Ensuring VoIP QoS A Comprehensive Guide
Ensuring quality of service on VoIP networks is crucial for a seamless user experience. This guide delves into the intricacies of VoIP QoS, from defining key performance indicators (KPIs) to implementing robust network infrastructure and prioritizing VoIP traffic. We’ll explore various methods for managing VoIP traffic, minimizing latency and jitter, and incorporating essential security measures. Understanding the challenges and solutions in different environments, from enterprises to residential settings, is vital for successful VoIP QoS implementation.
The discussion will cover network architecture design, necessary equipment configurations, and comparisons of network protocols. It will also include a detailed explanation of queuing disciplines, algorithms, and their impact on QoS. Furthermore, we will analyze the importance of monitoring, troubleshooting, and security considerations to maintain optimal VoIP performance.
Defining Quality of Service (QoS) in VoIP Networks
VoIP, or Voice over Internet Protocol, relies on the internet’s infrastructure for voice communication. However, the unpredictable nature of the internet can significantly impact the quality of calls. Quality of Service (QoS) mechanisms are crucial for ensuring a reliable and consistent voice experience for users. These mechanisms prioritize voice traffic over other network traffic, guaranteeing sufficient bandwidth and minimizing packet loss, jitter, and latency.QoS in VoIP networks ensures a high-quality voice experience by dedicating resources to voice calls, guaranteeing predictable performance.
This translates to clearer audio, fewer dropped calls, and smoother conversations, essential for a positive user experience.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for VoIP QoS
Accurate measurement of VoIP quality is essential for effective QoS management. Several KPIs provide insight into the performance of the VoIP network.
- Packet Loss Rate (PLR): The percentage of packets lost during transmission. A lower PLR indicates better network performance and a more stable voice connection.
- Jitter: The variation in packet arrival times. Low jitter leads to smoother voice, while high jitter results in a choppy or distorted audio experience.
- Latency: The delay between sending and receiving a packet. Lower latency is crucial for real-time applications like VoIP, ensuring minimal delay in conversation.
- Call Completion Rate: The percentage of calls successfully completed. A high completion rate indicates a stable and reliable network for users.
- Mean Opinion Score (MOS): A subjective measure of the perceived quality of the voice call, based on user feedback. A higher MOS indicates a better user experience.
QoS Mechanisms in VoIP Networks
Various mechanisms are employed to ensure quality of service in VoIP networks.
| Mechanism Type | Description | Example Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Priority Queuing | Prioritizes voice packets over other data packets in the network queue. | Ensuring that voice packets are processed before less time-sensitive data packets. |
| Bandwidth Allocation | Allocates specific bandwidth resources to voice traffic. | Guaranteeing sufficient bandwidth for voice calls, especially during periods of high network traffic. |
| Traffic Shaping | Controls the rate at which data is transmitted, often by slowing down non-voice traffic. | Ensuring that voice traffic has a consistent and predictable flow by adjusting the flow of other traffic. |
| RSVP (Resource Reservation Protocol) | Dynamically reserves resources for voice calls in advance, ensuring the availability of necessary bandwidth and network resources. | Prioritizes VoIP traffic by reserving the necessary bandwidth in advance. |
| DiffServ (Differentiated Services) | Classifies and prioritizes different types of network traffic, including voice traffic. | Ensuring voice calls receive the appropriate priority based on their network class. |
Bandwidth Allocation and QoS in VoIP
Bandwidth allocation plays a critical role in achieving QoS in VoIP networks. Sufficient bandwidth ensures that voice packets are transmitted without excessive delay or loss. Insufficient bandwidth can lead to packet loss, jitter, and high latency, resulting in a poor user experience. Bandwidth allocation mechanisms are essential for dedicating the necessary resources for VoIP calls.
“A properly allocated bandwidth ensures consistent and predictable performance, essential for maintaining a high-quality VoIP experience.”
Adequate bandwidth is crucial for ensuring that VoIP traffic is not affected by other network traffic, especially during periods of high network activity. This prevents congestion and allows for consistent transmission of voice packets.
Network Infrastructure for VoIP QoS: Ensuring Quality Of Service On Voip Networks
VoIP, or Voice over Internet Protocol, relies heavily on the underlying network infrastructure to deliver high-quality voice calls. Ensuring a consistent and reliable experience requires careful design and implementation of Quality of Service (QoS) mechanisms. This involves prioritizing VoIP traffic over other network traffic to minimize latency and packet loss, leading to clearer calls and fewer dropped calls.Effective VoIP QoS implementation hinges on a well-structured network architecture and appropriate configuration of network devices.
A properly designed network prioritizes the transmission of VoIP packets, ensuring that voice calls are not affected by other network activities. This is crucial for maintaining the quality and reliability of VoIP services.
Network Architecture for VoIP Prioritization
Network architecture plays a critical role in the successful implementation of QoS for VoIP. A hierarchical network design, with VoIP traffic segregated from other types of traffic, is often used. This segregation allows for specific prioritization mechanisms to be applied to VoIP packets, ensuring they receive the necessary bandwidth and processing resources. A robust network architecture is essential to accommodate the specific needs of VoIP traffic, ensuring consistent call quality and minimizing interruptions.
Necessary Network Equipment and Configurations
Proper network equipment and their configurations are vital for ensuring QoS in VoIP networks. Routers and switches are fundamental components. Routers are configured to use Quality of Service (QoS) features, such as priority queuing and traffic shaping, to give VoIP packets preference. Switches, too, are configured to prioritize VoIP traffic by assigning different priorities to network ports.
Ensuring quality of service on VoIP networks is crucial for a smooth user experience. However, like the rapid spread of the Sobig F variant, which caused the fastest outbreak ever documented spreading sobig f variant fastest outbreak ever , network vulnerabilities can quickly lead to disruptions. Robust security measures and efficient protocols are therefore essential for maintaining a reliable VoIP infrastructure.
- Routers: Routers are configured with QoS mechanisms to classify and prioritize VoIP traffic. This often involves setting up queuing disciplines that give VoIP packets precedence over other traffic. For instance, Weighted Fair Queuing (WFQ) assigns different weights to different traffic types, allowing VoIP to receive a larger share of bandwidth. Class-based Weighted Fair Queuing (CBWFQ) further refines this by creating different traffic classes with different priorities.
Moreover, routers can use techniques like Explicit Congestion Notification (ECN) to signal congestion before it affects VoIP packets.
- Switches: Switches play a crucial role in QoS by enabling prioritization of VoIP packets at the Layer 2 level. This can be accomplished using different queuing mechanisms. Port-based QoS allows administrators to assign different priorities to ports, ensuring that VoIP traffic on specific ports receives preferential treatment. VLANs (Virtual LANs) can also be used to segment VoIP traffic, isolating it from other network traffic and enhancing QoS.
Comparison of Network Protocols for QoS
Different network protocols offer varying levels of support for QoS in VoIP. These protocols play a key role in effectively handling VoIP traffic.
- IP Precedence: A legacy mechanism for marking the priority of IP packets. It’s less flexible and granular compared to newer protocols.
- DiffServ (Differentiated Services): A more sophisticated protocol for classifying and prioritizing traffic. It allows for more granular control over traffic flows.
- MPLS (Multiprotocol Label Switching): A powerful protocol that enables sophisticated traffic engineering. MPLS can be used to create specific paths for VoIP traffic, ensuring high bandwidth and low latency.
QoS Implementation on Routers and Switches
QoS mechanisms are implemented on routers and switches through various configurations. The implementation details depend on the specific network equipment and the chosen QoS protocols.
| Device | QoS Mechanism | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Router | Weighted Fair Queuing (WFQ) | Distributes bandwidth based on assigned weights to different traffic types. VoIP traffic can be given a higher weight. |
| Router | Class-Based Weighted Fair Queuing (CBWFQ) | More granular control than WFQ. Creates classes of traffic with different priorities. VoIP traffic can be assigned to a higher priority class. |
| Switch | Port-Based QoS | Prioritizes traffic based on the network port it enters. VoIP traffic can be assigned a higher priority on specific ports. |
VoIP Traffic Management and Prioritization
Ensuring a smooth and reliable VoIP experience requires careful management of traffic within the network. This involves prioritizing VoIP packets over other network traffic to guarantee the quality of service (QoS) needed for clear calls and minimal interruptions. Effective traffic management strategies are crucial for maximizing VoIP performance and user satisfaction.
VoIP Traffic Prioritization Methods
Various techniques can be employed to prioritize VoIP traffic. These methods leverage network infrastructure capabilities to ensure VoIP packets receive preferential treatment, minimizing latency and jitter. The specific method chosen depends on the network’s architecture and the required level of QoS.
- Scheduling and Queuing Disciplines: VoIP packets are often placed in queues for processing. Implementing specific queuing disciplines can significantly impact the delivery of VoIP traffic. By prioritizing VoIP packets, networks can maintain consistent call quality and avoid packet loss.
- Differentiated Services (DiffServ): This approach classifies network traffic into different service types, assigning specific priorities to VoIP packets. Network devices use these labels to prioritize VoIP traffic during routing and queuing. This method allows network administrators to ensure predictable performance for VoIP calls.
- Resource Reservation Protocol (RSVP): RSVP allows VoIP applications to reserve network resources in advance, guaranteeing a specific bandwidth allocation for the call. This reservation ensures a predictable level of service, preventing congestion and call drops.
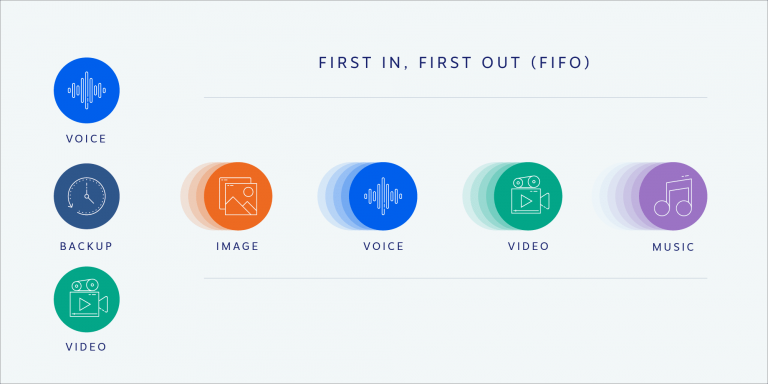
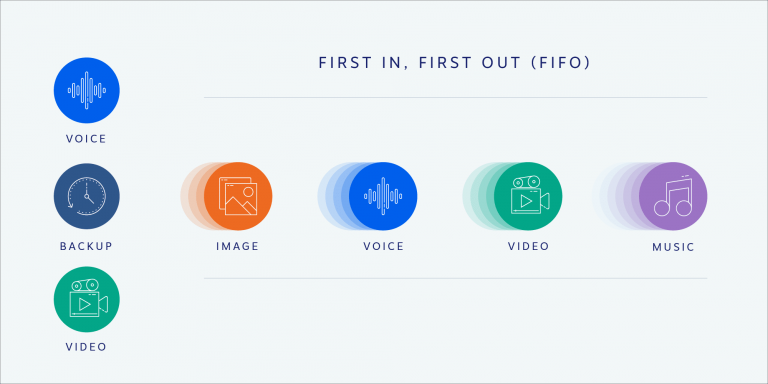
Queuing Disciplines for VoIP Packets, Ensuring quality of service on voip networks
Queuing disciplines are essential for managing VoIP packets within the network. Different disciplines prioritize packets based on various criteria, directly impacting call quality. Implementing appropriate queuing disciplines can effectively mitigate packet loss and jitter.
- First-In, First-Out (FIFO): This is the simplest queuing discipline, processing packets in the order they arrive. While straightforward, FIFO doesn’t prioritize VoIP packets and can lead to increased latency and jitter for VoIP calls.
- Priority Queuing: Priority queuing assigns different priorities to various types of traffic. VoIP packets are often given higher priority than other traffic types, ensuring their timely processing. This method improves VoIP call quality by reducing delays and packet loss.
- Weighted Fair Queuing (WFQ): WFQ dynamically allocates bandwidth to different traffic types based on their weight. VoIP traffic can be assigned a higher weight, ensuring a consistent and predictable amount of bandwidth for calls. This method is well-suited for environments with multiple VoIP users.
Implementation of Queuing Algorithms
Implementing queuing algorithms requires careful configuration of network devices. The choice of algorithm significantly affects the QoS of VoIP traffic.
| Queuing Algorithm | Characteristics | Suitability for VoIP Traffic |
|---|---|---|
| FIFO | Simple, straightforward, but doesn’t prioritize VoIP traffic. | Poor suitability due to potential latency and jitter. |
| Priority Queuing | Prioritizes VoIP traffic, reducing latency and jitter. | Good suitability for consistent call quality. |
| WFQ | Dynamically allocates bandwidth based on weight, suitable for multiple VoIP users. | Excellent suitability for environments with high VoIP traffic volumes. |
Implementing the correct queuing algorithm can significantly improve VoIP call quality by ensuring timely delivery of VoIP packets and reducing latency.
Addressing Latency and Jitter in VoIP
VoIP, or Voice over Internet Protocol, relies heavily on the stability and reliability of the network infrastructure. Two critical factors that significantly impact VoIP call quality are latency and jitter. Understanding their effects and implementing strategies to mitigate them is essential for providing a seamless and high-quality user experience.Latency and jitter are inherent challenges in any network, but they manifest differently in VoIP, often resulting in frustrating and disruptive call experiences.
A significant amount of research and development has gone into addressing these issues, resulting in effective solutions that network engineers can deploy.
Impact of Latency and Jitter on VoIP Call Quality
Latency, or delay, directly affects the perceived responsiveness of the call. A noticeable delay can cause a feeling of disconnect and make conversations seem unnatural. Jitter, on the other hand, refers to variations in the delay experienced during a call. These variations manifest as interruptions or a choppy sound, significantly impacting the overall call quality. Both issues can severely hinder communication, making VoIP calls frustrating or unusable in certain scenarios.
Techniques for Minimizing Latency in VoIP Networks
Minimizing latency in VoIP networks requires a multifaceted approach. A crucial step is optimizing network infrastructure. This includes deploying high-bandwidth connections, ensuring sufficient network capacity, and strategically placing network equipment to reduce the distance data needs to travel.Implementing QoS (Quality of Service) mechanisms is another key technique. Prioritizing VoIP traffic over other network traffic through QoS policies can significantly reduce latency.
Using specialized routers and switches designed for VoIP traffic can also contribute to improved performance.
Techniques for Controlling Jitter in VoIP Networks
Controlling jitter is crucial for maintaining consistent call quality. Employing techniques like buffering can absorb variations in packet arrival times, mitigating the impact of jitter. Network congestion management is vital; implementing strategies to reduce congestion on the network helps ensure consistent packet delivery, thereby reducing jitter.
Examples of Network Optimization Techniques to Reduce Latency
Network optimization techniques can significantly reduce latency. A good example is optimizing the routing path for VoIP traffic. Network engineers can leverage routing protocols and analysis tools to identify and optimize the most efficient paths for VoIP data packets. This can significantly reduce the time it takes for data to travel from one point to another.Another example is implementing caching mechanisms.
Caching can store frequently accessed data, reducing the need for constant retrieval from the source. This can be particularly beneficial in VoIP networks where the same data is frequently accessed.
Ensuring quality of service on VoIP networks is crucial for a smooth user experience. This often involves intricate network configurations and robust protocols. Interestingly, the recent Japanese push towards open-source solutions, like japan strikes against microsoft with open source , might offer alternative, potentially more efficient ways to tackle these challenges. Ultimately, finding the best approach to ensure quality of service remains a key focus for VoIP providers.
Methods for Controlling Jitter in VoIP Networks
Controlling jitter requires careful consideration of the network infrastructure and the protocols employed. Buffering mechanisms are often used to absorb fluctuations in packet arrival times. Larger buffers can accommodate more variability in packet arrival, leading to a smoother and more consistent call experience. For example, routers can use buffers to absorb variations in packet arrival times, thereby reducing the impact of jitter.Properly configuring network devices, such as routers and switches, is crucial.
Configuration settings can impact how packets are handled and prioritized. Carefully adjusting these settings to optimize VoIP traffic can significantly reduce jitter. Properly configuring these settings can significantly reduce jitter.
Security Considerations for VoIP QoS
VoIP, with its inherent reliance on network infrastructure, is susceptible to a variety of security threats. Implementing Quality of Service (QoS) mechanisms can inadvertently introduce vulnerabilities if not carefully considered. This discussion delves into the crucial security aspects of VoIP networks that employ QoS, highlighting potential threats and best practices for mitigating them.Security is paramount in any VoIP network, especially those utilizing QoS.
Ensuring the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of voice communications is critical. Protecting VoIP traffic from malicious attacks while maintaining QoS levels requires a multi-layered approach, addressing both network and application security.
Importance of Security Measures in QoS-Enabled VoIP Networks
Robust security measures are essential in VoIP networks employing QoS to prevent disruptions and maintain the integrity of voice communication. Compromised security can lead to denial-of-service attacks, eavesdropping, and unauthorized access to sensitive information, all impacting the quality of service. Protecting VoIP traffic from malicious attacks is directly tied to the network’s overall security posture.
Ensuring quality of service on VoIP networks is crucial, and we’re constantly looking for innovative solutions. Recent advancements in computer simulations, like those explored in computer simulations modeling the future , offer a powerful new tool to predict and optimize network performance. These models can help us anticipate potential bottlenecks and congestion, allowing for proactive measures to maintain consistent quality and reliability in VoIP services.
Protecting VoIP Traffic from Malicious Attacks
Protecting VoIP traffic from attacks while maintaining QoS requires a layered security strategy. Firewalls and intrusion detection systems (IDS) should be configured to identify and block malicious traffic attempting to exploit QoS mechanisms. Implementing secure protocols, like TLS/SSL, for VoIP signaling and media streams is vital for protecting the confidentiality and integrity of communications.
Potential Security Vulnerabilities Related to VoIP QoS Implementations
Several vulnerabilities can arise from misconfigurations or inadequate security measures in QoS-enabled VoIP networks. These include:* Denial-of-service (DoS) attacks: Attackers can flood the network with excessive VoIP traffic, overwhelming the QoS mechanisms and disrupting legitimate calls.
Man-in-the-middle (MitM) attacks
Malicious actors can intercept and manipulate VoIP traffic, potentially compromising the privacy and security of conversations.
Unauthorized access to QoS configurations
If unauthorized individuals gain access to QoS parameters, they can manipulate prioritization rules, potentially compromising the quality of service for legitimate users.
Exploiting QoS prioritization
Attackers may leverage QoS mechanisms to prioritize malicious traffic, effectively circumventing security defenses.
Security Best Practices for VoIP Networks Implementing QoS
Implementing strong security measures in VoIP networks with QoS is crucial. These practices should be followed:
- Secure Network Segmentation: Segment the network to isolate VoIP traffic from other sensitive data streams. This limits the impact of potential breaches.
- Firewall Configuration: Implement strict firewall rules to control VoIP traffic flow and block known malicious patterns.
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS): Deploy IDS/IPS to detect and prevent attacks targeting VoIP traffic and QoS mechanisms.
- Secure Protocols: Utilize secure protocols like TLS/SSL to encrypt VoIP signaling and media streams. This prevents eavesdropping and man-in-the-middle attacks.
- Regular Security Audits: Conduct regular security audits to identify and address vulnerabilities in the QoS implementation.
- Strong Authentication and Authorization: Implement robust authentication and authorization mechanisms to control access to QoS configurations and VoIP resources.
- Regular Software Updates: Keep all VoIP-related software and network devices updated with the latest security patches to mitigate known vulnerabilities.
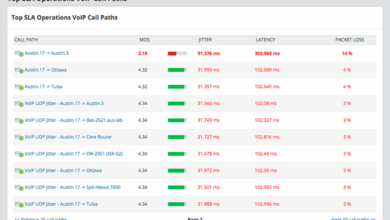
Monitoring and Troubleshooting VoIP QoS
Keeping VoIP calls crystal clear requires constant vigilance. Monitoring QoS parameters and promptly addressing any issues are crucial for maintaining a high-quality user experience. Effective monitoring and troubleshooting ensure that VoIP services remain reliable and responsive, minimizing disruptions and maximizing user satisfaction.
Importance of Monitoring VoIP QoS Parameters
Monitoring VoIP QoS parameters is essential for proactively identifying and resolving potential problems before they impact users. By tracking key metrics like packet loss, delay (latency), jitter, and bandwidth utilization, network administrators can pinpoint bottlenecks and optimize performance. This proactive approach prevents service degradation, ensuring a consistent and high-quality VoIP experience for all users.
Tools for Monitoring VoIP QoS
Several tools are available for monitoring VoIP QoS. These tools provide real-time insights into network performance, enabling administrators to identify and address potential issues swiftly.
- Network Management Systems (NMS): NMS platforms offer comprehensive monitoring capabilities. They provide dashboards for visualizing network performance, displaying key QoS metrics, and alerting administrators to potential problems. Examples include SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor and Nagios. These tools allow for granular analysis, enabling quick identification of issues affecting VoIP traffic.
- Dedicated VoIP Monitoring Tools: These specialized tools focus specifically on VoIP traffic. They provide detailed information on call quality metrics, allowing for a more in-depth understanding of VoIP performance. Some tools focus on identifying call quality issues, including packet loss, jitter, and latency. These tools are often integrated with existing NMS systems.
- Packet Analyzers: Tools like Wireshark allow for deep packet inspection, providing detailed insights into VoIP traffic. By analyzing packet headers and payloads, administrators can gain a comprehensive understanding of network behavior and identify potential QoS issues.
Troubleshooting VoIP QoS Issues
Troubleshooting VoIP QoS problems involves a systematic approach. This involves identifying the root cause, implementing corrective actions, and verifying the effectiveness of the solutions.
- Identifying the Root Cause: The first step is to determine the specific cause of the QoS problem. This may involve analyzing logs, monitoring tools, and potentially using packet analyzers to investigate the problem.
- Implementing Corrective Actions: Based on the identified cause, appropriate corrective actions can be implemented. This might involve adjusting bandwidth allocation, optimizing network configurations, or upgrading network hardware.
- Verifying Effectiveness: Once corrective actions have been implemented, it’s crucial to verify that the solutions have effectively resolved the QoS issues. This involves monitoring key performance indicators and assessing user feedback.
Analyzing Network Logs to Identify QoS Problems
Network logs contain valuable information about network behavior. Analyzing these logs can reveal patterns and anomalies that point to QoS problems.
- Identifying Patterns: Consistent errors or high-frequency events in logs can indicate recurring QoS issues. Analyzing the time stamps and types of events can pinpoint the source and time of occurrence of problems.
- Correlating with Monitoring Data: Combining log analysis with monitoring data helps to establish a clearer picture of the problem. Correlating the log entries with monitoring data provides more comprehensive insights into the behavior of VoIP traffic and the network.
- Searching for Error Codes: Error codes within network logs often provide specific details about the nature of the problem. These error codes can be critical in identifying the cause and implementing appropriate solutions.
Case Studies of VoIP QoS Implementations
Real-world VoIP deployments often face unique challenges, demanding tailored QoS solutions. Understanding how different organizations have addressed these issues provides valuable insights into successful implementation strategies. This section delves into case studies showcasing diverse approaches and their effectiveness in various environments.Successful VoIP QoS implementations are not a one-size-fits-all solution. The effectiveness of different strategies depends heavily on the specific needs and characteristics of the network.
This section examines how businesses and residential users alike have tackled these challenges, and how these solutions compare across diverse contexts.
Enterprise VoIP QoS Implementation
Enterprise environments often require robust QoS to support critical applications like video conferencing and remote collaboration. These deployments typically involve high bandwidth demands and strict latency requirements.
- A large financial institution implemented a tiered QoS model. This involved prioritizing voice traffic over other data streams using Quality of Service (QoS) mechanisms. This approach ensured consistent voice quality during high-volume trading periods. The network was configured to automatically adjust priorities based on real-time traffic loads, guaranteeing uninterrupted communication during peak hours.
- A multinational corporation with extensive global offices implemented a network infrastructure that supports real-time communication. They deployed dedicated circuits for voice traffic and used advanced traffic shaping techniques to guarantee predictable performance. They used packet marking and queuing mechanisms to prioritize voice traffic. This approach resulted in significantly reduced latency and improved call quality for employees across all global offices.
Residential VoIP QoS Challenges
Residential VoIP deployments often face limitations in terms of bandwidth and network complexity. The primary goal in these situations is to maintain acceptable voice quality, despite potential fluctuations in network conditions.
- A residential VoIP provider optimized its network infrastructure for QoS by implementing traffic shaping techniques. This allowed for consistent voice quality, even during peak usage hours. They used a combination of router configuration and network management software to manage traffic effectively, providing a seamless experience for subscribers.
- Another provider employed a hybrid approach, combining bandwidth allocation with prioritization techniques. This ensured that voice traffic maintained sufficient bandwidth while also accommodating other internet activities. They offered tiered service plans with varying bandwidth allocations to cater to different subscriber needs and budget constraints.
VoIP QoS in Healthcare
Real-time communication is crucial in healthcare settings for patient care, especially for remote consultations and emergency services. Maintaining reliable VoIP service is essential for timely medical intervention.
- A hospital implemented VoIP with QoS policies that prioritized voice calls over other network traffic. The system dynamically adjusted priorities to ensure minimal latency during critical situations, which contributed to improved patient care and reduced response times for medical emergencies.
Comparison of QoS Solutions
Various QoS solutions, including traffic shaping, prioritization, and queuing mechanisms, have proven effective in different contexts. The choice of solution often depends on the specific requirements of the environment.
| QoS Solution | Strengths | Weaknesses | Suitable Environments |
|---|---|---|---|
| Traffic Shaping | Efficiently manages bandwidth, minimizing congestion | May not be effective for real-time applications requiring low latency | Residential networks, general office environments |
| Prioritization | Ensures critical traffic receives dedicated bandwidth | Can lead to performance degradation for non-prioritized traffic | Enterprise environments with high priority traffic |
| Queuing Mechanisms | Manages network traffic efficiently, reducing latency | Requires careful configuration to avoid bottlenecks | High-traffic environments with fluctuating bandwidth demands |
Future Trends in VoIP QoS
VoIP quality of service (QoS) is constantly evolving, driven by advancements in networking technologies and increasing user demands. Emerging technologies promise to further enhance the reliability, performance, and security of VoIP communications. This section explores the potential impact of these innovations on the future of VoIP QoS.
Emerging Technologies Enhancing VoIP QoS
Future VoIP QoS enhancements will rely on a combination of sophisticated network infrastructure and innovative approaches to traffic management. Key technologies include Software-Defined Networking (SDN), Network Function Virtualization (NFV), and advancements in network slicing. These technologies offer greater flexibility, scalability, and control over network resources, leading to improved VoIP QoS.
SDN and NFV for Improved VoIP QoS
Software-Defined Networking (SDN) and Network Function Virtualization (NFV) are poised to revolutionize VoIP QoS management. SDN decouples network control from the data plane, enabling dynamic configuration and centralized control of network resources. This allows for real-time adaptation to varying VoIP traffic patterns, prioritizing critical calls and ensuring consistent quality. NFV virtualizes network functions, enabling flexible deployment and scaling of QoS features.
This results in a more agile and cost-effective approach to managing VoIP QoS, especially in dynamic environments.
Impact of the Internet of Things (IoT) on VoIP QoS
The increasing proliferation of Internet of Things (IoT) devices is creating new challenges and opportunities for VoIP QoS. The influx of data from connected devices can potentially overwhelm existing network infrastructure, impacting the quality of VoIP calls. However, IoT devices can also provide valuable data for predictive modeling and proactive QoS management. For instance, data on device usage patterns can be used to anticipate peak traffic periods and optimize network resources.
This data-driven approach can help improve VoIP QoS in an environment with growing IoT integration.
Future Directions in VoIP QoS Research and Development
Future VoIP QoS research and development will likely focus on integrating machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI) into network management systems. ML algorithms can analyze real-time network data to identify and predict potential QoS issues, allowing for proactive interventions. This proactive approach can minimize disruptions and ensure a consistent user experience. Furthermore, researchers are exploring new methods of network slicing to create dedicated virtual networks for VoIP traffic, isolating it from other types of traffic and providing dedicated QoS guarantees.
End of Discussion
In conclusion, ensuring quality of service on VoIP networks requires a multifaceted approach encompassing network infrastructure, traffic management, and security considerations. By understanding the various aspects discussed, including the role of bandwidth allocation, latency minimization, and security best practices, organizations can achieve a reliable and high-quality VoIP experience. This comprehensive guide serves as a roadmap for successful VoIP QoS implementation in diverse settings, preparing for future trends and challenges.