Digital TV Transition Bill Committee Approval
Digital TV transition bill wins committee approval, marking a significant step toward the digital future of television. This legislation, with its intricate provisions and potential impact on consumers, broadcasters, and the broader economy, promises a fascinating journey. The bill’s journey through committee, encompassing technical, economic, and social considerations, sets the stage for a nationwide transition. This detailed analysis delves into the bill’s background, consumer impact, and broader implications.
The bill’s approval by the committee signifies a crucial milestone in the digital television transition. This pivotal moment necessitates careful consideration of its implications across various stakeholders, including consumers, broadcasters, and the broader media landscape. The bill’s key provisions and the expected timeline for the transition will be explored, highlighting potential challenges and benefits for all involved parties.
The legislation, aiming to modernize the broadcast sector, is a multifaceted issue requiring a deep dive into its complexities.
Background of the Digital Television Transition Bill
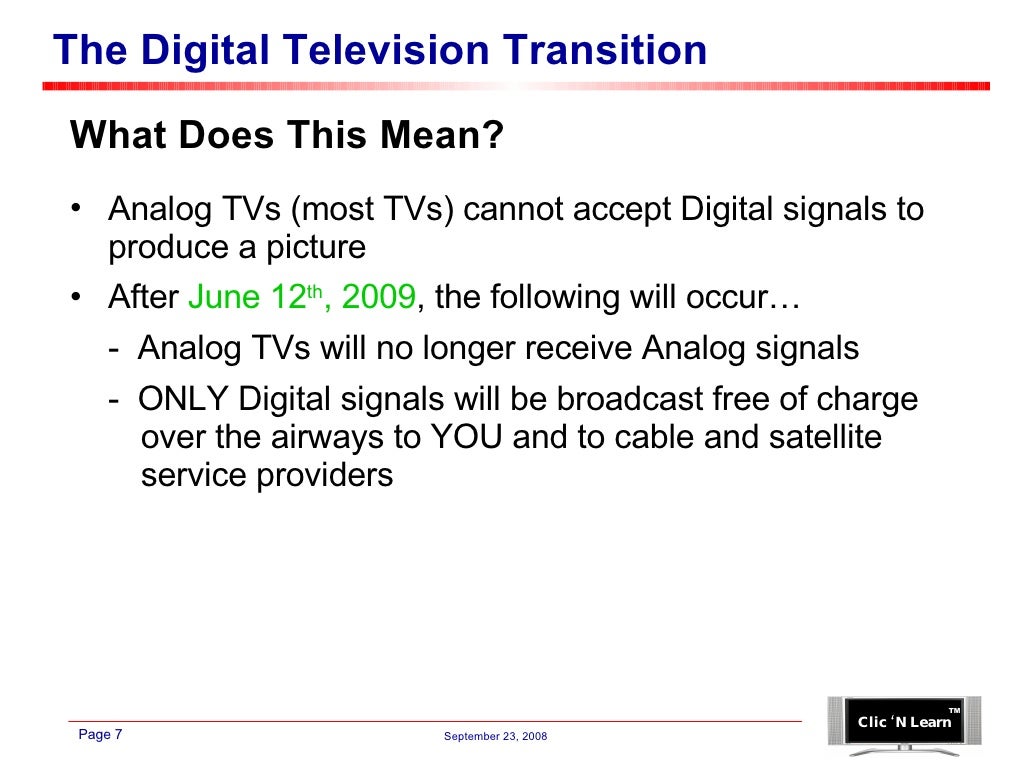
The digital television transition bill, a crucial piece of legislation, mandates the shift from analog to digital television broadcasting. This transition, while seemingly technical, has significant implications for consumers, broadcasters, and the media landscape as a whole. It’s a complex process requiring careful consideration of various stakeholders and technological advancements.This bill aims to streamline the transition, ensuring a smooth and efficient shift to digital broadcasting.
The legislation is expected to enhance viewer experience and open the door for future technological developments in the broadcasting industry.
Key Provisions of the Bill
The bill Artikels specific requirements for broadcasters, including deadlines for transitioning to digital signals. These requirements are critical for ensuring a seamless transition, minimizing disruption, and promoting a unified digital broadcasting standard. Key provisions are designed to accommodate various stakeholders, balancing the needs of broadcasters, consumers, and government regulators.
- Technical Specifications: The bill details the technical specifications for digital television signals, including resolution, channel allocation, and frequency bands. These technical specifications are essential for ensuring compatibility and minimizing interference among different broadcasting platforms.
- Transition Schedules: The bill establishes specific deadlines for broadcasters to cease analog transmissions and switch entirely to digital. These schedules are designed to ensure a phased approach to the transition, giving broadcasters ample time to adapt to the new technologies and infrastructure changes.
- Consumer Support: The bill mandates consumer support programs, including free digital television converters for low-income households. This is a crucial component of the bill, as it helps bridge the digital divide and ensures that all segments of the population have access to digital television.
- Spectrum Management: The bill addresses the management of the spectrum used for television broadcasting after the transition. This includes strategies for re-allocating the spectrum for other communication needs, such as mobile or internet services.
Legislative History
The bill’s journey through the legislative process involved several stages of committee hearings, debates, and votes. Each stage presented opportunities for amendments and refinements to the legislation.
- Committee Actions: The bill was first introduced to the committee, which held hearings to gather input from various stakeholders. This allowed for public comment and testimony from industry experts, consumer advocates, and affected parties.
- Amendments and Revisions: The bill underwent several revisions and amendments based on the feedback received during the committee hearings. These changes addressed concerns and improved the bill’s provisions to accommodate the interests of all involved.
- Committee Votes: The bill received final approval in the committee through a vote. The vote reflected the committee’s support for the legislation and its commitment to the digital television transition.
Political Context, Digital tv transition bill wins committee approval
The political climate surrounding the bill’s introduction and approval played a significant role in its final form. The political climate influenced the bill’s focus, content, and final passage.
- Stakeholder Influence: The political context often involves various stakeholders, including government agencies, industry groups, and consumer organizations, each with their own interests and perspectives. These different viewpoints are considered and balanced to create the most comprehensive bill.
- Public Opinion: Public opinion and support for the bill often influenced the legislative process. Public engagement with the transition process often drives the need for the legislation.
- Party Politics: Political affiliations sometimes played a role in shaping the bill’s progress through the legislative process. These affiliations might impact the approach and specifics of the legislation.
Comparison with Previous Versions
| Feature | Previous Version 1 | Previous Version 2 | Current Bill |
|---|---|---|---|
| Transition Deadline | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 |
| Consumer Support | Limited programs | Expanded converter program | Enhanced converter program, digital literacy initiatives |
| Spectrum Management | No specific plan | Preliminary spectrum allocation | Detailed spectrum allocation plan |
The current bill represents a significant update from previous versions, addressing concerns and incorporating feedback to ensure a more comprehensive and effective transition.
Impact on Consumers
The Digital Television Transition Bill, now moving through committee approval, will bring about significant changes in how consumers access television programming. This transition, while necessary for technological advancement, presents both opportunities and challenges for viewers, particularly concerning access, cost, and the availability of programming options. The bill’s impact on consumers with older television sets will also require careful consideration.
Access to Digital Television Services
The bill mandates the transition to digital television broadcasting. This shift will make digital signals the standard, effectively phasing out analog signals. Consumers will need to either purchase a digital-ready television set or a converter box to receive these signals. This transition will eliminate the use of analog broadcasts, forcing consumers to adjust to the new digital standard.
The digital TV transition bill’s committee approval is a huge step forward. It’s a sign of our nation embracing the digital age, which naturally leads us to consider other crucial digital advancements. For instance, acquiring a worldwide computer certification, like those offered by joining the digital ranks worldwide computer certification , is essential for anyone looking to thrive in today’s tech-driven world.
This digital literacy, coupled with the new TV transition, will position us well for the future. Ultimately, the bill’s approval is a positive sign for the digital evolution of our society.
Failure to adapt will result in a loss of reception of their television programming.
Financial Implications for Consumers
The financial impact on consumers varies. Purchasing a new digital television set or a converter box involves an upfront cost. However, long-term savings may arise from reduced reliance on cable or satellite subscriptions, as digital antennas offer an alternative to these subscription services. The savings potential varies depending on individual viewing habits and the availability of free-to-air digital channels.
Consumers may face initial expenses but could potentially save money over time if they adopt digital-only solutions.
Availability of Channels and Programming Options
The digital transition offers the potential for a wider variety of channels and programming options. Digital broadcasting can support higher quality images and sound compared to analog transmissions. Consumers may gain access to channels previously unavailable through analog broadcast. This is particularly true in areas with limited channel options or where signal interference was prevalent. Broadcasting in digital format opens up opportunities for the inclusion of interactive elements and specialized programming.
Impact on Consumers with Older Television Sets
Consumers with older television sets will face challenges during the transition. These older sets will not be able to receive digital signals directly. To maintain access to broadcast television, they will need to acquire a digital converter box. The bill often includes provisions for assistance in acquiring converter boxes or financial support for this expense. Consumers should research options and prepare accordingly.
Timeline and Impact on Consumer Segments
| Consumer Segment | Timeline (Estimated) | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Consumers with Digital-Ready TVs | Immediate Access | Minimal impact. No need for additional equipment. |
| Consumers with Analog TVs | Transition Period (1-2 years) | Need to acquire a converter box. |
| Consumers in Areas with Limited Signal Strength | Transition Period (1-2 years) | May face signal issues requiring upgrades to antenna systems. |
| Consumers relying on Cable/Satellite TV | Transition Period (1-2 years) | May experience minimal changes depending on their existing services. |
The table provides a simplified overview of the expected timeline and impact. Specific timelines and impacts may vary depending on regional factors and local implementation strategies. Consumers are advised to consult local broadcast authorities for precise details on their region.
Impact on Broadcasters

The Digital Television Transition Bill heralds a significant shift in the broadcasting landscape, demanding a profound transformation for broadcasters across the spectrum. This transition will affect their operational procedures, technical infrastructure, and, inevitably, their revenue models. Understanding these implications is crucial for both broadcasters and policymakers alike.
Technical Adaptations for Compliance
Broadcasters will need to undertake substantial technical upgrades to transition to digital broadcasting. This involves replacing or modifying their current broadcasting equipment to transmit and receive digital signals. Upgrading studio equipment, transmission systems, and receiving antennae are essential steps. Digital signal processing, including encoding and decoding, will be crucial for ensuring high-quality transmission. Additionally, broadcasters will need to invest in new infrastructure to handle the increased data capacity associated with digital signals.
Successfully transitioning to digital broadcasting requires careful planning and execution to maintain broadcast quality and reliability.
Impact on Revenue Streams
The shift to digital broadcasting can potentially affect broadcasters’ revenue streams in various ways. The elimination of analog broadcasting could result in lost revenue from viewers who do not upgrade to digital receivers. However, the expansion of the digital viewing audience and the potential for new revenue streams, such as targeted advertising and premium content, could offset these losses.
For example, broadcasters might leverage data collected from digital viewers to tailor their programming and advertising strategies for enhanced effectiveness. Furthermore, digital broadcasting may facilitate new business models, such as streaming and on-demand services.
Implications for Broadcasters Serving Smaller Markets
The digital transition presents unique challenges for broadcasters primarily serving smaller markets. These broadcasters may have limited resources to invest in the necessary technical upgrades. The cost of converting to digital broadcasting might be disproportionately high compared to their revenue potential. This could potentially lead to consolidation, as smaller broadcasters might struggle to compete with larger, better-resourced entities.
Consequently, there might be a need for government subsidies or incentives to assist these smaller broadcasters in their transition.
Costs Associated with Converting to Digital Broadcasting
| Broadcaster Type | Estimated Conversion Costs (USD) | Justification |
|---|---|---|
| Large National Broadcasters | $5,000,000 – $20,000,000+ | Extensive network infrastructure, high-volume content production, and significant personnel requirements. |
| Regional Broadcasters | $500,000 – $5,000,000 | Moderately complex network upgrades, potentially requiring external support for some elements. |
| Local Broadcasters | $100,000 – $500,000 | Relatively simpler network upgrades; may require external consulting for optimization. |
The costs associated with converting to digital broadcasting vary considerably depending on the broadcaster’s size, reach, and current infrastructure. Large national broadcasters, with extensive networks and large-scale production, face significantly higher costs compared to smaller local broadcasters. The provided table offers a general overview; specific costs will depend on individual circumstances.
Technological Considerations: Digital Tv Transition Bill Wins Committee Approval
The digital television transition is fundamentally about changing the way signals are transmitted and received. This shift from analog to digital technology brings a host of new possibilities and challenges, affecting everything from viewer experience to the infrastructure required to support broadcasting. Understanding the technical underpinnings of this transition is crucial for navigating its implications.The core of the digital television transition lies in the shift from analog signals, which represent information as continuous waves, to digital signals, which represent information as discrete sequences of 0s and 1s.
This change has a profound impact on signal quality, security, and the potential for new features and services.
Digital Signal Transmission and Reception
Digital signal transmission leverages advanced encoding techniques that make signals more resistant to interference and noise. This leads to improved picture and sound quality, allowing for more intricate and vivid images and richer audio. Digital signal reception involves specialized equipment designed to decode these discrete digital signals back into usable video and audio content. This technology requires receivers capable of understanding and interpreting the digital code.
Impact of New Technologies on the Transition
Several new technologies have accelerated the digital transition. The development of high-speed internet and advanced compression algorithms, like MPEG-4 and H.264, allowed for the efficient delivery of high-quality digital television signals over existing infrastructure. These advancements have led to greater bandwidth efficiency, enabling more channels and better picture quality without significantly increasing the infrastructure demands. The proliferation of smart TVs and streaming services has also significantly contributed to the shift, as consumers increasingly demand access to digital content beyond traditional broadcasting.
Standards and Specifications for Digital Television Broadcasting
International and national standards are crucial to ensure interoperability and compatibility across different devices and regions. These standards define the format of digital signals, including the resolution, frame rate, and audio encoding. Examples include ATSC (Advanced Television Systems Committee) standards in North America and the DVB (Digital Video Broadcasting) standards in Europe. These standards are continuously evolving, keeping pace with advancements in technology and consumer demands.
Good news for digital TV transition! The bill just sailed through committee approval, which is a huge step forward. Meanwhile, tech news is buzzing about Microsoft patching a new vulnerability worm, expected to be a significant security issue. This development, as detailed in microsoft patches new vulnerability worm expected , highlights the constant need for updates and security in our increasingly digital world.
Ultimately, the digital TV transition bill’s progress is still very positive.
This ensures a consistent and reliable viewing experience for everyone.
Equipment Required for Digital Television Reception
The transition requires consumers to update their equipment. This typically involves replacing older analog television sets with digital-capable television sets. These digital-ready sets have built-in tuners capable of receiving and decoding digital signals. Digital tuners can be added to older televisions, too. Furthermore, set-top boxes may be necessary for certain digital signals or to access specific services.
The specifications of these devices must align with the digital standards adopted in a particular region. The required equipment for digital television reception may vary based on the specific standards used in a particular area. These considerations affect consumers directly, as their equipment needs to be compatible with the transition.
Regulatory and Legal Implications
The digital television transition isn’t just about swapping signals; it’s a complex legal and regulatory undertaking. Understanding the existing legal framework, the roles of regulatory bodies, and potential challenges is crucial for a smooth transition. This section dives into the legal landscape surrounding this significant technological shift.
Legal Framework Surrounding the Digital Transition
The digital television transition is governed by a multitude of existing laws and regulations. These frameworks, often encompassing broadcasting, telecommunications, and consumer protection, are tailored to the unique characteristics of each jurisdiction. These laws are often amended or updated to align with technological advancements and societal needs. For instance, some laws may Artikel the specific procedures for spectrum allocation or licensing for digital broadcasting.
Good news for digital TV viewers! The digital TV transition bill just cruised through committee approval, which is fantastic. It’s a big step forward for the industry, but it also reminds us of the ongoing need for thorough scrutiny of technology, particularly when it comes to voting machines. Just like the recent Diebold case, where the company retracted legal threats over voting machine flaws , ensuring reliability and transparency is paramount.
All this points to the need for careful checks and balances in tech developments, even when it’s good news like this digital TV transition bill.
Role of Regulatory Bodies in the Transition
Regulatory bodies play a critical role in guiding and overseeing the digital television transition. Their responsibilities typically include ensuring compliance with established regulations, setting technical standards for the transition, and mediating any disputes that may arise. For example, they may be tasked with overseeing the implementation of technical standards for digital television signals to ensure interoperability and quality.
They also often have the authority to impose penalties for non-compliance.
Enforcement Mechanisms for Compliance
Enforcement mechanisms vary depending on the specific laws and regulations in place. These can include fines for non-compliance with the transition timetable or for broadcasting analog signals beyond the permitted cut-off date. Additionally, regulatory bodies can issue cease-and-desist orders, requiring broadcasters to stop using outdated equipment or signals. These mechanisms aim to ensure a smooth and timely transition.
Potential Legal Challenges Related to the Bill
Potential legal challenges could arise from various sources, such as disputes over spectrum allocation, concerns about consumer protection during the transition period, or challenges related to the enforcement of deadlines. One potential challenge could be the transition of broadcast licenses and rights for the new digital platforms. Another is the need to address the impact of the transition on those who have invested in analog infrastructure.
Examples of such challenges are evident in other similar transitions worldwide, such as the shift to digital radio.
Summary of Relevant Regulations and Legal Precedents
| Regulation Area | Relevant Regulations | Legal Precedents |
|---|---|---|
| Spectrum Allocation | Federal Communications Commission (FCC) rules in the US, Ofcom rules in the UK | Cases involving spectrum reallocation and licensing in previous technological transitions |
| Broadcasting Standards | National standards for digital television broadcasting | Court rulings on broadcasting standards and consumer rights |
| Consumer Protection | Laws protecting consumers from unfair practices during the transition | Cases involving consumer protection in similar technological shifts |
| Licensing and Permits | Requirements for broadcasters to obtain licenses for digital broadcasting | Legal precedents regarding broadcasting license renewals and transitions |
Note: This table provides a general overview and may not encompass all relevant regulations and precedents in every jurisdiction. Specific details should be researched based on the particular digital television transition bill in question.
Public Awareness and Education
The digital television transition is a significant shift, and successful implementation hinges heavily on effective public awareness and education campaigns. Ignorance about the transition can lead to confusion and frustration, potentially hindering adoption of the new technology. Clear communication and accessible information are crucial to ensuring a smooth and positive user experience for all.
Importance of Public Awareness Campaigns
Public awareness campaigns play a vital role in preparing the public for the digital transition. They help mitigate potential anxieties and address concerns about the change, such as the need to purchase new equipment. By fostering understanding and knowledge, these campaigns can encourage a smoother transition for everyone, preventing widespread confusion and facilitating broader adoption of the new technology.
Strategies for Educating Consumers
Various strategies can be employed to educate consumers about the digital transition process. Targeted outreach through different media channels is essential. These channels should include easily accessible formats, such as online resources, videos, and print materials. Additionally, community events and workshops can provide hands-on learning opportunities. Demonstrations of the new technology and interactive sessions are crucial to making the transition more accessible.
Government-Led Initiatives to Help Consumers Adapt
Government initiatives can significantly aid consumers in adapting to the digital transition. Financial assistance programs for purchasing new equipment can ease the burden on lower-income households. Dedicated help lines and online resources for addressing technical issues can also be helpful. These initiatives will help facilitate a more equitable and accessible transition for everyone.
Examples of Public Awareness Initiatives
Government agencies can implement diverse public awareness initiatives, tailored to specific target audiences and needs. These initiatives will be more effective if they use a multi-faceted approach.
| Initiative | Target Audience | Effectiveness Measures |
|---|---|---|
| Public service announcements (PSAs) on television and radio | General public | Measured by surveys on public understanding of the transition and increased awareness of new equipment needs. |
| Workshops and demonstrations at community centers | Older adults and low-income households | Measured by attendance numbers and feedback on understanding of the process. Follow-up surveys to assess actual implementation of new knowledge. |
| Online tutorials and FAQs on government websites | Tech-savvy individuals and those with internet access | Measured by website traffic, number of questions answered, and perceived clarity of information. |
| Interactive kiosks in public places | General public, particularly those with limited access to the internet | Measured by engagement with the kiosks and understanding demonstrated through participation in demonstrations. |
Economic Impact
The Digital Television Transition Bill presents a complex interplay of economic forces, impacting various sectors and potentially reshaping the media landscape. Understanding the potential economic ramifications is crucial for stakeholders, from broadcasters to consumers, as the bill ushers in a new era of television viewing. The bill’s impact will be felt not only in the broadcasting industry, but also in related sectors such as electronics manufacturing, equipment suppliers, and ultimately, the general economy.The economic impact of the transition extends beyond the immediate financial gains or losses.
The bill’s influence on employment, innovation, and technological advancement holds considerable weight in shaping the long-term economic health of the nation. It’s vital to analyze these effects in detail to forecast potential benefits and challenges.
Overall Economic Impact
The overall economic impact of the bill is multifaceted and depends heavily on factors like the speed of adoption, government support, and the market’s response. Some projections indicate a net positive impact, driven by new opportunities in the digital sector, but others highlight potential job losses in the traditional broadcast industry.
Effects on Employment and Job Creation
The transition to digital television is likely to generate some job losses in traditional broadcasting roles, as the industry adapts to the new technologies. However, it also presents opportunities for new employment in areas such as digital content creation, streaming services, and related technology fields. The exact magnitude of these changes is uncertain and depends on factors like the rate of technological advancement and government incentives.
Potential for Innovation and Growth in the Digital Television Sector
The digital television transition offers a fertile ground for innovation. New digital content creation platforms, streaming services, and related technologies will emerge, potentially creating new markets and driving economic growth. This transition fosters competition and encourages the development of new business models.
Projections for Economic Benefits or Losses
“Predicting the precise economic benefits or losses of the bill is challenging, as it depends on various factors. A comprehensive economic impact assessment should include detailed analysis of specific industries, projected consumer adoption rates, and government support programs.”
While some industries may experience short-term setbacks, long-term benefits from increased competition, innovation, and technological advancement are likely.
Table Outlining Potential Employment Changes
| Industry | Potential Job Losses | Potential Job Gains |
|---|---|---|
| Traditional Broadcasters | Technical staff, on-air personnel, some administrative roles | Digital content creators, streaming service employees, digital media technicians, software developers |
| Electronics Manufacturing | Manufacturing roles for older equipment | Manufacturing roles for digital television equipment, production of related components |
| Equipment Suppliers | Suppliers of analog equipment | Suppliers of digital broadcasting equipment, digital content distribution services |
| Related Industries (e.g., cable, satellite) | Potential for restructuring, staff redeployment | Adaptation to new digital technologies, new revenue streams |
Alternatives and Comparisons
The digital television transition bill represents a significant shift in broadcasting infrastructure. Understanding alternative approaches and comparing them with the proposed legislation, along with examining successful transitions in other countries, provides valuable context for assessing the bill’s potential impact and effectiveness. Comparative analysis of costs and benefits can help refine the strategy and ensure optimal outcomes for all stakeholders.A thorough evaluation of alternative models, coupled with a critical comparison of the proposed bill to similar legislation worldwide, is essential to ensuring a smooth and beneficial transition.
This involves considering both the technical and economic aspects of different approaches, alongside the experiences of other nations. Such an examination will ultimately contribute to a more informed discussion and potentially lead to improvements in the proposed bill.
Potential Alternative Approaches
Alternative strategies for transitioning to digital television encompass various approaches to phasing out analog signals. These range from staggered shutdowns to incentivized upgrades for consumers and broadcasters. For instance, a slower, more gradual transition might provide more time for consumers to adapt and potentially mitigate initial economic disruption. Conversely, a rapid transition, while potentially less costly in the long run, could lead to higher initial consumer costs and potentially exacerbate existing inequalities in access to technology.
Comparison with Other Countries’ Legislation
Numerous countries have successfully transitioned to digital television, each employing unique approaches tailored to their specific contexts. Examining these experiences offers valuable insights for refining the proposed bill. For example, some countries have offered subsidies or incentives to encourage consumer adoption of digital receivers, while others have relied on stricter deadlines for the analog switch-off. The effectiveness of each approach in terms of cost-effectiveness, consumer impact, and broadcaster adaptability can be examined.
Successful Digital Transition Strategies in Other Countries
Several countries have successfully implemented digital television transitions, offering lessons for the current initiative. Countries like the UK and Canada implemented a comprehensive awareness campaign and provided financial incentives to consumers for acquiring digital set-top boxes. This strategy proved effective in ensuring a smooth transition with minimal disruption. A comparative analysis of the different strategies and their effectiveness can be found in various reports published by international broadcasting organizations.
Comparative Analysis of Costs and Benefits of Different Transition Models
The cost-benefit analysis of various digital transition models is critical. A gradual transition might result in lower initial costs for consumers, but potentially higher long-term costs due to prolonged use of older technology. Conversely, a rapid transition might lower long-term costs, but could lead to higher initial consumer expenses. Economic modeling and real-world examples of successful transitions in different contexts will help to evaluate these factors.
Strengths and Weaknesses of the Proposed Bill Compared to Alternative Strategies
| Feature | Proposed Bill | Alternative: Gradual Transition | Alternative: Incentives-Driven Approach |
|---|---|---|---|
| Consumer Impact | Potential for initial costs to consumers, but potential long-term savings. | Lower initial cost for consumers, but longer transition period. | Lower initial cost for consumers with financial incentives. |
| Broadcaster Costs | Potential costs associated with upgrading infrastructure and content production. | Lower upfront costs for broadcasters due to extended transition. | Potential costs associated with funding incentives and regulatory compliance. |
| Regulatory Complexity | Potential for administrative hurdles and compliance issues. | Lower regulatory complexity due to slower implementation. | Increased regulatory complexity to administer and monitor incentives. |
| Technological Advancement | Alignment with current technological standards. | Potential for technology obsolescence during the transition. | Potential for stimulating technological innovation and adoption. |
This table provides a concise comparison of the proposed bill with alternative strategies, highlighting key aspects such as consumer impact, broadcaster costs, regulatory complexity, and alignment with technological advancement. A more detailed analysis would require a deeper dive into the specifics of each approach and the potential impact on various stakeholders.
Future Implications
The digital television transition bill heralds a significant shift in the media landscape, impacting not just television viewing but potentially reshaping the entire entertainment industry. This transition represents more than simply replacing analog signals; it opens doors to a future filled with possibilities and challenges, demanding careful consideration of long-term consequences.The digital transition is fundamentally altering how we consume media.
It’s paving the way for more personalized experiences, interactive content, and a wider array of entertainment options. However, the transition also brings with it the need to address potential disparities in access and affordability, particularly for underserved communities.
Potential Long-Term Consequences
The digital television transition bill will have a ripple effect across various sectors. The migration to digital signals presents opportunities for innovation in broadcasting, but also requires careful planning to avoid exacerbating existing inequalities. The long-term consequences will depend on how effectively the transition is managed and how it integrates with other evolving technologies.
Role of Digital Television in the Future of Media and Entertainment
Digital television is evolving beyond a simple replacement for analog broadcasting. It’s becoming a platform for interactive experiences, streaming services, and the integration of other forms of media. This convergence is creating new opportunities for content creators, distributors, and consumers alike. For example, the rise of virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) technologies is already beginning to integrate with digital television, creating immersive viewing experiences.
Impact on Other Forms of Media
The digital transition isn’t isolated to television. It will influence other media forms, such as film, music, and even print. The digital infrastructure created for television will likely be repurposed for these other mediums, driving innovation and cost reductions. Digital distribution models, prevalent in music and film, are already influencing the way television content is produced and distributed.
Future Technological Advancements
The digital television transition will likely be intertwined with further technological advancements. For example, the development of 8K resolution, high-dynamic range (HDR) technology, and more sophisticated streaming protocols will enhance the viewing experience. Furthermore, the Internet of Things (IoT) will potentially allow for more integrated and personalized experiences, connecting television viewing with other devices and services. The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) could further personalize content recommendations and user interfaces.
Potential Future Scenarios and Impacts
The table below Artikels potential future scenarios stemming from the digital television transition bill, illustrating their respective impacts on consumers and businesses.
| Scenario | Impact on Consumers | Impact on Businesses |
|---|---|---|
| Increased accessibility and affordability of high-quality content | Consumers gain access to a wider variety of content, often at lower costs, through streaming and on-demand services. | Content providers benefit from increased viewership and subscription revenue, potentially driving further innovation. |
| Rise of personalized entertainment experiences | Consumers enjoy tailored content recommendations and interactive viewing options. | Businesses must adapt their strategies to leverage personalization and interactive technologies. |
| Digital divide persists, limiting access for some consumers | Unequal access to digital television services may disadvantage lower-income households and those in underserved communities. | Businesses may face challenges in reaching certain demographics if the digital divide isn’t addressed. |
| Emergence of new business models | Consumers experience new interactive and immersive viewing experiences. | Businesses adapt to new business models, such as pay-per-view, subscriptions, and interactive advertising. |
End of Discussion
In conclusion, the digital TV transition bill’s committee approval represents a major advancement in the nation’s broadcast infrastructure. This landmark legislation will reshape the television landscape, impacting consumers, broadcasters, and the economy. The transition process, with its technical, economic, and social dimensions, will be a significant undertaking, demanding careful consideration of all stakeholders. The upcoming stages, including public awareness campaigns and the eventual rollout, will be crucial in ensuring a smooth and successful transition for everyone.


