Computing Invades the Living Room
Computing invades the living room, a journey from clunky mainframes to sleek smart devices. We’ll explore the fascinating evolution of home computers, from their humble beginnings to the sophisticated ecosystems of today. Imagine the early days of personal computing in the home, and how far we’ve come! This journey chronicles the milestones, the technology, and the impact on our lives.
This exploration dives into the current trends, examining the devices we use in our living rooms today, including smart TVs, game consoles, and interconnected home systems. We’ll see how these devices blend entertainment with productivity, and how smart home technology plays a crucial role in our daily lives.
Introduction to Computing in the Living Room

The integration of computing into our homes has been a gradual but profound transformation. From simple calculators to sophisticated gaming consoles and smart home systems, computers have evolved from being niche tools to indispensable parts of our daily routines. This evolution mirrors broader technological advancements, reflecting the growing power and accessibility of computing.The early days of home computing were characterized by a sense of wonder and a desire to bring the power of technology into personal spaces.
This desire to have computing power at home, though initially limited, drove the innovation and refinement of home computing devices. This journey has been shaped by technological leaps, user needs, and evolving design aesthetics.
Early Home Computing Devices
Early computing devices in the home, while rudimentary by today’s standards, were revolutionary for their time. These devices were often large, expensive, and required specialized knowledge to operate. Early personal computers, like the Apple II and the Commodore 64, were game-changers, offering a glimpse into the potential of computing at home. They weren’t just for number crunching; they offered educational software, simple games, and a taste of a future where personal computing would become more common.
Evolution of Interfaces and User Experiences
The user experience of home computing has undergone a dramatic shift. Early interfaces were often command-line based, requiring users to type specific commands to perform tasks. The advent of graphical user interfaces (GUIs) with icons and windows drastically improved ease of use. This evolution from command-line interfaces to graphical ones significantly lowered the barrier to entry for home users.
The introduction of touchscreens and voice control further refined the interaction between humans and computers, making them more intuitive and accessible.
Timeline of Key Milestones in Home Computing
This timeline highlights pivotal moments in the integration of computing into the living room.
- 1970s: The first personal computers (PCs) begin to appear, marking the beginning of personal computing. These early PCs were often large and expensive, with limited functionality and usability.
- 1980s: The rise of the home computer. Computers like the Apple II and Commodore 64 become more accessible, allowing a wider range of people to use them for personal and educational purposes. The development of more user-friendly interfaces, such as the graphical user interface (GUI), began to make them more user-friendly.
- 1990s: The proliferation of personal computers. The Internet becomes more widespread, and PCs become essential tools for communication and information access in the home. The development of more powerful processors and larger storage capacities expanded the possibilities for home users.
- 2000s: The rise of the Internet and mobile devices. The integration of computing into everyday life becomes more significant. The home computing landscape becomes more diversified, with the advent of personal digital assistants (PDAs) and the increasing use of mobile devices.
- 2010s-Present: Smart homes and ubiquitous computing. Home computing evolves into interconnected smart home systems, allowing users to control various aspects of their homes through devices and applications. The ability to connect devices and control them remotely is now a reality, blurring the lines between computing and home life.
Comparison of Home Computing Devices
The following table contrasts different types of home computing devices across time, highlighting their features and interfaces.
| Device Type | Era | Features | User Interface |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mainframe Computers | 1950s-1970s | Large, centralized computers used for complex calculations and data processing. Limited personal use. | Command-line interfaces, requiring specialized knowledge. |
| Early Personal Computers (e.g., Apple II, Commodore 64) | 1970s-1980s | Smaller, more affordable computers with basic processing power. Included games, educational software, and word processing. | Mostly command-line interfaces, but early GUI elements emerged. |
| Desktop Computers | 1980s-Present | Powerful processing, storage, and display capabilities. Supported diverse software applications. | Graphical User Interface (GUI) based. |
| Laptops | 1990s-Present | Portable computing power, allowing users to work from anywhere. | GUI-based, often with touch-screen support. |
| Smartphones and Tablets | 2000s-Present | Mobile computing with internet access, apps, and media consumption. | Touchscreen interfaces, voice control. |
Current State of Computing in the Living Room
The living room, once a sanctuary of relaxation, is increasingly becoming a hub for digital interaction. Modern home computing has evolved beyond the occasional desktop or laptop, transforming the way we entertain ourselves, manage our schedules, and connect with the world around us. This evolution is driven by a confluence of factors, including the affordability and accessibility of technology, the rise of seamless connectivity, and the desire for integrated solutions.The living room of today is a digital landscape, where streaming services, smart displays, and voice-controlled assistants seamlessly blend into the environment.
These technologies are not merely additions but integral components of modern living, redefining how we interact with our homes and each other.
Current Trends in Home Computing
Home computing trends are heavily influenced by the relentless pursuit of user-friendliness and seamless integration. Voice assistants are becoming increasingly sophisticated, allowing users to control various aspects of their homes with simple commands. The focus is on intuitive interfaces that minimize the need for complex configurations, enabling a wider range of users to leverage these powerful tools. Smart displays are evolving from simple information hubs to sophisticated control centers, often acting as the central point for interacting with smart home systems.
Types of Devices Commonly Found in Modern Living Rooms
The living room is now a convergence point for diverse digital devices. Smart televisions, often equipped with voice control and streaming capabilities, dominate the entertainment landscape. Streaming devices like Roku and Fire TV provide a multitude of entertainment options, allowing users to access various content platforms. Smart speakers, like Amazon Echo and Google Nest, act as central control points for managing smart home devices and interacting with information sources.
High-quality sound systems are becoming integrated into these smart home environments, providing immersive audio experiences. Other notable devices include smart lighting systems, smart thermostats, and security cameras, all designed to enhance convenience and safety.
Role of Smart Home Technologies
Smart home technologies are transforming the living room experience by streamlining tasks and improving efficiency. Automation features, like pre-programmed lighting routines or temperature adjustments, enhance comfort and convenience. Smart home integration allows users to manage various aspects of their living environment from a single point of control, often through a smartphone app or a smart display. These systems improve security by allowing for remote monitoring and control of security systems.
These technologies contribute to a more automated and personalized home experience.
Comparison of Smart Home Platforms
| Platform | Key Features | Connectivity | Ease of Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amazon Alexa | Voice control, smart home integration, music streaming, shopping | Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, Z-Wave | High; intuitive voice commands |
| Google Assistant | Voice control, smart home integration, information retrieval, app integration | Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, Thread | High; natural language processing |
| Apple HomeKit | Simple home automation, seamless integration with Apple devices, secure connection | Wi-Fi, Bluetooth | High; integrated with iOS ecosystem |
The table above highlights the diverse capabilities and functionalities of prominent smart home platforms. Each platform provides a different approach to automation, control, and integration with existing devices. These platforms have varying strengths and weaknesses, with users often choosing based on their existing technology ecosystem and specific needs.
Integration of Entertainment and Productivity Tools
The blurring lines between entertainment and productivity are evident in the living room. Smart TVs can now double as workspaces for video conferencing, while smart speakers can be used for scheduling meetings or managing to-do lists. The integration of entertainment and productivity tools allows for a more fluid transition between leisure and work. This integration is crucial for the evolving needs of modern lifestyles, where individuals often juggle multiple responsibilities.
Future Possibilities of Computing in the Living Room: Computing Invades The Living Room
The living room, once a sanctuary from the digital world, is increasingly becoming a hub for interconnected technologies. As computing power shrinks and becomes more integrated into everyday objects, the potential for transformative experiences within the home is immense. This evolution promises to redefine how we interact with our homes, manage our lives, and even entertain ourselves.The future of computing in the living room hinges on advancements in several key areas, including the development of sophisticated interfaces, the integration of emerging technologies, and the responsible consideration of privacy and security implications.
These developments will significantly impact our daily routines and will need to be thoughtfully considered for a positive and inclusive user experience.
Emerging Technologies and Their Potential Impact
Several emerging technologies hold the key to reshaping the living room computing landscape. These include advancements in artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and the Internet of Things (IoT). AI-powered assistants will become more sophisticated, learning our preferences and anticipating our needs. ML algorithms will optimize energy consumption, automate household tasks, and personalize entertainment experiences. The proliferation of interconnected devices will enable seamless integration and automation within the home.
Examples of Future Devices and Their Functionalities
Imagine smart furniture that adapts to your needs and preferences. A sofa that adjusts its firmness based on your posture, a table that lights up with ambient mood lighting based on your activity, or a coffee table that doubles as a wireless charging pad for your devices. These interactive and intelligent surfaces are possible through advances in materials science and responsive design.
The Role of Augmented and Virtual Reality
Augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) technologies are poised to dramatically enhance the living room experience. Imagine an AR interface overlaying information about your home’s energy consumption onto your walls, guiding you towards more efficient practices. VR could transport you to immersive entertainment experiences, from virtual travel to interactive educational environments, all within the comfort of your living room.
VR games could seamlessly integrate with the smart home environment, for example, by projecting game elements onto the walls or using the home’s layout for virtual challenges.
Scenarios for the Future of Home Computing
| Scenario | Technology | User Experience | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Personalized Home Entertainment | AI-powered recommendation systems, VR/AR integration | Tailored entertainment experiences based on individual preferences, seamless transitions between physical and virtual worlds. | Increased user engagement and satisfaction; potential for personalized learning experiences. |
| Smart Home Automation | IoT devices, AI-driven scheduling | Automated tasks and optimized resource management based on user needs and environmental conditions. | Reduced energy consumption, improved efficiency in household management, and increased comfort. |
| Interactive Learning Environments | AR/VR overlays, personalized learning platforms | Immersive and engaging educational experiences that adapt to individual learning styles. | Improved educational outcomes and accessibility to diverse learning materials. |
Potential Benefits and Drawbacks
The advancements in computing will offer many benefits, such as increased convenience, personalized experiences, and energy efficiency. However, concerns about privacy, security, and the potential for job displacement exist. The integration of sensitive data and personalized algorithms raises concerns about data security and misuse.
Implications for User Privacy and Security
As computing systems become more integrated into our lives, safeguarding user privacy and data security becomes paramount. Robust security measures and transparent data policies are crucial to prevent unauthorized access and misuse of personal information. Strict adherence to data privacy regulations and user control over their data will be essential for maintaining user trust.
The Impact on Lifestyle and Society
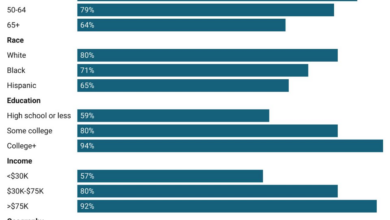
Home computing has profoundly reshaped daily life, impacting social interactions, economies, family dynamics, and educational opportunities. From managing schedules to connecting with loved ones across continents, the pervasiveness of home computing continues to evolve and redefine our expectations of convenience and accessibility. This influence extends beyond the individual, affecting various sectors and driving societal shifts.The ubiquity of home computing has woven itself into the fabric of modern life, altering how we interact, work, and learn.
My living room’s now a tech hub, with smart TVs and streaming services everywhere. But, as computing invades our living rooms, it’s also important to consider the digital clutter. California is taking a proactive step to curb unwanted messages by enacting a law to ban all spam, california law to ban all spam , which hopefully will lead to a cleaner digital space for everyone.
This new regulation will likely impact how we interact with tech in our homes, especially as more and more devices connect to the network.
This pervasive influence extends beyond the individual, influencing family dynamics, economic structures, and the broader social landscape. The changes are profound, from the way we communicate to the services we demand.
Smart TVs and streaming devices are making computing a ubiquitous presence in the living room. This seamless integration, however, raises questions about copyright enforcement, especially given recent legal challenges to the Recording Industry Association of America’s (RIAA) tactics in court, like riaa tactics in question after dismissal of suit. Ultimately, as technology continues to reshape our homes, navigating these evolving legal landscapes is key to ensuring a future where innovation and access coexist in the living room.
Influence on Daily Routines
Home computing has significantly altered daily routines. From scheduling appointments and managing finances to connecting with family and friends, these tools have become indispensable. Digital calendars, reminders, and to-do lists streamline tasks, enabling individuals to better manage their time and responsibilities. The ability to access information and services remotely empowers individuals to perform tasks outside traditional work hours, promoting greater flexibility and work-life balance.
The ability to order groceries, schedule appointments, and complete tasks online has greatly influenced daily routines.
Impact on Social Interactions
Home computing has facilitated new forms of social interaction. Social media platforms and video conferencing tools have shrunk geographical distances, enabling individuals to connect with family and friends across the globe. This accessibility fosters stronger relationships and supports individuals who may be geographically isolated. These digital platforms are also changing how we socialize, creating new avenues for community building and collaboration.
The rise of online communities and forums has fostered new forms of social interaction.
Economic Implications for Industries
Home computing has revolutionized industries by altering consumer expectations and market dynamics. The rise of e-commerce, online education, and remote work has fundamentally reshaped how businesses operate and interact with consumers. Home computing platforms provide new ways to market and sell products, leading to innovative business models and increased competition. The ability to access global markets from a home office has significantly impacted international trade and commerce.
Influence on Family Dynamics
Home computing has redefined family dynamics. Shared access to digital tools fosters communication and collaboration, connecting family members despite physical distance. Online gaming and shared digital spaces can strengthen bonds and create opportunities for shared experiences. This technology, however, can also present challenges. Balancing screen time and maintaining healthy communication patterns is vital in maintaining healthy family relationships.
Digital tools have brought families closer but require careful management to avoid issues.
Impact on Educational Opportunities
Home computing has broadened educational opportunities, particularly for those in underserved communities or those with limited access to traditional educational institutions. Online courses, educational apps, and digital libraries provide access to information and learning materials previously unavailable. This democratization of education can empower individuals to pursue their interests and acquire new skills, promoting lifelong learning and personal growth.
The accessibility of online educational resources has greatly expanded educational opportunities.
Environmental Impact
The increased use of home computing devices, while offering many benefits, also raises environmental concerns. The manufacturing and disposal of these devices contribute to electronic waste, and the energy consumption of computers and associated equipment can have a significant impact. Promoting energy-efficient devices, responsible disposal, and sustainable practices are essential to mitigate these negative environmental impacts. The environmental impact of computing devices needs to be addressed with sustainable practices.
The living room, once a haven for relaxation, was rapidly becoming a digital playground. Suddenly, personal computers weren’t just in offices; they were appearing in homes. This trend was significantly accelerated by companies like lindows com, who in 1998, revolutionized the space with their groundbreaking CD-based internet-ready PC. lindows com launches cd based internet ready pc This innovative approach made computing more accessible and affordable for the average household, further driving the trend of computers invading the living room.
Possible Societal Changes
- Increased remote work and reduced commute times.
- Rise of digital economies and the transformation of traditional industries.
- Enhanced global connectivity and cross-cultural understanding.
- Increased access to education and information.
- Potential for social isolation and the need for digital literacy programs.
- The need for cybersecurity measures to protect sensitive information.
- Shifting family dynamics and new expectations of communication.
The points above highlight potential societal shifts that could result from the pervasive influence of home computing. Careful consideration of the positive and negative implications is essential for harnessing the benefits while mitigating potential risks.
User Experience and Interface Design

The living room, once a sanctuary of passive entertainment, is now a hub of interactive experiences. This transformation hinges critically on user interfaces that are not just functional but also intuitive, engaging, and accessible. The evolution of these interfaces reflects the broader technological advancements and evolving user expectations. The challenge lies in crafting interfaces that seamlessly integrate with the existing home environment, minimizing disruption while maximizing user control.Modern home computing interfaces must go beyond simple command-line interactions or clunky graphical interfaces.
They need to leverage the power of intuitive design principles to empower users with effortless control over their digital experiences. A well-designed interface not only streamlines tasks but also enhances the overall user experience, making home computing a seamless and enjoyable part of daily life.
Evolution of User Interfaces in Home Computing
The evolution of user interfaces in home computing mirrors the larger trajectory of computing technology. Early interfaces were often text-based, demanding specific commands and a degree of technical proficiency. The rise of graphical user interfaces (GUIs) marked a significant shift, making computing more accessible to a broader audience. Today, we see an increasing trend toward touchscreens, voice controls, and even gestural interfaces, reflecting the ongoing quest for more natural and intuitive interactions.
Different Design Philosophies
Different design philosophies shape the approach to user interface design. Some interfaces prioritize minimalism, emphasizing simplicity and a clean aesthetic. Others favor a more feature-rich approach, providing extensive options and customization. A successful design often blends elements from both approaches, providing a balance between functionality and ease of use. An ideal interface doesn’t overwhelm the user with unnecessary features while also not limiting them in any way.
Key Design Principles for Intuitive Interfaces
Intuitive interfaces rely on several key design principles. Consistency in design elements, clear visual hierarchy, and effective feedback mechanisms contribute significantly to user understanding and ease of navigation. Well-placed visual cues, clear labels, and logically organized layouts contribute to the overall clarity of the interface. The importance of these elements cannot be overstated.
Importance of Accessibility and Inclusivity in Home Computing
Accessibility and inclusivity are paramount in designing home computing interfaces. Features such as adjustable text sizes, keyboard navigation options, and screen reader compatibility ensure that interfaces are usable by people with disabilities. This consideration not only meets ethical obligations but also expands the potential user base, ultimately making home computing more beneficial to a wider segment of society.
A truly successful interface embraces diversity in its design and functionality.
Significance of Personalization and Customization
Personalization and customization allow users to tailor the interface to their specific needs and preferences. This can range from customizing the home screen layout to configuring the interface’s appearance and behavior. Allowing users to adapt the interface enhances user satisfaction and engagement. Personalization allows the system to adapt to the individual’s needs, enhancing efficiency and enjoyment.
User Interface Design Elements for Home Computing, Computing invades the living room
| Element | Description | Functionality | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Visual Hierarchy | Organization of elements based on importance. | Guides the user’s eye to critical information. | Using larger fonts for headings, highlighting key actions, and placing important controls prominently. |
| Consistent Design Language | Using similar visual cues and patterns throughout the interface. | Reduces cognitive load and improves usability. | Employing a consistent color scheme, font style, and button shapes across all sections of the interface. |
| Intuitive Navigation | Easy-to-understand pathways within the interface. | Facilitates user movement between different sections and functions. | Employing clear labels, logical organization, and well-designed menus for accessing different features. |
| Feedback Mechanisms | Visual or auditory cues that confirm actions. | Provides immediate user confirmation that actions are processed and understood. | Visual indicators such as checkmarks, loading bars, and animated feedback upon completing a task. |
| Customization Options | Allowing users to personalize their experience. | Increases user engagement and satisfaction by catering to individual preferences. | Adjusting the layout, color schemes, and functions based on user preferences. |
Conclusive Thoughts
In conclusion, the evolution of computing in the living room has been nothing short of remarkable. From simple terminals to sophisticated smart home hubs, the technology has dramatically changed how we interact with entertainment and productivity. The future holds even more exciting possibilities, with the potential to reshape our daily routines, social interactions, and even our families. The impact on society, both positive and negative, is profound, and warrants careful consideration as we navigate this ever-evolving technological landscape.