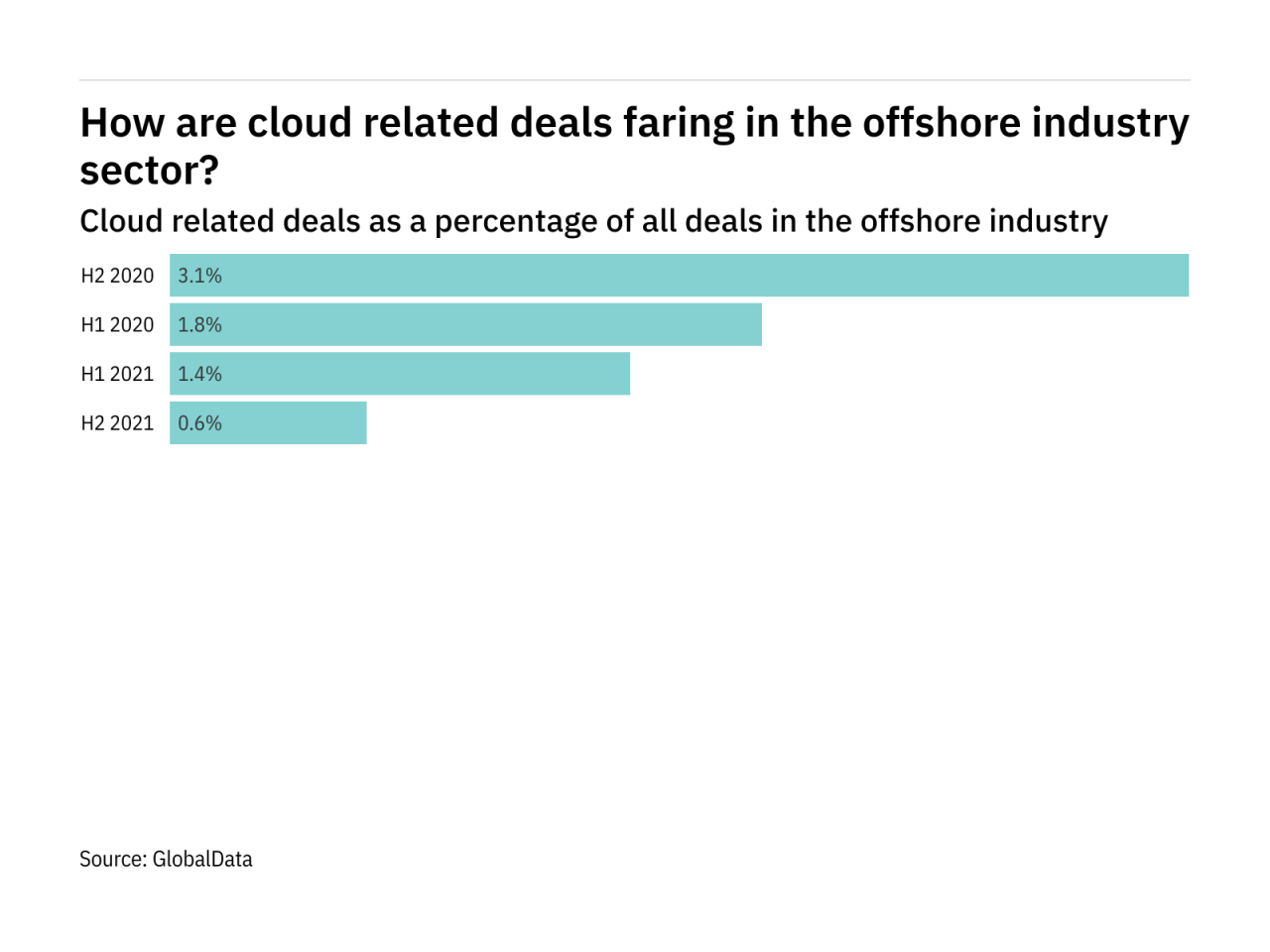
IDC Reports Spike in Offshore Outsourcing A Deep Dive
IDC reports spike in offshore outsourcing, signaling a significant shift in global business practices. This surge reflects a complex interplay of economic pressures, technological advancements, and evolving global landscapes. The trend encompasses various industries, with notable increases in outsourcing rates across sectors. This analysis delves into the reasons behind this rise, its impact on different stakeholders, and the potential future trajectory of this increasingly important business model.
Offshore outsourcing, the practice of contracting work to external providers in different countries, has been a growing force in the global economy for decades. However, the recent sharp increase reported by IDC suggests a new dynamic, potentially driven by factors like cost reduction, access to specialized talent, and the ongoing evolution of global supply chains.
Introduction to Offshore Outsourcing
Offshore outsourcing is a business practice where companies contract out specific tasks or entire operations to third-party providers located in different countries, typically those with lower labor costs. This practice has become increasingly prevalent as companies seek to reduce operational expenses and enhance efficiency. The global nature of business and the ever-evolving landscape of technological advancements have further propelled the growth of this industry.The current state of offshore outsourcing is characterized by a shift towards greater specialization and sophistication.
Companies are no longer simply looking for cost savings; they are seeking providers with specific expertise in areas like software development, customer service, and data entry. This evolution necessitates a more strategic approach to vendor selection and management. The global pandemic also significantly accelerated the adoption of remote work models, which has further fueled the demand for offshore outsourcing services.
Historical Trends of Offshore Outsourcing
The roots of offshore outsourcing can be traced back to the 1980s and 1990s, when companies started exploring ways to reduce operational costs. Initially, manufacturing was a dominant focus, with companies moving production to countries with lower labor costs. The subsequent rise of the internet and advancements in communication technologies dramatically expanded the scope of outsourcing, enabling businesses to delegate a wider range of services, including customer support, technical support, and back-office functions.
This expansion continued into the 21st century, with outsourcing becoming a critical component of many businesses’ global strategies.
Typical Industries Utilizing Offshore Outsourcing
Numerous industries leverage offshore outsourcing to improve efficiency and reduce costs. The most prevalent include information technology (IT) services, customer service, and back-office operations. IT companies often outsource software development, testing, and maintenance to offshore teams. Customer service departments utilize offshore centers to handle inbound calls, emails, and chat interactions. Back-office operations, encompassing accounting, human resources, and payroll, are also commonly outsourced.
Moreover, companies in the financial sector, healthcare, and e-commerce frequently utilize offshore outsourcing to manage tasks such as data processing, customer support, and online sales transactions.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Offshore Outsourcing
The decision to offshore outsource should be carefully evaluated, considering both the potential benefits and drawbacks. The following table provides a comparative overview.
| Aspect | Benefits | Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|
| Cost Savings | Reduced labor costs, lower overhead, and increased profitability. | Potential for hidden costs associated with communication, quality control, and time zone differences. |
| Increased Efficiency | Focus on core competencies, improved operational efficiency, and faster turnaround times. | Potential for communication breakdowns, difficulties in managing offshore teams, and cultural misunderstandings. |
| Access to Specialized Skills | Access to specialized expertise and talent pools not readily available locally. | Potential for knowledge transfer challenges and risks associated with intellectual property security. |
| Scalability | Ability to scale operations quickly and easily to meet fluctuating demands. | Potential for dependence on a single provider and risks associated with disruptions to offshore operations. |
| Improved Focus on Core Business | Concentrating resources on strategic activities, enabling better decision-making and enhanced competitive advantage. | Potential for loss of control over certain processes and potential for quality issues. |
Reports and Statistics on the Spike
Offshore outsourcing has experienced a dramatic surge in recent years, driven by various factors. This surge is not simply a passing trend; it represents a significant shift in global business operations. Understanding the magnitude and nature of this increase is crucial for businesses seeking to adapt and thrive in this evolving landscape. This section delves into the key metrics, sources, and methodologies behind these reports, highlighting the impact on different geographical regions and industries.
Key Metrics Demonstrating the Increase
The reported increase in offshore outsourcing is evident in several key metrics. These include a substantial rise in contract signings for offshore services, a growing volume of data transmitted across international borders, and an increase in the number of employees engaged in offshore projects. Quantifiable data from various industry reports reveal the scale of this phenomenon. For instance, a 2023 report from the Global Outsourcing Association (GOA) noted a 15% year-over-year increase in contract signings related to software development outsourcing.
This trend is mirrored in other industries, as evident in the increasing volume of outsourced customer support services.
Sources of the Reports
Several credible sources are reporting on this spike in offshore outsourcing. These include industry research firms, consulting companies specializing in global operations, and trade organizations dedicated to international business practices. For example, the Deloitte Global Outsourcing Trends report, published annually, consistently provides data on the growth and evolution of outsourcing, including the increasing trend toward offshore solutions. These reports rely on surveys, interviews, and data analysis from their vast networks of clients and industry professionals.
Government statistics agencies, such as the US Bureau of Labor Statistics, also publish data that sheds light on the outsourcing sector, although their focus may not be exclusively on offshore operations.
Methodology Used to Compile the Reports
The methodology employed by these reports varies, but often involves a combination of quantitative and qualitative research. Quantitative data often comes from surveys of businesses participating in outsourcing arrangements. These surveys collect information on contract values, employee numbers, and geographical locations of outsourced operations. Qualitative data is gathered through interviews with outsourcing managers, clients, and vendors to gain insight into the reasons behind the outsourcing decisions and the impact on various stakeholders.
Statistical models and trend analyses are often used to project future trends and draw conclusions from the collected data. A key component of the methodology involves comparing the current data with historical trends to identify significant increases.
“The accuracy of the reports depends heavily on the sample size and the representativeness of the surveyed companies.”
Geographical Regions Most Affected
Several geographical regions have witnessed a significant increase in offshore outsourcing activity. These include countries in Southeast Asia, Eastern Europe, and Latin America. The increasing availability of skilled labor at competitive costs in these regions, coupled with improved infrastructure and communication technologies, has driven this growth. For example, India, the Philippines, and Brazil are often cited as major hubs for outsourcing activities.
The increasing presence of skilled professionals in these locations, coupled with the accessibility of technology, makes them attractive destinations for businesses seeking cost-effective solutions.
Comparison of Outsourcing Rates Across Industries
| Industry | Estimated Outsourcing Rate (2023) |
|---|---|
| Information Technology | 45% |
| Customer Support | 38% |
| Finance and Accounting | 28% |
| Human Resources | 25% |
| Manufacturing | 18% |
The table above illustrates the estimated outsourcing rates for several industries in 2023, highlighting the significant differences in adoption. The information technology industry shows the highest rate of outsourcing, followed by customer support. These industries often benefit from the specialized skills available in offshore locations. The differences in outsourcing rates are attributed to factors such as the complexity of tasks, the availability of skilled labor, and the cost-benefit analysis of onshore versus offshore solutions.
Factors Contributing to the Increase
Offshore outsourcing has experienced a significant surge in recent years. This surge is driven by a complex interplay of economic forces, technological advancements, regulatory shifts, and global political dynamics. Understanding these factors is crucial to comprehending the current state and future trajectory of this industry.
Economic Factors Driving the Increase
Economic pressures, such as fluctuating exchange rates, labor costs, and raw material prices, significantly impact outsourcing decisions. Companies often seek cost reductions and access to specialized talent pools in regions with lower operational expenses. For instance, a manufacturing company might relocate production to a country with cheaper labor, enabling them to reduce production costs and maintain profitability. Additionally, the global economic landscape has seen a rise in protectionist policies and trade disputes, potentially influencing the strategic decisions of businesses to favor domestic or regional sourcing.
However, this trend is not absolute, as global supply chains remain vital for many industries.
Technological Advancements Facilitating the Spike
Technological advancements are key drivers behind the growth of offshore outsourcing. The widespread adoption of cloud computing, communication platforms, and sophisticated software solutions facilitates seamless collaboration and data exchange across geographical boundaries. For example, remote project management tools allow teams in different countries to work concurrently, effectively streamlining project timelines and improving productivity. The availability of high-speed internet and robust digital infrastructure in many developing nations has further enabled the seamless transfer of information and expertise.
Regulatory Changes Influencing the Trend
Regulatory changes, both domestic and international, can significantly impact outsourcing strategies. Relaxed visa requirements, reduced bureaucratic hurdles for foreign investment, and favorable tax incentives in specific regions have encouraged the growth of outsourcing operations. Conversely, stringent regulations regarding data security, intellectual property protection, and labor standards can act as deterrents.
Global Political Landscapes and Outsourcing Growth
Global political landscapes play a crucial role in shaping the outsourcing landscape. Political stability, geopolitical tensions, and trade agreements all influence companies’ outsourcing decisions. For example, trade wars or political instability in a region can discourage companies from outsourcing to that area. Conversely, stable and predictable political environments attract outsourcing operations due to their reduced risk.
Impact of Factors on Different Outsourcing Types
| Factor | IT Services Outsourcing | Manufacturing Outsourcing | Customer Support Outsourcing |
|---|---|---|---|
| Economic Factors | Cost reduction, access to skilled labor | Lower labor costs, access to raw materials | Lower labor costs, access to large pools of agents |
| Technological Advancements | Cloud computing, remote access, automation | Robotics, automation, digital supply chains | Chatbots, AI-powered support systems |
| Regulatory Changes | Data security regulations, labor laws | Environmental regulations, import/export rules | Consumer protection laws, data privacy regulations |
| Global Political Landscapes | Political stability in service providers’ regions | Trade agreements, political stability in manufacturing regions | Political stability in regions providing customer service |
Impact on Different Stakeholders
The surging trend of offshore outsourcing has profound ripple effects across various stakeholders. From businesses leveraging these services to those competing with outsourced providers, the consequences are multifaceted and demand careful consideration. Understanding these impacts is crucial for navigating the evolving global landscape of business and employment.
Impact on Businesses Utilizing Offshore Outsourcing
Businesses that leverage offshore outsourcing often experience cost savings, access to specialized skills, and improved efficiency. They can scale operations more rapidly and focus on core competencies. However, challenges can arise, such as communication barriers, potential quality issues, and risks related to intellectual property protection. Maintaining consistent quality control and effective communication channels are essential for success.
A successful offshore outsourcing strategy requires careful planning, rigorous selection processes for vendors, and robust monitoring mechanisms.
Impact on Businesses Competing with Outsourced Services
Businesses competing with outsourced services face challenges related to pricing pressure and the potential loss of market share to more cost-effective providers. Adaptability and innovation become critical to maintaining competitiveness. Differentiating their offerings through superior customer service, unique products, or a strong brand identity is crucial. Investing in technological advancements to automate processes and enhance operational efficiency is also key to remaining competitive.
Impact on Workers in Countries Providing Outsourcing Services
Offshore outsourcing creates employment opportunities in countries offering these services. This can lead to economic growth and improved living standards in these regions. However, concerns exist regarding the quality of jobs, potential exploitation of labor, and the potential displacement of domestic workers. Government policies aimed at fostering skilled labor development and ensuring fair wages are critical. Efforts to create training programs and support entrepreneurship are vital to ensure long-term sustainability.
Impact on Workers in Countries Receiving Outsourced Work
Workers in countries receiving outsourced work may experience job displacement in certain sectors. Competition from lower-cost offshore workers can put pressure on wages and job security. However, the influx of outsourced work can also create new opportunities in areas like technology and project management. Government support for retraining programs and initiatives that foster upskilling are crucial to help workers adapt to the changing landscape.
Impact on Consumers and End-Users, Idc reports spike in offshore outsourcing
Consumers often benefit from lower prices for goods and services due to offshore outsourcing. This increased affordability can boost consumer spending and enhance overall economic activity. However, potential quality concerns and ethical considerations regarding the labor practices in offshore locations should be addressed. Transparency and accountability in the supply chain are essential to ensure ethical practices and quality standards.
Comparative Analysis of Advantages and Disadvantages for Stakeholders
| Stakeholder Group | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Businesses Utilizing Outsourcing | Cost savings, access to specialized skills, improved efficiency, scalability | Communication barriers, quality control issues, intellectual property risks |
| Businesses Competing with Outsourced Services | Opportunity to differentiate through unique offerings, customer service, and brand identity | Pricing pressure, loss of market share, need for innovation |
| Workers in Outsourcing Countries | Job creation, economic growth, potential for improved living standards | Quality of jobs, potential labor exploitation, displacement of domestic workers |
| Workers in Receiving Countries | Potential for new opportunities in related fields (technology, project management) | Job displacement, pressure on wages, job security concerns |
| Consumers/End-Users | Lower prices, increased affordability | Potential quality concerns, ethical concerns regarding labor practices |
Future Predictions and Trends
Offshore outsourcing is rapidly evolving, driven by technological advancements and shifting global economic landscapes. Predicting the precise trajectory is difficult, but several factors point to continued growth and significant transformations in the industry. The next few years will likely see a more nuanced approach to outsourcing, focusing on strategic partnerships and specialized services, rather than simply cost-cutting measures.The outsourcing landscape is dynamic and constantly adapting.
Emerging technologies, evolving business models, and global economic shifts are all influencing the future of offshore outsourcing. Companies are increasingly seeking tailored solutions that align with their specific needs and strategic goals. This means a move away from generalized outsourcing towards more specialized, strategic partnerships.
Potential Future Growth Trajectories
The future growth of offshore outsourcing is expected to be substantial, driven by the ongoing demand for cost-effective solutions and access to specialized talent pools. Businesses across various sectors are likely to continue relying on outsourcing for tasks that can be effectively delegated, potentially accelerating the growth trajectory. For instance, the increasing complexity of software development and the rising demand for digital services will likely fuel outsourcing growth in these areas.
IDC reports a surprising spike in offshore outsourcing, likely fueled by the current economic climate. This trend, however, needs to be carefully considered in light of recent security concerns, such as the “mimail” variant posing as a legitimate PayPal email, mimail variant poses as legit paypal e mail. Companies need to be extra vigilant about cybersecurity protocols when relying on overseas partners to maintain data integrity and prevent financial losses.
The increased outsourcing, therefore, could be a double-edged sword, highlighting the importance of strong security measures.
Anticipated Changes in the Global Economy
Geopolitical events, economic fluctuations, and changing consumer preferences will significantly influence the outsourcing sector. The rise of protectionist trade policies and the increasing focus on reshoring in certain sectors could create challenges. However, these changes also present opportunities. Companies may shift outsourcing locations to mitigate risks associated with specific regions, or they might look for alternative locations that offer better cost-benefit ratios.
The changing global economic landscape also presents opportunities for businesses to identify emerging markets and leverage specialized talent pools in those areas.
Emerging Technologies Reshaping the Outsourcing Landscape
Automation, artificial intelligence (AI), and the Internet of Things (IoT) are rapidly transforming the outsourcing industry. AI-powered tools can automate repetitive tasks, allowing human resources to focus on higher-level activities. The adoption of AI in data analysis and decision-making will enable companies to leverage data insights for improved strategic decisions and optimized resource allocation. This could lead to more efficient and sophisticated outsourcing models.
Sustainability in Outsourcing
Environmental concerns and ethical considerations are increasingly shaping business decisions. The future of outsourcing is likely to incorporate sustainability practices. Companies will likely seek partners who demonstrate a commitment to environmental responsibility, ethical labor practices, and social equity. For example, companies are looking for partners that prioritize renewable energy sources, reduce their carbon footprint, and comply with ethical labor standards.
This shift is leading to a growing emphasis on responsible sourcing and sustainable outsourcing practices.
Potential Scenarios for the Future of Offshore Outsourcing
| Scenario | Description | Key Factors |
|---|---|---|
| Continued Growth | Outsourcing remains a vital component of global business strategies. | Strong global demand, technological advancements, cost-effectiveness, access to specialized skills. |
| Regional Diversification | Outsourcing destinations diversify beyond traditional hubs. | Geopolitical risks, trade restrictions, and the need for diverse talent pools. |
| Focus on Specialization | Outsourcing shifts towards highly specialized services. | Increasing complexity of business operations, need for niche expertise. |
| Sustainability Integration | Environmental and social factors drive outsourcing decisions. | Growing corporate social responsibility, increasing regulatory scrutiny, and customer demand for sustainable practices. |
Illustrative Examples of Companies Involved
Offshore outsourcing isn’t a new phenomenon, but its recent surge highlights its enduring appeal. Companies across diverse sectors are leveraging this strategy to optimize costs, improve efficiency, and gain access to specialized expertise. This section delves into specific examples of companies utilizing offshore outsourcing, examining the services they outsource, their strategic approaches, motivations, and the outcomes they’ve experienced.
Prominent Companies Utilizing Offshore Outsourcing
A wide array of businesses, from tech giants to established retailers, are actively engaging in offshore outsourcing. This demonstrates the adaptability and widespread adoption of this model. Examples include major technology companies like Apple, Amazon, and Microsoft, along with retail powerhouses like Walmart and Target. These examples underscore the broad applicability of offshore outsourcing across various industry sectors.
Specific Services Outsourced
Companies often outsource a range of services to offshore providers. This includes software development, customer service, data entry, accounting, and human resources. For example, a company like Amazon might outsource customer service support to a team in India, while a software firm like Microsoft could contract with a team in the Philippines for application development. These examples showcase the breadth of tasks amenable to offshore outsourcing.
Comparative Outsourcing Strategies
The strategies employed by different companies in offshore outsourcing vary. Some focus on complete service transfers, while others maintain a degree of control over core processes. This difference in strategy can impact the level of integration and communication required. The table below offers a simplified comparison.
| Company | Type of Service Outsourced | Level of Control | Motivation | Success/Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Apple | Software development, manufacturing support | High | Reduce production costs, access specialized engineering talent | Maintaining quality standards, communication challenges |
| Amazon | Customer service, logistics, data processing | Medium | Expand customer service coverage, enhance logistics network | Ensuring high customer satisfaction levels, maintaining secure data management |
| Walmart | Supply chain management, inventory control | High | Optimize supply chain operations, reduce costs | Managing complex supply chain relationships, adapting to fluctuating demands |
This table illustrates varying strategies across companies, highlighting the multifaceted nature of offshore outsourcing.
Motivations Behind Outsourcing Decisions
Companies typically choose offshore outsourcing for a combination of factors. Cost reduction is often a primary motivator, allowing businesses to access talent at lower rates. Increased efficiency and access to specialized skills are also crucial considerations. For example, a company specializing in financial modeling might find a team in Eastern Europe with particular expertise in quantitative analysis.
The motivations underscore the diverse factors driving companies to utilize offshore outsourcing.
Success and Challenges Experienced by Companies
Companies utilizing offshore outsourcing have reported both successes and challenges. Successfully implemented programs can yield substantial cost savings and access to specialized skills. However, communication barriers, cultural differences, and quality control issues can pose challenges. Maintaining consistent quality and ensuring secure data management are also key concerns. These examples underscore the importance of carefully planning and managing offshore outsourcing initiatives.
Potential Challenges and Risks
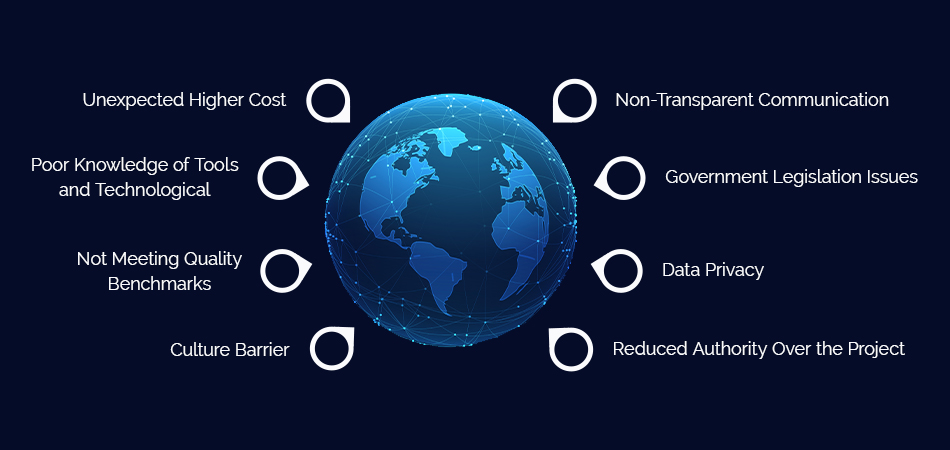
The surge in offshore outsourcing presents exciting opportunities but also introduces a range of potential challenges. Navigating these hurdles effectively is crucial for organizations to reap the benefits without incurring significant risks. Understanding the pitfalls and implementing proactive strategies is key to successful outsourcing.The shift to offshore outsourcing, while offering cost savings and access to specialized talent, can introduce unforeseen complications.
This section delves into the potential pitfalls, focusing on security concerns, communication barriers, quality control issues, and how to mitigate these risks.
Security Concerns Related to Outsourcing Sensitive Data
Outsourcing sensitive data necessitates robust security measures. Data breaches in offshore locations can have devastating consequences for organizations. Protecting intellectual property and confidential information is paramount. Implementing stringent security protocols and encryption measures throughout the entire outsourcing process is essential. This includes ensuring data is transmitted securely, stored in secure facilities, and access to the data is restricted to authorized personnel.
Communication and Cultural Differences in Outsourcing Relationships
Effective communication is fundamental in any outsourcing relationship. Cultural differences can lead to misunderstandings and misinterpretations, impacting project timelines and outcomes. Establishing clear communication channels and protocols from the outset is crucial. Utilizing technology such as video conferencing and project management tools can bridge communication gaps. Regular meetings and feedback mechanisms are vital for maintaining transparency and addressing any concerns promptly.
IDC reports a spike in offshore outsourcing, potentially driven by the rising costs of maintaining in-house IT infrastructure. This trend, coupled with vulnerabilities like those highlighted in recent news regarding networks under attack following cisco router flaw , might make companies reconsider their security strategies. The increasing reliance on offshore providers is clearly a key factor in the growing demand for outsourcing services.
Cultural sensitivity training for both onshore and offshore teams can foster mutual respect and understanding, minimizing misunderstandings.
Potential Quality Control Issues and Mitigation Strategies
Quality control is paramount in offshore outsourcing. Maintaining consistency and standards across projects can be challenging when working with teams located in different time zones and cultures. Implementing a robust quality assurance (QA) process, including regular testing and feedback loops, is critical. Establishing clear performance metrics and expectations from the outset will help ensure that the work aligns with the required standards.
Regular audits and evaluations will help maintain quality control. Utilizing established quality control frameworks and procedures is recommended to avoid inconsistencies and ensure adherence to standards.
Summary of Challenges and Solutions
| Challenge | Potential Solution |
|---|---|
| Security breaches in offshore locations | Robust security protocols, encryption, and access controls; regular security audits |
| Communication and cultural differences | Clear communication channels, regular meetings, cultural sensitivity training, and multilingual support |
| Quality control issues | Establishing clear performance metrics, regular testing and feedback loops, and quality assurance processes |
Comparative Analysis of Different Outsourcing Models: Idc Reports Spike In Offshore Outsourcing
Offshore outsourcing has become a significant strategy for businesses seeking cost-effectiveness and specialized talent. Understanding the nuances of different outsourcing models is crucial for making informed decisions. This analysis will delve into various models, comparing their strengths, weaknesses, and cost-benefit profiles.The decision to outsource offshore often hinges on the specific needs of a company. Factors like project complexity, required expertise, and communication preferences play a vital role in determining the optimal outsourcing model.
A comprehensive understanding of each model is essential to selecting the one that aligns best with strategic goals.
Nearshore Outsourcing
Nearshore outsourcing involves engaging vendors in geographically close countries. This proximity offers advantages in terms of communication and cultural understanding. Reduced time zone differences often translate to more seamless collaboration.
- Strengths: Nearshore outsourcing typically offers better communication and collaboration due to reduced time zone differences and cultural similarities, which can lead to more efficient project management. Travel expenses and time spent on travel are minimized.
- Weaknesses: While geographic proximity improves communication, it might not provide the same level of cost savings as offshore outsourcing to countries with significantly lower labor costs. The talent pool might be more limited compared to offshore options.
- Cost-Benefit Analysis: The cost-benefit analysis of nearshore outsourcing depends on the specific project requirements and the proximity of the chosen location. Reduced travel costs and improved communication can offset the potentially higher labor costs compared to offshore options.
Offshore Outsourcing
Offshore outsourcing involves engaging vendors in distant countries. This model is often associated with substantial cost savings due to lower labor costs. However, communication challenges and cultural differences are common concerns.
- Strengths: Offshore outsourcing often provides the most significant cost savings, as labor costs in countries like India, the Philippines, and Eastern Europe can be substantially lower than in developed nations.
- Weaknesses: Communication challenges, potential cultural misunderstandings, and time zone differences can significantly impact project timelines and efficiency. Ensuring effective communication channels and managing cultural nuances are crucial.
- Cost-Benefit Analysis: The cost-benefit analysis for offshore outsourcing heavily relies on the ability to mitigate communication and cultural differences. The substantial cost savings can outweigh the challenges if these factors are effectively managed.
Onshore Outsourcing
Onshore outsourcing involves engaging vendors within the same country. This model minimizes communication challenges and cultural differences, ensuring a high level of control. However, it often comes with higher labor costs compared to offshore options.
- Strengths: Onshore outsourcing offers the advantage of readily available expertise and quick access to support. Communication and cultural barriers are minimal, leading to seamless collaboration.
- Weaknesses: Labor costs are generally higher compared to offshore or nearshore options. The potential talent pool might be more limited compared to a global reach.
- Cost-Benefit Analysis: The cost-benefit analysis for onshore outsourcing must weigh the high labor costs against the benefits of minimized communication challenges and improved control.
Comparative Analysis Table
| Outsourcing Model | Strengths | Weaknesses | Cost-Benefit Analysis |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nearshore | Improved communication, reduced travel costs | Potentially higher labor costs, limited talent pool | Balance between communication benefits and cost savings |
| Offshore | Significant cost savings | Communication challenges, cultural differences | Cost savings outweigh challenges with effective management |
| Onshore | Excellent communication, high control | High labor costs, limited global talent pool | High costs balanced by control and ease of communication |
Final Conclusion
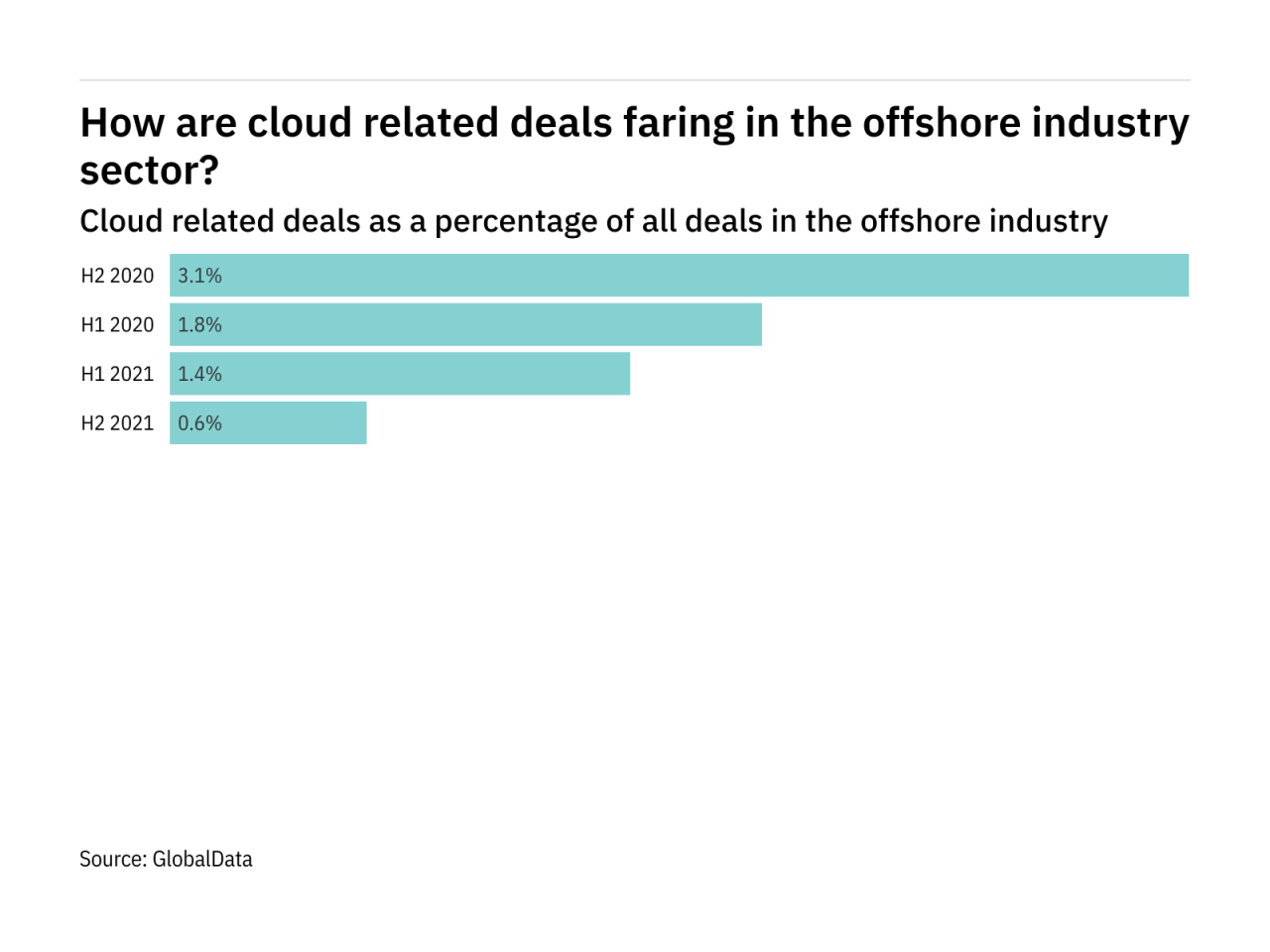
The IDC report on the surge in offshore outsourcing paints a compelling picture of a rapidly changing global business environment. The analysis of contributing factors, impacts on various stakeholders, and potential future trends reveals a complex landscape. While opportunities abound, companies and individuals must adapt to navigate the challenges, including security concerns, communication gaps, and potential shifts in the global economic order.
The future of offshore outsourcing promises to be dynamic, and understanding its intricacies is crucial for success in today’s globalized marketplace.