FCC Move Boosts Wireless Broadband Impact & Implications
With FCC move boosts wireless broadband taking center stage, we’re diving deep into the potential ripple effects this action will have. This isn’t just about faster internet; it’s about reshaping the entire landscape of wireless communication, from consumer access to provider strategies and technological advancements. Expect a detailed look at the anticipated impact on consumers, providers, and the industry as a whole.
This FCC initiative aims to improve broadband access, particularly in underserved areas. It promises increased competition, potentially driving down prices and expanding service availability. However, there are also potential drawbacks and challenges that need careful consideration, including the financial implications for providers and the potential for regulatory hurdles.
Overview of FCC Move
The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) has recently undertaken a significant action impacting wireless broadband access. This move aims to address critical issues surrounding the expansion and affordability of this essential service, with the potential to revolutionize how Americans access and use the internet. Understanding the specifics of this action, its goals, and anticipated effects is crucial for anyone interested in the future of communication technologies.The FCC’s action, specifically focused on fostering a more competitive and accessible wireless broadband environment, seeks to achieve several key objectives.
This includes driving investment in infrastructure, improving service quality, and lowering costs for consumers. The anticipated impact is a widespread enhancement in internet access, particularly in underserved areas, potentially leading to increased digital inclusion and economic growth.
Specific FCC Action
The FCC’s recent actions, aimed at boosting wireless broadband, include measures to encourage competition among wireless carriers. These measures are designed to improve network infrastructure and services. These actions are also meant to ensure the continued development and innovation within the wireless industry.
Key Provisions and Goals
The FCC’s move features several key provisions, primarily focusing on stimulating competition and expanding broadband access. These include mandates for greater transparency in pricing and service offerings, encouraging investment in high-speed networks, and promoting the development of innovative technologies. The overarching goal is to ensure that more Americans have access to reliable and affordable wireless broadband, bridging the digital divide.
The FCC’s move to boost wireless broadband is a game-changer, paving the way for faster internet access. This opens up exciting possibilities, particularly in the realm of nanotechnology, which could be crucial in developing even faster, more efficient wireless systems. Companies looking to turn nanotech into profit turning nanotech into profit could use this as a springboard, potentially leading to revolutionary advancements in the sector.
Ultimately, the FCC’s initiative is a step towards a more connected future, thanks to the potential applications of nanotech.
Anticipated Impact on the Industry
The anticipated impact on the wireless broadband industry is substantial. Increased competition is expected to drive down prices and improve service quality for consumers. New entrants may emerge, leading to a more dynamic and innovative market. This could result in more robust and extensive wireless networks, especially in rural and underserved areas. This could also lead to a surge in investment in 5G and other future technologies, potentially creating new jobs and opportunities.
Historical Context of Similar FCC Actions
The FCC has a history of taking actions to shape the wireless communications landscape. These actions have often aimed to address market issues, promote competition, and improve consumer access. The FCC’s past actions regarding spectrum allocation, licensing procedures, and consumer protections have set the stage for the current initiatives. Understanding the historical context of these efforts provides valuable insights into the present situation and potential future outcomes.
| Date | Action | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1996 | Telecommunications Act | Deregulation of the telecommunications industry | Increased competition, lower prices, and wider access to services. |
| 2002 | Spectrum Auctions | Auction of spectrum licenses | Increased competition and efficiency in wireless services. |
| 2015 | Net Neutrality Rules | Regulation of internet traffic | Ensured equal access to all content online. |
| Present | Wireless Broadband Boost | Encouraging competition and affordability | Expected to increase competition, lower prices, and improve service quality for consumers. |
Impact on Consumers
The FCC’s move to boost wireless broadband promises significant changes for consumers, potentially leading to faster speeds, lower costs, and increased competition. However, the actual impact will depend on various factors, including the level of industry participation and the effectiveness of regulatory oversight. This analysis delves into the potential benefits and challenges consumers may face.The FCC’s actions are intended to improve access to reliable high-speed internet for all Americans.
This shift towards a more competitive wireless broadband market could result in a wide range of outcomes for consumers, depending on their specific needs and circumstances.
Potential Benefits for Consumers
The core benefit for consumers is the potential for increased competition in the wireless broadband market. This competition can drive down prices and increase the availability of high-speed internet options. Faster speeds and lower prices translate to better online experiences, improved productivity, and enhanced opportunities for education and entertainment.
The FCC’s move to boost wireless broadband is a game-changer, paving the way for faster internet access for everyone. This improvement is crucial, especially when considering the future of peer-to-peer file sharing, and the evolution of this technology is something I’m exploring in depth in an insightful interview with Streamcast CEO Michael Weiss, which way for p2p an interview with Streamcast CEO Michael Weiss.
Ultimately, this increased broadband access will be vital for the success of these innovative technologies, making the FCC’s efforts even more significant.
Potential Drawbacks and Challenges for Consumers
Despite the potential benefits, some drawbacks and challenges may arise. One concern is the potential for disparities in access to these improved services. Rural areas, for example, may face challenges in attracting and maintaining broadband providers, leading to limited availability and higher costs. Furthermore, the transition period could involve hiccups and difficulties in implementation, resulting in temporary disruptions or inefficiencies in service.
Impact on Pricing and Availability of Wireless Broadband Services
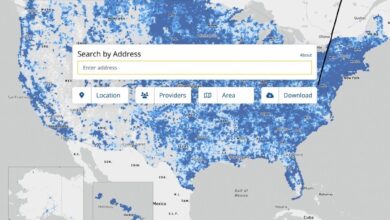
The FCC’s actions aim to make high-speed internet more affordable and accessible. Increased competition could lead to lower prices for consumers. However, the degree of price reduction will depend on the intensity of competition and the willingness of providers to pass on cost savings. The availability of services may improve in areas currently underserved, but challenges in infrastructure deployment in remote or rural areas may persist.
Potential for Increased Competition and Consumer Choice
The FCC’s move aims to foster a more competitive wireless broadband market. This increased competition should provide consumers with more options and choices, allowing them to select the best service based on their individual needs and budget. Consumers might have access to a broader range of plans, data allowances, and devices to better suit their requirements.
Consumer Scenarios Before and After the FCC Move
| Consumer Scenario | Before FCC Move | After FCC Move |
|---|---|---|
| Low-income | Limited access to high-speed internet, often expensive and unreliable options. | Potentially lower prices and more options, but the affordability of the most competitive plans will depend on the market dynamics. |
| High-income | Generally have access to high-speed internet with various choices. | Likely to see more options and potential for even better pricing and services. |
| Rural | Significant challenges in accessing high-speed internet, often limited options with higher prices. | May see improvements, but infrastructure challenges could persist, and the presence of providers might not be consistent across all rural areas. |
This table provides a general overview of how different consumer segments might be affected. Individual experiences may vary based on specific location, economic factors, and the responsiveness of providers to the changing market conditions.
Impact on Providers

The FCC’s move to boost wireless broadband access presents both opportunities and challenges for providers. The shift towards increased competition and potentially higher consumer demand could significantly reshape the landscape of the telecommunications industry. Understanding these potential effects is crucial for providers to adapt and thrive in this evolving market.The implications for wireless broadband providers are multifaceted, ranging from increased infrastructure investment to adjustments in business models.
Large providers with extensive networks and resources may find it easier to adapt, while smaller companies might face greater hurdles. Navigating the evolving regulatory environment and consumer expectations will be key to success for all.
Potential Effects on Large Providers
Large telecommunication companies, often with existing extensive infrastructure, may be better positioned to absorb the costs and benefits of the FCC’s initiative. They typically have access to substantial capital for investments in expanding their network and upgrading equipment. The potential for increased demand from consumers seeking faster and more reliable wireless broadband could translate to higher revenue streams.
However, the need to compete with new entrants and established competitors in the market could necessitate aggressive pricing strategies and potentially erode profit margins. Furthermore, the increased demand may also strain existing infrastructure, requiring substantial investment in network upgrades and maintenance.
Potential Effects on Small Providers
Smaller providers, particularly those operating in less densely populated areas, might face significant challenges. Limited capital may restrict their ability to upgrade their networks to meet the demands of the FCC’s initiative. Moreover, the need to compete with larger, more established players could be overwhelming, making it difficult to attract and retain customers. Aggressive pricing strategies by large companies could also put immense pressure on smaller providers’ profitability.
Strategies to remain competitive might include focusing on niche markets, partnering with larger providers, or leveraging emerging technologies.
Financial Implications, Fcc move boosts wireless broadband
The financial implications for providers are substantial and varied. Positive impacts include increased potential revenue streams due to higher demand and the ability to capture a larger market share. However, significant upfront investments in network upgrades, equipment, and personnel could place a strain on providers’ financial resources. Increased competition may lead to lower profit margins, and maintaining a strong competitive position could necessitate a significant amount of investment.
Furthermore, the potential for regulatory hurdles could add to financial uncertainty and create a complex regulatory landscape.
Adapting Strategies
Providers can adopt several strategies to adapt to the changes. These strategies might include:
- Investing in advanced network technologies to enhance speed and capacity. This could include implementing 5G infrastructure or exploring innovative solutions like fiber-to-the-home (FTTH) to address future demands.
- Developing innovative business models, such as partnering with other providers or exploring opportunities in emerging markets.
- Focusing on niche markets or underserved areas where the demand for higher bandwidth might be less competitive, enabling them to maintain profitability.
- Aggressively pursuing strategic mergers and acquisitions to expand their network and customer base.
Regulatory Hurdles and Solutions
The transition to higher-speed wireless broadband may create new regulatory hurdles for providers. For example, there might be issues regarding spectrum allocation, network neutrality rules, and licensing requirements.
| Regulatory Hurdle | Potential Solution |
|---|---|
| Spectrum Allocation | Collaborate with regulatory bodies to secure necessary spectrum licenses and explore the possibility of using shared spectrum to minimize interference and maximize bandwidth availability. |
| Network Neutrality | Advocating for clear guidelines and policies on network neutrality to ensure fair access for all providers and consumers. Transparency on pricing models and access points would be beneficial. |
| Licensing Requirements | Working with regulatory bodies to streamline the licensing process and reduce bureaucratic hurdles to deployment and operation. Establishing clear timelines and procedures would alleviate uncertainty. |
Technological Advancements
The FCC’s move to boost wireless broadband promises a wave of technological advancements. This isn’t just about faster speeds; it’s about fundamentally reshaping how we interact with the digital world, impacting everything from communication to entertainment to critical infrastructure. This push for innovation could lead to more efficient network designs and a wider array of services.This increased competition and investment in infrastructure will likely stimulate the development of new and improved wireless technologies.
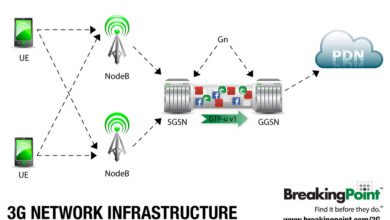
The potential for improved network infrastructure, encompassing both the physical towers and the underlying software, is significant. This could mean more reliable connections, reduced latency, and greater capacity to handle future demands.
Potential Advancements in Wireless Technologies
The FCC’s actions are poised to accelerate innovation across the wireless spectrum. The drive for higher bandwidth and improved reliability will likely see accelerated research and development in areas like millimeter wave technology, and the exploration of new frequency bands. This is already evident in the burgeoning 5G rollout, and will undoubtedly drive the next generation of wireless communications.
Influence on 5G and Beyond
The move is likely to further refine 5G technology, potentially leading to faster speeds, lower latency, and enhanced capacity. This could be particularly impactful for applications requiring real-time communication, such as autonomous vehicles and remote surgery. Beyond 5G, the FCC’s actions could pave the way for even more advanced wireless technologies. For example, the development of technologies like 6G and beyond is anticipated to focus on even greater bandwidth and improved reliability.
This is crucial for applications like virtual and augmented reality, which require seamless and high-speed connectivity.
Improved Network Infrastructure
The increased investment in wireless infrastructure, spurred by the FCC’s actions, will likely lead to more robust and resilient networks. This includes upgrades to existing infrastructure, such as more advanced cell towers and improved signal boosters. Furthermore, the potential for small cell deployment and distributed antenna systems could lead to a denser network, enhancing coverage and reducing signal interference in densely populated areas.
Increased network capacity is expected to reduce congestion and provide a more reliable experience for consumers. Examples of this are evident in areas with recent upgrades to their cell towers.
Geographic Variations in Innovation
The pace and nature of innovation in different geographic regions will vary. Factors like existing infrastructure, government support, and the presence of skilled labor will influence the development and adoption of new wireless technologies. Regions with a strong existing digital infrastructure, robust funding for research and development, and a skilled workforce are likely to experience more rapid innovation.
Conversely, areas with limited resources may face challenges in adopting these technologies, possibly leading to a digital divide. For example, rural communities may experience slower adoption of advanced wireless technologies compared to urban centers.
Policy Implications

The FCC’s move to boost wireless broadband access has significant policy implications, extending far beyond the immediate impact on consumers and providers. This decision signals a potential shift in the regulatory landscape, influencing future telecommunications policies and potentially creating unforeseen consequences. Understanding these broader implications is crucial for assessing the long-term effects of this initiative.
Broader Regulatory Implications
The FCC’s actions may set a precedent for future regulatory decisions concerning infrastructure development and technological advancements in the telecommunications sector. This precedent could influence policies related to 5G deployment, satellite internet expansion, and even the regulation of emerging technologies like the Internet of Things (IoT). A key consideration is how the approach to incentivizing broadband expansion might influence other sectors needing infrastructure improvements.
Potential Unintended Consequences
While the FCC’s move aims to benefit consumers, unintended consequences are always a possibility. One potential issue is the uneven distribution of benefits. Areas with already strong broadband infrastructure might see only minor improvements, while underserved communities may not experience significant gains. Furthermore, the focus on private sector investment could potentially result in reduced public funding for broadband initiatives in certain regions, creating a disparity in access.
Another concern relates to the potential for increased competition, potentially causing mergers or consolidations in the industry, which could impact consumer choice and pricing. Historical instances of similar regulatory changes have demonstrated that these unintended consequences can sometimes be substantial and require further policy adjustments.
Comparison to Other Telecommunications Policy Changes
Recent telecommunications policy changes, such as those related to net neutrality or spectrum allocation, offer valuable insights into the potential impacts of the FCC’s current initiative. Comparing these previous changes to the current move can help identify potential challenges and opportunities. For instance, the net neutrality debate highlighted the complexities of balancing innovation with consumer protection. A comparison of these issues can reveal possible parallels and differing outcomes, emphasizing the need for careful consideration in policy formulation.
Potential Policy Debates
The FCC’s move is likely to spark numerous policy debates, covering a wide range of concerns. These debates will involve discussions about the appropriate balance between government intervention and private sector investment, as well as the definition of “adequate” broadband access. This move could also generate discussions regarding the role of government subsidies in supporting infrastructure development.
| Potential Policy Debate | Description |
|---|---|
| Public Funding vs. Private Investment | Discussions regarding the optimal allocation of resources between government funding and private sector investment for broadband infrastructure. |
| Definition of “Adequate” Broadband Access | Defining measurable standards for satisfactory broadband speeds and reliability to ensure that the benefits reach all areas and demographics. |
| Regional Disparities | Addressing potential disparities in broadband access among different regions and communities, ensuring equitable distribution of benefits. |
| Consumer Protection | Examining how the FCC’s move affects consumer rights, pricing, and choices in the broadband market. |
| Spectrum Allocation and Use | Discussions regarding the allocation of spectrum for broadband services and potential impact on existing and future technologies. |
Public Opinion and Response: Fcc Move Boosts Wireless Broadband
The FCC’s move to boost wireless broadband has ignited a complex tapestry of public opinion, ranging from enthusiastic support to staunch opposition. Understanding these diverse perspectives is crucial to evaluating the long-term impact of the initiative. Public reaction will undoubtedly shape the future trajectory of the policy, influencing its implementation and potential for success.Public sentiment towards the FCC’s move is multifaceted, encompassing a spectrum of concerns and hopes.
Stakeholders, from individual consumers to large telecommunications corporations, hold differing views based on their specific interests and potential impacts. Understanding these divergent viewpoints is vital for comprehending the overall public response to the proposed changes.
Potential Public Reaction
The public’s response to the FCC’s initiative will likely be influenced by the perceived benefits and drawbacks. Positive aspects, such as improved internet access and potentially lower costs, may generate enthusiasm. Conversely, concerns about potential negative consequences, like increased data caps or reduced privacy, could foster resistance. Historical precedents suggest that major policy changes often encounter mixed public reactions, and this initiative is no exception.
Different Perspectives from Stakeholders
Various stakeholders hold distinct perspectives on the FCC’s move. Consumers, eager for faster and more affordable internet access, are likely to view the changes positively. Providers, however, might express reservations regarding the potential regulatory burdens and financial implications of implementing the new policies. Advocacy groups focused on digital equity may welcome the move if it expands access to underserved communities, but they may also voice concerns about potential unintended consequences.
These different perspectives will play a vital role in shaping the overall public narrative surrounding the initiative.
Potential Controversies
Several controversies may emerge surrounding the FCC’s initiative. One potential point of contention is the fairness of the proposed changes, particularly concerning the distribution of benefits among different consumer groups. Another potential controversy relates to the potential for unintended consequences, such as increased data consumption or changes to existing data plans. Additionally, the potential for market consolidation or the impact on smaller providers may lead to further controversy.
Examples of Public Statements
Public statements from industry leaders and advocacy groups offer valuable insights into the diverse perspectives on the FCC’s initiative. Industry leaders may express concerns about the feasibility of implementation or the financial implications for their companies. Conversely, advocacy groups might highlight the benefits for underserved communities or advocate for specific provisions within the policy. Tracking these statements will provide a clearer picture of the evolving public discourse.
The FCC’s recent move to boost wireless broadband is a significant step forward. This increased access to high-speed internet, however, is also likely to have an interesting ripple effect on other areas of the tech world. For example, as more people have reliable internet access, the demand for features like personalized ring tones might see a spike, as seen in the recent surge in ring tones ring up record revenue.
Ultimately, this FCC initiative will likely have a positive impact on the entire digital landscape, fostering innovation and growth across multiple sectors.
Table Illustrating Public Opinion
| Stakeholder Group | Potential Opinion | Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| Consumers | Positive or Negative | Depends on perceived benefits (lower costs, faster speeds) versus potential drawbacks (increased data caps, privacy concerns). |
| Telecommunication Providers | Mixed | May face increased costs in upgrading infrastructure or adapting to new regulations. |
| Advocacy Groups (Digital Equity) | Positive or Negative | Positive if the move expands access for underserved communities, but negative if unintended consequences arise. |
| Government Regulators | Neutral or Supportive | Aim to balance the interests of consumers, providers, and the public good. |
International Comparison
The FCC’s move to boost wireless broadband is a significant step, but its success hinges on understanding how other nations are tackling similar challenges. Examining international initiatives provides valuable insights into potential pitfalls and best practices. International comparisons highlight the nuances of regulatory frameworks and technological approaches, offering a broader perspective on the path forward.Looking beyond the US borders reveals diverse approaches to fostering wireless broadband access.
Some countries emphasize government subsidies and infrastructure investments, while others prioritize market-driven solutions. Understanding these varied strategies is critical for crafting effective policies that maximize both affordability and technological advancement.
Regulatory Environments
Different countries have varying regulatory environments for wireless broadband. Some nations employ strict government control over spectrum allocation and infrastructure development, while others rely on market forces and competition. This spectrum of approaches affects the pace and nature of broadband deployment and consumer access.
- Spectrum Allocation Policies: Different countries adopt various strategies for spectrum allocation, reflecting varying priorities. Some countries prioritize auctions, others favor licensing models, and some use a mix of approaches. This diversity in spectrum allocation policies significantly impacts the availability and cost of spectrum for wireless broadband providers.
- Regulatory Bodies: The structure and authority of regulatory bodies responsible for overseeing wireless broadband vary considerably. Some countries have dedicated agencies with strong oversight powers, while others might distribute these responsibilities among different government departments. This difference in regulatory structures affects how efficiently policies are implemented and how quickly they respond to technological advancements.
- Market Structure: Countries exhibit varying degrees of competition within the wireless broadband sector. Some countries have a more consolidated market, with a smaller number of major providers, whereas others feature a more competitive landscape with numerous companies. This affects the pricing strategies of providers and the quality of service consumers receive.
Technological Approaches
Countries employ different technological strategies for boosting wireless broadband infrastructure. Some focus on expanding 4G networks, while others are investing heavily in 5G deployments and future-proof technologies.
- 5G Deployment: Countries vary significantly in their 5G deployment plans and timelines. Some have aggressive targets for 5G coverage and adoption, while others are taking a more measured approach. This difference in focus reflects differing technological priorities and infrastructure capabilities.
- Fixed Wireless Access: Some countries are actively exploring and investing in fixed wireless access technologies as an alternative to fiber optic networks for underserved areas. This strategy, when successful, can improve broadband access and reduce infrastructure costs.
Lessons Learned
International comparisons reveal valuable lessons about successful and unsuccessful strategies for boosting wireless broadband. Understanding these experiences is crucial for shaping effective policies and maximizing the benefits of wireless broadband.
- Success Factors: Examining successful wireless broadband initiatives in other countries reveals common factors such as government support, strategic investments in infrastructure, and policies that encourage competition. This understanding can inform future policy decisions in the US.
- Failures and Challenges: Examining the failures of wireless broadband initiatives in other countries helps avoid repeating similar mistakes. Understanding why certain policies didn’t work can provide valuable insights for avoiding unforeseen problems and maximizing the benefits of new initiatives.
Policy Implications
International comparisons can offer valuable insights for future policy development related to wireless broadband. Lessons from other countries’ experiences can inform the development of more effective and efficient strategies.
- Adapting Policies: Learning from international initiatives can help the FCC tailor policies to address specific challenges and opportunities unique to the US market. This could involve adopting strategies that have proven successful in other countries while adapting them to the unique context of the US.
- International Collaboration: International collaboration can lead to knowledge sharing and best practice adoption, potentially accelerating progress in wireless broadband development.
Wrap-Up
The FCC’s move to boost wireless broadband is a significant step, promising a more connected future. While the potential benefits are substantial, the implementation and impact will depend on various factors, including consumer adoption, provider responses, and potential regulatory adjustments. This discussion highlights the complex interplay of technological advancements, policy implications, and public response in shaping the future of wireless communication.