Untreated Mental Disorders A Global Crisis
Global surveys find mental disorders often untreated, revealing a significant gap in access to care across the globe. This pervasive issue affects individuals of all ages, socioeconomic backgrounds, and geographical locations, highlighting profound disparities in mental healthcare systems worldwide. The problem extends far beyond individual suffering, impacting public health and potentially escalating into severe conditions. Understanding the prevalence, barriers, and potential solutions is crucial for creating a healthier future for all.
This in-depth look at the crisis examines the alarming scope of untreated mental disorders, exploring the societal, cultural, and economic factors that contribute to this global challenge. From the staggering rates of untreated conditions in different regions to the personal stories of those affected, the discussion will cover the full spectrum of this critical issue. We’ll delve into the consequences of untreated mental disorders on individuals and communities, exploring the impact on well-being, quality of life, and public health.
Ultimately, this article aims to spark dialogue and inspire action towards a more equitable and supportive mental healthcare system.
Prevalence and Scope of Untreated Mental Disorders
The global burden of mental illness is staggering, impacting individuals across all demographics and socioeconomic strata. A significant portion of those affected by mental disorders fail to receive the necessary treatment, leading to further complications and perpetuating a cycle of suffering. Understanding the prevalence, scope, and contributing factors of untreated mental illness is crucial for developing effective interventions and policies.The prevalence of mental disorders worldwide is substantial, impacting countless lives.
Numerous studies consistently highlight the significant global burden of conditions like depression, anxiety, and schizophrenia. However, the crucial issue of access to and utilization of mental healthcare services often remains significantly underdeveloped in various regions.
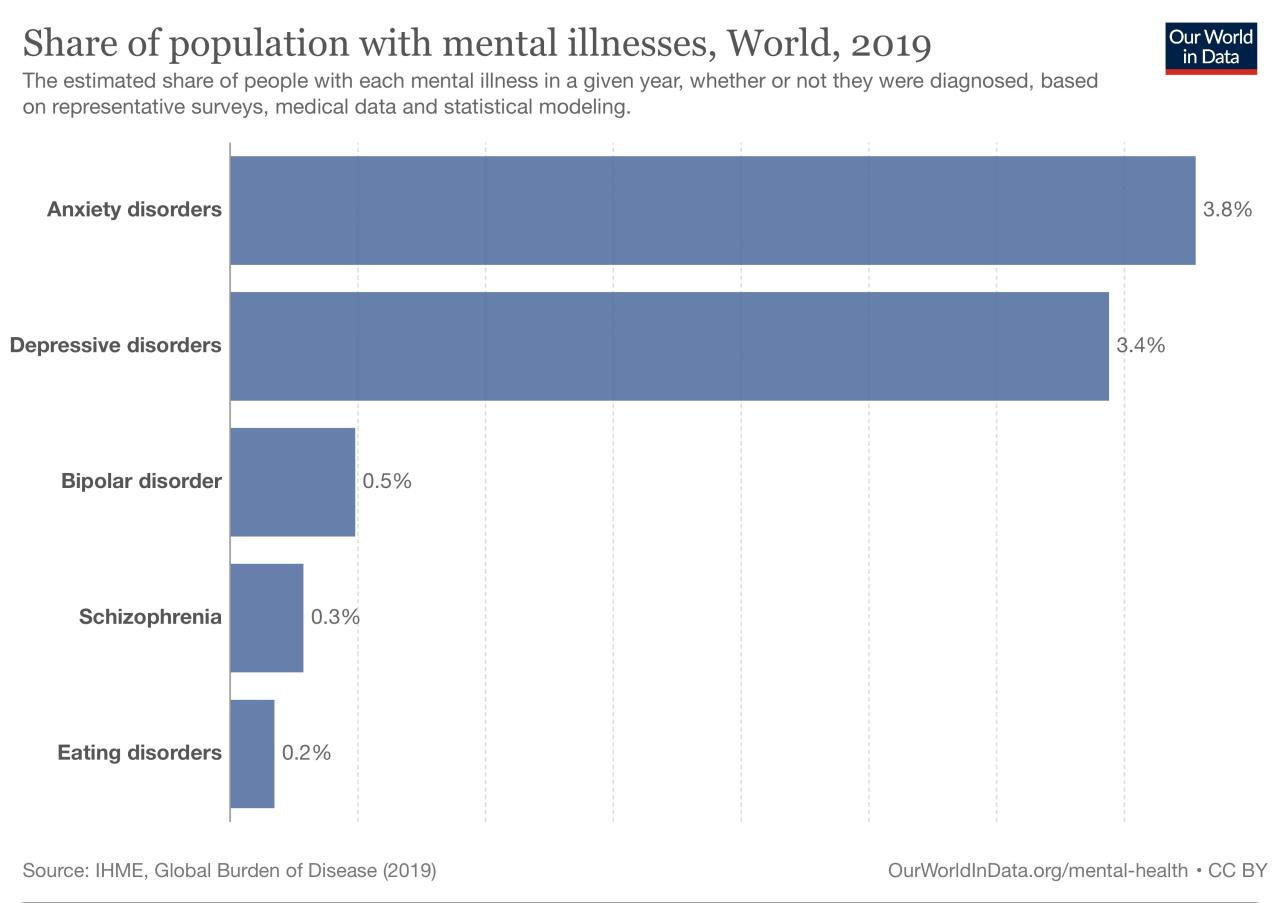
Global Prevalence of Mental Disorders
A multitude of factors influence the prevalence of mental disorders across the globe. Cultural norms, societal stigma, and varying levels of economic development play critical roles in shaping access to treatment. Furthermore, differences in diagnostic criteria and reporting methodologies can complicate cross-country comparisons.
Proportion of Untreated Mental Disorders
Reliable data on the precise proportion of individuals with mental disorders who do not receive treatment is challenging to obtain due to varying reporting standards and methodologies across different countries. However, available evidence consistently points to a significant gap in access to care, particularly in low- and middle-income countries.
Demographic Factors Associated with Untreated Mental Disorders
Several demographic factors are strongly correlated with a lack of mental healthcare. Age, socioeconomic status, and geographic location are frequently identified as significant contributors. Younger populations, those with lower socioeconomic status, and individuals residing in rural or remote areas often face greater barriers to accessing appropriate care. The reasons for these disparities often stem from a combination of factors, including financial constraints, lack of awareness, and cultural stigma.
Disparities in Access to Mental Healthcare
Significant disparities in access to mental healthcare exist across different regions. High-income countries generally have more developed mental healthcare systems, offering a wider range of services and greater access for their citizens. Conversely, low- and middle-income countries often face significant challenges in providing adequate mental healthcare resources, leading to considerable unmet needs. The availability of trained mental health professionals, infrastructure, and affordable treatment options vary substantially between regions.
Comparison of Untreated Mental Disorders Across Regions
| Region | Estimated Proportion of Untreated Mental Disorders | Key Contributing Factors |
|---|---|---|
| Sub-Saharan Africa | High, often exceeding 70% in some areas | Limited mental health professionals, financial constraints, stigma, and lack of awareness |
| South Asia | High, often exceeding 60% in some areas | Cultural stigma, limited access to mental health services, and social taboos |
| North America | Moderate, often between 20-40% depending on specific factors | Stigma, cost of care, and lack of insurance coverage |
| Europe | Moderate, often between 15-35% depending on specific factors | Access to services varies across countries; cost and insurance coverage are often key |
The table above presents a simplified comparison. Actual figures and contributing factors can vary significantly within specific regions and countries. Further research is necessary to fully understand the nuanced realities of access to mental healthcare.
Barriers to Mental Healthcare Access
Accessing mental healthcare is often challenging for many individuals, and a multitude of factors contribute to this difficulty. These barriers are deeply rooted in societal structures, cultural norms, economic realities, and individual experiences. Understanding these obstacles is crucial to developing effective strategies for improving mental health services and ensuring equitable access for all.
Societal and Cultural Factors
Cultural norms and societal perceptions surrounding mental illness significantly impact help-seeking behaviors. In some cultures, mental health issues are stigmatized and perceived as a sign of weakness or a personal failing. This stigma discourages individuals from seeking professional help, fearing judgment or social ostracism. Furthermore, societal expectations and gender roles can also play a part. For example, men may be less likely to acknowledge or address mental health concerns due to societal pressures to appear strong and resilient.
Language barriers can also present a significant hurdle for those seeking mental health support, especially in diverse communities.
Global surveys consistently highlight a concerning trend: mental health disorders often go untreated. This is a significant issue, and while initiatives like sendmail partners with Microsoft and Yahoo to stop spam tackle digital issues, the underlying mental health crisis demands more comprehensive solutions. The lack of treatment underscores the need for increased awareness and better access to care.
Economic Factors
The financial burden of mental healthcare can be a substantial barrier to accessing treatment. The cost of therapy, medication, and other related services can be prohibitive for many individuals, particularly those with low incomes or limited insurance coverage. Even with insurance, deductibles, co-pays, and out-of-pocket expenses can make treatment inaccessible. Additionally, lost wages due to time off work for appointments can be a significant economic hardship, especially for those who rely on their income for basic needs.
The absence of mental health benefits in some workplaces can further exacerbate this financial barrier.
Stigma and Discrimination
The stigma surrounding mental illness often leads to discrimination, creating an environment that prevents individuals from seeking help. Fear of judgment, social isolation, and even job loss or housing instability can deter people from acknowledging their struggles. This stigma can be perpetuated by misinformation and misconceptions about mental health conditions, leading to harmful stereotypes and prejudices. Negative experiences with healthcare providers, where individuals feel unheard or judged, can further reinforce this stigma and discourage future help-seeking.
Systemic Issues
The lack of mental healthcare services in certain communities, and inadequate mental health support systems within schools, workplaces, and the criminal justice system, contribute to the limited access to treatment. A lack of mental health professionals, especially in rural or underserved areas, can lead to long wait times for appointments and make it challenging to find appropriate care. Insufficient mental health resources in educational settings can leave students struggling to cope with their mental health needs.
Similarly, a lack of culturally sensitive and appropriate care in the criminal justice system can hinder the proper support for individuals experiencing mental health crises.
Illustrative Table of Barriers
| Type of Barrier | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Societal/Cultural | Stigma, cultural norms, gender roles, language barriers. | Discourages help-seeking, isolation, fear of judgment. |
| Economic | Cost of treatment, lack of insurance, lost wages. | Inability to afford care, limited access, financial hardship. |
| Stigma/Discrimination | Fear of judgment, social isolation, potential for job loss or housing instability. | Deters help-seeking, perpetuates negative experiences. |
| Systemic | Lack of mental health professionals, inadequate resources in communities, schools, and the justice system. | Long wait times, limited access to care, unmet needs. |
Impact of Untreated Mental Disorders
Untreated mental health conditions can have a devastating impact on individuals, families, and communities. The consequences extend far beyond the individual experiencing the disorder, affecting their ability to function, build relationships, and pursue their goals. Understanding these impacts is crucial for developing effective interventions and support systems.The consequences of untreated mental disorders are multifaceted and often far-reaching. These conditions can significantly diminish an individual’s overall well-being and quality of life.
The absence of appropriate treatment can lead to a downward spiral of worsening symptoms, increased isolation, and a diminished capacity to participate in daily activities.
Consequences on Individual Well-being and Quality of Life
Untreated mental health conditions can lead to a cascade of negative consequences for individuals. These range from difficulties in maintaining healthy relationships and employment to physical health problems stemming from stress and poor self-care. The lack of support can further exacerbate feelings of isolation and hopelessness.
Global surveys consistently show a troubling trend: mental health disorders are often left untreated. This pervasive issue, unfortunately, isn’t limited to any one area. While the tech world is buzzing with the latest console wars, like the fierce competition between Xbox and PlayStation, which Microsoft is throwing down the gauntlet in this exciting new arena , the need for accessible and effective mental health resources remains critically important.
This highlights the urgent need for broader solutions to address the mental health crisis worldwide.
- Impaired Cognitive Functioning: Untreated conditions can impact memory, concentration, and decision-making abilities, making it difficult to perform daily tasks effectively. For example, someone with untreated depression might struggle to focus at work or complete household chores.
- Relationship Difficulties: Mental health conditions can strain interpersonal relationships, leading to conflicts, misunderstandings, and emotional distance. A person with untreated anxiety, for instance, might withdraw from social interactions, causing friction with loved ones.
- Decreased Productivity and Employment Issues: Difficulty concentrating, fatigue, and emotional instability can make it challenging to maintain employment or pursue educational goals. Someone with untreated bipolar disorder, for example, might experience periods of extreme energy followed by crashes, affecting their work performance.
- Increased Risk of Physical Health Problems: Chronic stress associated with untreated mental disorders can contribute to a range of physical health issues, such as cardiovascular problems, weakened immune systems, and digestive problems. Untreated PTSD, for example, can lead to persistent stress hormones that harm physical health.
Impact on Public Health, Global surveys find mental disorders often untreated
Untreated mental disorders have a significant impact on public health. They can lead to increased healthcare costs, reduced productivity, and a greater burden on social support systems. The absence of effective treatment strategies contributes to a cycle of worsening conditions, perpetuating the problem and impacting society as a whole.
- Increased Healthcare Costs: Untreated conditions often escalate into more severe forms, necessitating costly emergency room visits, hospitalizations, and long-term care. This places a strain on public and private healthcare systems.
- Economic Burden: Reduced productivity due to absenteeism, presenteeism, and lost earning potential in individuals with untreated mental illnesses has a significant economic impact. Untreated conditions can also contribute to crime rates.
- Strain on Social Support Systems: Families and communities often bear the brunt of caring for individuals with untreated mental illnesses, placing a heavy strain on their resources and support systems. This can lead to burnout and other problems within families.
Escalation to More Severe Conditions
Untreated mental health conditions can escalate into more severe and complex issues over time. Without appropriate intervention, symptoms can worsen, leading to difficulties in daily functioning and potentially life-altering consequences.
- Progression to Chronic Conditions: Untreated conditions can develop into chronic and long-lasting mental health disorders, requiring ongoing treatment and support. Anxiety disorders, for example, if left untreated, can progress to more severe forms like panic disorder or generalized anxiety disorder.
- Increased Risk of Substance Abuse: Individuals struggling with untreated mental health conditions may turn to substance abuse as a coping mechanism, further complicating their situation and increasing the risk of addiction. This is especially true for conditions like depression and PTSD.
Correlation with Suicide Attempts
There’s a strong correlation between untreated mental disorders and an increased risk of suicide attempts. The absence of proper support and treatment can lead to feelings of hopelessness, despair, and a sense of being overwhelmed. This can, tragically, culminate in suicidal ideation and attempts.
- Hopelessness and Despair: Untreated conditions can contribute to feelings of hopelessness and despair, increasing the vulnerability of individuals to suicidal thoughts and actions. People who feel trapped by their symptoms and unable to cope with their mental health struggles are at a higher risk.
Severity Levels of Consequences
| Consequence | Severity Level | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Impaired cognitive functioning | Moderate | Difficulty concentrating, remembering, and making decisions |
| Relationship difficulties | Moderate | Conflicts, misunderstandings, and emotional distance in relationships |
| Decreased productivity | Moderate | Reduced ability to work or study effectively |
| Increased risk of physical health problems | High | Increased risk of cardiovascular issues, weakened immune system, and digestive problems |
| Progression to chronic conditions | High | Development of long-lasting mental health disorders requiring ongoing treatment |
| Increased risk of substance abuse | High | Turn to substances to cope with symptoms |
| Increased risk of suicide attempts | Critical | Significant risk of suicidal thoughts and actions |
Potential Solutions and Interventions
Addressing the global burden of untreated mental disorders requires multifaceted approaches that tackle both the systemic barriers and the individual needs of those affected. Effective solutions must encompass improved access to care, reduced stigma, and innovative delivery models tailored to diverse populations. These solutions are crucial to fostering mental well-being and enabling individuals to thrive.The crucial step toward reducing the prevalence of untreated mental disorders is to implement and reinforce comprehensive strategies.
These strategies encompass a range of interventions, from enhancing access to quality care to reducing the stigma associated with mental illness. Innovative approaches to care delivery, particularly in underserved communities, play a vital role in ensuring equitable access to mental healthcare.
Improving Access to Mental Healthcare
Improving access to mental healthcare requires a multi-pronged strategy focusing on removing practical barriers. These barriers often include geographical limitations, financial constraints, and a lack of culturally competent providers.
- Expanding mental health services in underserved areas: This involves establishing community mental health centers in rural and remote areas, and increasing the availability of telehealth services to connect individuals with providers in distant locations. For example, programs in rural Montana have shown success in expanding access to care through mobile clinics and telehealth partnerships with urban hospitals.
- Increasing the number of mental health professionals: A significant shortage of qualified mental health professionals exists worldwide. Addressing this shortage through scholarships and training programs aimed at increasing the supply of psychiatrists, psychologists, and social workers is crucial. This includes developing streamlined training pathways for general practitioners to expand access to basic mental health services.
- Making mental healthcare more affordable and accessible: Implementing subsidies, insurance coverage expansions, and sliding-scale payment options can significantly reduce the financial burden associated with seeking mental healthcare. Pilot programs in some states have shown positive results in increasing patient access by providing low-cost or free counseling.
Reducing the Stigma Associated with Mental Illness
Stigma surrounding mental illness significantly hinders individuals from seeking help. Addressing this stigma through public awareness campaigns and education programs is crucial.
- Public awareness campaigns: These campaigns should highlight the prevalence of mental disorders, dispel myths, and promote empathy and understanding. For example, campaigns focusing on mental health awareness during World Mental Health Day have demonstrated effectiveness in reducing stigma in certain communities.
- Education programs in schools and workplaces: Integrating mental health education into school curricula and workplace training programs can help destigmatize mental illness. This includes promoting a supportive environment where individuals feel comfortable discussing their mental health needs without fear of judgment.
- Media representation: Encouraging positive and accurate portrayals of mental health conditions in the media can foster empathy and understanding. Examples of media initiatives promoting mental health literacy and reducing stigma include the use of diverse and inclusive representations in films and television programs.
Innovative Approaches to Delivering Mental Healthcare in Underserved Populations
Addressing the needs of underserved populations requires culturally sensitive and adaptable approaches.
- Culturally adapted interventions: Developing culturally appropriate mental health services, including community-based programs that respect cultural values and traditions, is vital. Examples of successful initiatives include community-based mental health programs designed by local community leaders in response to specific needs in the Latino population in California.
- Telehealth: Expanding the use of telehealth to reach remote or underserved populations is crucial. Telehealth platforms can provide accessible mental health services in areas lacking adequate healthcare infrastructure. This is particularly important for populations facing significant geographical barriers.
- Peer support groups: Peer support groups can play a crucial role in providing support and encouragement to individuals with mental health conditions. These groups can be particularly helpful in providing a sense of belonging and shared experience.
The Importance of Community-Based Interventions
Community-based interventions are essential for fostering mental well-being and reducing the burden of untreated mental disorders.
- Community mental health centers: These centers provide a range of services, from counseling to support groups, and aim to address the needs of individuals in their community. These centers play a vital role in providing ongoing care and support to individuals with mental health conditions.
- School-based programs: Early intervention and support programs in schools can help identify and address mental health issues in adolescents. These programs can provide crucial support to young people who are at risk of developing mental health conditions.
- Workplace initiatives: Promoting mental health awareness and providing resources in the workplace can create a supportive environment for employees. These initiatives include providing mental health days, employee assistance programs, and workshops.
Comparative Analysis of Intervention Models
| Intervention Model | Description | Effectiveness | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Community Mental Health Centers | Provide comprehensive mental health services within local communities. | Effective in providing access to care for diverse populations. | May face funding challenges and resource constraints. |
| Telehealth | Utilize technology to deliver mental health services remotely. | Effective in increasing access to care in underserved areas. | Requires reliable internet access and digital literacy. |
| Peer Support Groups | Offer support and encouragement from individuals with similar experiences. | Demonstrated effectiveness in reducing isolation and promoting self-management. | Requires trained facilitators and ongoing support. |
Illustrative Case Studies: Global Surveys Find Mental Disorders Often Untreated
Untreated mental disorders can have a devastating impact on individuals, leading to a cascade of negative consequences that affect various aspects of their lives. Understanding these impacts is crucial to advocating for early intervention and effective treatment. This section presents fictional case studies to illustrate the far-reaching effects of untreated mental illness.The stories presented here, while fictional, are designed to highlight the common experiences of individuals struggling with mental health challenges.
Global surveys consistently show a troubling trend: mental health disorders often go untreated. This highlights a critical need for better access to care and resources. Interestingly, Microsoft’s commitment to security, as explored in their recent report on microsoft security and the road ahead , could potentially offer valuable insights into how to address similar challenges in healthcare, particularly regarding data privacy and accessibility.
Ultimately, the issue of untreated mental health disorders demands a multi-faceted approach, encompassing both individual support and systemic improvements.
They are meant to underscore the importance of seeking help and the potential for recovery with appropriate support and treatment.
Impact on Personal Relationships
Untreated mental disorders can strain and ultimately damage relationships with family, friends, and romantic partners. These disorders often manifest in behaviors that are difficult for others to understand and cope with. Difficulties in communication, emotional regulation, and trust can create significant distance and conflict, leading to isolation and loneliness.
Impact on Academic and Professional Performance
Individuals struggling with untreated mental disorders often experience difficulties in their academic or professional pursuits. Symptoms like anxiety, depression, and difficulty concentrating can significantly impact productivity, motivation, and overall performance. This can lead to missed opportunities, setbacks in career progression, and a decline in self-esteem.
Impact on Physical Health
Untreated mental disorders can have a profound impact on physical health. Chronic stress associated with mental health issues can weaken the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to physical illnesses. Poor self-care, including inadequate nutrition and lack of exercise, can further exacerbate physical health problems. Mental health struggles can also contribute to substance abuse as a coping mechanism, further impacting physical well-being.
Impact on Daily Functioning
Untreated mental disorders can severely disrupt daily functioning. Individuals may struggle with basic tasks like personal hygiene, managing finances, or maintaining household responsibilities. This can lead to further isolation and dependence on others, creating a vicious cycle of decline. These challenges often stem from difficulties with memory, concentration, and decision-making, making it hard to engage in even the most fundamental activities of daily life.
“Sarah, a bright young woman in her early twenties, struggled with undiagnosed and untreated bipolar disorder. Initially, her mood swings were attributed to typical teenage angst. As the disorder worsened, her relationships fractured, her academic performance plummeted, and she developed a dependence on caffeine and sugar to cope with the manic episodes. The lack of treatment led to a spiral of self-destructive behaviors, including risky financial decisions and social isolation. She ultimately lost her apartment and her job, highlighting the devastating consequences of untreated mental illness on all aspects of life.”
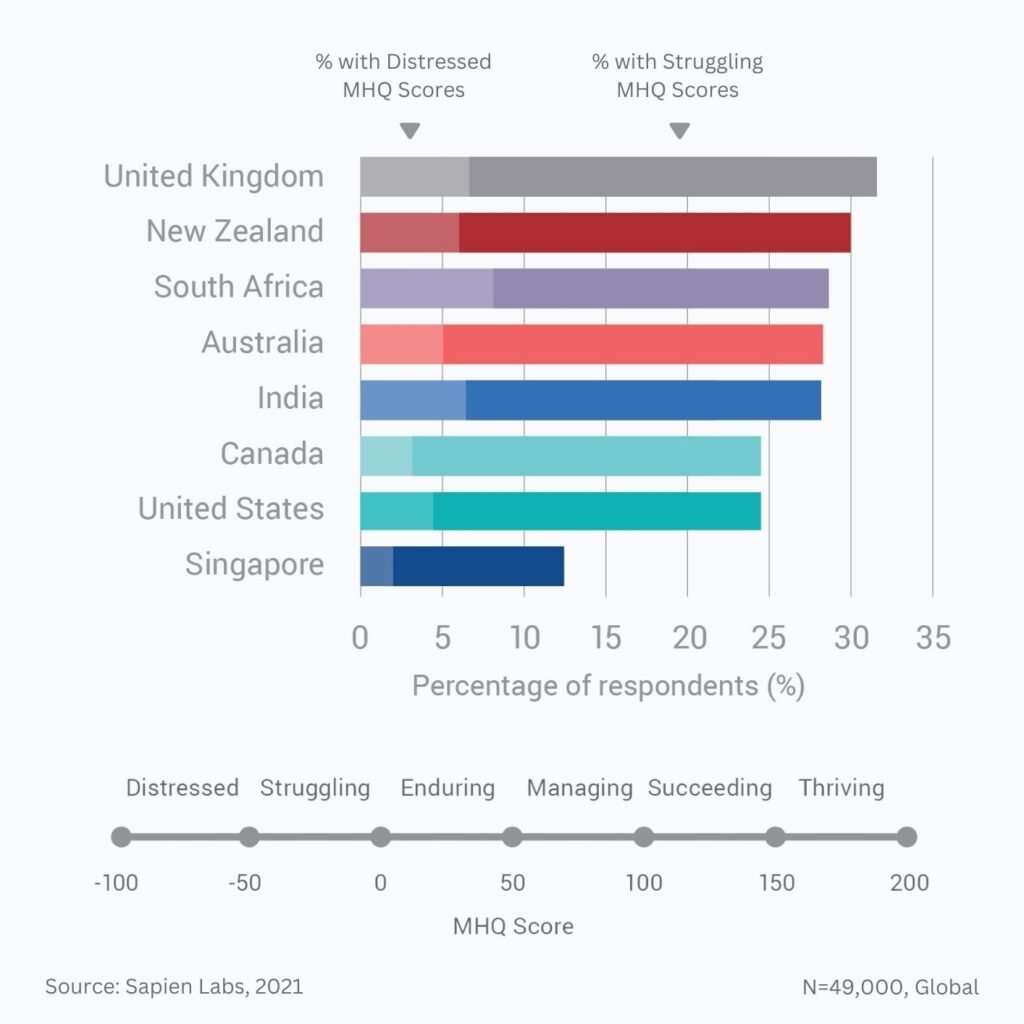
Global Comparisons and Trends
A critical look at mental health reveals significant disparities in treatment access and approaches across the globe. Understanding these variations is essential for developing effective, culturally sensitive strategies to address the global mental health crisis. The uneven distribution of resources, varying cultural perceptions of mental illness, and differing levels of government investment all contribute to these disparities.The global landscape of mental health is marked by a complex interplay of factors that significantly influence treatment access and outcomes.
These factors include economic development, cultural norms surrounding mental health, and the availability of trained mental health professionals. Recognizing these diverse influences is crucial to crafting effective interventions that can bridge the gaps in care and improve mental well-being globally.
Regional Variations in Mental Health Treatment Access
Different regions exhibit distinct approaches to mental healthcare, often shaped by unique historical, cultural, and socioeconomic factors. These variations affect not only the prevalence of mental disorders but also the methods employed for diagnosis, treatment, and support. For example, some cultures might emphasize community-based support systems, while others prioritize individual therapy. These differences can influence the types of services offered and the populations reached.
Prevalence and Treatment Approaches in Different Regions
The prevalence of mental disorders varies significantly across different regions. Factors such as socioeconomic status, cultural stigma, and access to healthcare services play a crucial role in shaping these variations. In some developed nations, mental health services are often integrated into primary care, making them more accessible. However, in other parts of the world, mental health services are less readily available, leading to higher rates of untreated mental illnesses.
Cultural perceptions surrounding mental illness also contribute to these differences, with some cultures exhibiting a stronger stigma than others. This stigma can discourage individuals from seeking help, thus exacerbating the issue.
Comparison of Mental Health Policies Across Regions
A comparative analysis of mental health policies across regions reveals substantial differences in approach and effectiveness. Different countries prioritize varying aspects of mental healthcare, reflecting diverse social values and economic priorities. Some nations focus on preventative care, while others emphasize treatment of acute crises. Effective policies often combine these approaches. For example, a comprehensive strategy might include early intervention programs for adolescents, access to affordable therapy for adults, and specialized support for individuals with severe mental illness.
| Region | Mental Health Policy | Effectiveness | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| North America | Integration of mental health into primary care, emphasis on prevention | Generally high access, but disparities exist | Cost of care, access to specialized services for complex cases |
| Europe | National health systems with varying levels of mental health integration | High levels of access in many countries, but some variations | Cultural sensitivity, stigma reduction efforts, affordability of treatments |
| South Asia | Limited resources, cultural stigma surrounding mental illness | Low access and high rates of untreated conditions | Community-based programs, culturally appropriate interventions, training of mental health professionals |
| Sub-Saharan Africa | Limited resources, shortage of trained mental health professionals | Very low access, significant burden of untreated conditions | Strengthening healthcare infrastructure, training local personnel, culturally sensitive interventions |
Outcome Summary
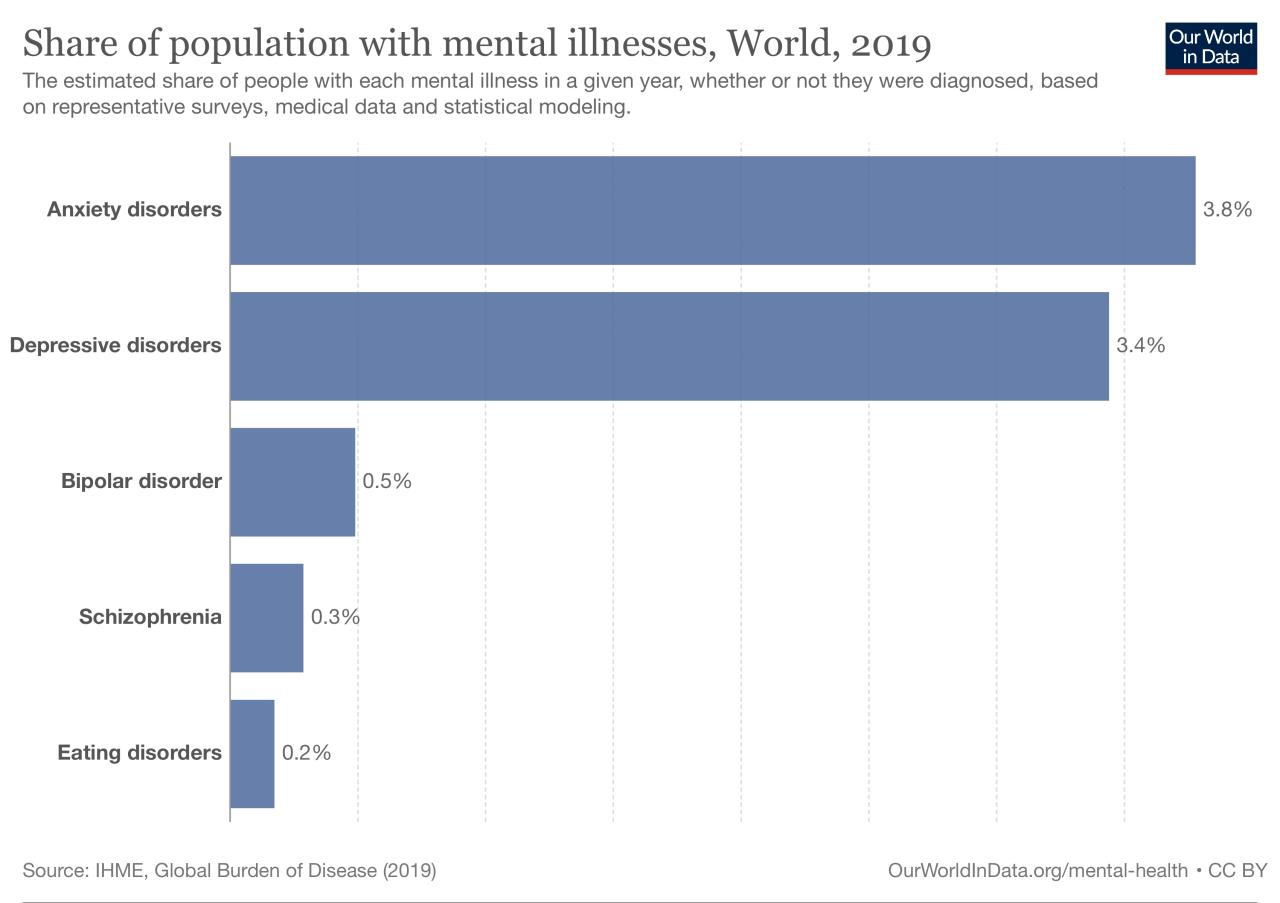
In conclusion, the global prevalence of untreated mental disorders is a stark reminder of the critical need for improved access to mental healthcare. This issue transcends geographical boundaries and socioeconomic disparities, impacting individuals and communities worldwide. While the challenges are significant, there’s hope for positive change. By understanding the barriers, embracing innovative solutions, and supporting community-based interventions, we can move toward a future where mental health is prioritized and everyone has the opportunity to thrive.
This discussion has highlighted the urgency and complexity of this global crisis and the critical need for collective action.