Intel Backs Clearwire WiMAX A Deep Dive
Intel throws weight behind Clearwire WiMAX, marking a significant move in the wireless communication landscape. This venture, steeped in Intel’s technological prowess and Clearwire’s WiMAX aspirations, promises an interesting look at the intersection of innovation and market forces. This exploration delves into the historical context, technical aspects, market analysis, and strategic considerations behind this partnership. What were the driving forces behind Intel’s investment, and what were the potential outcomes for both companies and the industry?
The partnership between Intel and Clearwire, focused on WiMAX technology, offers a fascinating case study in technology development. The history of both companies, their individual challenges, and the broader wireless market dynamics are crucial to understanding the intricacies of this strategic alliance. This analysis explores the fundamental principles of WiMAX, comparing its strengths and weaknesses to other competing technologies like 3G and 4G.
A key element will be examining the market analysis surrounding WiMAX adoption at the time of Intel’s involvement. Further, the strategic considerations for Intel, including potential benefits and risks, will be evaluated, as well as the potential synergies between their respective strengths. Finally, we’ll consider the overall impact on the wireless communication industry and the eventual outcome, learning the lessons of success and failure for both parties.
Background of Intel and Clearwire: Intel Throws Weight Behind Clearwire Wimax
Intel, a powerhouse in the semiconductor industry, has a long and storied history of innovation. From its humble beginnings as a small company focused on memory chips, Intel has consistently pushed the boundaries of technology, transforming personal computing and beyond. Its relentless pursuit of technological advancements has led to breakthroughs in microprocessors, memory, and other crucial components. Clearwire, on the other hand, emerged as a pioneer in the wireless communications arena, particularly in the WiMAX (Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access) standard.
This standard promised high-speed broadband access, but faced considerable challenges in its rollout.Intel’s investment in Clearwire reflects a strategic move to leverage its technological expertise and market presence in the burgeoning wireless broadband sector. The WiMAX technology, though initially promising, faced competition from other wireless standards like Wi-Fi and 3G. This competitive landscape, coupled with the need for substantial capital investment in infrastructure and network expansion, created a challenging environment for Clearwire.
Intel’s decision to partner with Clearwire, therefore, was not without its risks, but it likely stemmed from a calculated assessment of the long-term potential of WiMAX, potentially aligning with Intel’s broader strategy to dominate various sectors of the telecommunications ecosystem.
Intel Corporation: A Historical Overview
Intel Corporation, founded in 1968, has consistently revolutionized the semiconductor industry. Early successes focused on memory chips, laying the foundation for its future dominance in microprocessors. The introduction of the Intel 8086 microprocessor in the mid-1970s marked a pivotal moment, fueling the growth of personal computers. Intel’s relentless focus on innovation, coupled with aggressive marketing and strategic partnerships, propelled it to become a global leader in the semiconductor industry.
Key technological advancements include the development of increasingly powerful and energy-efficient microprocessors, along with advancements in memory technologies. This constant pursuit of progress, coupled with effective business strategies, enabled Intel to establish a strong presence across various industries.
Clearwire and the WiMAX Technology
Clearwire, established in 2001, was a key player in the development and deployment of WiMAX technology. WiMAX promised high-speed broadband access via wireless networks, aiming to compete with cable and DSL technologies. The initial market positioning of WiMAX was ambitious, envisioning a future where wireless broadband would become the dominant mode of internet access. However, the technology faced hurdles including significant infrastructure requirements and stiff competition from existing wireless standards like 3G and emerging Wi-Fi technologies.
The challenge of building out the necessary infrastructure and convincing consumers to adopt the technology proved to be significant obstacles for Clearwire.
Business Context: Intel’s Involvement with Clearwire
Intel’s involvement with Clearwire came at a crucial juncture in the wireless broadband market. The rise of mobile broadband and the expansion of 3G networks presented formidable competition. The wireless broadband market was still in its early stages, with significant uncertainty regarding the eventual winner of the standards war. Intel’s investment in Clearwire can be seen as a strategic bet on the long-term potential of WiMAX, while simultaneously potentially mitigating risk and establishing a foothold in the emerging wireless broadband market.
Intel likely recognized that the success of WiMAX would hinge on overcoming technological challenges, achieving widespread interoperability, and garnering sufficient consumer adoption.
Key Milestones in Intel and Clearwire’s Partnership
| Date | Event | Intel’s Role | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2005 | Intel invests in Clearwire | Strategic investment | Demonstrated confidence in WiMAX technology’s potential. |
| 2007 | Expansion of Clearwire’s network | Technological support and partnership | Provided Clearwire with Intel’s expertise in network infrastructure. |
| 2009 | Challenges with WiMAX adoption | Continued involvement in development and support | The technology’s potential proved more challenging to realize than anticipated. |
| 2010 | Clearwire’s restructuring | Partnership continued despite market shifts | Intel’s investment faced challenges in the face of a rapidly evolving market. |
WiMAX Technology Overview
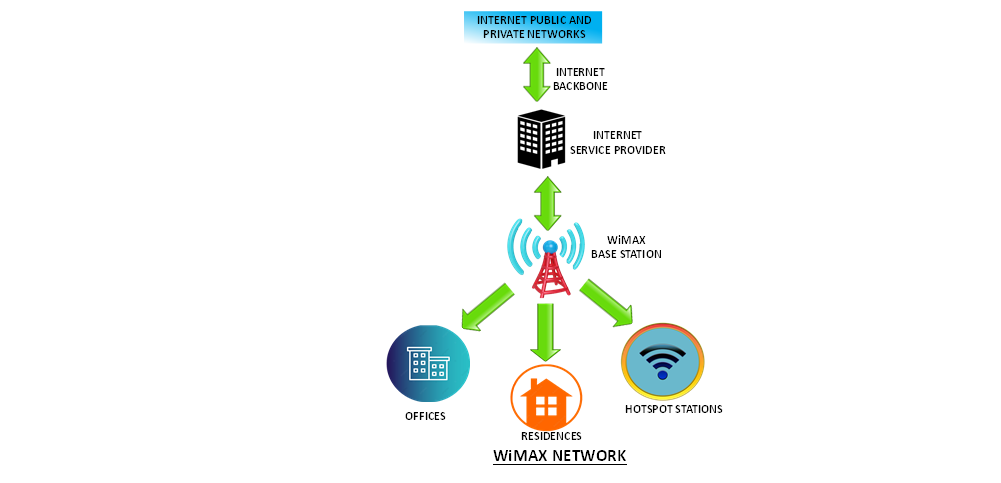
WiMAX, or Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access, emerged as a promising wireless broadband technology, aiming to bridge the digital divide by offering high-speed internet access to underserved areas. It leverages microwave radio frequencies to transmit data over long distances, a key advantage for rural or remote communities lacking traditional wired infrastructure. This technology, while facing competition from newer standards, continues to hold relevance in specific niche applications.WiMAX technology operates on the principle of utilizing radio waves to establish a wireless connection between a base station and user terminals.
This connection allows for the transmission of data, voice, and video signals. Key to its operation is the use of orthogonal frequency-division multiple access (OFDMA) techniques, enabling multiple users to share the same frequency band simultaneously. This approach maximizes network capacity and ensures efficient resource allocation.
Fundamental Principles of WiMAX
WiMAX relies on a set of standardized protocols and specifications for interoperability and compatibility across different devices and networks. These standards define the air interface, which encompasses the physical layer, the medium access control (MAC) layer, and the upper layers responsible for data transmission and reception. The core principle is to establish a robust and scalable wireless broadband network capable of handling various data rates and types of traffic.
Intel’s backing of Clearwire’s WiMAX technology is a significant step, especially considering how broadband connections are rapidly replacing dial-up in major markets. This shift highlights the increasing demand for faster, more reliable internet access. This push for WiMAX by Intel suggests a strong belief in the future of this technology, despite the challenges in the market.
Technical Specifications and Capabilities
WiMAX networks boast significant data transmission capabilities. Standards such as IEEE 802.16 define the specifications for the WiMAX air interface. These specifications encompass aspects like modulation techniques, coding schemes, and channel access mechanisms. WiMAX networks can support a range of data rates, from relatively low speeds for basic internet access to high speeds suitable for video streaming and other bandwidth-intensive applications.
The technology also features mobility support, allowing users to move around the network while maintaining a stable connection.
Strengths and Weaknesses Compared to Other Wireless Technologies
WiMAX, like other wireless technologies, possesses both strengths and weaknesses. Compared to 3G and 4G cellular technologies, WiMAX excels in its ability to provide extended coverage areas. This characteristic is particularly advantageous for rural or sparsely populated regions. However, WiMAX’s peak data rates might fall short of the higher speeds offered by newer generations of cellular standards like 4G LTE and 5G.
Intel’s backing of Clearwire’s WiMAX technology is definitely interesting, but it’s also worth noting how advancements like Atis Hypermemory are changing the game. This technology, which uses system memory for graphics processing, atis hypermemory uses system memory for graphics , could potentially revolutionize how we use computing resources. Ultimately, it all points back to Intel’s strategy of staying ahead of the curve in wireless connectivity, and Clearwire is a significant part of that strategy.
The evolving nature of the mobile industry has led to the continued evolution of cellular technology, impacting WiMAX’s competitiveness.
Comparison Table: WiMAX vs. 3G vs. 4G
| Technology | Speed | Range | Cost | Reliability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WiMAX | Variable, typically lower than 4G | Generally broader than 3G, but potentially less than 4G | Deployment costs can be higher initially, but potentially lower per user in certain scenarios | Good reliability in stable environments, but may be impacted by interference |
| 3G | Relatively low compared to 4G and WiMAX | Moderate range | Typically lower deployment and user costs | Reliability can vary depending on network conditions |
| 4G | High data rates | Broader range than 3G | Deployment and user costs can vary | High reliability in most cases |
Evolution of WiMAX Technology
The development of WiMAX has seen several key innovations. Initial WiMAX deployments focused on providing basic broadband access. Subsequent advancements have aimed to enhance data rates and network capacity. The evolution of WiMAX has also focused on adapting to the changing needs of the mobile and wireless broadband market. These advancements demonstrate the continuous refinement and improvement of the technology, though its prominence has diminished in favor of newer wireless standards.
Market Analysis of WiMAX
The wireless communication market in the early 2000s was a dynamic and competitive landscape. Various technologies vied for dominance, and the introduction of WiMAX, promoted by Intel and Clearwire, aimed to carve out a significant portion of this market. Understanding the broader market context and the competitive landscape is crucial to evaluating Intel’s strategic decision to support Clearwire’s WiMAX deployment.
Intel’s backing of Clearwire’s WiMAX technology is definitely noteworthy, but it’s interesting to see how other tech giants are also innovating. For example, AMD and IBM are extending their chip processing partnership, which could potentially impact future tech developments. This is all part of the broader push for faster, more efficient computing, and ultimately, will likely influence Intel’s own WiMAX endeavors as well.
amd and ibm extend chip processing deal This reinforces the competitive landscape in the tech industry, and how different companies’ moves affect the larger picture of wireless communication.
Wireless Communication Market Overview
The wireless communication market in the early 2000s was characterized by a proliferation of technologies. 3G networks were expanding, but faced limitations in terms of coverage and data speeds. Other contenders, such as Wi-Fi, were prevalent in local area networks but lacked the range and capacity for broader deployments. The need for a high-speed, wide-area wireless solution was apparent, and WiMAX emerged as a potential solution.
This created a fertile ground for competition and innovation in the wireless sector.
Competitive Landscape for WiMAX
WiMAX faced stiff competition from existing wireless technologies. 3G networks, while mature, were still evolving, offering increasing data speeds. Wi-Fi, though limited in range, offered a viable solution for local networks. Furthermore, other emerging technologies, such as LTE, were beginning to gain traction. This competitive landscape forced WiMAX to differentiate itself through its features, such as its wider coverage area and greater bandwidth capacity, to capture market share.
Market Trends and Intel’s Decision
Several market trends influenced Intel’s decision to partner with Clearwire. The growing demand for broadband access beyond traditional wired solutions, coupled with the need for higher data speeds, played a significant role. The possibility of achieving substantial market penetration with a standardized technology, such as WiMAX, was also an important factor. Furthermore, the strategic advantage of being at the forefront of a new technology, along with potential revenue streams from the technology and related products, contributed to Intel’s decision.
Ultimately, the combination of these trends made WiMAX an attractive investment opportunity for Intel.
Factors Impacting WiMAX Adoption
Several factors influenced the adoption of WiMAX. These factors are summarized below:
- Infrastructure Costs: The initial investment required for deploying WiMAX infrastructure, including base stations and network equipment, was a significant barrier for many potential adopters. This was a significant consideration for carriers, and it had a significant impact on the technology’s initial adoption rate.
- Consumer Demand: The level of consumer demand for high-speed wireless access, along with awareness and education regarding the benefits of WiMAX, were essential drivers. Lack of awareness and education, coupled with limited access to devices and services compatible with WiMAX, significantly impacted adoption.
- Government Regulations and Policies: Government regulations and policies, including spectrum allocation and licensing procedures, significantly impacted the deployment of WiMAX networks. Differing regulations across regions impacted market penetration.
- Interoperability: The ability of different WiMAX devices and systems to communicate effectively with each other was a crucial factor. Lack of interoperability and standardization posed significant challenges to widespread adoption.
Market Share of Wireless Technologies
The table below provides an approximate representation of the market share of different wireless technologies during the period of Intel’s involvement with Clearwire. Exact figures are difficult to obtain due to the evolving nature of the market and varying reporting methodologies.
| Technology | Market Share (%) | Growth Rate (%) | Key Players |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3G | 45-55 | 5-10 | Various mobile carriers |
| Wi-Fi | 20-30 | 10-15 | Various vendors and consumer electronics companies |
| WiMAX | 5-10 | 15-25 | Clearwire, Intel |
| Other Emerging Technologies | 5-10 | Variable | Various startups and research organizations |
Intel’s Strategic Considerations

Intel’s foray into the WiMAX market through its investment in Clearwire marked a significant strategic shift. The company, renowned for its processor technology, sought to expand its reach into the burgeoning wireless communication sector. This venture presented both exciting opportunities and potential pitfalls, demanding careful consideration of Intel’s overall technological strategy and the specific risks and rewards of the Clearwire partnership.Intel’s investment in Clearwire’s WiMAX technology reflected a broader strategy of diversifying its portfolio beyond its core processor business.
The wireless communication market was emerging as a key growth area, and Intel likely saw WiMAX as a pathway to gain a foothold in this sector, potentially leading to future partnerships and revenue streams.
Intel’s Overall Technological Strategy
Intel’s technological strategy during this period focused on expanding its reach beyond its core processor business. The company recognized the potential of the wireless communication market and sought to leverage its expertise in semiconductor technology to develop innovative solutions. This involved developing and integrating chipsets and other components crucial for wireless infrastructure, potentially creating a wider ecosystem around its products.
Potential Benefits and Risks of Intel’s Investment
Intel’s investment in Clearwire’s WiMAX technology presented several potential benefits. The company could gain significant market share in the burgeoning wireless broadband market. Moreover, the partnership could lead to valuable technological advancements and innovation in wireless communication infrastructure. Intel could leverage its existing expertise in chip design and manufacturing to develop cost-effective and high-performance WiMAX solutions.However, the investment also carried significant risks.
The WiMAX market was highly competitive, and Clearwire faced considerable challenges in achieving profitability and securing sufficient funding. Intel’s foray into a relatively new and uncertain technology sector could also result in substantial financial losses if the market did not develop as anticipated. The success of WiMAX adoption by consumers and businesses was uncertain, and this uncertainty was a significant risk for Intel.
Intel’s Strategic Goals and Objectives
Intel’s strategic goals and objectives in its involvement with Clearwire likely included:
- Gaining a foothold in the wireless communication market and diversifying its revenue streams.
- Leveraging its core competencies in semiconductor technology to develop innovative WiMAX solutions.
- Establishing strategic partnerships with telecommunication companies to further expand its market reach.
- Creating a wider ecosystem around its products, enhancing their value proposition.
These goals aimed to establish Intel as a significant player in the wireless communication landscape, potentially leading to future growth and market dominance.
Potential Synergies Between Intel’s Core Competencies and Clearwire’s WiMAX Technology
Intel’s core competencies in semiconductor design and manufacturing could significantly benefit Clearwire’s WiMAX technology. Intel’s expertise in creating high-performance, energy-efficient chips could lead to improved WiMAX network performance and reduced operational costs for Clearwire. The company could also potentially develop specialized chipsets optimized for WiMAX, providing a significant competitive advantage.
Financial and Strategic Gains from Supporting Clearwire
| Potential Gain | Expected Return | Risks | Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Increased Market Share in Wireless Broadband | Higher revenue streams from WiMAX-related products and services | High competition in the wireless market | Develop innovative solutions and differentiate Intel’s offerings. |
| Technological Advancement | Gaining valuable knowledge and expertise in wireless communication technologies | Uncertainty of market adoption | Engage in extensive market research and partner with key industry players. |
| Establishment of Strategic Partnerships | Expansion of business network and increased potential revenue streams | Risk of partnership failure | Thorough due diligence and clear contract stipulations. |
| Diversification of Revenue Streams | Reduced dependence on the processor market | Uncertainty in WiMAX market growth | Simultaneous investment in multiple growth areas. |
Impact on the Wireless Communication Industry
Intel’s backing of Clearwire’s WiMAX technology significantly impacted the wireless communication industry, although ultimately not in the way many had initially hoped. This strategic alliance, while aiming to establish a dominant force in the burgeoning wireless market, faced headwinds from competing technologies and evolving market demands. The outcome serves as a cautionary tale about the importance of anticipating technological shifts and adapting to market realities.
Influence on the Broader Wireless Communication Landscape
Intel’s involvement spurred innovation in some areas but also highlighted the complexities of wireless technology adoption. The push for WiMAX standards fostered some advancement in wireless infrastructure, particularly in areas with limited coverage. However, the eventual market dominance of LTE (Long Term Evolution) and later 5G technologies demonstrated that WiMAX’s approach, while innovative, did not fully capture the market’s desire for higher speeds and broader coverage.
Impact on Innovation and Competition
The introduction of WiMAX spurred competition among wireless providers, albeit briefly. Various companies, inspired by Intel’s investment, developed their own WiMAX solutions. This competitive environment led to advancements in the standardization of wireless protocols. However, the intense competition also showcased the difficulty in achieving widespread adoption of a new technology without substantial market demand. The ultimate triumph of LTE, with its faster speeds and greater bandwidth, dramatically shifted the landscape, demonstrating the rapid pace of technological evolution in the wireless sector.
Effect on Consumer Access to Wireless Services
Intel’s backing of Clearwire aimed to bring high-speed wireless internet access to consumers in underserved areas. While WiMAX did provide some consumers with improved connectivity, the eventual failure of Clearwire meant that access remained uneven across different regions. The impact on consumer access was ultimately limited by the broader market acceptance of more advanced technologies.
Analysis of the Overall Outcome on Future Wireless Technology Development
The Clearwire/Intel partnership, though not a resounding success, provided valuable insights into the intricacies of wireless technology development. The experience highlighted the need for a robust and adaptable technology roadmap. It also underscored the importance of consumer demand and the ever-changing technological landscape. The failure of WiMAX served as a crucial learning experience for the wireless industry, encouraging a more cautious and nuanced approach to new technologies.
Timeline and Impact on 4G Development
The development of 4G wireless technology was significantly influenced by the WiMAX experiment. WiMAX’s introduction and subsequent setbacks, though not directly causing the delays in 4G deployment, helped to refine the development process. The timeline for 4G development was, in some ways, influenced by the need to adapt to the market’s response to WiMAX. Companies learned valuable lessons about developing standards and technologies that truly resonated with consumer needs.
The development of LTE, a direct competitor to WiMAX, became the dominant 4G technology.
Lessons Learned
The Clearwire-Intel WiMAX partnership, while ambitious, ultimately fell short of its goals. Analyzing the factors contributing to this outcome reveals valuable lessons about technology investment, market analysis, and strategic alignment. This analysis provides insights into the pitfalls of overestimating market demand and the importance of understanding evolving technological landscapes.The failure of Clearwire’s WiMAX deployment, and the associated challenges faced by Intel, serves as a cautionary tale.
Understanding the mistakes made can guide future technological ventures, ensuring they are better equipped to navigate the complexities of the market. This exploration highlights the critical need for thorough market research, clear strategic vision, and adaptable business models in the face of rapidly changing technological paradigms.
Key Factors Contributing to Clearwire’s WiMAX Deployment Challenges
Clearwire’s WiMAX deployment faced several significant hurdles. Competition from established players like Verizon and AT&T proved intense. The technology, while promising, lacked widespread adoption among consumers. Additionally, the initial rollout struggled to attract sufficient subscriber numbers, making the business model unsustainable. The high capital expenditure required for infrastructure development and deployment also played a significant role.
Finally, evolving consumer preferences and technological advancements in the wireless communication sector also influenced the company’s difficulties.
Lessons Learned by Intel and Clearwire
Intel and Clearwire learned valuable lessons from this venture. Overestimating market demand and underestimating the challenges of competing against established players are crucial takeaways. Clearwire, in particular, faced difficulties in building a strong and profitable customer base, highlighting the importance of targeted marketing strategies and effective customer acquisition plans. Intel likely recognized the limitations of simply providing technology without a robust and sustainable business model.
The failure to adequately anticipate evolving consumer demands and market shifts played a significant role in their challenges.
Importance of Market Analysis and Strategic Alignment
Thorough market analysis is crucial for any significant technology investment. The partnership’s failure underscores the need for a precise understanding of market dynamics, including competitor strategies, technological trends, and consumer preferences. Strategic alignment between the technology provider (Intel) and the deployment company (Clearwire) is vital for success. This alignment ensures that the technology aligns with the specific needs of the target market and that both parties share a common vision for the project.
Broader Implications on Technology Development
The Clearwire-Intel partnership illustrates the complexities of bringing new technologies to market. The challenges encountered in this specific case highlight the importance of adaptability and flexibility in the face of changing market conditions. Furthermore, it underscores the significance of understanding the entire value chain, from technology development to market penetration and sustained customer acquisition, to ensure the long-term viability of any technological venture.
Factors Influencing Clearwire’s Failure, Intel throws weight behind clearwire wimax
Clearwire’s failure was influenced by a multitude of factors. Competition from established players with extensive networks and infrastructure significantly hampered their efforts. The company struggled to secure funding and maintain financial stability. Furthermore, the technology itself, while innovative, faced challenges in attracting a broad consumer base. The high cost of infrastructure deployment and the need for substantial capital investment also presented significant hurdles.
These factors, combined with an evolving market landscape and changing consumer preferences, contributed to Clearwire’s eventual difficulties.
Last Point
Intel’s investment in Clearwire’s WiMAX technology, while ultimately not achieving its full potential, serves as a valuable case study in technology partnerships. It highlights the complex interplay of technological advancement, market dynamics, and strategic decision-making. The analysis reveals crucial factors that contributed to the success or failure of Clearwire’s WiMAX deployment. Lessons learned, including the importance of thorough market analysis and strategic alignment, offer insights for future technology investments.
This partnership’s impact on the development of 4G wireless technology, and the broader wireless communication industry, are topics worth considering as well.