of your credentials.
- Employ multi-factor authentication (MFA): MFA adds an extra layer of security beyond a password. This requires a second verification step, such as a code sent to a phone or a security key, making unauthorized access considerably more difficult. This is a fundamental practice for enhancing security in today’s digital landscape.
- Regularly change passwords: Change passwords periodically, especially for sensitive accounts like banking or email. This mitigates the risk of past breaches, and updates the security posture of your accounts.
Identifying and Avoiding Phishing Scams
Phishing attacks remain a significant online threat. These fraudulent attempts aim to trick users into revealing sensitive information, such as usernames, passwords, and credit card details. Understanding how these attacks work is critical for avoidance.
- Verify email addresses and links: Before clicking on links or downloading attachments, thoroughly inspect the sender’s email address and the link’s destination. Look for inconsistencies in the sender’s address or any unusual requests. Scrutinizing these details is crucial in identifying phishing attempts.
- Be wary of suspicious requests: Never respond to emails or messages demanding immediate action or personal information. If something seems too good to be true or too urgent, it likely is. Exercise caution and skepticism when dealing with unsolicited communications.
- Report suspicious emails: Report suspicious emails to the appropriate authorities to help prevent others from falling victim to similar scams. This collective action contributes to a more secure online environment.
Firewall Configuration for Optimal Security
Proper firewall configuration is crucial for a strong defense. Understanding how to configure firewall settings effectively can significantly improve security.
Ever wondered if those consumer-grade firewalls are truly secure? While Microsoft and HP’s recent announcements at Telecom World, like new networking gear, might seem unrelated, they actually highlight a crucial point. Microsoft HP announce new products at telecom world shows a push towards more robust security solutions, suggesting that even the best consumer firewalls might not provide the same level of protection as enterprise-grade hardware.
So, the answer to the original question remains a bit complex. It depends on your needs and budget.
- Enable firewalls on all devices: Ensure firewalls are enabled on all devices connected to the network, including computers, smartphones, and other network-enabled devices. This creates a multi-layered defense against potential threats.
- Restrict inbound connections: Limit inbound connections to only necessary services and ports. This prevents unauthorized access to your devices and network. Configure the firewall to deny access to unwanted traffic.
- Regularly update firewall software: Ensure your firewall software is up-to-date with the latest security patches and updates. Keeping the software current addresses known vulnerabilities and ensures your security is always current with the latest threat landscape.
Describing Future Trends in Consumer-Grade Firewalls
Consumer-grade firewalls are constantly evolving to meet the ever-increasing demands of a complex digital landscape. As internet usage and reliance on connected devices grow, these firewalls must adapt to new threats and provide robust protection for home users. This section explores potential future developments, emerging trends, and the factors impacting the future of consumer-grade firewall security.Future firewalls will likely incorporate more sophisticated threat detection and response mechanisms.
This evolution is driven by the rise of sophisticated malware and the need for proactive security solutions. Expect enhanced real-time threat intelligence feeds and more advanced machine learning algorithms to identify and mitigate emerging threats.
Integration with Home Networks and IoT Devices
The proliferation of Internet of Things (IoT) devices within homes presents both opportunities and challenges for consumer-grade firewalls. Future firewalls will likely play a more central role in managing and securing these interconnected devices. This integration will involve advanced filtering capabilities to control device communication and traffic, potentially through centralized management interfaces. These interfaces will provide users with a clear picture of the activity on their home network and the security posture of their IoT devices.
Users will be able to easily identify and block potentially malicious devices or connections.
Enhanced AI and Machine Learning Capabilities
Machine learning algorithms are poised to revolutionize consumer-grade firewall security. The future will see more sophisticated AI-powered threat detection systems capable of identifying patterns and anomalies in network traffic that traditional methods might miss. This includes real-time analysis of network activity to identify and block malicious actors before they can cause significant harm. These systems will be capable of adapting to evolving threats and learning from past incidents to improve their detection accuracy.
For instance, a firewall could learn the normal behavior of a user’s devices and identify unusual activity, such as a sudden surge in data transfer or unusual communication patterns.
Multi-Factor Authentication and Enhanced User Experience
Future firewalls will likely incorporate more robust multi-factor authentication (MFA) mechanisms. This will help strengthen the security posture of the network by adding an extra layer of protection against unauthorized access. The user experience will also be enhanced, with intuitive interfaces and personalized security profiles. These personalized security profiles will allow users to customize their security settings based on their specific needs and preferences, streamlining the overall security process.
This is essential for the increasing number of users with varying levels of technical expertise.
Cloud-Based Threat Intelligence and Updates
Cloud-based threat intelligence will become increasingly important for consumer-grade firewalls. This will enable firewalls to access and leverage real-time threat data from a wider network of sources, enabling them to adapt quickly to evolving threats. Automatic updates and continuous monitoring will ensure that firewalls are always equipped with the latest threat detection and mitigation techniques. Users will benefit from consistently updated threat intelligence without needing to manually update their software.
Factors Impacting Future Development
- Rise of IoT Devices: The increasing number of interconnected devices in homes demands robust security mechanisms to control and monitor traffic. This will drive development in firewall capabilities to address the security implications of IoT.
- Sophistication of Cyber Threats: The evolution of sophisticated malware and cyberattacks requires firewalls to adapt with more advanced detection and response mechanisms.
- User Expectations: Consumers expect seamless and intuitive security experiences. Firewalls will need to meet these expectations by providing easy-to-use interfaces and personalized security settings.
- Technological Advancements: The continuous advancement of machine learning, AI, and cloud computing will significantly impact the development of future firewalls, enabling enhanced security features and functionalities.
Closing Summary
In conclusion, while consumer-grade firewalls offer a basic level of protection, their security is not foolproof. Their effectiveness relies heavily on proper configuration, user awareness, and ongoing maintenance. While they’re a valuable first line of defense, they shouldn’t be the only security measure employed. Combining them with other security tools, such as antivirus software and strong passwords, is crucial for comprehensive protection.
Ultimately, a multi-layered approach is key to robust online security.