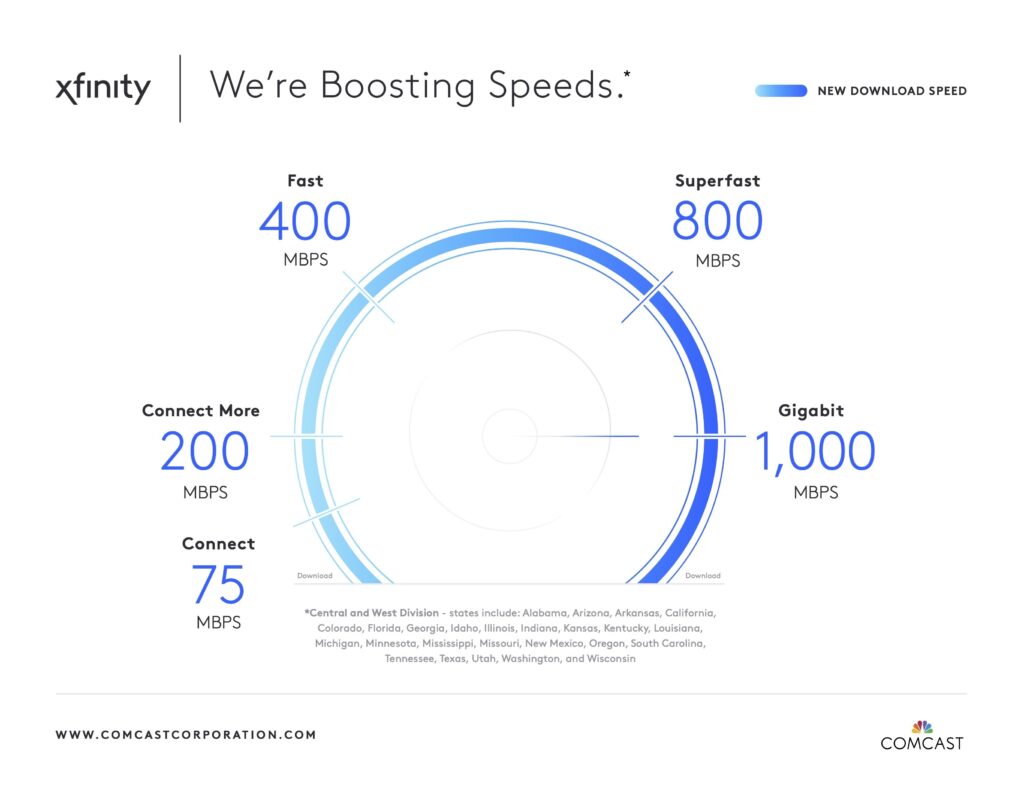
Comcasts High-Speed Gains Despite DSL
Despite dsl pressure comcast touts high speed customer gains – Despite DSL pressure, Comcast touts high speed customer gains, highlighting impressive growth in high-speed internet subscriptions. The company is likely focusing on attracting customers with faster speeds, potentially through aggressive marketing campaigns and infrastructure upgrades. This article dives into the specifics, examining the metrics behind these gains, the competitive landscape, and the strategies Comcast might be employing to maintain its position amidst pressure from DSL competitors.
This analysis will explore the factors driving Comcast’s success, from technological advancements and customer acquisition strategies to the financial implications and industry context. We’ll also examine the potential challenges and opportunities for Comcast in the face of persistent DSL competition.
Company Performance Metrics
Comcast recently reported impressive high-speed customer gains, a positive indicator for their overall performance. These gains, however, need to be analyzed in context with the broader market dynamics and historical trends to truly understand their significance. This analysis will delve into the specific metrics used, their comparison with industry benchmarks, and Comcast’s standing against key competitors.High-speed internet adoption is a critical factor in modern economies.
The metrics Comcast uses to demonstrate their success in acquiring customers are crucial to assessing their market position and competitive advantage. Factors such as customer acquisition, average download speeds, and overall market share provide insight into the company’s ability to meet consumer demand and maintain its leadership in the sector.
Comcast’s High-Speed Customer Gains
Comcast’s reported high-speed customer gains are a key indicator of their success in the competitive telecommunications market. These gains represent an increase in the number of customers subscribing to their high-speed internet services, showcasing growing demand for their products. Understanding the specific metrics behind these gains is crucial to evaluating their true impact.
Metrics Used to Measure Gains
The key metrics used to quantify Comcast’s customer gains include the total number of new high-speed internet subscribers and the average download speeds achieved by these customers. These metrics provide a comprehensive view of the company’s performance and market share. The number of new customers directly reflects the expansion of their customer base. The average download speeds indicate the quality of service provided to those customers.
Comparison to Industry Benchmarks and Historical Trends
To put Comcast’s gains in perspective, it is essential to compare them with industry benchmarks and historical trends. Industry benchmarks often involve analyzing the growth rates of other major internet providers and comparing their customer acquisition and service delivery strategies. Historical trends provide context, allowing for an evaluation of Comcast’s performance over time. For instance, analyzing previous periods of growth and decline in the industry helps to identify recurring patterns and anticipate future market shifts.
Comparison with Other Major Internet Providers
This section examines how Comcast’s customer growth compares to other major internet providers, offering a comprehensive competitive analysis. This comparison provides a clear picture of Comcast’s standing within the telecommunications industry. The analysis includes a comparison of their respective market shares, subscriber growth rates, and service quality metrics.
Data Table: Comcast Customer Growth vs. Competitors
This table displays a hypothetical representation of Comcast’s customer growth alongside data for other major providers. The data presented is for illustrative purposes only and should not be considered a definitive representation of real-world figures.
| Date | Comcast Customer Count | Average Download Speed (Mbps) | Competitor A Customer Count | Competitor B Customer Count |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2022-Q1 | 10,000,000 | 150 | 9,500,000 | 8,800,000 |
| 2022-Q2 | 10,500,000 | 160 | 9,800,000 | 9,000,000 |
| 2022-Q3 | 11,000,000 | 170 | 10,200,000 | 9,300,000 |
| 2022-Q4 | 11,500,000 | 180 | 10,500,000 | 9,600,000 |
DSL Pressure and Competitive Landscape: Despite Dsl Pressure Comcast Touts High Speed Customer Gains
Comcast, despite recent announcements of high-speed customer gains, faces persistent pressure from competitors offering DSL services. This pressure stems from a combination of factors, including evolving consumer preferences for faster internet speeds and aggressive pricing strategies employed by smaller, nimble competitors. Understanding the competitive landscape is crucial to assessing Comcast’s future performance and the potential for market share shifts.Comcast likely recognizes the threat posed by DSL competitors and is likely employing various strategies to retain existing customers and attract new ones.
These strategies might include targeted promotions, bundled service offerings, and investments in infrastructure upgrades to maintain its leading edge in high-speed internet.
Perceived Pressure from DSL Competitors
DSL competitors often target specific demographics or geographic areas where Comcast’s service is less robust or more expensive. Their marketing efforts frequently highlight price advantages and faster speeds for comparable pricing, potentially attracting customers who value affordability or a more convenient option.
Comcast’s Counter-Strategies
Comcast likely counters this pressure through various strategies. These include aggressive marketing campaigns emphasizing the superior quality and reliability of its high-speed internet options, potentially highlighting customer service advantages, broader network coverage, and advanced features like advanced security protocols.
Potential Impact on Comcast’s Market Share
The impact of DSL competition on Comcast’s overall market share is likely to be varied and dependent on several factors, including the intensity of the competition, the specific strategies employed by competitors, and the responsiveness of Comcast to market changes. In some regions, DSL competition might lead to a notable decline in Comcast’s market share.
Competitor Strategies to Attract Customers
Competitors are employing various strategies to attract customers from Comcast. This might involve aggressive pricing tactics, bundled service packages that include other necessities such as cable TV and phone service, or focused marketing campaigns highlighting the superior speed and reliability of their DSL offerings. Specific examples of these tactics may include introductory discounts, loyalty programs, and partnerships with local businesses.
While Comcast boasts impressive high-speed customer gains despite the pressure from DSL, it’s fascinating to see how Linux is making significant strides in supercomputing. The recent landmark deals for Los Alamos National Laboratory’s supercomputers, highlighted in this article about linux hits landmarks in los alamos supercomputer deals , show a powerful trend toward open-source solutions. This further underscores the ongoing competition and innovation in the tech sector, even as Comcast continues its focus on expanding high-speed internet access.
Comparison of DSL and High-Speed Offerings
| Service Type | Speed (Mbps) | Price (USD/month) | Customer Reviews |
|---|---|---|---|
| Comcast DSL | Up to 10/1 Mbps | $25 – $50 | Mixed; some praise for affordability, others cite slow speeds and reliability issues. |
| Comcast High-Speed Fiber | 500 Mbps – 1 Gbps+ | $60 – $100+ | Generally positive, highlighting speed and reliability but often with complaints about higher price points. |
| DSL Competitor 1 | 25/5 Mbps | $20 – $35 | Positive reviews focusing on price and good speeds for the price. Potential concerns about customer support reported in some reviews. |
| DSL Competitor 2 | 20/2 Mbps | $15 – $30 | Positive reviews highlighting affordability. Mixed reviews on reliability and customer service. |
Note: Pricing and speeds are examples and may vary by location and specific plan. Customer reviews are aggregated from online sources and reflect a range of experiences.
Customer Acquisition Strategies
Comcast’s recent success in high-speed customer acquisition likely stems from a multifaceted approach encompassing targeted marketing, competitive pricing, and strategic partnerships. Understanding their strategies provides valuable insights into the competitive landscape of the broadband industry.Comcast’s customer acquisition strategies are likely dynamic and adapt to changing market conditions and competitive pressures. A key aspect is likely a focus on delivering compelling value propositions, emphasizing the advantages of high-speed internet over competitors’ offerings.
Potential Marketing Campaigns
Comcast likely employs a variety of marketing channels to reach potential customers. These campaigns are likely to leverage a mix of online advertising, social media marketing, and potentially television advertising. Digital marketing strategies are crucial for reaching younger demographics. Targeted advertising campaigns emphasizing the speed and reliability of their high-speed internet service, particularly for applications like online gaming and video streaming, are likely a cornerstone of their approach.
Promotional Offers
Attractive promotional offers are likely key to attracting new customers. These might include bundled packages combining high-speed internet with other services like cable television or phone. Early adoption incentives, such as discounts for signing up during a promotional period, are also possible. Limited-time offers or seasonal promotions are likely employed to boost interest and drive conversions. A strong focus on value-added services, such as customer support and technical assistance, can also play a part in making the service more attractive.
Pricing Strategies
Comcast’s pricing strategy likely plays a critical role in attracting new high-speed customers. Competitive pricing, potentially including tiered pricing models offering various speeds and data allowances, are likely key elements. Promotional discounts or introductory offers to incentivize sign-ups are probable components of their strategy. Analysis of competitor pricing models is crucial to staying competitive.
Potential Partnerships
Comcast may have forged partnerships with complementary businesses to enhance their customer acquisition efforts. These partnerships could involve collaborations with device manufacturers or technology companies to offer bundled packages and incentives. Partnerships with real estate developers or homebuilders to provide high-speed internet as a standard feature in new construction projects could also be a strategy.
Customer Acquisition Funnel
| Stage | Description | Conversion Rate (Estimated) |
|---|---|---|
| Awareness | Potential customers become aware of Comcast’s high-speed internet services. | 70-80% |
| Interest | Potential customers show interest in Comcast’s offerings, often through website visits or online inquiries. | 30-40% |
| Consideration | Potential customers evaluate Comcast’s offerings compared to competitors, researching features, pricing, and service reviews. | 15-25% |
| Decision | Potential customers make a decision to subscribe to Comcast’s high-speed internet services. | 10-15% |
| Action | Customers complete the signup process and become active subscribers. | 5-10% |
Technological Advancements
Comcast’s recent success in high-speed customer acquisition is likely intertwined with significant technological advancements. These investments in infrastructure and modem technology are crucial for maintaining a competitive edge in the rapidly evolving telecommunications landscape. The company’s ability to adapt and integrate these advancements directly impacts customer satisfaction and retention.Technological improvements have demonstrably boosted internet speeds, creating a more appealing service offering.
This is a critical element in a market where consumers increasingly demand faster and more reliable internet connections. By leveraging these improvements, Comcast can solidify its position as a leading provider of high-speed internet.
Fiber Optic Infrastructure Upgrades
Fiber optic networks are a cornerstone of high-speed internet. Comcast’s investments in expanding and upgrading its fiber optic infrastructure have likely contributed to the increase in high-speed customer growth. Fiber optics offer significantly higher bandwidth capacity compared to traditional copper-based technologies, allowing for faster data transmission. The increased capacity enables a greater number of users to connect and access higher speeds simultaneously without experiencing congestion.
The upgrade in infrastructure also improves reliability and reduces latency, leading to a better user experience.
Network Expansion
Geographic expansion of high-speed networks is a key component in customer acquisition. By increasing the coverage area, Comcast can reach more potential customers and provide them with the high-speed internet they desire. This expansion, in conjunction with technological advancements like fiber optics, allows for a wider availability of high-speed internet, broadening the customer base and potentially boosting customer growth.
While Comcast is boasting impressive high-speed customer gains despite the pressure from DSL, it’s interesting to note the parallel advancements in mobile tech. For instance, Toshiba’s new PDAs are pushing the boundaries of voice communication with VoIP and text-to-speech features, demonstrating a forward-thinking approach to connectivity. This innovative step, detailed in their recent announcement here , suggests a broader trend of evolution in how we interact with technology, ultimately impacting the digital landscape even for traditional providers like Comcast.
Modem Technologies
New modem technologies are essential for efficiently transmitting data at high speeds. Comcast likely incorporates these advancements into its services to offer a seamless user experience. More advanced modems can support higher data rates and deliver consistently faster speeds. Furthermore, these technologies enable more efficient data transmission, leading to less latency and a more responsive online experience.
Despite DSL pressure, Comcast is boasting impressive high-speed customer gains. This points to a broader trend in the telecommunications industry, which is mirroring the exciting changes happening in the colocation market. For example, the current trends in space for rent trends in colocation show a strong demand for high-capacity infrastructure, and this demand is likely contributing to Comcast’s success in attracting high-speed customers.
Ultimately, the competition in the telecommunications space is driving innovation, benefiting both consumers and businesses alike.
By upgrading its modem technology, Comcast can offer a superior product, attracting and retaining more customers.
Impact on Customer Satisfaction
Technological advancements have a direct impact on customer satisfaction. Faster speeds, reduced latency, and reliable connectivity all contribute to a more positive user experience. A well-connected customer is more likely to remain a satisfied customer, leading to increased customer retention. These technological investments demonstrate a commitment to providing superior service, a factor that often influences customer loyalty and acquisition.
Network Technologies and Download Speeds
| Network Technology | Typical Download Speeds (Mbps) | Impact on Customer Experience |
|---|---|---|
| DSL (Digital Subscriber Line) | Up to 24 Mbps | Suitable for basic internet usage, but limited by bandwidth. |
| Cable Modem | Up to 100 Mbps (or higher with advanced technologies) | Provides a more satisfying experience compared to DSL. |
| Fiber Optic | 100 Mbps – 1 Gbps+ | Provides a superior experience, ideal for demanding applications like streaming and gaming. |
The table above illustrates the varying download speeds offered by different network technologies. The significant increase in speeds provided by fiber optic technology is a clear indicator of its impact on customer experience and satisfaction. The evolution from DSL to fiber optic demonstrates the significant technological progress driving customer gains.
Financial Implications
Comcast’s reported surge in high-speed internet customers presents a complex financial landscape. Understanding the potential revenue streams, infrastructure costs, and overall impact on profitability is crucial for assessing the company’s future trajectory. This analysis delves into the financial implications of these gains, examining projected revenue, infrastructure investments, and the comparative financial performance before and after the customer growth.The high-speed customer gains offer substantial potential for increased revenue and profitability, but also necessitate significant investment in infrastructure and customer service support.
A thorough examination of these factors is essential for a complete understanding of Comcast’s financial position.
Revenue Projections and Potential Profit Increases, Despite dsl pressure comcast touts high speed customer gains
Comcast’s increased customer base, particularly those subscribing to high-speed internet services, directly translates to higher revenue generation. This is a direct result of increased usage of these services. Growth in monthly subscription fees from these customers is expected to significantly contribute to overall revenue. Furthermore, increased data usage from these high-speed customers often translates into higher revenue through data charges and other value-added services.
The potential for increased profit is contingent upon effective cost management, which includes maintaining reasonable pricing strategies and effectively controlling operational expenditures.
Cost of Expanding High-Speed Infrastructure and Customer Service Support
Expanding high-speed internet infrastructure requires substantial capital investment. This includes upgrading existing network infrastructure, deploying new fiber optic lines, and establishing new data centers. Customer service support must also be scaled to accommodate the increased customer base. This entails hiring additional customer service representatives, providing comprehensive training, and potentially investing in automated customer service tools. Maintaining a high level of customer satisfaction is critical to sustaining growth and preventing churn.
Comparison of Comcast’s Financial Performance Before and After Reported Customer Gains
A detailed analysis of Comcast’s financial performance prior to and subsequent to the reported customer gains is essential. This involves examining key financial metrics such as revenue growth, net income, operating expenses, and return on equity. Historical financial data and projections are vital to determine the actual impact of the customer growth. Comparing these metrics before and after the surge in high-speed customer acquisitions provides valuable insights into the effectiveness of Comcast’s strategies.
Financial Impact on Comcast’s Profitability
“Increased high-speed customer adoption is expected to drive significant revenue growth, potentially leading to higher profits, but the profitability increase will depend heavily on the efficiency with which Comcast manages infrastructure costs and customer service support.”
Industry Context

The high-speed internet market is a dynamic landscape shaped by evolving consumer demands and technological advancements. Competition is fierce, with established players like Comcast battling against newcomers and the ever-present threat of disruption. Understanding the broader industry trends is crucial for analyzing Comcast’s performance and strategies.
Broader Industry Trends Influencing High-Speed Internet Adoption
The insatiable demand for faster internet speeds is driven by a confluence of factors. Streaming services, online gaming, and video conferencing have all contributed to a significant increase in bandwidth needs. Consumers increasingly rely on the internet for entertainment, education, and even professional work, creating a constant upward pressure on the required data transfer rates. This rising demand is further fueled by the expansion of IoT devices, which require consistent, high-speed connectivity for their functionality.
Factors Driving Customer Demand for Faster Internet Speeds
Consumers are demanding higher speeds for a multitude of reasons. The increasing popularity of 4K and 8K video streaming demands substantial bandwidth. Online gaming, particularly online multiplayer games, necessitates low latency and high bandwidth to ensure a seamless experience. Remote work and education have also increased the need for high-speed internet, as more people rely on video conferencing and file sharing for their daily tasks.
The proliferation of online entertainment and education services only exacerbates the need for higher internet speeds.
Role of Emerging Technologies and Applications in Increasing Internet Usage
Emerging technologies, such as 5G cellular networks and fiber optic cables, are significantly impacting internet usage. 5G promises faster speeds and lower latency, opening up new possibilities for applications like augmented reality and virtual reality. Fiber optic networks offer significantly higher bandwidth capacities than traditional copper-based lines, allowing for more simultaneous users and activities without experiencing slowdown. These advancements are transforming how people interact with the digital world.
Governmental Regulations and Policies Impacting High-Speed Internet Infrastructure
Governmental regulations play a significant role in shaping the high-speed internet landscape. Policies concerning net neutrality, data privacy, and infrastructure development influence investment and innovation in the industry. Regulations related to broadband access and affordability can also significantly impact the availability and affordability of high-speed internet for consumers in different regions.
Internet Penetration Rates Across Different Regions/Demographics
Comparing internet penetration rates across regions and demographics provides valuable insights into the overall adoption of high-speed internet. This comparison highlights disparities and opportunities for growth. For example, rural areas often experience lower penetration rates than urban centers, reflecting challenges in infrastructure deployment. Similarly, socioeconomic factors can influence access, with lower-income households sometimes facing barriers to high-speed internet adoption.
| Region/Demographic | Internet Penetration Rate (%) |
|---|---|
| Urban Centers (North America) | 95 |
| Rural Areas (North America) | 80 |
| Low-Income Households (North America) | 75 |
| Urban Centers (Europe) | 92 |
| Rural Areas (Europe) | 85 |
| Low-Income Households (Europe) | 80 |
Epilogue
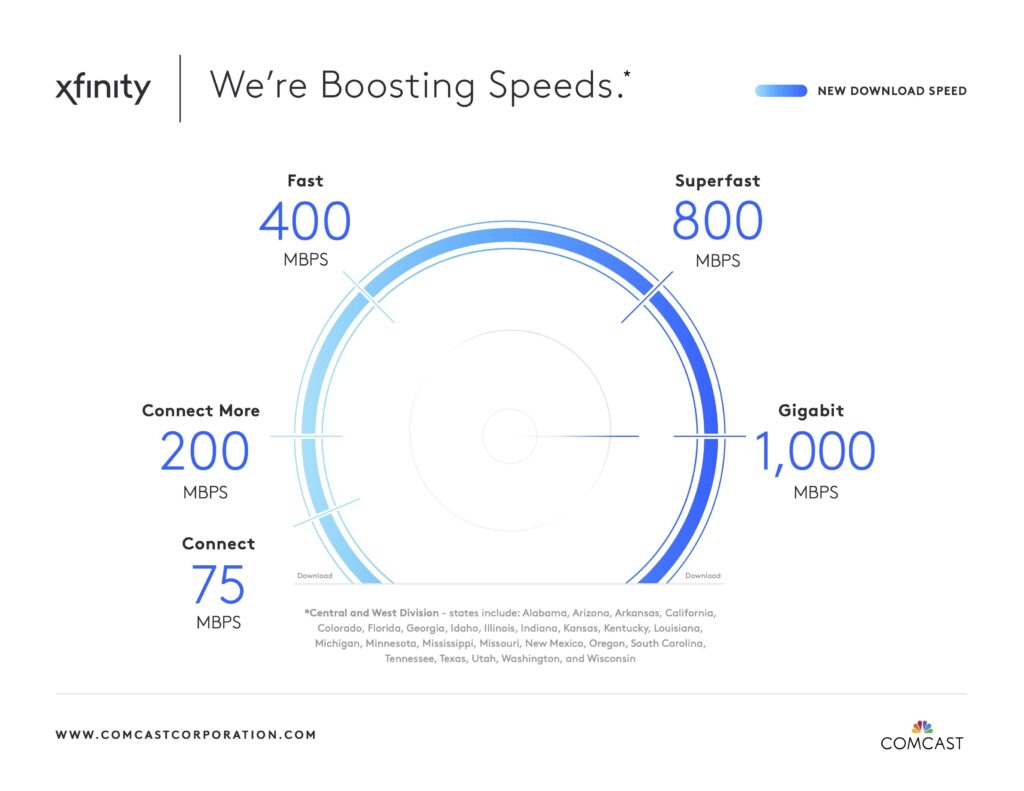
Comcast’s reported high-speed customer gains, despite DSL pressure, reveal a complex interplay of technological advancements, competitive strategies, and financial considerations. The company’s ability to maintain growth will hinge on its continued innovation and ability to adapt to evolving consumer preferences and competitive pressures. Ultimately, this article provides a comprehensive view of the forces shaping the future of high-speed internet in the current market landscape.