Computers Learning to Read Human Intentions Unveiling the Future
Computers learning to read human intentions is rapidly evolving, opening up exciting possibilities and raising critical questions. From understanding subtle cues in speech and body language to anticipating needs before they’re expressed, this technology promises to revolutionize how we interact with machines. This exploration delves into the methods, applications, ethical considerations, and future of this fascinating field.
The concept hinges on computers interpreting the underlying motivations behind human actions. This goes beyond simple command-following, instead aiming for a deeper understanding of what a person wants to achieve, enabling systems to anticipate and respond more intuitively. This sophisticated approach has the potential to transform diverse sectors, from healthcare and education to customer service and beyond.
Defining Human Intention Recognition in Computers
Human intention recognition is a crucial area of research in artificial intelligence, aiming to enable computers to understand and predict human actions based on various cues. This understanding is pivotal for developing more intuitive and user-friendly computer systems, from personalized recommendations to automated assistance in diverse fields. By recognizing intentions, computers can anticipate user needs, allowing for more proactive and helpful interactions.This involves a complex interplay of interpreting language, observing behavior, and considering contextual factors.
The goal is not simply to identify actions, but to understand the underlying motivations and goals driving those actions. This understanding is a significant step towards building truly intelligent systems that can adapt and respond effectively to human needs.
Defining Human Intentions, Computers learning to read human intentions
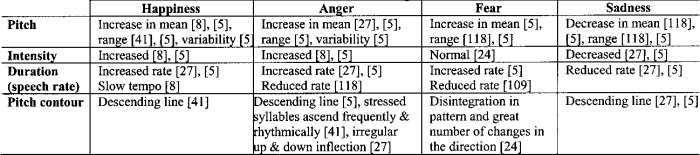
Human intentions are multifaceted and encompass a broad spectrum of motivations. They can be categorized in several ways, including emotional, cognitive, and physical intentions. Emotional intentions relate to feelings and desires, while cognitive intentions involve thoughts and reasoning processes. Physical intentions refer to planned actions and movements.
Categorizing Intention Types
Intentions can be further categorized by their complexity. Simple intentions, like wanting a cup of coffee, are straightforward to identify. More complex intentions, such as planning a weekend trip, involve multiple steps and require deeper analysis.
Challenges in Interpretation
Accurately interpreting human intentions from various sources like language, behavior, and context presents numerous challenges. Ambiguity in language, variations in nonverbal cues, and the influence of context can significantly affect the accuracy of interpretation. For example, a simple statement like “I’m tired” could indicate a variety of intentions, from wanting to rest to needing a specific action. Similarly, body language can be misinterpreted, and contextual factors, such as social norms and cultural background, play a critical role.
Computers are getting increasingly adept at deciphering human intentions, a fascinating development. This advancement, combined with the increasing importance of secure online connections, is why Microsoft is pushing VPNs to mainstream adoption. Microsoft pushes VPN to mainstream is a smart move, recognizing the growing need for privacy and security in our digital lives. Ultimately, as computers become more attuned to our intentions, these security measures become even more crucial.
Methods for Intention Recognition
- Analyzing linguistic cues: This involves examining the words, phrases, and sentence structure used by a person. Natural Language Processing (NLP) techniques can be applied to identify s, sentiment, and the overall meaning conveyed.
- Observing behavioral patterns: This approach involves tracking and analyzing various forms of human behavior, such as facial expressions, gestures, and body language. Machine learning algorithms can be trained to recognize patterns indicative of specific intentions.
- Considering contextual factors: The surrounding circumstances, including the time, place, and social environment, significantly influence human intentions. Integrating contextual information into the analysis enhances the accuracy of intention recognition.
Illustrative Table of Intention Recognition
| Intention Type | Signal Source | Interpretation Method | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Physical Intention | Body language, gestures | Machine learning model trained on videos of actions | Picking up a phone to call someone |
| Emotional Intention | Facial expressions, tone of voice | Sentiment analysis of text and audio | Expressing anger or sadness |
| Cognitive Intention | Language, search queries | Natural Language Processing (NLP) to extract meaning and intent | Planning a trip to a specific location |
| Social Intention | Conversation dynamics, social context | Analyzing social interactions and patterns | Greeting someone |
Methods for Recognizing Human Intentions
Unveiling the inner workings of the human mind—determining intentions—has long been a challenge for computer science. As machines become more integrated into our daily lives, the ability to anticipate and respond to human intentions is crucial for seamless interaction. This quest necessitates the development of sophisticated methods that can interpret diverse human inputs, from speech and facial expressions to body language and written text.Machine learning algorithms, combined with advanced signal processing techniques, are key components in this endeavor.
By analyzing patterns in data, these methods aim to predict future actions based on observed behaviors. This involves intricate processes of data extraction, feature selection, and model training, each with its own set of challenges and opportunities.
Machine Learning Approaches
Various machine learning models are employed to recognize human intentions. Supervised learning, where algorithms are trained on labeled data of intentions and corresponding inputs, is a common approach. This method relies on the availability of substantial, well-categorized datasets. For example, a dataset containing images of facial expressions associated with specific emotions (joy, anger, sadness) could be used to train a model to recognize emotional intentions.
Other models, like deep learning architectures, can learn intricate patterns from data without explicit labeling, making them adaptable to complex, unstructured inputs. Recurrent neural networks (RNNs) excel at processing sequential data, like speech, enabling them to capture the temporal dynamics of intentions.
Signal Processing Techniques
Signal processing techniques are crucial for extracting meaningful information from raw human inputs. These techniques involve filtering, feature extraction, and noise reduction. For example, in speech recognition, techniques like short-time Fourier transform (STFT) convert audio signals into frequency representations, facilitating the identification of speech patterns associated with specific intentions. Similarly, in analyzing facial expressions, techniques like Principal Component Analysis (PCA) can reduce dimensionality, focusing on the key features that indicate the intended emotion.
Furthermore, methods for analyzing body language, such as motion capture or optical flow, allow the extraction of kinematic information that reveals the underlying intentions.
Data Sources for Intention Recognition
Different data sources offer varying insights into human intentions. Speech provides rich information about the content and emotional tone of communication. Facial expressions, often subtle, convey emotional states and intentions. Body language, encompassing posture and gestures, reveals social cues and intentions. Textual data, encompassing written communication, offers a record of intentions through the words and phrases employed.
The choice of data source depends on the specific context and the type of intention to be recognized.
Comparison of Data Sources
| Data Source | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Speech | Rich information on content and emotion; relatively abundant data | Can be affected by background noise; Requires sophisticated acoustic modeling |
| Facial Expressions | Subtle indicators of emotional states; Relatively fast analysis | Limited information on the context of the expression; Difficult to interpret complex emotions |
| Body Language | Reveals social cues and intentions; Provides contextual information | Requires complex models for accurate interpretation; Affected by external factors |
| Text | Direct representation of intended communication; Relatively easy to process | Limited information on non-verbal cues; Can be influenced by language nuances |
Potential Biases and Limitations
Current methods for intention recognition are susceptible to various biases and limitations. Datasets used for training may not be representative of the diversity of human populations, leading to biased models. Moreover, interpreting subtle or complex intentions can be challenging, particularly when dealing with ambiguous or conflicting cues. Cultural differences can also affect the accuracy of intention recognition, as non-verbal cues may have different meanings in different cultural contexts.
Furthermore, the context of the interaction plays a vital role in understanding intentions.
Applications of Intention Recognition in Computers: Computers Learning To Read Human Intentions
Intention recognition in computers is rapidly evolving, moving beyond simple command-based interactions to understand and anticipate user needs. This sophisticated approach enables computers to react more intelligently, enhancing user experience and overall efficiency across diverse sectors. By deciphering the underlying intent behind user actions, computers can personalize interactions and tailor responses to individual needs, leading to a more intuitive and satisfying experience.This understanding of user intent empowers computers to proactively assist users, anticipating their requirements and guiding them through complex tasks.
This is particularly beneficial in areas like healthcare, education, and customer service, where a more personalized and responsive approach can significantly improve outcomes. These advancements promise to streamline processes, reduce errors, and ultimately improve the quality of life for individuals interacting with technology.
Diverse Applications of Intention Recognition
Understanding user intent is key to creating truly user-friendly and efficient systems. This approach allows for a more personalized and responsive interaction. From simple tasks to complex operations, intention recognition empowers computers to anticipate and react to user needs.
- Healthcare: Intention recognition systems can analyze patient interactions with medical devices, virtual assistants, or even electronic health records. For example, if a patient repeatedly asks questions about a specific medication, the system can proactively suggest additional information, such as dosage guidelines or potential side effects. This proactive approach can improve patient safety and adherence to treatment plans.
Computers are getting increasingly adept at deciphering human intentions, which is pretty cool. Imagine a future where technology anticipates our needs before we even articulate them. This kind of advancement is fascinating, especially considering Google’s recent purchase of its first humble abode. This purchase, as reported in google buys its first humble abode , highlights the company’s ongoing investment in real-world applications.
Ultimately, such developments in both human-computer interaction and real estate point to an exciting future where technology and human interaction become even more intertwined.
- Education: In educational settings, intention recognition can be used to personalize learning experiences. Systems can analyze student interactions with learning materials, identify areas where students are struggling, and offer tailored support. For instance, if a student consistently struggles with a particular mathematical concept, the system can provide additional practice exercises or suggest alternative learning resources.
- Customer Service: Intention recognition can enhance customer service interactions by enabling systems to anticipate customer needs. For example, if a customer frequently asks about a specific product’s features, the system can automatically provide detailed information, reducing wait times and improving customer satisfaction.
Examples of Computer Reactions Based on Recognized Intentions
Computer responses vary based on the context and the specific intention recognized. These reactions can range from simple actions to more complex interactions.
- Example 1 (Healthcare): A patient uses a smart thermometer to take their temperature. The system recognizes the user’s intent to monitor their health and automatically sends a notification to the doctor if the temperature exceeds a predefined threshold.
- Example 2 (Education): A student asks a virtual tutor about a complex physics concept. The system recognizes the student’s intent to understand the concept and provides interactive simulations, animated explanations, and links to relevant resources. The system can also track the student’s understanding and adapt the teaching method accordingly.
- Example 3 (Customer Service): A customer interacts with a chatbot to order a product. The system recognizes the customer’s intent to purchase and automatically guides the customer through the ordering process, providing relevant information and options.
Impact on Various Sectors
Intention recognition systems are impacting multiple sectors by enhancing efficiency and user experience. This approach is especially relevant in sectors where personalization and proactive assistance are crucial.
| Application Area | Intention Recognized | System Example |
|---|---|---|
| Healthcare | Monitoring patient health status, seeking information about medications | Smart medical devices, virtual health assistants |
| Education | Understanding a concept, seeking additional practice, requesting feedback | Adaptive learning platforms, virtual tutors |
| Customer Service | Placing an order, seeking information about a product, expressing a complaint | Chatbots, virtual assistants |
Ethical Considerations of Intention Recognition
The ability of computers to understand human intentions holds immense promise for improving various aspects of our lives. From personalized recommendations to automated assistance, the potential applications are vast. However, this capability also raises significant ethical concerns that need careful consideration and proactive mitigation strategies. Intention recognition systems, if not designed and implemented responsibly, could lead to unintended consequences and exacerbate existing societal inequalities.Intention recognition in computers faces the challenge of navigating the complexities of human motivation and behavior.
While these systems can identify patterns and correlations, they often struggle to fully grasp the nuanced context behind human actions. This inherent limitation can lead to inaccurate or biased interpretations, potentially creating unfair or harmful outcomes. Therefore, a thorough understanding of the ethical dimensions is crucial for responsible development and deployment.
Potential Ethical Dilemmas
The potential for misuse of intention recognition technology is significant. Computers capable of understanding human intentions could be exploited for manipulation, surveillance, or discrimination. Privacy violations are a major concern, as systems might collect and analyze vast amounts of personal data to infer intentions. Furthermore, the lack of transparency in how these systems operate can lead to a loss of trust and accountability.
The accuracy of intention recognition systems is also a critical factor; flawed or biased systems could lead to unjust or harmful outcomes.
Privacy Concerns
Intention recognition systems often require access to extensive personal data, ranging from online browsing history to social media interactions. This data collection raises significant privacy concerns, as individuals may not be fully aware of how their data is being used or the potential for misuse. The potential for data breaches and unauthorized access further compounds these concerns. Protecting user privacy requires robust data security measures and clear guidelines for data collection and usage.
Computers are getting increasingly sophisticated at deciphering human intentions, which is pretty cool. Imagine a future where your computer anticipates your needs before you even type a command. This kind of advancement relies heavily on processing power, and recent breakthroughs, like the Intel P4 Extreme boosting performance off the clock intel p4 extreme boosts performance off the clock , are paving the way for these incredible leaps in AI.
This faster processing speed will likely be crucial for enabling computers to more accurately interpret subtle cues and ultimately understand our intentions more intuitively.
Security Risks and Manipulation
Intention recognition systems are susceptible to malicious attacks. Malicious actors could potentially manipulate these systems to infer false intentions or to gain unauthorized access to sensitive information. This manipulation could have severe consequences, ranging from financial fraud to political manipulation. Robust security measures, including encryption and authentication protocols, are crucial to prevent these attacks. Systems should also be designed with safeguards to prevent manipulation and ensure accuracy.
Mitigation Strategies for Biased or Inaccurate Recognition
Bias in intention recognition systems can arise from various sources, including the data used to train the system and the algorithms employed. To mitigate this risk, systems should be rigorously tested for bias and fairness. Diverse and representative datasets should be used for training, and algorithms should be carefully designed to minimize unintended biases. Regular audits and independent evaluations are also crucial to ensure ongoing fairness and accuracy.
Examples of Potential Misuse
Intention recognition could be misused in various ways. For example, employers might use it to assess employee intentions, potentially leading to discrimination or unfair treatment. Similarly, law enforcement agencies could use it to predict criminal behavior, potentially violating due process or targeting specific communities. In the educational context, systems could misinterpret student behavior, leading to inappropriate interventions.
Ensuring Transparency and Accountability
Transparency in intention recognition systems is crucial for building trust and accountability. Users should be informed about how their intentions are being assessed and the potential limitations of the system. Clear guidelines and ethical frameworks should be established to govern the development and deployment of these systems. Mechanisms for redress should be in place in case of harm or bias.
| Ethical Issue | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|
| Privacy violations | Robust data security measures, clear data usage policies, user consent mechanisms |
| Security risks | Strong encryption, authentication protocols, regular security audits |
| Bias and inaccuracy | Diverse and representative training data, algorithm fairness evaluations, regular audits |
| Manipulation | Robust security measures, user education, transparent system design |
| Lack of transparency | Clear documentation, user interfaces explaining system workings, mechanisms for user feedback |
Future Trends and Advancements
The future of human-computer interaction hinges on the ability of computers to understand and anticipate human intentions. As AI and machine learning technologies continue to evolve, the sophistication of intention recognition systems will dramatically improve, leading to more intuitive and user-friendly interfaces. This will have profound implications across numerous sectors, from personalized education to automated customer service.The field of human intention recognition is rapidly advancing, fueled by advancements in deep learning, natural language processing, and multimodal data analysis.
These advancements are enabling computers to process a wider range of input signals, including speech, facial expressions, body language, and even physiological signals, to better infer user intentions. This leads to more nuanced and accurate predictions of what a user wants to achieve.
Emerging Technologies and Their Impact
Emerging technologies like multimodal learning, where computers process multiple data streams simultaneously, will significantly enhance the accuracy of intention recognition. This includes not only analyzing visual cues but also incorporating audio and physiological data. For example, a system might combine a user’s facial expressions with their voice tone and heart rate to predict their level of engagement or frustration with a task.
This integrated approach will allow for more comprehensive and accurate understanding of the user’s intent. Similarly, advancements in natural language processing will enable computers to grasp the subtle nuances of human language, recognizing not just the literal words but also the underlying meaning and intent behind them.
Advancements in AI and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning algorithms are continuously improving, enabling computers to learn from massive datasets of human behavior. These algorithms are becoming more adept at identifying patterns and anomalies in human interactions, allowing for more proactive and anticipatory systems. For instance, a personalized learning system could anticipate a student’s need for additional support based on their past performance and real-time physiological feedback.
This personalized approach will lead to more efficient and effective learning outcomes. Reinforcement learning techniques are also being explored to train systems to adapt to individual user preferences and behaviours.
Proactive Intention Recognition Systems
The possibility of creating systems that proactively anticipate human intentions is a significant area of research. Imagine a system that anticipates a user’s need for information before they even articulate it. This could be implemented in various contexts, from intelligent personal assistants to automated customer support systems. A system might anticipate a user’s need for a specific piece of information based on their past search history, current context, and even their emotional state.
The key here is to combine vast amounts of data with sophisticated predictive models to go beyond simply reacting to user input and anticipate their future actions.
Predicted Advancements in Computer-Human Interaction
| Area of Advancement | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Multimodal Intention Recognition | Systems will process multiple data streams (visual, auditory, physiological) to gain a more comprehensive understanding of user intentions. | Enhanced accuracy and nuance in intention recognition. |
| Natural Language Understanding | Improved ability to interpret subtle nuances in human language, including sarcasm, humor, and emotional context. | More effective communication and interaction with computers. |
| Proactive Intention Recognition | Systems will anticipate user needs and provide relevant information or actions before the user explicitly requests them. | Increased efficiency and user satisfaction, improved user experience. |
| Personalized Learning Systems | Systems will adapt to individual user learning styles, identifying potential roadblocks and proactively providing support. | Improved learning outcomes and tailored educational experiences. |
Illustrative Examples of Intention Recognition in Action
Intention recognition in computers is moving beyond simple commands to understanding the underlying desires and goals behind user actions. This deeper understanding allows for more intuitive and personalized interactions, impacting various sectors from smart homes to virtual assistants. The ability to anticipate needs and proactively offer assistance is a significant advancement.This section will delve into real-world examples of intention recognition in action, demonstrating its practical applications and the personalized experiences it fosters.
We’ll examine how computers interpret human intentions in different contexts, highlighting the impact on user experience.
Smart Home Applications
Smart homes are a prime example of intention recognition’s potential. By learning user routines and preferences, these systems can anticipate needs and adjust accordingly. For instance, a smart thermostat can recognize the pattern of a user leaving for work and automatically adjust the temperature to conserve energy. Similarly, a smart lighting system can automatically dim the lights in a room when it senses that a user is about to go to sleep.
Furthermore, these systems can recognize specific commands like “turn off all lights” or “set the temperature to 72 degrees” and perform the task without explicit instruction.
Virtual Assistant Interactions
Virtual assistants, like Siri and Alexa, are already using intention recognition to enhance user experience. Beyond basic commands, these assistants can understand more complex requests. For example, if a user says “I’m feeling hungry and want something healthy,” the assistant can understand the intention behind the statement and recommend healthy recipes, provide a list of nearby restaurants serving healthy food, or even order groceries online based on the user’s preferred delivery service.
This level of understanding allows the assistant to proactively assist with tasks and provide relevant information.
E-commerce and Customer Service
In e-commerce, intention recognition can personalize the shopping experience. By analyzing browsing history, past purchases, and current interactions, systems can predict what products a user might be interested in. This allows for targeted recommendations and tailored product displays, leading to higher conversion rates. In customer service, intention recognition can help agents quickly understand the customer’s issue, routing them to the appropriate support team or providing a solution immediately.
Comparison of Intention Recognition Examples
| Scenario | Intention Recognized | Computer Action | Impact on User Experience |
|---|---|---|---|
| Smart Home | User leaving for work | Adjusts thermostat, dims lights | Increased energy efficiency, personalized comfort |
| Virtual Assistant | User is hungry and wants something healthy | Recommends recipes, restaurants, or orders groceries | Personalized recommendations, proactive assistance |
| E-commerce | User browsing specific products | Displays targeted recommendations | Improved product discovery, higher conversion rates |
| Customer Service | User needs technical support for a specific product | Routes to appropriate support team or provides a solution | Faster issue resolution, improved customer satisfaction |
Personalization Through Intention Recognition
Intention recognition empowers systems to tailor experiences to individual users. By understanding user preferences, habits, and goals, computers can personalize the user interface, content recommendations, and service offerings. This personalization results in a more intuitive and enjoyable experience, ultimately increasing user satisfaction and engagement. For example, a news aggregator can personalize the news feed based on the user’s interests and the news sources they frequently engage with.
Outcome Summary
In conclusion, computers learning to read human intentions is a rapidly advancing field with immense potential. While challenges remain in accurately interpreting complex human behavior and ensuring ethical implementation, the benefits for enhanced user experience and efficiency are significant. This evolving technology promises a future where interactions between humans and computers become more seamless and intuitive, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible.