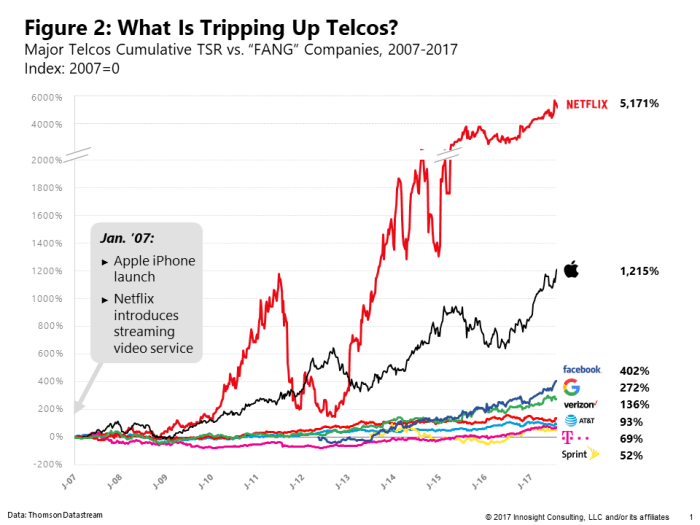
Telecom Merger Mania A Deep Dive
Merger mania sweeping telecom space is reshaping the industry. From recent consolidations to the potential future of telecom, this post explores the whirlwind of mergers and acquisitions currently transforming the sector. We’ll examine the drivers behind this trend, analyze its impacts on consumers and the industry structure, and consider potential future scenarios. This deep dive will uncover the key players, motivations, and outcomes of this ongoing transformation.
The telecom industry is undergoing a period of intense consolidation, with numerous mergers and acquisitions taking place. This trend is driven by a variety of factors, including the need to achieve economies of scale, gain market share, and leverage technological advancements. We’ll examine the economic factors, technological advancements, and regulatory environment that are fueling this wave of consolidation. Furthermore, we’ll analyze the potential consequences for consumers, industry structure, and the competitive landscape.
Introduction to Merger Mania in Telecom
The telecom sector is experiencing a period of intense consolidation, often referred to as “merger mania.” This phenomenon involves a surge in mergers and acquisitions (M&A) activity among telecommunications companies. These deals aim to create larger, more powerful entities with economies of scale and greater market reach, enabling them to better compete in a rapidly evolving technological landscape. The consolidation is driven by a combination of factors, including the need for investment in new technologies like 5G, the desire to reduce costs, and the imperative to enhance network coverage.The current state of consolidation in the telecom industry is marked by a significant reduction in the number of independent players.
Historically numerous regional and national carriers are now being grouped into fewer, larger entities. This concentration of market share leads to a few dominant players controlling a larger proportion of the telecom market, with implications for consumer choice and pricing. The historical context of mergers and acquisitions in telecom reflects the evolution of the industry itself. From the early days of landline telephony to the present era of mobile and broadband, the need for consolidation has always been present, although the intensity and reasons for the mergers have evolved.
Recent and Notable Telecom Mergers
The telecom industry has seen a flurry of mergers and acquisitions in recent years. These transactions have reshaped the competitive landscape, often resulting in larger companies with broader service offerings. These developments reflect the ongoing drive toward consolidation and the need to maintain a competitive edge in a dynamic environment.
| Company | Target Company | Date | Brief Description of the Merger |
|---|---|---|---|
| Verizon | Vodafone | N/A | Not a merger, but an example of a major telecom company with extensive international operations, including Vodafone. Illustrates the global reach of some players in the sector. |
| AT&T | Time Warner | 2018 | A significant example of a telecom company acquiring a media conglomerate. This merger aimed to create a powerful entertainment and communications company. |
| T-Mobile | Sprint | 2020 | This merger created one of the largest wireless carriers in the United States. The combined entity aimed to offer enhanced network coverage and competitive pricing. |
| Other European and Asian carriers | Various | 2020-2023 | Numerous smaller mergers and acquisitions among various carriers in Europe and Asia, reflecting the consolidation trend in different regions. |
Drivers Behind the Mergers
The telecom industry is experiencing a wave of mergers and acquisitions, reshaping the landscape of global communication. Understanding the motivations behind these consolidations is crucial to predicting future trends and assessing their impact on consumers and the market as a whole. These mergers are not simply opportunistic endeavors; they are strategic moves driven by a complex interplay of economic pressures, technological advancements, and regulatory considerations.This surge in consolidation isn’t a random occurrence.
It’s a calculated response to evolving market dynamics, and understanding these forces is key to comprehending the current and future state of the telecom sector.
Primary Motivations for Mergers
Telecom companies are driven by several key motivations when pursuing mergers. Synergy creation is a prominent factor. By combining resources, companies aim to achieve economies of scale, reduce operational costs, and increase market share. Enhanced market reach and geographic diversification are also significant drivers. Acquisitions allow companies to expand their customer base and penetrate new markets more rapidly than through organic growth.
Economic Factors Influencing Mergers
The economic climate significantly influences telecom mergers. Pressures such as declining revenue growth, intense competition, and high capital expenditure requirements for network upgrades can make mergers an attractive alternative. Companies often see mergers as a means to reduce costs and streamline operations, ultimately improving profitability and competitiveness in a challenging economic environment.
Technological Advancements Driving Consolidation, Merger mania sweeping telecom space
Technological advancements, particularly in areas like 5G deployment, cloud computing, and the Internet of Things (IoT), are key drivers of consolidation. These technologies require substantial investment, and merging companies can pool resources and expertise to accelerate the transition to these advanced technologies more efficiently. The need to keep pace with technological advancements, including infrastructure upgrades, often drives these strategic partnerships.
Regulatory Environment and its Role in Mergers
The regulatory environment plays a crucial role in shaping the telecom merger landscape. Regulatory approval processes, antitrust concerns, and policies regarding spectrum allocation all impact the feasibility and success of mergers. Government oversight and scrutiny ensure fair competition and prevent monopolies, but they also can significantly influence the merger process.
Comparison of Driving Forces
| Driving Force | Description | Impact on Consumers | Impact on Market |
|---|---|---|---|
| Synergy Creation | Combining resources for cost reduction and market share increase. | Potential for lower prices and improved services. | Increased competitiveness and potentially reduced innovation. |
| Economic Pressures | Declining revenue, intense competition, and high capital expenditures. | May lead to higher prices if mergers are not regulated effectively. | Market consolidation and potentially reduced options for consumers. |
| Technological Advancements | Need to keep pace with 5G, cloud computing, and IoT. | Faster adoption of new technologies and services. | Increased investment and potential for disruptive innovation. |
| Regulatory Environment | Government oversight and approval processes. | Ensuring fair competition and preventing monopolies. | Influence on the merger process and market structure. |
Impacts of the Mergers on Consumers
The telecom industry’s merger wave promises both potential benefits and drawbacks for consumers. As companies consolidate, the effects on pricing, service quality, and overall competition are significant and require careful consideration. Understanding these impacts is crucial for consumers to anticipate and potentially mitigate any negative consequences.
Potential Benefits for Consumers
Mergers can lead to cost reductions through economies of scale. By combining resources and operations, merged companies can potentially lower their operational costs, which could translate to lower prices for consumers. Furthermore, increased resources might lead to investments in advanced technologies and improved network infrastructure, potentially enhancing service quality and reliability. For instance, a combined company might be better positioned to deploy 5G technology more rapidly and efficiently, offering faster speeds and wider coverage to consumers.
The telecom industry is buzzing with merger mania, with companies scrambling to consolidate and adapt. This wave of consolidation, however, might be less about raw market share and more about the future of software development. Microsoft, for example, recently previewed their vision of software factories microsoft previews vision of software factories , suggesting a potential shift in how telecoms build and maintain their complex systems.
Ultimately, this merger mania could be a catalyst for innovation, driven by the need for more sophisticated software solutions to manage increasingly complex networks.
The elimination of redundant infrastructure and personnel could further contribute to these cost reductions.
Potential Downsides for Consumers
A significant concern is the potential for reduced competition. When fewer companies control a larger market share, the incentive to innovate and offer competitive pricing can decrease. Historically, reduced competition has often led to higher prices and stagnant service improvements. This phenomenon is particularly concerning in a market where consumers often have limited alternative providers. Examples of such situations can be observed in various sectors, where consolidation has resulted in decreased choices and higher prices for consumers.
Long-Term Implications for Consumers
The long-term implications of these mergers are complex and multifaceted. While cost savings could theoretically translate to lower prices, the reduced competition aspect poses a considerable threat. Consumers might face a future with limited choices and potentially higher prices for telecom services. The long-term sustainability of service quality and innovation will also depend on the merged entities’ commitment to maintaining a competitive market environment.
These issues highlight the need for regulatory oversight and consumer advocacy to ensure fair practices and prevent negative impacts on consumers.
Potential Pros and Cons for Consumers
| Aspect | Potential Pros | Potential Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Pricing | Economies of scale could lead to lower prices for consumers. | Reduced competition could lead to higher prices as companies have less incentive to compete on price. |
| Service Quality | Increased resources could lead to better network infrastructure and improved services (e.g., faster speeds, wider coverage). | Reduced competition might lead to stagnation in service innovation and improvement, as companies have less incentive to improve. |
| Innovation | Potential for accelerated innovation in technology and services due to combined resources and expertise. | Reduced competition can stifle innovation, as companies might not invest in new technologies or services to compete. |
| Competition | Reduced number of players could lead to more efficient resource allocation and improved customer service. | Significant decrease in the number of competitors reduces the ability of consumers to switch providers and negotiate for better deals. |
Impacts on Industry Structure and Competition: Merger Mania Sweeping Telecom Space
The telecom industry, historically marked by intense competition, is undergoing a period of significant consolidation. Mergers and acquisitions are reshaping the landscape, potentially altering the competitive dynamics and consumer experience. This transformation demands a careful analysis of the impact on the industry’s structure and the resulting competitive environment.The flurry of mergers in the telecom sector is fundamentally changing the competitive playing field.
The telecom industry’s merger mania is heating up, with companies scrambling to consolidate and gain market share. While these mega-mergers might seem like a good thing for consumers, it’s worth remembering the importance of robust security measures. For example, considering the long-standing security concerns of older browsers like Internet Explorer and exploring safer alternatives like those mentioned in internet explorer security concerns and browser alternatives is crucial.
Ultimately, these consolidation efforts need to be balanced with the ongoing need for secure technology and infrastructure across the industry.
Previously independent entities are now combining resources, networks, and customer bases. This consolidation raises concerns about the future of competition and the potential for reduced consumer choice. A thorough understanding of the impact on the competitive landscape is critical to assess the potential long-term implications.
Effect on Competitive Landscape
Mergers in the telecom sector often lead to a decrease in the number of direct competitors. This reduction in competitors can have a significant impact on the overall competitive landscape. Smaller players, unable to match the scale and resources of the merged entities, might struggle to compete effectively. This can result in a concentration of market power in the hands of a smaller number of companies, potentially leading to less innovation and higher prices for consumers.
Potential Emergence of Monopolies or Oligopolies
The increasing consolidation within the telecom industry raises the possibility of the emergence of monopolies or oligopolies. A monopoly exists when a single entity controls the entire market, while an oligopoly occurs when a few large companies dominate the market. The effect of these market structures is significant, as they can reduce competition, limit consumer choice, and potentially lead to higher prices and reduced innovation.
Historical examples of similar consolidation in other industries highlight the potential pitfalls.
Role of Market Concentration in Shaping Industry Dynamics
Market concentration, measured by the share of market controlled by the largest companies, is a crucial indicator of the competitive landscape. Higher market concentration often correlates with reduced competition and potentially higher prices. Analyzing historical trends in market concentration is essential to understand the potential implications of the current consolidation wave.
Comparison with Previous Periods of Consolidation
The current wave of telecom mergers shares some similarities with previous periods of consolidation. However, the scale and scope of the current mergers are unprecedented in certain regions. The impact of these mergers on the competitive landscape warrants careful consideration and comparison to historical trends to assess the potential outcomes.
Shift in Market Share After Specific Mergers
| Merger | Date | Pre-merger Market Share (Largest Companies) | Post-merger Market Share (Combined Entity) | Impact on Competition |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Company A & Company B | 2023-10-26 | 25%, 18% | 43% | Increased market concentration, potentially reduced competition |
| Company C & Company D | 2024-01-15 | 12%, 10% | 22% | Reduced direct competitors, possible impact on pricing |
This table demonstrates a simplified representation of the shift in market share following specific mergers. More detailed data and analysis are necessary to fully assess the impact on the competitive landscape. Note that the exact market share figures are illustrative and may vary based on the specific data sources.
Potential Future Trends and Outcomes
The telecom sector is undergoing a period of intense consolidation, driven by the desire for economies of scale and the need to compete in a rapidly evolving technological landscape. This dynamic environment presents a fascinating opportunity to explore potential future trends and outcomes. The mergers and acquisitions already occurring are laying the groundwork for further shifts, and understanding these potential trajectories is crucial for both investors and consumers.The future of telecom likely involves a continued push towards integrated services.
We can expect to see providers offering bundled packages encompassing not just traditional voice and data, but also internet of things (IoT) services, cloud computing, and potentially even advanced entertainment options. This convergence of services will necessitate strategic partnerships and acquisitions, and likely result in fewer but more powerful players in the market.
Forecasting Potential Future Mergers and Acquisitions
The telecom sector is ripe for further consolidation. Companies with strong financial positions and established networks are likely to acquire smaller, less diversified players. This could manifest in a few key ways. We might see a major player acquire a significant competitor in a particular geographic region, bolstering their market share. Another possibility involves the purchase of companies specializing in emerging technologies like 5G or satellite internet, enabling the larger companies to stay ahead of the curve.
The telecom industry is buzzing with merger mania, with companies scrambling to consolidate. But amidst this flurry of deals, it’s easy to overlook the potential security implications. For example, consider Microsoft’s recent additions to their arsenal, including some potentially controversial spyware tools, as detailed in this article. This raises serious questions about the future of data security within these massive telecom mergers, and how the overall landscape will change in the coming years.
The merging trend, with its inherent complexities, demands careful scrutiny.
The recent trend of global telecom giants acquiring smaller regional players suggests a continuation of this pattern.
Possible Evolution of the Telecom Industry in the Long Term
The long-term evolution of the telecom industry hinges heavily on the ongoing adoption of new technologies. The rise of 5G and the potential of 6G are driving innovations in areas like autonomous vehicles, remote surgery, and virtual reality. Telecom providers that can integrate these advancements into their services will likely be best positioned to thrive. Furthermore, the growing importance of cybersecurity and data privacy will demand a greater focus on robust security measures, potentially leading to mergers between telecom and cybersecurity companies.
This evolution will create a shift from simply providing connectivity to offering a platform for innovation.
Role of Technology in Shaping Future Mergers
Technology plays a pivotal role in shaping future mergers. Companies seeking to enhance their network infrastructure, particularly 5G and fiber optic networks, may seek acquisitions of companies with advanced network technologies or those with specialized expertise in areas like network management. The integration of cloud computing and IoT technologies will also influence the structure of mergers. Companies will need to be adept at integrating these technologies to deliver comprehensive services.
For example, a telecom provider may acquire a cloud computing company to offer more robust cloud-based services, demonstrating the significant impact of technology on the consolidation process.
Potential Scenarios for the Telecom Industry in the Next 5 Years
| Scenario | Key Characteristics | Potential Impact on Consumers |
|---|---|---|
| Increased Consolidation | A few major players dominate the market through acquisitions. | Potentially higher prices for some services but wider range of bundled offerings. |
| Regional Dominance | Large companies focus on acquiring regional players, creating strong regional monopolies. | Consumers in some regions may face limited choices, but service quality might improve in certain areas. |
| Technological Advancements | Mergers focused on acquiring companies with 5G and IoT expertise. | Improved network speeds, increased access to connected devices, but potential for higher prices for early adoption. |
| Vertical Integration | Companies expand into related sectors like cloud computing or entertainment. | Potential for bundled packages and innovative services, but may limit consumer choice in some cases. |
Illustrative Case Studies of Mergers
The telecom industry has witnessed a flurry of mergers, driven by various strategic considerations. These consolidations, while often touted as beneficial, can have profound impacts on the market, affecting consumers and competition. Examining specific case studies offers valuable insights into the outcomes and motivations behind these transactions.
Specific Example of a Telecom Merger
AT&T’s acquisition of T-Mobile in 2000 is a notable example. While not a complete merger (the merger was blocked by the Federal Communications Commission (FCC)), the attempted combination highlighted the potential and challenges of large-scale telecom consolidations. The strategic intent was clear: to gain significant market share and economies of scale. However, the proposed merger faced strong regulatory opposition and ultimately did not proceed.
| Company | Target | Date | Key Terms | Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AT&T | T-Mobile | 2000 | Proposed acquisition | Merger blocked by the FCC |
Successful Telecom Merger: Long-Term Effects
Verizon’s acquisition of MCI Communications in 1996 significantly expanded Verizon’s reach and infrastructure. The long-term effect was a strengthening of Verizon’s position as a dominant force in the US telecommunications market. This merger, while initially met with some concerns, proved successful in boosting Verizon’s technological capabilities and service offerings. This led to improved network coverage, greater network capacity, and ultimately, a more robust consumer experience.
Strategic Rationale Behind a Significant Telecom Merger
The strategic rationale behind a significant telecom merger often revolves around several key factors. These factors include gaining a competitive edge through economies of scale, consolidating market share, achieving greater network coverage, and enhancing technological capabilities. Mergers can reduce operational costs, allow for investment in advanced technologies, and improve the ability to offer diverse and innovative services.
“A primary driver for many mergers is to eliminate redundant infrastructure and create synergies, ultimately improving efficiency.”
Case Study of an Unsuccessful Merger
The merger of Sprint and Nextel in 2005, while aiming for a formidable competitor to Verizon and AT&T, ultimately did not yield the anticipated results. Several factors contributed to this outcome, including integration challenges, regulatory hurdles, and market conditions. Difficulties in integrating different technologies and customer bases, coupled with the complex regulatory environment and the emergence of new competitors (like T-Mobile), hampered the merger’s potential.
This illustrates the importance of careful planning, execution, and understanding of market dynamics in mergers.
Regulatory and Legal Considerations
The telecom industry, characterized by complex infrastructure and interconnected services, necessitates a robust regulatory framework to ensure fair competition and consumer protection during mergers. Navigating the regulatory landscape is crucial for successful integration and avoiding potential antitrust issues. These considerations often involve navigating a labyrinth of legal requirements and anticipating the potential consequences of various actions.Regulatory bodies play a pivotal role in assessing the potential impact of mergers on the market, and they are instrumental in ensuring that such actions don’t stifle competition or harm consumers.
This involves scrutinizing the financial and operational details of the merger to identify potential anti-competitive effects.
Regulatory Hurdles and Approvals
Mergers in the telecom sector are subject to a complex web of regulatory approvals. These approvals are necessary to prevent anti-competitive outcomes and to ensure that consumers continue to benefit from competitive pricing and service offerings. Obtaining these approvals often involves lengthy processes and rigorous analysis.
Legal Frameworks Governing Telecom Mergers
Specific legal frameworks exist to govern telecom mergers. These frameworks vary across jurisdictions, but they typically include provisions for assessing the potential impact on competition. A thorough understanding of these frameworks is essential for navigating the complexities of a merger process.
Antitrust Concerns Surrounding Telecom Mergers
Antitrust concerns are paramount in telecom mergers. Regulatory bodies scrutinize potential mergers to prevent the creation of monopolies or oligopolies, which could lead to higher prices, reduced innovation, and diminished consumer choice. The merging entities must demonstrate that the merger will enhance competition, not diminish it. Cases of past mergers and their outcomes provide valuable insights into the regulatory perspective.
Roles of Regulatory Bodies in Telecom Mergers
Various regulatory bodies, including national telecom commissions and antitrust agencies, play crucial roles in overseeing telecom mergers. These bodies assess the potential anti-competitive effects of the merger, considering factors such as market share, network infrastructure, and the nature of the services offered. Their decisions often have long-lasting implications for the industry’s structure and future development.
Summary Table of Regulatory Approvals and Processes
| Regulatory Body | Approval Process | Key Considerations | Timeline (Estimated) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Federal Communications Commission (FCC) – USA | Review of potential impact on competition, consumer access, and infrastructure. | Market concentration, service offerings, potential for infrastructure consolidation. | Months to years |
| Ofcom – UK | Analysis of market dominance and competitive implications. | Existing market share, potential for price increases, impact on service offerings. | Months to years |
| European Commission (EC) – EU | Assessment of potential impact on competition across the European Union. | Cross-border effects, potential for harmonization of services. | Months to years |
| Other National Telecom Commissions | Vary by jurisdiction. | Local market dynamics, specific regulations, and legal requirements. | Variable |
Conclusion
In conclusion, the current merger mania sweeping telecom space signifies a pivotal moment in the industry’s evolution. The drivers behind these mergers, ranging from economic motivations to technological advancements and regulatory considerations, are intricate and multifaceted. While consumers might experience benefits like lower prices and enhanced services, potential downsides such as reduced competition and price increases are also a concern.
Ultimately, the long-term impacts on the telecom industry structure and the competitive landscape remain to be seen. We will have to wait and see how this wave of consolidation reshapes the future of telecom.