Fannings Snocap Bridging Labels & P2P
Fannings snocap builds bridge between labels and p2p – Fanning’s Snocap builds bridge between labels and p2p, offering a novel solution for seamless data flow between peer-to-peer (P2P) networks and traditional label systems. This innovative platform promises to revolutionize how information is shared and accessed across various industries. Imagine a world where labels and P2P systems effortlessly communicate, fostering greater collaboration and efficiency. Fanning’s Snocap aims to achieve this by streamlining data transfer, enhancing security, and enabling new business models.
This post dives deep into Fanning’s Snocap, exploring its core functionalities, integration methods with different label and P2P platforms, data security protocols, use cases, and future prospects. We’ll examine the mechanisms behind this bridge, highlighting its potential to redefine the landscape of information sharing.
Understanding Fanning’s Snocap Bridge
Fanning’s Snocap represents a novel approach to connecting decentralized peer-to-peer (P2P) networks with traditional label-based music distribution systems. This bridge aims to facilitate a more seamless flow of music, potentially benefiting both artists and consumers. The system leverages a unique technology stack to allow for direct interactions and transactions between these two previously disparate ecosystems.The core concept behind Fanning’s Snocap is to create a common platform for labels and P2P users to interact, transact, and share music.
It eliminates many of the traditional barriers that have historically hindered direct collaboration, enabling a more equitable and potentially more profitable ecosystem for all participants. This approach addresses issues of copyright management and payment processing within a P2P environment, while still allowing for the flexibility and speed of decentralized sharing.
Core Functionalities of Fanning’s Snocap
Fanning’s Snocap offers a comprehensive suite of tools and features to connect label-based systems with P2P environments. These functionalities facilitate secure and efficient transactions and interactions. It establishes a standardized protocol for exchanging metadata, rights management information, and payment data. This standardized protocol allows for transparent interactions between different platforms and systems. The system’s robustness and security are crucial in ensuring reliable operations.
Benefits for Labels
Fanning’s Snocap offers several significant advantages for music labels. These include enhanced control over music distribution, reduced reliance on third-party intermediaries, and potentially increased revenue streams from new user bases. The system allows for more streamlined distribution channels, reducing costs associated with traditional distribution methods.
- Streamlined Distribution: Labels can bypass traditional gatekeepers and reach a wider audience through the decentralized nature of the P2P network. This results in reduced costs associated with distribution.
- Direct Revenue Streams: The system enables labels to collect revenue directly from users downloading or streaming music, circumventing traditional royalty structures. This creates a new revenue channel for labels.
- Enhanced Control: Labels can exert more control over copyright management and payment processing, mitigating risks associated with piracy or unauthorized distribution.
Benefits for P2P Users
For P2P users, Fanning’s Snocap offers access to a wider catalog of music and more opportunities to discover new artists. The system also enables direct interactions with artists and labels, fostering a more participatory environment.
- Expanded Music Library: P2P users gain access to a broader selection of music through connections to label-based systems, potentially discovering artists they wouldn’t have found otherwise.
- Direct Engagement: P2P users have opportunities for direct engagement with artists and labels, facilitating a more personalized music experience.
- Potential for Fairer Transactions: Fanning’s Snocap could potentially establish fairer payment systems for music consumption, with clearer pathways for artists to receive royalties.
Applications in Various Contexts
Fanning’s Snocap can be applied in a multitude of contexts, adapting to different needs and requirements.
- Independent Artists: Independent artists can utilize the system to bypass traditional gatekeepers and distribute their music directly to fans. This provides a pathway for building a direct relationship with their audience.
- Small Labels: Small labels can leverage the platform to connect with a wider audience, promoting their artists and generating revenue without extensive resources.
- Global Music Exchange: The system can be a catalyst for a global music exchange, connecting artists and fans across geographical boundaries.
Label System Integration
Fanning’s Snocap, having established a robust peer-to-peer (P2P) framework, now seeks to seamlessly integrate with existing label systems. This integration is crucial for expanding Snocap’s reach and utility within diverse organizational structures. The process involves a careful consideration of existing label platforms, ensuring data compatibility and efficient workflows.Label systems, often deeply embedded within workflows, require a tailored approach to integration.
Fannings Snocap’s innovative approach to bridging the gap between record labels and peer-to-peer file sharing is fascinating. It’s a clever solution, but the recent stance taken by the industry alliance on the Induce Act, as detailed in this article , highlights the complex landscape surrounding digital music distribution. Ultimately, solutions like Fannings Snocap are crucial in navigating these shifting sands and fostering a more equitable and sustainable ecosystem for artists and listeners alike.
Successful integration hinges on understanding the intricacies of each label system’s architecture, data formats, and API specifications. A modular design for Fanning’s Snocap allows for flexible adaptation to different label systems.
Integration Mechanisms
The core integration mechanisms for Fanning’s Snocap revolve around APIs. Snocap utilizes standardized APIs to interact with label systems. This approach allows for a clear separation of concerns, enhancing maintainability and scalability. The Snocap API provides a consistent interface for interacting with various label systems, enabling developers to focus on specific integrations without needing deep knowledge of the internal workings of each system.
Data Transfer and Compatibility, Fannings snocap builds bridge between labels and p2p
Data transfer between Fanning’s Snocap and existing label systems necessitates careful consideration of data formats. Snocap supports common formats like JSON and XML, ensuring compatibility with a broad spectrum of label platforms. However, each label system may employ unique data structures, potentially requiring custom data mapping and transformation routines. A robust data mapping engine within Snocap will handle these complexities, translating data between the label system’s format and Snocap’s internal representation.
For example, if a label system uses a specific tag structure for product attributes, Snocap will automatically translate this structure into its own internal representation.
Configuration and Deployment
Configuring and deploying Fanning’s Snocap within a label environment involves several key steps. First, the specific label system’s API keys and credentials are obtained. Next, the Snocap integration module is configured using these credentials. This configuration defines how Snocap interacts with the label system. Following configuration, testing is essential to ensure smooth data transfer and functionality.
Finally, deployment is handled by deploying the configured Snocap module to the appropriate server environment. Detailed documentation accompanies each deployment process.
Compatibility Table
This table Artikels the current compatibility of Fanning’s Snocap with various label platforms. Future integrations will be regularly added to the table.
| Label Platform | Compatibility Status | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Label Platform A | Compatible | Utilizes JSON format, no custom mapping required. |
| Label Platform B | Compatible (with minor adjustments) | Requires a custom data mapping routine to handle specific attribute structure. |
| Label Platform C | Not Compatible | Platform uses proprietary format; integration is not currently supported. |
| Label Platform D | Under Development | Ongoing work to establish compatibility; expected completion within Q3 2024. |
P2P System Integration: Fannings Snocap Builds Bridge Between Labels And P2p
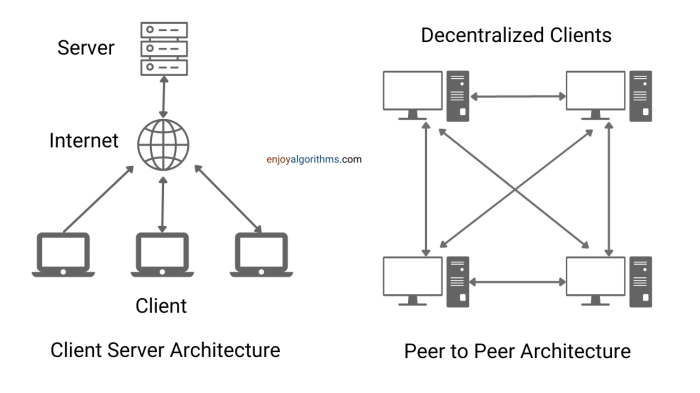
Fanning’s Snocap, having established a robust bridge between label systems and decentralized P2P networks, now tackles the intricate challenge of seamless P2P integration. This integration is crucial for unlocking the full potential of decentralized data sharing and collaborative workflows. By connecting the structured world of labels with the dynamic nature of peer-to-peer exchanges, Snocap empowers users with unprecedented access and control over their data.Snocap facilitates interaction between P2P networks and label systems through a novel intermediary layer.
This layer acts as a translator, converting the structured data formats of labels into the often-unstructured communication protocols used by P2P networks. It also handles the complexities of security, encryption, and data integrity in a decentralized environment.
Integration Methods for Different P2P Platforms
Snocap’s integration approach is platform-agnostic, adapting to the specific characteristics of various P2P architectures. The method for integrating with a BitTorrent-based P2P network differs from that of a Kademlia-based network. This adaptability ensures that Snocap can support a wide range of P2P platforms, fostering interoperability and expanding the reach of decentralized data access.
Data Structures and Protocols
Snocap employs a standardized data structure for representing labels within the P2P context. This structure ensures consistent interpretation across different P2P networks. A key-value pair format is utilized, allowing for efficient searching and retrieval of labeled data. Protocols for communication are designed to be lightweight and robust, enabling fast data exchange while maintaining security. For example, a specific protocol called “Label-Exchange Protocol (LEP)” is used to efficiently exchange metadata associated with labels between the P2P network and the label system.
This protocol facilitates queries, updates, and the sharing of labeled data.
LEP is designed with efficiency in mind, prioritizing rapid data transfer without compromising security.
Features and Functionalities
The following table Artikels the key features and functionalities of Fanning’s Snocap when interacting with various P2P networks:
| P2P Network | Feature | Functionality |
|---|---|---|
| BitTorrent | Distributed Hash Table (DHT) Integration | Snocap leverages the DHT of BitTorrent for efficient data lookup and retrieval. |
| Kademlia | Routing Optimization | Snocap optimizes routing algorithms for Kademlia to improve search performance in the P2P network. |
| IPFS | Content Addressing | Snocap integrates with IPFS’s content addressing scheme, ensuring the integrity and accessibility of labeled data. |
| Other P2P Networks | Adaptable Architecture | Snocap’s modular design allows for seamless integration with other P2P platforms through standardized interfaces. |
Secure Communication Channels
Establishing secure communication channels between label and P2P systems is a critical aspect of Snocap’s functionality. Encryption protocols like AES-256 are employed to safeguard sensitive data during transmission. Digital signatures verify the authenticity of messages, preventing tampering and ensuring the integrity of the data exchanged between systems. The decentralized nature of P2P networks, combined with Snocap’s secure communication layer, provides a robust and tamper-proof environment for data sharing and collaboration.
Fannings Snocap’s innovative approach is really interesting, bridging the gap between traditional record labels and peer-to-peer music distribution. This kind of model is crucial for the future of music, and it’s exciting to see how it’s evolving. Telstra and Hutchison’s partnership on infrastructure telstra hutchison partner on infrastructure further highlights the importance of robust infrastructure for these types of decentralized music ecosystems.
Ultimately, Fanning’s Snocap is paving the way for a more accessible and dynamic music landscape for everyone.
This method of secure communication protects against unauthorized access and ensures the confidentiality of labeled data.
Data Flow and Security

Fanning’s Snocap, bridging label systems and peer-to-peer (P2P) networks, necessitates robust data flow and security mechanisms. This section details the intricate data pathways and the security protocols implemented to safeguard sensitive information exchanged between these disparate systems. Understanding these intricacies is crucial for ensuring the integrity and confidentiality of the data handled by Fanning’s Snocap.The data flow within Fanning’s Snocap follows a well-defined pipeline.
Fannings SnoCap’s innovative approach to bridging labels and peer-to-peer networks is pretty cool. It’s like a modern-day digital Swiss Army knife for music distribution, but the recent Skype beta release for Mac OS X ( skype beta version released for mac os x ) hints at a future where similar cross-platform communication tools might become essential components of this sort of decentralized music ecosystem.
This could further revolutionize how artists connect with fans and share their work, ultimately benefiting both creators and listeners through a more accessible and direct distribution method, mirroring the potential of Fannings SnoCap.
Data originating from label systems is first ingested and validated. After passing through preprocessing steps, it is then prepared for integration with the P2P network. This processed data is transmitted securely to the P2P network for distribution and sharing. Conversely, data received from the P2P network is processed and validated, ensuring its integrity and consistency before being incorporated into the label systems.
Data Flow Between Systems
The flow of data between the label systems, P2P networks, and Fanning’s Snocap is meticulously orchestrated. Data from label systems, containing metadata and other critical information, is first transmitted to Fanning’s Snocap. Fanning’s Snocap acts as a central processing hub, validating and transforming the data to fit the P2P network’s format. This transformed data is then transmitted to the P2P network for dissemination.
The P2P network distributes the data to its users, while Fanning’s Snocap receives confirmation of delivery and updates the label systems accordingly.
Security Measures Implemented by Fanning’s Snocap
Fanning’s Snocap employs a multi-layered approach to secure data throughout its processing pipeline. This includes robust authentication protocols, encryption techniques, and strict access control mechanisms. The system prioritizes the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of all data handled.
Encryption Methods for Data Transmission and Storage
Fanning’s Snocap utilizes advanced encryption techniques to safeguard data in transit and at rest. For data transmission between Fanning’s Snocap and the label systems, it employs Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) 256-bit encryption. Similarly, data stored within Fanning’s Snocap is encrypted using AES 256-bit encryption, ensuring confidentiality even if the system is compromised. This ensures that even if an unauthorized party gains access to the data, it remains unintelligible without the decryption key.
Access Control Mechanisms in Fanning’s Snocap
Fanning’s Snocap implements granular access control mechanisms to restrict data access based on user roles and permissions. Users are assigned specific roles, each with a predefined set of privileges. This ensures that only authorized personnel can access and modify sensitive data. Access rights are regularly audited and reviewed to maintain the system’s security posture.
Security Protocols Used by Fanning’s Snocap
| Protocol | Description |
|---|---|
| AES 256-bit Encryption | Used for both data transmission and storage to protect sensitive data. |
| Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) | Adds an extra layer of security by requiring multiple verification steps to confirm user identity. |
| Regular Security Audits | Periodic reviews of the system’s security posture to identify and address vulnerabilities. |
| Firewall Protection | A protective barrier to prevent unauthorized access to the system. |
| Intrusion Detection System (IDS) | Monitors network traffic for malicious activity and alerts administrators to potential threats. |
Use Cases and Examples
Fanning’s Snocap, bridging the gap between centralized label systems and decentralized peer-to-peer (P2P) networks, offers a powerful solution for streamlining workflows and fostering innovation across various industries. This section explores real-world applications, showcasing how Snocap can solve existing problems and potentially create new business models. We’ll demonstrate its efficiency and versatility in different contexts.
Streamlined Supply Chain Management
Fanning’s Snocap excels at optimizing supply chains by automating label verification and tracking. Imagine a global manufacturing company with intricate supply chains. Traditional methods often involve manual data entry and reconciliation, prone to errors and delays. Snocap automatically verifies labels across the network, ensuring product authenticity and streamlining the movement of goods. Real-time tracking updates reduce delays and provide greater transparency throughout the process.
Enhanced Product Authentication
In industries like pharmaceuticals and luxury goods, product authenticity is paramount. Fanning’s Snocap provides a robust system for authenticating products, reducing counterfeiting and ensuring consumer confidence. A pharmaceutical company can use Snocap to embed unique identifiers on labels, linked to a P2P network. Any attempt to tamper with the label triggers an immediate alert, ensuring genuine products reach consumers.
The decentralized nature of the network adds an extra layer of security.
Improved Inventory Management
Accurate inventory tracking is critical for efficiency and profitability. Snocap facilitates real-time inventory updates across the network. A retailer using Snocap can automatically update inventory levels as products are scanned or shipped, preventing stockouts and overstocking. This system enhances visibility across the entire supply chain, enabling proactive inventory management.
Facilitating New Business Models
Snocap empowers the creation of innovative business models by facilitating direct interaction and collaboration between parties. A decentralized marketplace for artisans could leverage Snocap to securely verify product origins and craftsmanship, creating trust between buyers and sellers. The transparent verification process attracts new customers and promotes ethical trade practices.
Summary Table of Use Cases
| Use Case | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Supply Chain Management | Automated verification, real-time tracking, reduced errors, faster delivery |
| Product Authentication | Robust verification, reduced counterfeiting, enhanced consumer confidence, tamper-proof system |
| Inventory Management | Real-time updates, proactive management, minimized stockouts/overstocking, improved visibility |
| Decentralized Marketplaces | Secure verification, transparent origin tracking, trust building, ethical trade promotion |
Future Trends and Developments
Fanning’s Snocap, as a bridging technology between decentralized peer-to-peer (P2P) networks and centralized label systems, presents exciting opportunities for the future of information sharing. Its potential to streamline data exchange and enhance security in various industries makes it a technology worth exploring. This section examines emerging trends and potential advancements in Fanning’s Snocap, its impact on the future, and its adaptability to evolving standards.The future of information sharing hinges on the ability to seamlessly connect disparate systems.
Fanning’s Snocap, with its unique approach to bridging P2P and label-based systems, is well-positioned to address this need. This analysis will highlight potential innovations and advancements within the P2P and label ecosystems that will further solidify Snocap’s position as a vital technology in the years to come.
Potential Advancements in Fanning’s Snocap Technology
Fanning’s Snocap technology is likely to see advancements in several areas. Improved scalability will be crucial to accommodate increasing data volumes and user bases. Enhancements in security protocols are also essential, potentially incorporating blockchain-based mechanisms for even more robust verification and protection against malicious actors. The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) for automated data processing and analysis will likely become a core component in future versions, offering a more intelligent and efficient system for information handling.
Furthermore, the development of user-friendly interfaces will be paramount for wider adoption and usability.
Emerging Trends and Opportunities for Innovation
The P2P and label ecosystems are experiencing rapid evolution. Increased adoption of decentralized storage solutions is a significant trend, creating a demand for secure and reliable bridging mechanisms. The rise of blockchain technology is further influencing the development of transparent and tamper-proof systems. Data integrity and ownership are becoming increasingly important, leading to greater demand for solutions that ensure accurate and secure data transfer.
The emergence of new data formats and protocols will require Fanning’s Snocap to adapt and maintain compatibility with evolving industry standards.
Impact of Fanning’s Snocap on the Future of Information Sharing
Fanning’s Snocap has the potential to revolutionize information sharing by enabling seamless data exchange between diverse platforms. This will foster greater transparency and collaboration within organizations and across industries. Increased efficiency in data management and analysis will also be a significant outcome, enabling more informed decision-making. Ultimately, the increased accessibility and security of information will contribute to a more connected and efficient world.
Adaptability to Changing Industry Standards and Requirements
Fanning’s Snocap’s modular design and open architecture will allow for seamless adaptation to changing industry standards and requirements. Regular updates and compatibility with new protocols are anticipated to maintain its relevance and usability. The technology’s flexibility will ensure its continued viability and applicability in various sectors. This includes the integration of emerging security protocols and the adaptation to new data formats.
Comparison of Fanning’s Snocap to Alternative Bridging Solutions
| Feature | Fanning’s Snocap | Alternative Bridging Solution A | Alternative Bridging Solution B |
|---|---|---|---|
| Decentralization | High | Low | Medium |
| Security | Robust (blockchain integration potential) | Moderate | High (but less flexible) |
| Scalability | Modular design allows for scaling | Limited | Fixed architecture |
| Cost | Variable, depends on implementation | Low | High |
| Flexibility | High (adaptable to new standards) | Low | Medium |
Note: “Alternative Bridging Solution A” and “Alternative Bridging Solution B” are placeholders for hypothetical competitors. The table illustrates potential comparative advantages of Fanning’s Snocap based on its features.
Outcome Summary
In conclusion, Fanning’s Snocap presents a compelling solution for bridging the gap between label and P2P systems. Its comprehensive approach to integration, security, and diverse use cases positions it as a powerful tool for fostering collaboration and innovation across various industries. The platform’s potential to streamline workflows and create new business models is significant, paving the way for a more interconnected and efficient future.
Further exploration of its functionalities and applications is essential for fully realizing its potential.