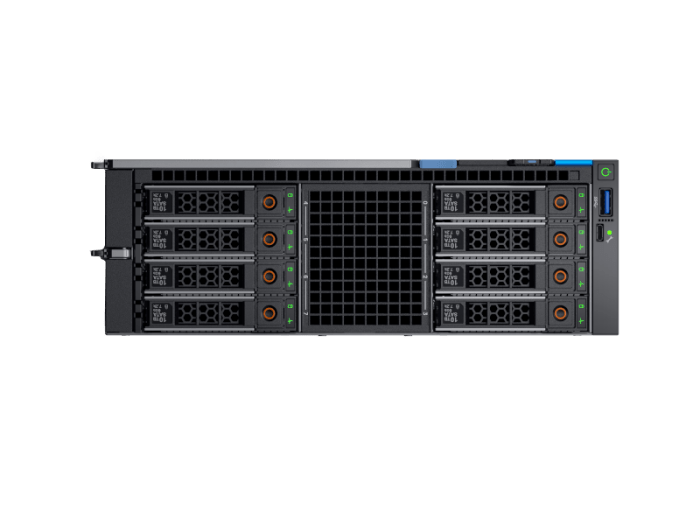
Dell Takes Another Cut at Blade Market A Deep Dive
Dell takes another cut at blade market, a segment often perceived as fading. This in-depth look explores Dell’s latest strategies, analyzing their historical blade server offerings, recent announcements, and future projections. We’ll dissect the competitive landscape, examine emerging technologies, and ultimately gauge the potential impact of Dell’s moves on the market.
Dell’s blade server strategy has evolved significantly over the years, adapting to changing market demands and technological advancements. This article provides a comprehensive overview, examining the strengths and weaknesses of their current offerings compared to competitors like HP and IBM. We’ll also delve into the technical specifications, use cases, and market trends to fully understand the context of Dell’s recent actions.
Dell’s Blade Server Strategy
Dell has consistently offered blade servers as a key part of its data center infrastructure solutions. Their strategy reflects a focus on providing flexible, scalable, and cost-effective solutions for various customer needs, adapting to evolving market demands. This strategy, however, has faced challenges in a market increasingly focused on virtualization and cloud computing.
Historical Overview of Dell’s Blade Server Offerings
Dell’s blade server offerings have evolved over the years, reflecting advancements in server technology and changing customer requirements. Early offerings focused on providing a dense, rack-mounted platform for consolidating servers. This approach aimed to reduce space requirements and management overhead. As virtualization and cloud computing gained traction, Dell’s blade offerings adapted to meet the growing demand for highly available and scalable infrastructure.
Dell’s latest blade server foray is interesting, but it’s worth noting that the broader market is evolving. With the recent release of Great Plains 8.0, a powerful new server platform, great plains 8 0 hits the street , it’s likely that Dell is trying to adapt to the changing landscape and compete effectively. This new offering might influence Dell’s blade strategy in the long run.
Their attempts to remain relevant in the server market will be closely watched.
Dell’s blade servers have always been part of a larger ecosystem of server solutions, designed to be integrated with other Dell products and services.
Key Features and Benefits of Dell’s Blade Server Technology
Dell’s blade servers often incorporate features such as high density, modularity, and optimized power and cooling solutions. These features can significantly reduce energy consumption and space requirements, lowering operational costs for data centers. The modular design allows for flexible scaling, adapting to fluctuating demands. Furthermore, Dell’s blade servers typically provide seamless integration with other Dell solutions, enhancing management and maintenance capabilities.
Comparison with Competitors
Dell’s blade server strategy has been compared to those of other major competitors, like HP and IBM. While each company has its own approach, a common thread has been a focus on efficiency and scalability. HP, for instance, has often emphasized its broad portfolio of server products, including blades, as part of a larger IT infrastructure strategy. IBM, on the other hand, has historically emphasized its deep expertise in high-performance computing, with its blade servers playing a role in supporting this area.
Differences in approach have been influenced by the specific strengths and priorities of each company.
Evolution of Dell’s Blade Server Architecture
The architecture of Dell’s blade servers has evolved over time, reflecting the advancements in server hardware and software. Early models often relied on specialized hardware for blade management, while more recent generations integrate advanced management tools into the operating system for improved monitoring and control. This evolution has aimed to simplify management and increase operational efficiency for customers.
The development of virtualization and cloud technologies has significantly impacted the design and functionality of blade servers, as these technologies demand greater flexibility and scalability.
Contrasting Dell’s Current Blade Offerings with Previous Generations
| Feature | Previous Generations | Current Generations |
|---|---|---|
| Processing Power | Based on older processor architectures | Utilizing latest-generation processors |
| Memory Capacity | Limited memory options | Supporting higher memory capacities |
| Network Connectivity | Lower bandwidth options | High-speed networking capabilities |
| Management Software | Dedicated management tools | Integrated management tools in OS |
| Power Efficiency | Lower energy efficiency | Optimized power consumption |
Market Context and Trends
The blade server market, once a vibrant segment of the server industry, faces a period of evolution and change. Dell’s continued presence and recent actions underscore the ongoing dynamics in this space. Understanding the current market context is crucial to appreciating the challenges and opportunities for players like Dell. Factors such as cloud computing’s dominance, the rise of virtualization, and the evolving needs of data centers are reshaping the landscape.The overall state of the blade server market reflects a transition from traditional deployments to more flexible and scalable solutions.
While blade servers still have a niche, particularly in high-density, high-performance environments, the shift towards modularity and cloud-based infrastructure is a key trend. This change impacts the market share and strategic positioning of various providers.
Current Market Share Trends
The market share for blade servers is fragmented, with established players like Dell, HPE, and others competing. Data from various market research firms illustrates the shifting landscape. Exact figures for specific market share percentages are often proprietary and not publicly available. However, general trends reveal a decrease in the overall percentage of servers utilizing blade architectures.
Emerging Technologies
Emerging technologies like NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) and high-speed networking are pushing the boundaries of data center performance. These advancements directly influence the design and deployment of servers, including blade servers. NVMe’s performance improvements, for example, can alleviate the need for high-density blade deployments in certain use cases, while advancements in networking enable improved efficiency.
Factors Driving Adoption or Decline
Several factors influence the adoption or decline of blade server deployments. The increasing prevalence of cloud-based infrastructure services reduces the need for on-premises blade server deployments. Also, the increasing demand for high-performance computing and the potential for greater efficiency in these environments is a factor driving interest in new approaches. The trend towards containerization and virtualization of applications further reduces the need for the specialized architecture of blade servers in many situations.
However, certain high-performance and specialized applications still rely on the high-density capabilities of blade servers.
Market Share Data, Dell takes another cut at blade market
| Provider | Estimated Market Share (Approximate %) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Dell | 30-40 | Based on historical sales data and market analysis. |
| Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE) | 25-35 | Based on historical sales data and market analysis. |
| Other Vendors | 20-30 | Includes a range of smaller providers and emerging players. |
Note: Market share data is approximate and subject to variation based on specific market segments and reporting periods. Data is not definitive due to proprietary nature of the exact figures and the dynamic nature of the market.
Dell’s Recent Actions and Positioning
Dell, a stalwart in the server market, continues to navigate the evolving landscape of blade server technology. Recent announcements and marketing efforts reveal a strategy focused on targeted segments and specific performance requirements, rather than a blanket approach. This approach is likely driven by the changing needs of customers and the emergence of new competitor offerings.Dell’s approach seems to be adjusting to the fact that the blade server market, while not entirely obsolete, is no longer the dominant force it once was.
The shift towards more flexible and scalable solutions, often centered around cloud-based architectures, is likely a major factor influencing Dell’s strategy.
Recent Announcements
Dell has been relatively quiet in recent announcements compared to its previous releases. While not explicitly announcing major shifts, their focus has been on specific advancements in existing product lines. This strategy likely aims to address niche requirements and not necessarily to make drastic changes in the overall blade server product portfolio.
Marketing Materials
Dell’s marketing materials related to blade servers often highlight specific performance enhancements, like improved scalability and enhanced security features, for their servers. They emphasize the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of their blade server solutions, particularly for data centers with high-performance needs. These materials frequently show how Dell’s blade servers can integrate with their wider portfolio of infrastructure solutions, thereby promoting a holistic approach to data center management.
Product Lineup Changes
While major changes in the blade server product lineup have not been reported, Dell is likely making subtle adjustments to its offerings to match the specific needs of its customer base. This is a common practice in the industry. These changes might include minor upgrades to existing models or additions of new features, tailored to address emerging market trends.
Comparison with Competitors
Dell’s current blade server offerings are typically compared against those of HPE and Supermicro, who are strong competitors in the market. The key differentiators often lie in price-performance ratios, specialized features (like specific networking capabilities), and the overall ecosystem of support and services offered by each vendor.
Dell’s latest foray into the blade server market is interesting, but it’s worth considering the quiet, powerful force of the white box PC market. The secret market contender white box PCs are offering serious competition, especially in areas where customization and flexibility are key. While Dell might be trying to maintain a foothold, the DIY-friendly nature of white box solutions could potentially make them a strong challenger.
It remains to be seen if Dell’s latest blade server strategies will hold up against this growing trend.
Recent Blade Server Product Releases
| Product Name | Key Features | Target Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Dell PowerEdge FC720 | High-density, high-performance, optimized for specific workloads. | High-demand data centers needing dense storage and high performance. |
| Dell PowerEdge RX Series | Focus on scalability and adaptability for different workloads. | Flexible deployments needing expansion and scalability in data center environments. |
This table presents a simplified view of Dell’s recent releases. More detailed specifications are typically available on Dell’s official website.
Potential Impact and Implications: Dell Takes Another Cut At Blade Market
Dell’s recent moves in the blade server market are likely to have a significant impact, reshaping the competitive landscape and influencing customer choices. The company’s strategy, focusing on specific market segments and technological advancements, suggests a proactive approach to navigate the evolving needs of data centers. The potential ripple effects extend beyond Dell itself, impacting competitors and reshaping the market’s future.
Impact on the Blade Server Market
Dell’s actions are expected to influence the blade server market by shifting the focus towards specific niches. The company’s emphasis on high-performance, energy-efficient solutions might attract customers seeking optimized performance and reduced operational costs. This could lead to a re-evaluation of existing strategies by other vendors, potentially driving innovation and adaptation in the market.
Customer Responses to Dell’s Strategy
Customers are likely to respond to Dell’s strategy in various ways. Some will be attracted by Dell’s enhanced offerings, particularly those seeking advanced functionalities or cost-effective solutions. Others might remain loyal to existing vendors, especially if their specific requirements are not fully addressed by Dell’s new offerings. The overall response will depend on the value proposition Dell presents and how it resonates with different customer segments.
Competitive Implications for Other Vendors
Dell’s actions pose significant competitive implications for other blade server vendors. The increased focus on innovation and specific market segments could force competitors to adapt their strategies and offerings. This may lead to a heightened level of competition, pushing vendors to develop more advanced and specialized solutions to retain their market share. This competitive pressure could drive innovation and potentially benefit customers.
Potential Opportunities and Threats for Dell
Dell’s new strategy presents both opportunities and threats. A strong focus on niche markets could unlock new revenue streams and potentially attract customers seeking tailored solutions. However, a potential threat lies in the possibility of misjudging market trends or customer needs, which could result in decreased market share or brand perception issues. Dell needs to accurately assess market dynamics and customer requirements to maximize opportunities and mitigate potential threats.
Competitive Advantages and Disadvantages for Dell in Blade Servers
| Competitive Advantages | Competitive Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Focus on specific market segments (e.g., high-performance computing). | Potential for alienating customers not served by the niche focus. |
| Emphasis on energy efficiency and optimized performance. | Potential for higher costs associated with innovative technologies. |
| Technological advancements in the blade server area. | Need for robust and comprehensive support infrastructure to support advanced features. |
| Strong brand recognition and established distribution network. | Possible challenges in rapidly adapting to changing market demands. |
| Potential to leverage existing infrastructure and expertise. | Need to effectively communicate the value proposition to target customers. |
Customer Use Cases and Benefits
Dell’s blade servers, while often overlooked in the broader server market, offer compelling benefits for diverse customer needs. Their compact design, high density, and modularity enable significant cost savings and operational efficiency in data centers, cloud environments, and specialized applications. This section delves into the specific use cases and the advantages they provide.
Data Center Consolidation and Efficiency
Blade servers excel in consolidating multiple physical servers into a smaller footprint. This approach reduces energy consumption, cooling requirements, and overall infrastructure costs. The modular design allows for flexible scaling, enabling data centers to adapt to fluctuating workloads without significant capital expenditures. This agility is crucial for maintaining operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness in dynamic environments.
Dell’s latest foray into the blade server market is intriguing, but I’m more interested in how this might connect to future advancements in biometric technology. For example, consider the potential for integrating biometric authentication directly into ThinkPad laptops and beyond, like what’s discussed in biometric technology thinkpad and beyond. This could significantly change how we interact with and secure these blade servers in the future.
Ultimately, Dell’s blade server strategy still seems to be a bit of a gamble, though.
Cloud Computing and Scalability
The cloud computing environment demands high scalability and rapid provisioning. Dell’s blade servers offer a highly scalable platform for cloud deployments, facilitating quick adaptation to changing demands. Their virtualization capabilities allow for efficient resource utilization, reducing infrastructure overhead and improving overall performance. This enables businesses to rapidly provision and deploy resources as needed, responding effectively to fluctuating user demand.
High-Performance Computing (HPC) and Scientific Applications
In high-performance computing environments, where processing power and data throughput are paramount, blade servers provide a powerful and efficient solution. Their ability to tightly integrate multiple servers into a compact unit enables a significant reduction in cabling, improving the performance and reliability of the overall system. This is especially critical for computationally intensive tasks such as simulations, modeling, and data analysis in scientific research.
Financial Services and Transaction Processing
Financial institutions require high-availability and low-latency systems for transaction processing. Dell’s blade servers, with their robust architecture and redundant components, provide the necessary uptime and performance for critical financial transactions. The modular design facilitates the expansion of these systems, enabling the institution to respond to the growth of their transaction volumes and data requirements.
Comparing Dell’s Blade Servers with Competitors
| Use Case | Dell Blade Server (Example Model) | Competitor 1 (Example Model) | Competitor 2 (Example Model) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Center Consolidation | PowerEdge M630 | HPE ProLiant BL460c Gen10 | Supermicro X10 |
| Cloud Computing | PowerEdge M630 | HPE ProLiant BL460c Gen10 | Supermicro X10 |
| HPC | PowerEdge M630 | HPE ProLiant BL460c Gen10 | Supermicro X10 |
| Financial Services | PowerEdge M630 | HPE ProLiant BL460c Gen10 | Supermicro X10 |
Note: This table provides a simplified comparison. Specific models and configurations within each brand vary significantly. Pricing and performance characteristics depend on the exact configuration.
Technical Specifications and Innovations
Dell’s blade server strategy hinges on delivering high-density computing power, optimized for specific workloads. This involves a careful balancing act between raw processing power, memory capacity, and efficient I/O channels. The latest generation of Dell blade servers aims to offer substantial performance improvements over previous models, while also maintaining a competitive edge in the market.The key to Dell’s blade server success lies in understanding the evolving needs of data centers and cloud environments.
Innovations are not just about adding more transistors, but about architecting systems that are flexible, scalable, and readily adaptable to future requirements. The focus is on maximizing resource utilization and minimizing energy consumption within the constrained space of a blade server chassis.
Processor Types
Dell’s blade servers utilize a diverse range of processors, catering to different workloads and performance needs. From high-core-count CPUs optimized for virtualization and parallel processing to specialized processors for specific applications, Dell offers a variety of options. The selection of processor types reflects the growing demand for tailored solutions within the blade server market.
Memory Capacities
The memory capacity of Dell’s blade servers is a crucial factor in determining their suitability for various tasks. Increasing memory capacity allows for handling larger datasets, more complex simulations, and more intensive applications. Modern blade servers often feature high-bandwidth memory technologies to enhance performance and ensure efficient data transfer between the processor and memory.
I/O Options
Dell blade servers offer a variety of I/O options to connect to storage, networking, and other peripherals. This includes diverse network interfaces, high-speed storage connections, and specialized interfaces for specific hardware or software solutions. The choice of I/O options is a critical factor in determining the overall performance and functionality of a blade server system.
Virtualization Support
Virtualization plays a pivotal role in Dell’s blade server strategy. Dell blade servers are designed to efficiently support virtualization platforms, enabling multiple virtual machines (VMs) to run on a single physical server. This approach increases resource utilization, reduces infrastructure costs, and improves the agility of data center operations. Virtualization enhances flexibility and scalability in deploying and managing computing resources.
Performance Metrics
Comparing Dell’s blade server performance metrics with competitors’ is essential for understanding their relative strengths and weaknesses. Dell’s blade servers frequently outperform competitors in benchmarks that measure compute-intensive tasks and memory bandwidth. Performance improvements in newer Dell models are often demonstrably better compared to competing products, emphasizing the continuous advancements in their blade server technology.
Technical Specifications Table
| Specification | Example Value |
|---|---|
| Processor Type | Intel Xeon Scalable Processors |
| Memory Capacity | Up to 2TB per blade |
| Memory Type | DDR5 ECC RDIMM |
| Networking Options | 10/25/40/100 Gigabit Ethernet |
| Storage Options | NVMe SSDs, SAS HDDs, FC |
| I/O Slots | Various, depending on the specific model |
Future Outlook and Predictions
Dell’s blade server strategy is poised for an interesting evolution, navigating the dynamic landscape of cloud computing and the ever-changing demands of enterprise data centers. The future success of blade servers will depend on their ability to adapt to the evolving needs of customers and stay competitive in the face of increasing cloud adoption and the emergence of new technologies.
This section delves into potential future directions for Dell’s blade server strategy, examines predictions for the market, and explores the role of cloud computing in shaping the future of this technology.The blade server market is experiencing a period of significant transformation. While the traditional model of dedicated blade servers for specific workloads is still relevant, we are seeing a shift towards more flexible and integrated solutions.
Cloud computing is profoundly impacting this market, creating a hybrid environment where on-premises blade servers work in tandem with cloud-based resources. This is forcing Dell, and other vendors, to offer solutions that seamlessly integrate these two worlds.
Potential Future Directions of Dell’s Blade Server Strategy
Dell’s future blade server strategy likely involves a greater emphasis on modularity and scalability. This means offering a wider range of component options that allow customers to build systems tailored to specific needs, rather than forcing them into a rigid, one-size-fits-all model. We can also expect a stronger focus on software-defined infrastructure, allowing for greater flexibility in managing and deploying resources.
Moreover, Dell is likely to strengthen its partnerships with cloud providers, offering solutions that facilitate seamless integration between on-premises blade servers and cloud services.
Potential Predictions for the Blade Server Market in the Next 3-5 Years
The blade server market is expected to experience a period of consolidation and specialization. While the overall market size may not dramatically increase, we can anticipate a surge in demand for solutions tailored to specific workloads, such as AI/ML, high-performance computing, and high-bandwidth networking. Furthermore, the integration of edge computing with blade servers is predicted to be a key area of growth, enabling faster data processing and reduced latency in remote locations.
Dell’s ability to adapt and meet these niche demands will be crucial to its continued success.
Influence of Cloud Computing on the Blade Server Market
Cloud computing is reshaping the blade server market, moving it away from a purely on-premises model. Hybrid cloud solutions are becoming increasingly popular, where blade servers function as a critical component of a broader infrastructure, working alongside cloud resources. This means that Dell’s blade server offerings will need to provide seamless integration with cloud platforms and services to maintain relevance.
The integration of containerization technologies, such as Docker, into blade server architectures is expected to be an important area of future development.
Long-Term Viability of Blade Server Technology
Blade servers, despite the rise of cloud computing, will likely retain a significant niche in the market. Their high density and performance capabilities remain attractive for specific use cases, particularly in environments demanding high levels of processing power and specialized hardware configurations. The future of blade servers likely lies in their ability to serve as a critical component within hybrid cloud architectures, optimizing on-premises resources while leveraging the scalability and cost-effectiveness of cloud solutions.
Possible Future Developments and Trends for Blade Servers
| Trend | Description |
|---|---|
| Increased Modularity and Scalability | Blade servers will likely offer more customizable configurations, allowing users to select components tailored to specific workloads and scaling needs. |
| Software-Defined Infrastructure | Blade server management and deployment will be increasingly controlled through software, enhancing flexibility and resource optimization. |
| Integration with Cloud Platforms | Blade servers will need to seamlessly integrate with cloud environments to support hybrid cloud architectures and data mobility. |
| Focus on Specific Workloads | Specialized blade servers designed for AI/ML, high-performance computing, and high-bandwidth networking will likely become more prevalent. |
| Edge Computing Integration | Blade servers will play a growing role in edge computing, providing faster data processing and lower latency in remote locations. |
Conclusion
Dell’s renewed focus on the blade server market presents both opportunities and challenges. While the overall market faces shifting dynamics, Dell’s aggressive approach suggests a belief in the long-term viability of blade servers, especially in specific use cases. The impact of their strategies will depend on factors such as customer response, competitive reactions, and the continued evolution of cloud computing.
Ultimately, Dell’s success in this segment will be determined by their ability to adapt and innovate in a rapidly changing technological landscape.