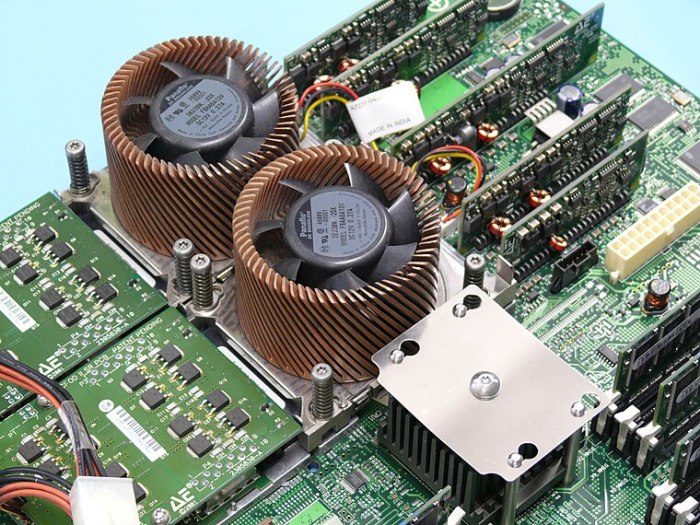
HP Moving Forward on Itanium Server Switch
HP moving forward on plans for Itanium server switch signals a significant shift in the server landscape. This decision, impacting existing users and the broader IT infrastructure, warrants careful consideration. We’ll delve into HP’s historical Itanium strategy, analyze the “moving forward” aspect, and explore potential customer and partner implications. Alternative server technologies and market trends will also be examined, along with the potential ripple effects on the IT infrastructure.
The transition away from Itanium, while potentially disruptive, offers a chance to understand the motivations behind the change. This analysis aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the situation and its broader industry context. From historical deployments to potential future adaptations, this discussion aims to provide clarity and insight for all stakeholders.
Background on HP’s Itanium Server Strategy
HP’s Itanium server strategy has evolved significantly over the years, reflecting the changing landscape of server technology and market demands. Initially a strong commitment to a proprietary architecture, HP’s Itanium deployments have faced challenges as the x86 architecture gained dominance. This evolution and the subsequent decisions regarding support and future plans have had a substantial impact on existing Itanium users.The Itanium platform, developed by Intel and initially supported by HP, offered unique performance characteristics.
However, its adoption rate was lower compared to the broader x86 ecosystem. This, coupled with increasing competition and the changing demands of the market, has led to the adjustments in HP’s strategy.
Historical Overview of HP’s Itanium Server Deployments
HP’s involvement with Itanium servers began with the introduction of the architecture. Early deployments focused on specific niches, leveraging the specialized features of Itanium, such as its ability to handle complex calculations. Over time, however, the broader server market shifted toward x86 processors, impacting the viability of Itanium-based solutions.
Current Status of Itanium Server Support from HP
HP’s current support for Itanium servers is a crucial aspect of this discussion. HP provides ongoing support for existing Itanium servers, though the extent of this support varies. Information on the exact scope of support should be readily available on HP’s official website. HP continues to provide some level of maintenance and technical assistance for these systems.
HP’s Announcements Regarding the Future of Itanium
HP has made public statements regarding the future of Itanium server support. These announcements often Artikel the timeline for support and the implications for existing users. It is essential to refer to official HP communications for precise details on this aspect.
HP’s continued push on Itanium server switch plans is interesting, given the current market trends. While server technology is crucial, the mobile gaming industry is rapidly becoming a major wireless cash cow, with mobile gaming latest wireless cash cow generating significant revenue. This shift in consumer demand might influence HP’s approach to server solutions, potentially leading to more innovative and adaptable designs for the future.
Ultimately, HP’s Itanium plans will need to adapt to the evolving technological landscape.
Reported Plans for Transitioning Away from Itanium
Reports suggest that HP is planning to reduce or eventually end its support for Itanium servers. These transitions are often gradual, allowing time for customers to migrate to alternative architectures. The specific timelines and details are crucial to understanding the impact on current Itanium users.
Potential Impact of These Plans on Existing Itanium Users
The impact on existing Itanium users is significant. The cessation of support could lead to difficulties in maintenance, upgrades, and potential security vulnerabilities. Users will need to carefully assess their needs and plan for a transition to a compatible platform.
Comparison of HP’s Itanium Server Offerings Over Time
| Generation | Key Features | Performance Characteristics ||—|—|—|| Itanium 1 | Early adoption, specific niche applications | Moderate performance, suitable for specific use cases || Itanium 2 | Improved performance, enhanced scalability | Enhanced performance compared to the first generation || Subsequent Generations | Further improvements in performance and efficiency | Varying performance improvements based on the specific generation |
Analysis of the “Moving Forward” Aspect

The phrase “moving forward” in relation to HP’s Itanium server strategy implies a decision point. It suggests HP is actively considering its options and planning for a future without exclusive reliance on Itanium processors. This signifies a potential shift in their approach to server architectures, and understanding the rationale behind this shift is crucial to predicting the impact on the market.HP’s use of “moving forward” implies a proactive, strategic response to changing market conditions and technological advancements.
It highlights a company acknowledging the need for adaptability in the face of evolving server needs and competitor actions. This proactive approach positions HP to adjust its offerings in response to emerging trends and customer demands.
Potential Timelines for HP’s Decisions
HP’s decisions regarding Itanium are likely to be phased, rather than immediate. A complete switch from Itanium to another architecture would likely involve a transition period for customers. This is often characterized by a period of support for existing Itanium-based systems, followed by a gradual introduction of new, alternative solutions. Historical examples of similar transitions in technology indicate a timeline spanning several years, allowing for existing contracts to be fulfilled and new systems to be rolled out gradually.
HP’s continued push on Itanium server switch plans is interesting, especially considering the recent developments in telephony. VoIP Inc’s Sr. Rodriguez, in a recent discussion about the state of telephony, voip inc s rodriguez discusses state of telephony , highlighted the need for robust, reliable infrastructure. This suggests HP’s Itanium server strategy might be a key component in future VoIP solutions, potentially leveraging the established reliability of Itanium systems.
This process typically includes deprecation notices, upgrade incentives, and support for existing clients, all aimed at mitigating disruption.
Potential Reasons Behind HP’s Plans for the Itanium Server Switch
Several factors could be driving HP’s decision to move away from Itanium. These include:
- Decreased demand for Itanium-based servers.
- Difficulty in attracting new talent and engineers to maintain Itanium support.
- Shifting market trends towards more widely adopted architectures, like x86.
- Higher development costs associated with Itanium-specific hardware and software.
- Potential for increased profitability by focusing on more commercially successful platforms.
The declining demand for Itanium servers suggests that customers are increasingly migrating to alternative technologies. This trend often correlates with the diminishing availability of specialized talent to support the older technology. The shift towards more widely used architectures, like x86, provides significant advantages in terms of software support and ecosystem development. This often results in cost reductions and faster time-to-market for new products.
Comparison of HP’s Itanium Strategy with Competitors
HP’s strategy regarding Itanium stands in contrast to some competitors who have maintained or expanded their support for this architecture. This difference highlights differing priorities and market positioning. Understanding how competitors manage their own Itanium strategies can provide insights into the rationale behind HP’s choices.
Potential Consequences of a Server Switch on HP’s Market Share
A server switch could have a significant impact on HP’s market share. A smooth transition could limit disruption, while a poorly executed change could result in lost customers and market share. The company must consider the potential for customer churn and the need for strategic marketing to maintain a competitive edge.
Key Factors Influencing HP’s Decision
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Market Demand | The level of demand for Itanium-based servers from current and potential customers. |
| Technological Advancements | The evolution of alternative server architectures and their suitability for current and future needs. |
| Financial Considerations | The cost of maintaining Itanium support versus the potential gains from transitioning to a different platform. |
| Competitive Landscape | The strategies and actions of competitors in the server market, particularly in relation to Itanium. |
These factors will significantly influence HP’s decisions. Understanding the interplay between these factors is crucial for predicting the outcome of HP’s strategy.
Potential Impact on Customers and Partners
HP’s decision to shift its focus on Itanium server strategy will undoubtedly ripple through its customer base and partner ecosystem. Understanding these potential impacts is crucial for both HP and those who rely on Itanium technology. This analysis delves into the likely effects on customers and partners, along with potential adaptation strategies.
Potential Effects on HP’s Customer Base
HP’s customer base is diverse, ranging from large enterprises leveraging Itanium for mission-critical applications to smaller businesses using the platform for specific needs. The transition away from Itanium will affect these segments differently. Enterprise customers heavily invested in Itanium infrastructure will face challenges in migrating to alternative platforms, potentially incurring significant costs and downtime. Smaller businesses, on the other hand, might find the shift less disruptive, depending on the complexity of their applications and their willingness to adapt.
Implications for Partners Relying on Itanium Servers
Partners who specialize in Itanium server support and maintenance will likely experience a reduction in demand as HP reduces its focus. This could lead to a need for diversification in their service offerings or a shift towards other server platforms. The impact will vary depending on the scale of their Itanium-specific business and their ability to adapt to the evolving market.
HP is pressing ahead with its Itanium server switch plans, a testament to their commitment to this powerful architecture. However, the current landscape is quite dynamic, with the mobile phone OS battle heating up, as seen in mobile phone os battle heats up. This competitive environment, though seemingly unrelated, highlights the need for companies like HP to stay agile and adaptable, continuing to invest in their Itanium server strategy for long-term success.
Strategies for Existing Itanium Users to Adapt
Existing Itanium users should proactively evaluate their application needs and potential migration paths. Assessing the feasibility of porting applications to alternative platforms, such as those based on Intel architecture, is critical. Considering the long-term implications of continued Itanium use, including potential software compatibility issues and support availability, is essential. Some companies might explore hybrid approaches, maintaining a portion of their infrastructure on Itanium while gradually transitioning others.
Potential Solutions for Customers Seeking to Continue Using Itanium
For customers desiring to continue using Itanium servers, HP might offer extended support options or specialized maintenance packages. This could include dedicated support teams, software updates, and compatibility testing for existing applications. The availability and specifics of these solutions will depend on the market demand and HP’s assessment of long-term Itanium support viability.
Summary of Customer Segments and Potential Responses
| Customer Segment | Likely Response |
|---|---|
| Large Enterprises with Mission-Critical Applications | Potential significant cost and downtime during migration; likely explore hybrid solutions to minimize disruption. |
| Smaller Businesses with Specific Needs | May be less affected depending on application complexity and willingness to adapt. |
| Partners Specializing in Itanium Support | Potential need to diversify services or transition to other platforms. |
Alternative Server Technologies and Their Comparisons
HP’s Itanium server strategy faces a challenging landscape with the rise of competing architectures. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of alternative technologies, such as x86 and ARM, is crucial for evaluating the future viability of Itanium and its potential impact on customers. This analysis delves into the comparative performance, cost, and compatibility aspects of these architectures.
Alternative Architectures: A Brief Overview, Hp moving forward on plans for itanium server switch
Modern server architectures encompass a spectrum of technologies, each optimized for different workloads and use cases. x86, the dominant architecture in the server market, leverages a well-established ecosystem of software and hardware. ARM, initially known for mobile devices, has increasingly gained traction in server environments due to its power efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Each architecture presents unique advantages and disadvantages that must be carefully considered.
x86 Architecture: Strengths and Weaknesses
x86, based on the Intel and AMD instruction sets, dominates the server market due to its broad software compatibility and extensive ecosystem. This translates into readily available software, drivers, and tools, reducing development time and costs for users. However, x86’s reliance on complex multi-core processors can lead to higher energy consumption compared to some alternatives, especially in workloads with low CPU utilization.
Furthermore, the ongoing need for constant hardware upgrades to maintain performance can be a significant cost factor over time.
ARM Architecture: Advantages and Drawbacks
ARM processors, used extensively in mobile devices, are increasingly used in server applications. Their efficiency and cost-effectiveness make them particularly attractive for specific workloads like cloud computing, IoT, and edge computing, where power consumption is critical. However, the software ecosystem for ARM servers is still developing, limiting the range of applications they can support. Finding compatible software and ensuring performance benchmarks can be a significant barrier for users.
While ARM is gaining traction, it is not yet as mature as x86 in the server space.
Itanium vs. Alternatives: A Comparative Analysis
The following table Artikels a comparative analysis of Itanium, x86, and ARM architectures. It highlights key differences in performance, cost, and compatibility.
| Feature | Itanium | x86 | ARM |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Historically strong in specific computationally intensive tasks. | Excellent overall performance across a wide range of workloads. | Growing performance in specific areas, but often with tradeoffs in certain workloads. |
| Cost | Historically higher initial cost due to specialized hardware. | Generally cost-effective due to high market share and mature supply chains. | Often more cost-effective in terms of power consumption and overall hardware cost. |
| Compatibility | Limited software compatibility, requiring significant porting efforts. | High software compatibility with a broad ecosystem. | Developing software ecosystem, potentially limiting applications in the short term. |
Potential Adoption by HP Customers
HP customers will need to carefully evaluate their specific workloads and requirements when considering alternative architectures. For customers with demanding computational needs, x86 remains a strong contender. Customers focused on energy efficiency and cost-effectiveness may find ARM increasingly attractive, especially as the software ecosystem matures. Itanium’s future in the market will depend on its ability to adapt to these changing dynamics and compete with alternatives on cost and compatibility.
Market Trends and Industry Developments: Hp Moving Forward On Plans For Itanium Server Switch
The server market is dynamic, constantly evolving with new technologies and shifting customer demands. HP’s decision to re-evaluate its Itanium server strategy must consider these trends to ensure long-term viability and customer satisfaction. Understanding the current landscape and potential future developments is critical for making informed choices.
Current Market Trends in Server Technology
The server market is experiencing a significant shift towards cloud-based computing, virtualization, and increasingly specialized hardware solutions. This shift is impacting the demand for traditional server architectures and driving innovation in areas like high-performance computing (HPC) and edge computing. The rise of containerization and microservices architectures is further influencing the need for flexible and scalable server infrastructure. These trends require businesses to adapt their strategies and offerings to remain competitive.
Key Industry Developments Influencing HP’s Decision
Several key industry developments could significantly impact HP’s Itanium server strategy. The increasing adoption of x86-based servers, coupled with the advancements in cloud computing infrastructure, has made a substantial impact on the market. This trend has resulted in a significant reduction in the demand for specialized server architectures, like Itanium. Furthermore, the rise of hyperscalers and their focus on standardized hardware solutions has created an environment where specialized platforms face increasing challenges.
Evolving Customer Demands in the Server Market
Customers are increasingly seeking solutions that offer enhanced scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. They prioritize the ability to adapt to fluctuating workloads and to optimize resource utilization. The need for greater agility in deployment and management of server infrastructure is also becoming a crucial factor. These evolving demands necessitate a deep understanding of customer requirements and a flexible approach to meeting them.
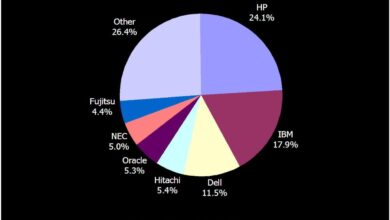
Market Share of Different Server Technologies
The following table provides a snapshot of the estimated market share of various server technologies. Note that these figures are approximations and may vary depending on the source and specific measurement criteria. This data is crucial for understanding the relative position of different server architectures in the market.
| Server Technology | Estimated Market Share (%) |
|---|---|
| x86-based servers | 80-90 |
| ARM-based servers | 5-10 |
| Other specialized architectures (including Itanium) | <5 |
Potential Long-Term Market Implications of the Switch
A decision to discontinue support for Itanium servers could lead to a loss of existing customers reliant on this architecture. However, it also presents an opportunity to refocus resources on more commercially viable platforms. The potential impact on HP’s brand image and reputation as a provider of innovative server solutions is significant. It is important to weigh the short-term costs against the long-term benefits of such a strategic shift.
An analysis of the specific applications that currently use Itanium servers is crucial in assessing the potential for migration to alternative solutions.
Potential Implications for the IT Infrastructure Landscape

HP’s planned Itanium server switch represents a significant shift in the IT infrastructure landscape, potentially reshaping the way businesses operate and interact with technology. This transition demands careful consideration of its ripple effects on existing systems, software, and the overall IT ecosystem. The implications extend beyond hardware, impacting software development, maintenance, and even business strategies.
Impact on Existing IT Components
The introduction of a new Itanium server switch will necessitate adjustments in various IT components. This is a critical aspect to understand to assess the potential challenges and opportunities. Existing infrastructure, including networking equipment, storage systems, and operating systems, might require upgrades or reconfigurations to seamlessly integrate with the new Itanium-based architecture. This ripple effect could influence the choice of other related technologies.
- Networking Infrastructure: The switch will likely demand specialized networking hardware and software optimized for Itanium’s unique characteristics. This might involve upgrading existing routers, switches, and firewalls to support the new architecture’s communication protocols. A transition to network virtualization technologies could also be considered.
- Storage Systems: Data storage solutions need to be compatible with the Itanium server architecture. This could involve selecting storage arrays that offer high performance and scalability to handle the increasing data volume expected with this new system. Existing SAN or NAS configurations may need adjustments.
- Operating Systems: The Itanium server switch will likely require specific operating system versions tailored to its architecture. The availability of compatible operating systems and their performance characteristics will be crucial for seamless integration. This might necessitate training staff to manage and maintain the new OS.
Potential Ripple Effects on Related Technologies
The shift to Itanium servers will have a cascade effect on other technologies and processes. The selection of hardware, software, and overall infrastructure design will be tightly coupled with the new server switch. The long-term impact will depend on the extent of compatibility with existing systems.
- Database Management Systems (DBMS): Existing DBMS applications might need adjustments to ensure seamless integration with the Itanium-based servers. This may involve selecting database solutions optimized for Itanium architecture.
- Application Software: Applications reliant on existing hardware platforms might require modifications or recompilation to run efficiently on the Itanium server switch. This could impact software maintenance and development cycles. Existing legacy applications may require careful migration or replacement.
Impact on Businesses
The transition to the Itanium server switch presents both challenges and opportunities for businesses. The scale and complexity of the transition will depend on the current IT infrastructure and the chosen implementation strategy.
| Business Aspect | Potential Challenges | Potential Opportunities |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Significant upfront investment in new hardware and software upgrades. | Potential cost savings in the long run through increased efficiency and performance. |
| Time | Transition periods and potential downtime during upgrades. | Potential for enhanced productivity and improved IT operations once the transition is complete. |
| Personnel | Need for specialized personnel and training. | Creation of new job roles and career development opportunities. |
Software Development and Maintenance Considerations
The switch to Itanium servers will undoubtedly impact software development and maintenance procedures. The need for specialized tools and expertise is a key factor.
“The new architecture requires a shift in software development methodologies, from development to deployment and maintenance.”
The impact on software development teams could be significant, as they will need to adapt to the new Itanium-based architecture and potentially learn new programming languages or tools. Software maintenance will require addressing potential compatibility issues and ensuring that applications continue to function effectively.
Closing Summary
HP’s decision to move forward on plans for the Itanium server switch presents a complex scenario with significant implications for the IT industry. The analysis underscores the importance of understanding the motivations, potential impacts, and alternative technologies. Ultimately, this transition will shape the future of server technology and will be crucial for HP to adapt to evolving market demands.
By examining alternative technologies and market trends, a clearer picture of the future of server architecture emerges.