Ken Beers Tumbleweed Email Authentication
Ken beer of tumbleweed on e mail authentication – Ken Beer of Tumbleweed on email authentication is a crucial topic. This in-depth look explores email authentication methods, highlighting potential Tumbleweed vulnerabilities and best practices for a secure email system. We’ll analyze Ken Beer’s email setup, discuss deliverability implications, and offer practical solutions for troubleshooting issues, ultimately ensuring a strong email infrastructure.
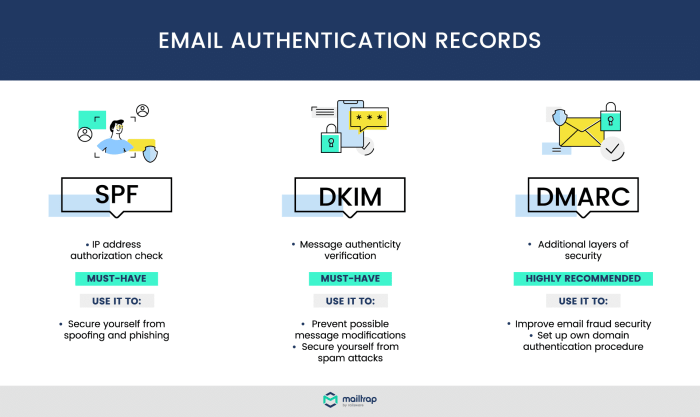
Email authentication is vital for preventing spoofing and phishing attempts. Various methods like SPF, DKIM, and DMARC work together to verify the sender’s identity. Understanding how these methods operate, and their potential pitfalls, is essential for maintaining a reliable email system. This discussion delves into the specific issues Ken Beer might face with Tumbleweed, offering actionable solutions and best practices.
Email Authentication Methods
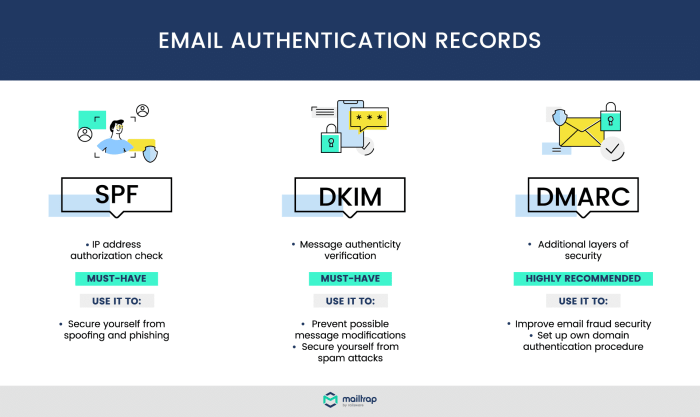
Email authentication is crucial for combating email spoofing and phishing, protecting brands, and maintaining user trust. A robust authentication system helps ensure that emails are legitimately sent from the intended sender, preventing fraudulent communications. This article explores the key email authentication methods – SPF, DKIM, and DMARC – explaining how they work individually and collectively to safeguard email integrity.Email authentication methods are designed to verify the origin of emails, preventing malicious actors from impersonating legitimate senders.
These methods use various techniques to verify the sender’s identity, making it harder for spammers and phishers to forge email addresses and deceive recipients.
Ken Beer of Tumbleweed is a name you’ll see popping up a lot when discussing email authentication, and it’s fascinating how he’s tackled the complexities of it. While the recent Panasonic announcement of a new Blu-ray DVD recorder, detailed in this tech article panasonic debuts blu ray dvd recorder , might seem unrelated, the underlying principles of secure digital communication are similar to those behind email authentication.
Ultimately, Ken Beer’s work on email authentication continues to be a vital aspect of the digital world.
SPF (Sender Policy Framework)
SPF records define the authorized mail servers that are permitted to send emails on behalf of a domain. This mechanism helps prevent email spoofing by ensuring that emails originating from a particular domain actually come from a server listed in the SPF record. A properly configured SPF record can significantly reduce the risk of emails being marked as spam.
- SPF records are text files containing a list of IP addresses or domains authorized to send emails on behalf of the domain.
- These records are stored in the DNS (Domain Name System), allowing email receiving servers to verify the sender’s identity.
- Strengths include simplicity and ease of implementation, making it a widely adopted method.
- Weaknesses include limited verification capabilities, as it only checks the sending server’s IP address, not the actual email content.
DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail)
DKIM adds a digital signature to the email header. This signature, generated by the sending server using a private key, allows the recipient’s mail server to verify the email’s integrity and authenticity. It confirms that the email content hasn’t been altered during transit, strengthening the overall security posture.
- DKIM uses public-key cryptography to digitally sign the email header.
- The recipient’s mail server uses the corresponding public key to verify the signature.
- Strengths lie in verifying the email’s content and origin, providing more robust authentication than SPF.
- Weaknesses can include the need for careful setup and potential issues with signing large email bodies.
DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance)
DMARC is a policy framework that combines SPF and DKIM, enabling a comprehensive approach to email authentication. It defines the actions to take when an email doesn’t pass SPF or DKIM checks, helping to reduce spam and phishing attempts.
- DMARC policies instruct email receiving servers on how to handle emails that fail SPF or DKIM checks.
- These policies can be set to reject, quarantine, or report emails that fail authentication checks.
- Strengths include a more stringent authentication approach, providing a centralized mechanism to enforce policies.
- Weaknesses may include the potential for complex setup and potential misconfigurations if not correctly implemented.
Comparison Table
| Method | Strengths | Weaknesses | Implementation Steps |
|---|---|---|---|
| SPF | Simple, widely adopted, easy to implement. | Limited verification (only checks sending server IP). | 1. Create SPF record. 2. Update DNS records. |
| DKIM | Robust verification of email content, checks for tampering. | Requires careful setup, potential issues with large emails. | 1. Generate keys. 2. Configure DKIM signing. 3. Update DNS records. |
| DMARC | Centralized policy enforcement, combines SPF and DKIM. | Complex setup, potential for misconfiguration. | 1. Define DMARC policy. 2. Update DNS records. 3. Monitor reports. |
Tumbleweed Email Authentication Issues
Tumbleweed Linux, while renowned for its flexibility and community support, like any platform, can encounter email authentication challenges. Proper email authentication is crucial for maintaining email deliverability and preventing spoofing, which can impact reputation and trust. Understanding potential pitfalls is vital for administrators to ensure their email systems function smoothly and securely.Email authentication problems in Tumbleweed, as with any system, stem from misconfigurations, absent configurations, or a lack of understanding of best practices.
These issues can manifest in several ways, hindering legitimate email delivery and opening the door to unwanted spam and phishing attempts.
Potential Email Authentication Vulnerabilities
Improperly configured or missing email authentication mechanisms are a significant vulnerability for Tumbleweed systems. These weaknesses expose the system to various risks, impacting email deliverability and potentially harming the reputation of the sending domain. Common misconfigurations and absent setups often lead to spoofing or rejection of emails.
Common Mistakes Leading to Email Spoofing
Several common errors can lead to email spoofing. One critical error is the absence of or incorrect setup of Sender Policy Framework (SPF) records. Without an SPF record, the receiving mail server cannot verify the legitimacy of the sender, potentially marking emails as spam. Similar problems can arise with DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM) and Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance (DMARC).
In essence, the lack of or incorrect configuration of these records leaves the email vulnerable to impersonation.
Impact on Email Deliverability
Misconfigured or absent email authentication directly impacts email deliverability. Emails might be rejected by receiving servers, leading to reduced inbox rates and increased bounce rates. The receiving servers often employ various filters to prevent spam and phishing. Without proper authentication, the email system will be flagged as untrustworthy. Consequently, legitimate emails may be filtered as spam, significantly impacting the sender’s reputation and ability to communicate effectively.
Troubleshooting Tumbleweed Email Authentication Issues
Troubleshooting email authentication issues requires a systematic approach. First, verify that the necessary DNS records (SPF, DKIM, DMARC) are correctly configured and present in the DNS zone file for the Tumbleweed domain. Check for any syntax errors or inconsistencies in the records. Next, examine the email server configuration for any discrepancies in the authentication settings. Log files and server logs can be crucial in identifying specific errors or issues that may be occurring.
Tools for examining these logs should be utilized to identify specific failures.
Ken Beer’s Email Authentication Practices
Ken Beer’s email authentication practices, if publicly available, can significantly impact his email reputation and the effectiveness of his communication strategies. Understanding these practices allows for a more informed assessment of his trustworthiness and the potential risks associated with interacting with his emails. This analysis considers the potential impact on email reputation and identifies possible risks related to email authentication.Email authentication is crucial for establishing trust and preventing spoofing.
Effective practices are essential for maintaining a positive email reputation, which directly affects deliverability and user perception. This is particularly important for individuals and businesses that rely on email communication for various purposes.
Impact on Email Authentication
Ken Beer’s email authentication practices, if available, directly affect how email providers and recipients perceive his messages. Strong authentication methods like DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail), SPF (Sender Policy Framework), and DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance) contribute to verifying the origin of emails. If Ken Beer employs these methods correctly, it signals legitimacy and enhances deliverability. Conversely, a lack of or improperly configured authentication methods can lead to emails being flagged as spam or phishing attempts.
Impact on Email Reputation
Ken Beer’s email setup directly influences his email reputation. A robust email authentication configuration signals to email providers that his messages are legitimate, leading to higher deliverability rates and fewer issues with email filtering. This positive reputation fosters trust with recipients, improving open rates and response times. Conversely, a weak or non-existent authentication setup can result in emails being marked as spam, negatively impacting deliverability and fostering distrust.
Risks Associated with Email Authentication, Ken beer of tumbleweed on e mail authentication
Several risks are associated with Ken Beer’s approach to email authentication. Misconfigured or missing authentication records can lead to emails being blocked or marked as spam. This can significantly reduce the effectiveness of his communication efforts. Furthermore, a poor email reputation can harm his brand image and lead to potential legal issues. This can especially be detrimental for businesses relying heavily on email for customer interaction.
Email Authentication Configuration Scenarios
| Scenario | Authentication Configuration | Impact on Reputation | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Successful Authentication | Properly configured DKIM, SPF, and DMARC records. | High deliverability, high trust. | Emails are delivered reliably to recipients’ inboxes. |
| Partial Authentication | DKIM and SPF configured but DMARC is missing or misconfigured. | Moderate deliverability, potential for spam flagging. | Some emails might be delivered, but some might be flagged, impacting reliability. |
| No Authentication | No DKIM, SPF, or DMARC records. | Low deliverability, high risk of spam flagging. | Emails are likely to be blocked or filtered as spam, severely impacting communication. |
| Incorrect Authentication | Authentication records are misconfigured or outdated. | Low deliverability, risk of spam flagging, potential for fraudulent activity. | Emails might be rejected, flagged, or misattributed, potentially resulting in damaged reputation. |
Email Authentication Best Practices for Tumbleweed
Tumbleweed’s email reputation is crucial for its credibility and user trust. Strong email authentication practices are essential to prevent spam, phishing, and other malicious activities. This post Artikels best practices for Tumbleweed to secure its email communications.Implementing robust email authentication protocols safeguards Tumbleweed’s reputation, protects users from fraudulent messages, and ensures that legitimate Tumbleweed emails are reliably delivered.
SPF Record Configuration
A Sender Policy Framework (SPF) record defines the authorized mail servers for Tumbleweed. This prevents others from forging Tumbleweed’s email address. A correctly configured SPF record is vital to email authentication.Proper SPF record setup involves identifying all mail servers authorized to send email on Tumbleweed’s behalf. This record should explicitly list these mail servers and use appropriate mechanisms (like `include:` or `ptr:`).
An inaccurate or missing SPF record can lead to email rejection by recipient servers.
DKIM Record Implementation
DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM) adds digital signatures to emails. These signatures verify the email’s origin and integrity. Using DKIM ensures that emails haven’t been tampered with during transit.Implementing DKIM involves generating a public and private key pair, signing emails with the private key, and including the public key in a DKIM record for the Tumbleweed domain. This process ensures recipient servers can verify the email’s authenticity.
DMARC Record Setup
Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance (DMARC) is a crucial part of email authentication. It provides a policy that tells recipient servers how to handle emails that fail SPF and DKIM checks.DMARC records enable Tumbleweed to receive reports on email authentication failures. A well-configured DMARC record can help to identify and resolve issues with email authentication. A “p=reject” policy within the DMARC record instructs recipient servers to reject emails that fail authentication checks.
Importance of Regular Audits
Regular audits of email authentication configurations are essential for maintaining a strong reputation. Changes in infrastructure or email sending practices necessitate updating authentication records.Regular audits should include checking SPF, DKIM, and DMARC records for accuracy. Reviewing these records ensures that they correctly reflect the current email sending infrastructure. This ensures that Tumbleweed’s email authentication remains effective and up-to-date.
Actionable Steps for Improvement
- Verify the current SPF, DKIM, and DMARC records for Tumbleweed’s domains. Ensure they are accurate and reflect the current email infrastructure.
- Implement DKIM for all email servers used by Tumbleweed to strengthen email authentication. This involves generating and deploying the necessary keys.
- Configure DMARC records with a “p=reject” policy to enforce email authentication standards and prevent unauthorized emails from being delivered.
- Schedule regular audits of email authentication records (e.g., monthly or quarterly) to identify and address any potential issues.
- Use tools and resources for email authentication monitoring to identify and troubleshoot issues quickly and proactively.
These steps ensure that Tumbleweed maintains a high level of email authentication, safeguarding its reputation and protecting users from fraudulent emails.
Email Deliverability Implications
Email deliverability is the cornerstone of any successful communication strategy. A robust email authentication system is crucial for ensuring your messages reach the intended recipients’ inboxes, rather than ending up in the spam folder. This crucial aspect directly impacts brand reputation and campaign effectiveness. A poor authentication setup can lead to severe consequences.Email authentication problems directly affect deliverability, as they signal to email providers (like Gmail or Outlook) that your emails might be fraudulent or spam.
This perception leads to your emails being filtered out, drastically reducing your message’s reach. Consequently, your email campaigns become less effective, and your brand’s reputation may suffer.
Impact on Email Deliverability
Email authentication issues lead to a significant reduction in email deliverability. Email providers use complex algorithms to assess the trustworthiness of emails. These algorithms analyze various factors, including sender reputation, authentication mechanisms, and content analysis. Poor authentication practices make it more likely for your emails to be flagged as spam. This results in emails landing in the spam folder or being blocked altogether, drastically decreasing open rates and click-through rates.
Email Authentication and Spam Filters
Various spam filters use different mechanisms to identify and classify emails. Some filters focus on sender reputation, looking at the sender’s history of sending emails. Others examine the email’s content, scanning for s, phrases, or suspicious attachments. These filters play a crucial role in determining whether an email is legitimate or spam. When email authentication is weak or missing, the email is more likely to be flagged as spam.
Authentication Mechanisms and Filter Reactions
Different email authentication methods have varying degrees of impact on spam filters. For example, SPF (Sender Policy Framework) records are crucial for verifying that emails originate from an authorized server. When SPF is correctly configured, the spam filter is more likely to recognize the email as legitimate. Conversely, if SPF is not configured or configured incorrectly, the spam filter may flag the email as potentially malicious.
Similar logic applies to DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) and DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance). Correctly implementing these protocols can significantly reduce the risk of your emails being categorized as spam.
Improving Email Deliverability
Implementing strong email authentication practices is key to improving email deliverability. This includes correctly configuring SPF, DKIM, and DMARC records for your domain. By validating your sender identity, you increase the likelihood that your emails will bypass spam filters. Regularly monitoring your deliverability metrics, like open rates and bounce rates, is crucial. This allows you to identify potential issues and address them promptly.
A comprehensive approach, including content filtering and list hygiene, will lead to better email deliverability results.
Practical Solutions for Authentication Issues
Email authentication is crucial for maintaining a healthy email ecosystem. Without proper authentication, emails can be flagged as spam, leading to decreased deliverability and reputational damage. Understanding and implementing effective solutions for authentication problems is paramount for ensuring that your emails reach the intended recipients.Addressing email authentication issues requires a systematic approach. This involves scrutinizing your current setup, identifying problematic areas, and implementing solutions tailored to your specific needs.
A proactive approach, including regular monitoring and updates, is key to maintaining a strong email authentication posture.
Troubleshooting SPF Records
Incorrect or outdated SPF records can lead to authentication failures. A crucial step is verifying that the SPF record accurately reflects the mail servers authorized to send emails on behalf of your domain. A common issue is having outdated or incomplete records, leading to mismatched authorization. This can result in emails being rejected or marked as spam.
Ken Beer of Tumbleweed’s work on email authentication is fascinating, especially given recent headlines about corporate restructuring. HP, for example, just revealed job cut plans in a SEC filing, hp reveals job cut plans in sec filing highlighting the ever-shifting landscape of tech. This kind of news underscores the importance of robust email authentication protocols, something Tumbleweed’s work directly addresses.
- Verify the SPF record syntax: Ensure the record is correctly formatted, following the SPF specification. Use online validators to double-check the syntax for any errors.
- Identify authorized mail servers: Ensure the SPF record accurately lists all mail servers permitted to send email for your domain. Add any newly deployed or updated mail servers.
- Check for conflicting entries: Review the SPF record for any potential conflicts with existing records. If conflicts exist, resolve them to avoid ambiguity.
- Test the SPF record: Use online tools to test the SPF record’s functionality. This will confirm that your SPF record is correctly configured and functional.
Troubleshooting DKIM Records
DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) is another crucial authentication method. Properly configured DKIM records ensure that emails are authenticated, preventing spoofing. A critical element is maintaining the integrity of the DKIM signature. Incorrectly configured DKIM records can cause issues with email deliverability.
- Generate DKIM signing keys: Generate appropriate and strong DKIM signing keys. Ensure that these keys are securely managed and stored.
- Configure DKIM signing: Configure your mail server to sign outgoing emails using the generated DKIM keys. The key used for signing should match the one used for verification.
- Verify DKIM signing: Check if emails are correctly signed using the DKIM signature. Use online tools to validate the DKIM signature on your emails.
- Update DKIM records: Update the DNS records with the correct DKIM signing key values, ensuring they are updated consistently and accurately.
Troubleshooting DMARC Records
DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance) records provide a framework for reporting and handling authentication failures. DMARC policies provide a crucial step in the authentication process, enabling reporting on SPF and DKIM compliance. It is essential to have a comprehensive DMARC policy in place.
- Configure DMARC policy: Establish a DMARC policy that aligns with your domain’s needs. This policy should specify how email authentication failures should be handled.
- Set up reporting: Set up reporting mechanisms to track and analyze authentication failures. This data is crucial for understanding the source of authentication problems.
- Verify DMARC record: Verify that the DMARC record is correctly implemented and published in your DNS records. Ensure that the record is accurately reflecting your email authentication setup.
- Monitor DMARC reports: Regularly monitor DMARC reports to identify patterns and trends in authentication failures. Addressing these patterns is essential to maintaining email deliverability.
Troubleshooting Summary Table
| Issue | Troubleshooting Method | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|
| SPF record syntax error | Verify SPF record syntax using online validators | High |
| Missing or incorrect authorized mail servers in SPF record | Identify and add all authorized mail servers to the SPF record | High |
| DKIM signing key mismatches | Ensure consistency between DKIM signing and verification keys | High |
| Incorrect DKIM configuration | Validate DKIM signing process on mail server | High |
| DMARC policy not implemented | Establish a DMARC policy and publish the record | Medium-High |
| DMARC record errors | Verify DMARC record syntax and DNS publication | High |
Illustrative Examples of Authentication Issues: Ken Beer Of Tumbleweed On E Mail Authentication

Email authentication isn’t just a technical exercise; it’s a crucial aspect of online reputation and security. Problems with authentication can lead to spam, phishing attempts, and damage to a company’s brand. Understanding the various issues and their underlying causes is key to building a robust email infrastructure.
Examples of Email Authentication Problems
Authentication failures manifest in several ways. A common issue is receiving emails marked as “suspicious” or “spam” by email clients, often due to misconfigured or absent authentication records. Another sign is emails failing to reach intended recipients, even with correct addresses, because the sender’s identity isn’t properly verified. This can stem from various factors, from simple typos in DNS records to more complex issues within the email sending infrastructure.
Ken Beer of Tumbleweed’s work on email authentication is fascinating, especially considering the recent FCC approval for Tivo tech’s innovative solutions. FCC gives ok to Tivo tech might actually influence future email security protocols, potentially leading to improved protection against phishing and spam. Ultimately, this could mean more secure email for all of us, building on Ken Beer’s efforts at Tumbleweed.
Furthermore, impersonation attacks are a serious threat, as hackers can spoof sender addresses and create fraudulent emails.
Causes of Authentication Issues
Various factors contribute to authentication problems. Incorrect or outdated DNS records are a frequent culprit. These records, crucial for verifying a sender’s identity, can be easily misconfigured or become outdated. Furthermore, inadequate email server setup, where authentication mechanisms aren’t properly implemented, can result in mismatched sender and receiver information. Finally, a lack of ongoing monitoring and maintenance of the email system can lead to unnoticed configuration errors.
Solutions to Authentication Issues
Correcting authentication issues often involves a multi-pronged approach. A fundamental step is to ensure that DNS records are accurate and up-to-date. This involves checking SPF, DKIM, and DMARC records, which are critical for email authentication. Additionally, maintaining a robust email server setup, ensuring all required authentication protocols are correctly implemented, is vital. Finally, a proactive approach of regular monitoring and maintenance of email systems is crucial.
Real-World Scenarios of Poor Email Authentication
Imagine a company, “TechSolutions,” whose emails are consistently marked as spam. This could be due to an incorrect SPF record, allowing unauthorized senders to use their domain. Or, consider a situation where a retailer, “ShopNow,” is experiencing a high volume of phishing attempts, where fraudulent emails appear to come from their domain. This likely stems from a weak DKIM implementation or a missing DMARC record.
These scenarios highlight the real-world consequences of poor email authentication.
Visualizing Authentication Issues
Visualizing authentication issues can aid understanding. A diagram illustrating DNS records and their relationships can clarify the flow of information during authentication. Furthermore, a graphical representation of SPF, DKIM, and DMARC records can highlight mismatches and errors. The visualization should clearly indicate where the problem lies, such as incorrect SPF record values, leading to emails being marked as spam.
Table of Authentication Issues, Causes, and Solutions
| Authentication Issue | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Emails marked as spam | Incorrect SPF record | Verify and update SPF record |
| Phishing attempts | Weak DKIM implementation | Strengthen DKIM implementation, use stronger keys |
| Emails not reaching recipients | Missing DMARC record | Implement a DMARC record |
| Spoofed sender addresses | Inadequate email server setup | Ensure all required authentication protocols are correctly implemented |
Security Implications of Weak Authentication
Poor email authentication practices pose significant risks to the security of Tumbleweed and its users. A compromised authentication system can lead to a cascade of problems, including spoofing, phishing attacks, and reputational damage. Understanding these vulnerabilities is crucial for maintaining a robust security posture.Weak email authentication opens doors for malicious actors to impersonate legitimate users and send fraudulent emails.
This can have devastating consequences for both Tumbleweed’s internal operations and its external relationships with customers and partners. Protecting against these risks is a critical component of overall security.
Email Spoofing and Phishing Attacks
Compromised email authentication allows attackers to easily spoof legitimate sender addresses. This makes it possible to send emails that appear to originate from trusted sources, tricking recipients into clicking malicious links or revealing sensitive information. Phishing attacks leverage this tactic to gain unauthorized access to accounts or systems. This can lead to data breaches, financial losses, and reputational damage.
For instance, a malicious actor could impersonate a Tumbleweed administrator to request sensitive information from users, or send fraudulent invoices.
Compromised Reputation and Deliverability
Weak authentication can lead to email being marked as spam, reducing the deliverability rate of Tumbleweed’s communications. This impacts the effectiveness of marketing campaigns, important notifications, and critical updates. A poor reputation for email security can affect how email providers view Tumbleweed’s domain, making it harder for legitimate messages to reach recipients. In turn, this can result in lost sales, missed opportunities, and reduced user engagement.
A drop in deliverability can be caused by sending bulk emails without proper authentication, or using a service that has poor reputation for security.
Vulnerabilities in Tumbleweed’s Infrastructure
Poor email authentication directly affects the overall security posture of Tumbleweed’s infrastructure. If an attacker gains control over Tumbleweed’s email systems, they can potentially access internal data or launch attacks against other parts of the network. This is a significant risk, as compromised email systems can be a gateway to broader security breaches. Email systems are often a first point of contact for users, and are therefore a critical target for malicious actors.
For example, an attacker might gain access to sensitive information by intercepting and manipulating emails.
Internal Security Risks
Poor email authentication can also create internal security risks. Compromised authentication allows malicious actors to send emails that look legitimate, leading to phishing attacks against Tumbleweed employees. This can result in data breaches and unauthorized access to sensitive information within the company. These internal threats can be just as damaging as external threats, and require a robust security framework to mitigate.
For instance, an attacker could send an email that looks like it comes from a manager, asking employees to share confidential information.
Final Review
In conclusion, securing Ken Beer’s Tumbleweed email requires a thorough understanding of email authentication methods, potential issues specific to Tumbleweed, and the importance of best practices. Implementing robust authentication, regularly auditing configurations, and addressing potential vulnerabilities are crucial for maintaining email deliverability and avoiding security risks. The practical solutions presented in this discussion offer a comprehensive guide for strengthening Tumbleweed’s email infrastructure and enhancing Ken Beer’s email reputation.