Canadian Recording Industry Hunts P2P Users
Canadian recording industry hunts p2p users, a complex issue with deep roots in the evolution of the music industry. From the historical significance of Canadian music to the impact of peer-to-peer file sharing, this exploration dives into the challenges and strategies employed by artists and labels. It examines the changing landscape of music consumption, including streaming services and licensing models, and assesses the impact of piracy on Canadian artists and labels.
This in-depth look at the issue will examine the legal framework surrounding copyright in Canada, exploring successful enforcement actions and the role of copyright collectives. We’ll also consider the future of the Canadian music industry, anticipating the influence of emerging technologies and the need for adapting copyright laws. The debate around p2p file sharing and its consequences will be analyzed from a Canadian perspective, considering the unique economic and cultural context.
Background of the Canadian Recording Industry
The Canadian recording industry, a vibrant and evolving sector, has played a significant role in the country’s cultural landscape and economy. From humble beginnings to a global presence, its journey mirrors the nation’s own artistic and entrepreneurial spirit. It has weathered technological advancements, economic fluctuations, and shifts in consumer preferences, emerging stronger and more adaptable.The industry’s enduring appeal lies in its ability to connect with Canadians through diverse musical expressions.
It fosters creativity, provides employment opportunities, and contributes to Canada’s cultural identity on a global stage. Understanding its history, economic impact, and current trends is crucial to appreciating its significance.
Historical Overview
The Canadian recording industry’s roots trace back to the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Early recordings primarily focused on popular music of the time, often reflecting international trends. The development of recording technology, coupled with the rise of radio broadcasting, significantly boosted the industry’s growth. Notable milestones include the emergence of prominent Canadian recording artists and labels, marking the industry’s evolution from a relatively nascent sector to a more established one.
The industry’s journey demonstrates its resilience and adaptation to evolving musical tastes and technologies.
Economic Importance
The Canadian recording industry is a substantial contributor to the Canadian economy. It generates revenue through various channels, including record sales, streaming royalties, and live performances. The industry supports numerous jobs in music production, distribution, marketing, and related fields. It also plays a vital role in promoting Canadian culture and attracting tourism. The industry’s influence extends beyond its immediate financial impact, as it fuels creativity and innovation within the broader cultural sector.
Genres and Subgenres
Canada boasts a diverse range of musical genres, reflecting the nation’s multicultural heritage. From classic rock and folk to contemporary pop and hip-hop, Canadian artists have made significant contributions to various music genres. Furthermore, the subgenres within each major category, such as indie rock, electronic dance music, and jazz, are prevalent and well-represented. This demonstrates the breadth and depth of musical talent within the country.
Revenue Streams
Canadian recording artists and labels rely on various revenue streams to sustain their operations. These include record sales, streaming royalties, licensing fees, merchandise sales, and live performances. The proportion of income from each stream varies depending on the artist’s popularity and the specific genre of music. This diversity of income sources highlights the adaptability and resourcefulness of the industry.
Technological Adoption and Market Trends
The Canadian recording industry has embraced technological advancements throughout its history. The transition from vinyl records to CDs and then to digital downloads and streaming services is a prime example of this evolution. This has fundamentally reshaped the way music is consumed and distributed. Current market trends highlight a strong emphasis on digital platforms, as well as a growing interest in live music performances and collaborations.
Role of Digital Platforms, Canadian recording industry hunts p2p users
Digital platforms have revolutionized the music industry globally, and Canada is no exception. Streaming services like Spotify, Apple Music, and others have become integral to how Canadians consume music. These platforms provide a convenient and accessible way for artists to reach audiences and for listeners to discover new music. The accessibility and affordability of digital music have broadened the reach of Canadian artists.
The shift to digital platforms has created new opportunities for artists to connect with fans worldwide.
P2P File Sharing in the Past and Present
The rise and fall of peer-to-peer (P2P) file-sharing networks dramatically reshaped the global music industry. Initially hailed as a revolutionary way to access music, P2P quickly became a source of controversy and legal battles, ultimately influencing how music is consumed and distributed today. This shift is a fascinating case study in the interplay between technological innovation and the established structures of an industry.The decentralized nature of P2P networks fundamentally altered the landscape of music distribution.
Users could share files directly with each other, bypassing traditional distribution channels and creating a new, largely unregulated, ecosystem. This accessibility was a double-edged sword, offering unprecedented access to music but also posing significant challenges to the recording industry’s business model.
Key Characteristics of P2P File-Sharing Networks
P2P networks rely on a distributed architecture where users act as both clients and servers. This allows for rapid file sharing as the network itself is not centralized. Files are fragmented and distributed across many computers, making them difficult to track and remove. The decentralized nature, while enabling rapid file sharing, also poses challenges in terms of enforcement and copyright protection.
The ease of access to copyrighted material was a crucial element in the controversies that followed.
Impact of P2P File Sharing on the Music Industry
P2P file sharing significantly impacted the music industry globally. It led to a substantial decline in music sales, especially in the early 2000s, as consumers increasingly opted for free downloads. Artists and record labels suffered financially, and the industry grappled with adapting to this new paradigm of music consumption. The shift towards digital music consumption, facilitated by P2P networks, was a critical factor in the industry’s eventual adaptation to the digital age.
The impact was particularly notable for independent artists, whose music often relied on physical sales and traditional distribution channels.
Legal Battles and Controversies
The legal battles surrounding P2P file sharing were intense and complex. Record labels and copyright holders filed lawsuits against users and operators of P2P networks, seeking injunctions and damages. The legal landscape surrounding copyright infringement became a crucial battlefield, with courts grappling with the balance between innovation and intellectual property rights. This period highlighted the challenges of adapting legal frameworks to new technological developments.
The legal battles often pitted individual users against large corporations, creating a significant societal discussion about fair use and the responsibility of technology companies.
Comparison of P2P Usage Across Countries
P2P file-sharing platforms were used in different countries, with varying levels of adoption. Cultural attitudes towards intellectual property, legal frameworks, and the availability of alternative music access played a role. In countries with a strong tradition of intellectual property protection and readily available alternative platforms, P2P usage might have been less prevalent. The usage patterns reflected the specific legal and cultural contexts in each nation.
Canada, like many other countries, experienced a rise and fall in P2P file sharing, with its usage mirroring global trends.
Strategies Employed by the Music Industry to Combat P2P File Sharing
The music industry implemented various strategies to combat P2P file sharing. These included legal action against users and network operators, lobbying for stricter copyright enforcement, and developing new business models like online music streaming. The industry’s response to the challenge was multifaceted, reflecting the industry’s efforts to adapt and survive in a rapidly changing digital landscape. They also employed public awareness campaigns to highlight the importance of copyright protection.
Technological Advancements Influencing the Decline of P2P File Sharing
Technological advancements played a crucial role in the decline of P2P file sharing. The rise of streaming services, offering legal and convenient access to music, significantly reduced the appeal of P2P networks. The increased availability of high-speed internet and reliable digital music delivery services, coupled with the introduction of new and convenient platforms, diminished the incentive for illegal downloads.
The ease of access to legal alternatives, coupled with the growth of digital rights management (DRM) technologies, were significant factors in the decline.
The Current Landscape of Music Consumption
The Canadian music scene is undergoing a dramatic transformation, shifting from traditional album sales to a predominantly digital and streaming-based model. This shift has profoundly impacted the revenue streams of artists and labels, necessitating a deep understanding of the current methods of consumption and the associated licensing models. This evolution demands a critical look at the interplay between music piracy, streaming services, and the role of digital rights management in safeguarding copyright.The contemporary Canadian music consumer enjoys a wealth of options for accessing music.
The Canadian recording industry’s crackdown on peer-to-peer file-sharing is a classic case of trying to stem the tide of digital distribution. But as technology evolves, perhaps a more effective strategy lies in embracing digital identity solutions like Microsoft Passport and the future of authentication. microsoft passport and the future of authentication could offer a more nuanced way to track and manage digital rights, which in turn might make the fight against unauthorized sharing more sustainable in the long run.
Ultimately, the Canadian recording industry still faces the challenge of adapting to the digital landscape.
Streaming services have become ubiquitous, offering a vast library of songs at a subscription fee. This accessibility contrasts sharply with the traditional model of purchasing albums, significantly altering the music industry’s financial dynamics. Understanding these contrasting methods and the various licensing models is crucial to comprehending the current state of the Canadian recording industry.
Current Methods of Music Consumption in Canada
Canadians predominantly consume music through streaming services. Platforms like Spotify, Apple Music, and others offer extensive music catalogs, accessible through subscriptions or ad-supported tiers. This model fosters convenience and widespread access, making music consumption more democratic than ever before. Further contributing to this trend are the rising popularity of music streaming services among younger demographics, which is further evidenced by the increased adoption of digital music streaming among younger generations.
Comparison of Streaming Services and Other Digital Music Platforms
Streaming services like Spotify and Apple Music dominate the market, offering vast catalogs of music with diverse genres and artists. These services compete with other digital music platforms, including those that focus on specific genres or emerging artists. These services provide a dynamic alternative for listeners seeking curated experiences or niche content. A comparison often highlights the varying price points, subscription models, and the specific features of each platform, which further shapes the consumer’s decision-making process.
Licensing Models Used by the Music Industry
The music industry relies on various licensing models to manage the rights of musical works. These models typically involve agreements between record labels, artists, and streaming platforms. Licensing agreements often specify royalty rates, usage terms, and the distribution of revenue among various stakeholders. The complexities of these models ensure the rights of all parties involved are appropriately protected and their earnings are fairly distributed.
Impact of Music Piracy on the Canadian Recording Industry
Music piracy remains a significant concern for the Canadian recording industry. Illegal downloads and streaming of copyrighted music deprive artists and labels of legitimate revenue, impacting their ability to create and promote new music. Piracy has a demonstrably negative effect on the industry, particularly in terms of the economic losses sustained by artists and labels. The availability of pirated content undermines the financial sustainability of the industry.
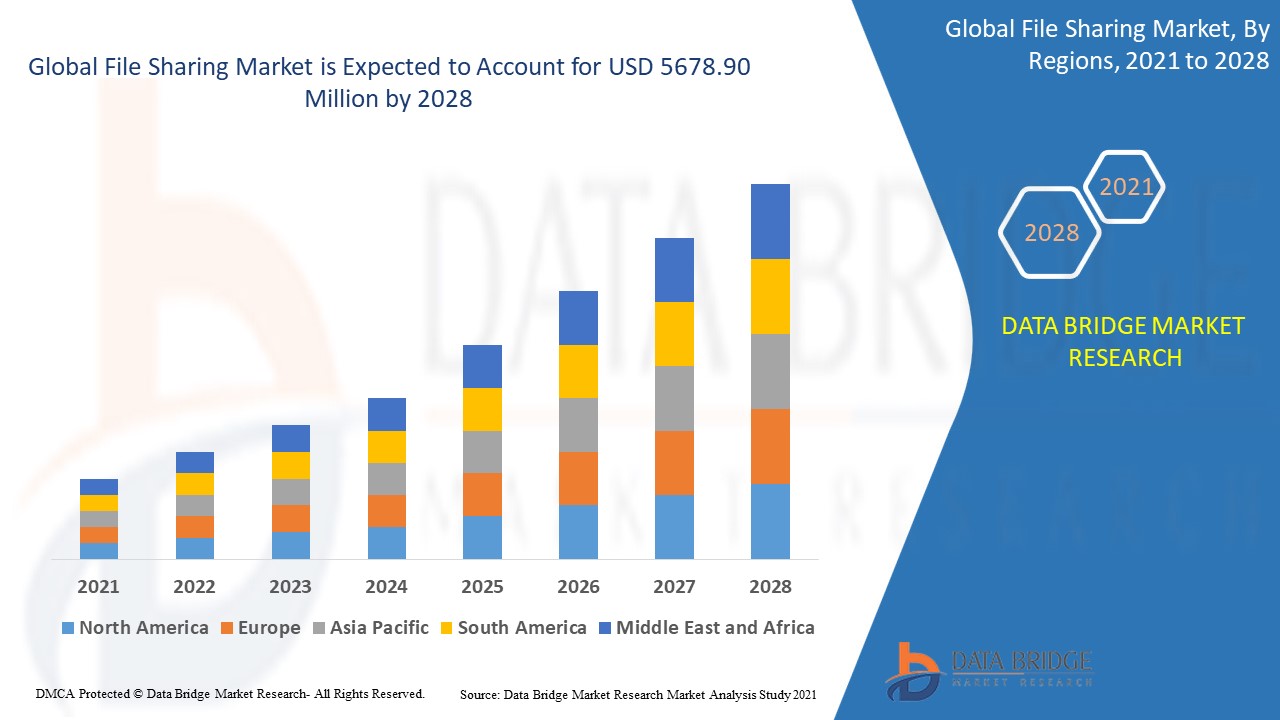
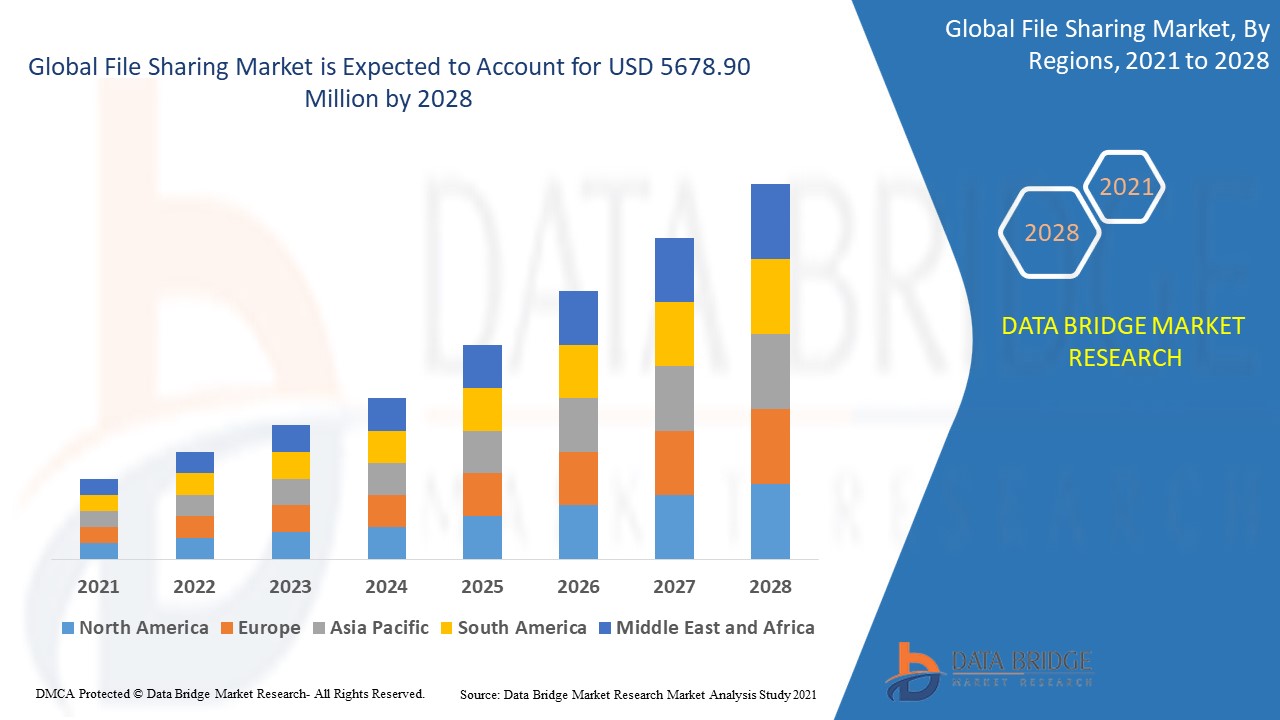
Table Comparing Revenue Streams from Traditional Sales versus Streaming Services
| Revenue Stream | Traditional Sales | Streaming Services |
|---|---|---|
| Artist Royalties | Based on album sales and physical copies | Based on streams, with variable rates depending on the licensing agreements |
| Label Revenue | From album sales, physical copies, and associated merchandise | From licensing deals with streaming platforms and artist royalties |
| Overall Impact | Revenue declines due to the shift to digital consumption | Significant revenue generation but with different financial dynamics |
The table highlights the fundamental differences in revenue generation between traditional and modern models. It showcases how the shift to digital music consumption has redefined how artists and labels generate income.
Role of Digital Rights Management (DRM) in Protecting Copyrighted Music
Digital rights management (DRM) technologies play a crucial role in safeguarding copyrighted music. DRM systems employ various techniques to restrict unauthorized copying and distribution of digital music files. These technologies are critical in mitigating music piracy and safeguarding the financial interests of artists and labels in the face of readily available digital formats. DRM plays a critical role in establishing a fair playing field in the digital music landscape.
Impact of P2P File Sharing on Canadian Artists and Labels
The rise of peer-to-peer (P2P) file sharing platforms in the early 2000s fundamentally altered the music industry landscape, particularly for Canadian artists and labels. This shift wasn’t just about technological change; it represented a significant paradigm shift in how music was consumed and monetized, leading to profound economic and artistic consequences. Canadian artists and labels, already navigating a complex and competitive marketplace, faced new challenges in adapting to this rapidly evolving environment.P2P file sharing created a readily available, often free, access point to music.
The Canadian recording industry’s crackdown on peer-to-peer file-sharing is nothing new, but it’s interesting to see how these issues connect to broader digital security concerns. For example, recent news about attack code targeting Windows Messenger service, as detailed in this article , highlights the constant evolution of digital threats. This ultimately underscores the ongoing struggle for the Canadian recording industry to combat illegal downloads and protect their artists’ livelihoods.
This ease of access, while convenient for consumers, severely impacted the revenue streams of artists and labels, primarily by circumventing the traditional distribution and sales channels. The loss of legitimate revenue had significant repercussions on the industry’s financial health and its ability to support Canadian musicians.
Challenges Faced by Canadian Artists and Labels
Canadian artists and labels faced numerous challenges due to P2P file sharing. The unauthorized downloading of music drastically reduced sales of physical and digital albums, significantly impacting the revenue streams crucial for artist support and label operations. This widespread practice created a significant hurdle for artists aiming to sustain their careers and for labels to maintain their profitability.
Economic Losses Experienced by Canadian Artists and Labels
The economic impact of P2P file sharing on Canadian artists and labels was substantial. Unauthorized downloads resulted in a significant decrease in album sales, royalties, and overall revenue for artists. Labels also lost revenue from sales of CDs and digital downloads, impacting their ability to invest in new music and artist development. These losses directly impacted the sustainability of the Canadian recording industry.
Estimates from industry reports highlight the significant financial strain on the sector. For example, a 2008 study by the Recording Industry Association of America (RIAA) estimated substantial losses due to piracy across the industry.
Strategies Used by Canadian Artists and Labels to Adapt to Changing Market Conditions
Canadian artists and labels employed various strategies to adapt to the evolving music consumption landscape. The transition to digital distribution and the creation of online platforms to directly engage with fans became increasingly important. New strategies included exploring alternative revenue streams, such as live performances, merchandise, and licensing opportunities. Artists also looked for new ways to connect with their fans, recognizing the importance of building a loyal fanbase.
Revenue Models Used by Canadian Recording Artists
- Streaming Services: Artists now receive revenue from streaming platforms like Spotify, Apple Music, and others. This revenue is typically based on the number of streams generated, and different models exist, such as pay-per-stream and a percentage of the platform’s revenue.
- Merchandise Sales: Artists can generate income by selling merchandise, such as T-shirts, posters, and other branded items. This strategy helps artists diversify their revenue sources and directly connect with fans.
- Live Performances: Live performances, including concerts, festivals, and other events, provide an essential source of revenue for artists. This revenue stream is often dependent on ticket sales and merchandise sales at the events.
- Licensing and Royalties: Music licensing for use in film, television, and advertising is another income stream for artists. This can include both sync licensing (using a song in a specific moment of a film or show) and broader licensing agreements.
- Subscription Services: Artists may participate in subscription services, providing exclusive content to subscribers in exchange for a recurring fee.
The diversification of revenue streams became crucial for Canadian artists to adapt to the changing market.
Examples of Successful Strategies Employed by Canadian Labels to Counter P2P File Sharing
Labels employed various strategies to combat P2P file sharing, including proactively developing digital distribution channels and offering artists more control over their online presence. This also involved partnering with streaming services and online retailers to offer music legally.
Effect of P2P File Sharing on the Overall Artistic Output in Canada
P2P file sharing, while damaging to revenue streams, did not significantly diminish artistic output in Canada. Canadian artists and labels, though facing substantial challenges, continued to produce music. The shift in the industry’s economic model prompted a re-evaluation of revenue generation and creative strategies, leading to alternative approaches to building audiences and generating income. It is important to note that the long-term effects of P2P file sharing are still being assessed.
Current Approaches to Copyright Enforcement
Navigating the complex digital landscape of music requires robust copyright enforcement. This crucial aspect protects creators’ rights and ensures a sustainable industry. The methods used to safeguard intellectual property are constantly evolving to keep pace with technological advancements. Understanding these approaches is vital for artists, labels, and consumers alike.The legal framework in Canada, while aiming to provide a comprehensive safety net, faces challenges in the rapidly shifting digital environment.
The balance between encouraging innovation and safeguarding creators’ rights is often a delicate one, demanding continuous adaptation and refinement.
The Canadian recording industry’s crackdown on P2P file-sharing is a fascinating case study in adapting to changing technology. While they pursue those who infringe copyright, it’s interesting to consider how technology like microsoft gives voice to mobile devices might eventually affect how music is consumed and shared, possibly making the entire P2P battle obsolete. This evolving landscape highlights the continuous struggle between protecting intellectual property and fostering innovation in the digital realm.
Legal Framework Governing Copyright in Canada
Canadian copyright law, rooted in the Copyright Act, provides legal protection for original works of authorship, including musical compositions. This framework Artikels the rights of copyright holders, including the exclusive right to reproduce, distribute, and perform the work publicly. The Act defines various categories of works and grants specific rights to their creators. The act also includes provisions for exceptions, such as fair dealing, that allow limited use of copyrighted material without permission.
This is essential to balance copyright protection with the public interest and allow for educational and critical use of copyrighted material.
Examples of Successful Copyright Enforcement Actions in Canada
Numerous successful copyright enforcement actions have been documented in Canada. These cases demonstrate the commitment of the legal system to protect the rights of music creators. These actions often involve takedown requests for unauthorized uploads on online platforms. Notable cases have involved significant financial penalties and injunctions against individuals or entities engaging in widespread copyright infringement. These actions serve as a deterrent and underscore the seriousness with which copyright violations are treated.
Roles of Copyright Collectives in the Music Industry
Copyright collectives play a vital role in the Canadian music industry. These organizations act as intermediaries, facilitating the licensing of music for various uses. They negotiate licensing agreements with users of copyrighted music, such as broadcasters, record stores, and online streaming platforms. They also collect royalties on behalf of songwriters and performers. This ensures a fair distribution of income to those who contribute to the creation and performance of music.
Importance of International Cooperation in Copyright Enforcement
International cooperation is crucial in addressing copyright infringement. Global challenges require global solutions. International treaties and agreements facilitate the sharing of information and coordination of enforcement efforts across borders. This collaborative approach helps tackle large-scale copyright violations, often facilitated by the ease of global online distribution. International cooperation is essential for the effective enforcement of copyright laws.
Challenges and Complexities of Enforcing Copyright in the Digital Age
The digital age presents unique challenges to copyright enforcement. The ease of replicating and distributing digital content online makes it significantly more difficult to monitor and control unauthorized use. Identifying and tracking infringers, especially in cases of peer-to-peer file sharing, has become more complex. Furthermore, the rapid evolution of technology necessitates continuous adaptation of legal frameworks and enforcement strategies.
Legal Avenues for Copyright Infringement in Canada
| Legal Avenue | Description |
|---|---|
| Civil Action | A legal action pursued in a civil court to seek damages and/or injunctions against infringers. |
| Criminal Prosecution | Legal action initiated by the Crown to prosecute individuals or entities engaging in significant or organized copyright infringement. |
| Administrative Actions | Procedures carried out by copyright collectives or designated bodies to enforce licensing agreements or address minor infringements. |
| Takedown Requests | Formal requests to online platforms to remove infringing content. |
Future Trends and Predictions: Canadian Recording Industry Hunts P2p Users
The Canadian recording industry is poised for a period of significant transformation, driven by rapid technological advancements and evolving consumer habits. Understanding these shifts is crucial for artists, labels, and industry stakeholders to navigate the future successfully. The convergence of technology and artistic expression will shape the landscape, demanding adaptability and a proactive approach to emerging trends.
Forecasting the Future of the Canadian Recording Industry
The Canadian recording industry is likely to see a continued shift towards digital consumption models. Streaming services will remain dominant, with subscription models further solidifying their position. The rise of personalized music recommendations and tailored playlists will influence how music is discovered and consumed. Independent artists will continue to find avenues for exposure and income generation through online platforms, social media, and direct-to-consumer strategies.
Impact of Emerging Technologies
Emerging technologies, such as virtual and augmented reality, could revolutionize the music listening experience. Immersive environments could provide new ways to engage with music, allowing for interactive and multi-sensory experiences. The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into music creation, distribution, and consumption will reshape the creative process and streamline business operations. Examples of AI’s potential include automated music composition, personalized recommendations, and enhanced marketing strategies.
Role of Artificial Intelligence in Music
AI is rapidly changing the way music is created, distributed, and consumed. AI-powered tools can generate original music compositions, assisting artists in creating new sounds and styles. AI algorithms can personalize music recommendations, providing tailored experiences for individual listeners. This personalization will be a key aspect of future music consumption. Furthermore, AI can enhance the efficiency of music distribution, automating tasks and optimizing marketing strategies.
Evolving Copyright Laws
Copyright laws need to adapt to the changing landscape of music creation and distribution, especially in light of new technologies. Copyright protection must be robust enough to accommodate the use of AI in music creation while also ensuring that artists receive fair compensation for their work. Clearer definitions of ownership and licensing rights in the context of AI-generated music are crucial.
Strategies for Canadian Artists and Labels
Canadian artists and labels must adapt to the evolving digital landscape by embracing new technologies and adopting innovative business strategies. Developing strong online presences, fostering engagement with fans through social media, and diversifying income streams are essential. Collaborations with other artists, creators, and tech companies can open new opportunities and broaden reach. Building direct relationships with fans through exclusive content and events is crucial for long-term sustainability.
Predicted Evolution of Music Consumption in Canada
| Year | Dominant Music Consumption Method | Emerging Trends |
|---|---|---|
| 2024-2028 | Streaming services (subscription and ad-supported) | Rise of personalized playlists, interactive music experiences |
| 2029-2033 | Immersive experiences (VR/AR), AI-powered personalized music | Decentralized music platforms, increased user-generated content |
| 2034-2038 | AI-generated and curated music experiences | Integration of AI into music creation, distribution, and consumption |
This table illustrates a potential trajectory for music consumption in Canada. The shift from traditional streaming to immersive and AI-driven experiences is expected.
Final Conclusion

In conclusion, the Canadian recording industry’s battle against p2p file sharing highlights the ongoing tension between innovation and intellectual property protection in the digital age. The strategies employed by Canadian artists and labels, along with the legal framework, will shape the future of the industry. Understanding this dynamic is crucial for appreciating the challenges and opportunities facing the Canadian music scene.
The future of Canadian music, therefore, hinges on a delicate balance between embracing new technologies and safeguarding the rights of creators.