Microsoft Eyes Google for Acquisition A Deep Dive
Microsoft eyes Google for acquisition, a move that could reshape the tech landscape. This potential mega-merger sparks intrigue, prompting questions about the motivations behind such a bold strategy. Will Microsoft gain a significant competitive edge by acquiring Google? This in-depth analysis explores the potential benefits, drawbacks, and impact on the tech industry, from market reactions to regulatory hurdles.
This article will delve into the history and current state of both Microsoft and Google, exploring the possible motives for acquisition, and the potential repercussions for the tech world. We’ll examine the challenges of merging two massive tech giants, and look at alternative strategies for Microsoft if acquisition isn’t the path forward. The analysis will be structured to provide a comprehensive understanding of this potential deal.
Background of Microsoft and Google: Microsoft Eyes Google For Acquisition

The tech industry is a dynamic landscape, constantly reshaped by innovation and fierce competition. Two titans, Microsoft and Google, have dominated this arena for decades, each with unique histories, evolving product portfolios, and significant market positions. Their ongoing rivalry shapes the future of technology, and understanding their past is key to grasping their present and potential future interactions.The rivalry between Microsoft and Google isn’t just about who has the most market share, but also about how they adapt and innovate in response to changing consumer needs and emerging technologies.
Their successes and challenges offer valuable insights into the broader competitive pressures and opportunities within the tech industry.
Microsoft’s History
Microsoft, founded in 1975, initially focused on operating systems. The launch of MS-DOS in the 1980s and the subsequent dominance of Windows cemented its position as a leader in personal computing. Key milestones include the development of Office Suite, Internet Explorer, and Windows NT, each significantly influencing the evolution of personal computers. Later, the company diversified into gaming (Xbox), cloud computing (Azure), and enterprise software, further solidifying its presence across various tech sectors.
| Company | Year | Event | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Microsoft | 1975 | Founded | Establishment of a software company focused on personal computing. |
| Microsoft | 1980s | MS-DOS and Windows | Dominated the personal computer operating system market. |
| Microsoft | 1990s | Office Suite, Internet Explorer | Expanded its product portfolio and established presence in office productivity and web browsing. |
| Microsoft | 2000s | Xbox, Windows NT, Azure | Diversified into gaming, enterprise software, and cloud computing. |
Google’s History
Founded in 1998, Google initially focused on search technology. The development of the PageRank algorithm and the creation of a user-friendly search engine catapulted Google to global prominence. Subsequently, Google expanded into diverse areas including advertising, mobile operating systems (Android), and cloud computing (Google Cloud Platform).
| Company | Year | Event | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1998 | Founded | Launched a revolutionary search engine based on the PageRank algorithm. | |
| Early 2000s | Search Engine Dominance | Became the dominant search engine globally. | |
| 2000s-2010s | Android, Chrome, Cloud Services | Expanded into mobile operating systems, web browsers, and cloud computing services. | |
| Present | AI and Big Data Focus | Continues to innovate in artificial intelligence and big data processing. |
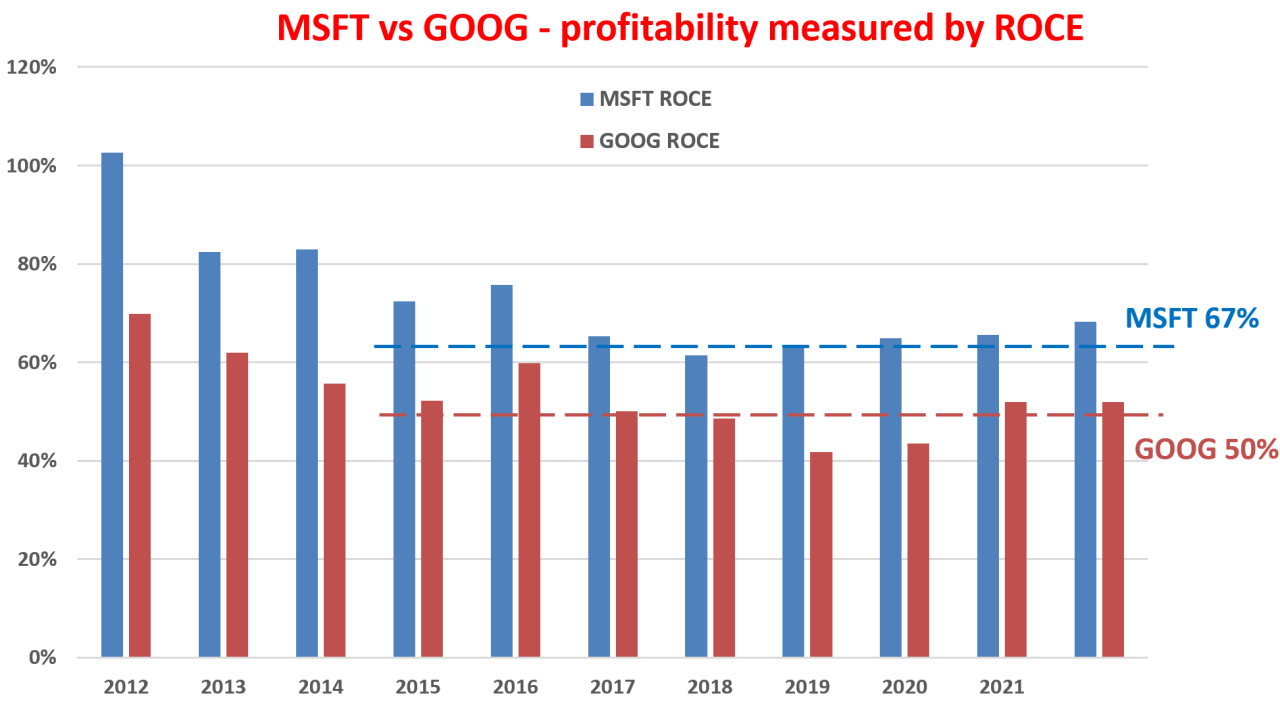
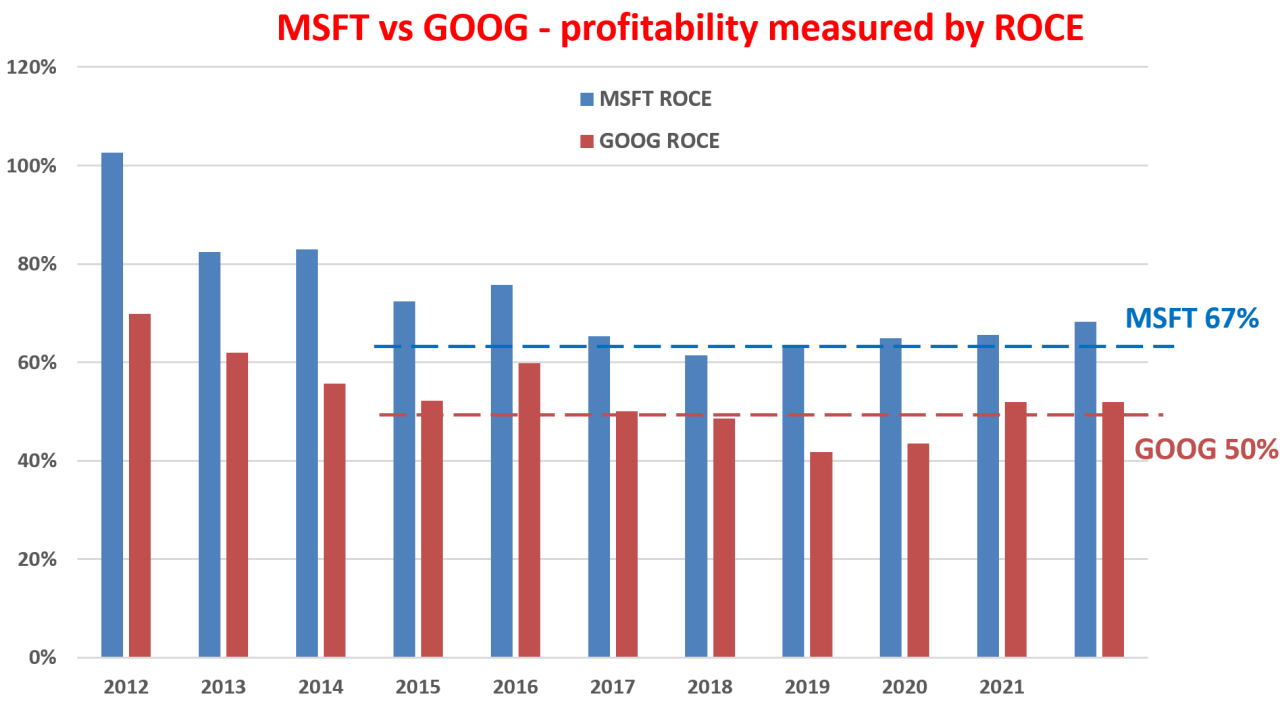
Current Market Positions and Financial Performance
Microsoft and Google are global tech giants with substantial market capitalization and revenues. Microsoft’s focus on cloud computing and enterprise software has propelled it to significant financial success. Google’s strength lies in its diverse revenue streams, including advertising and cloud services.
Competitive Landscape
The tech industry is highly competitive. Companies constantly strive to innovate and maintain their market share. The rivalry between Microsoft and Google is intense, encompassing areas like operating systems, cloud computing, search, and mobile devices. The ongoing competition drives innovation and pushes both companies to expand their product portfolios and improve their services.
Potential Motives for Acquisition
The tech world is rife with speculation, and the possibility of Microsoft acquiring Google is no exception. Such a move, while seemingly improbable, would undoubtedly shake the foundations of the digital landscape. Understanding the potential motivations behind such a significant undertaking is crucial to comprehending the possible ramifications.
Microsoft’s Potential Motivations
Microsoft, a stalwart in the software and hardware industry, has consistently sought to expand its reach and influence. Acquiring Google, a dominant force in search, advertising, and cloud computing, could significantly bolster Microsoft’s position across several key areas. This acquisition could be driven by a desire to consolidate market share, gain access to cutting-edge technologies, or even counterbalance the growing influence of other competitors.
The pursuit of synergistic benefits, combining Microsoft’s strengths with Google’s innovative prowess, is another probable motivation.
Strategic Advantages for Microsoft
Acquiring Google could provide Microsoft with numerous strategic advantages. Firstly, it would grant access to Google’s vast user base, enhancing Microsoft’s reach and market penetration. Secondly, it would introduce a significant boost to Microsoft’s cloud computing infrastructure and capabilities, directly challenging Amazon Web Services’ dominance. Finally, integrating Google’s search technology could improve Microsoft’s existing search products and services, potentially strengthening its position against Google itself.
The potential for accelerated innovation and product development through knowledge sharing and combined resources is also a compelling motivator.
Microsoft’s rumored interest in acquiring Google is certainly a big deal, sparking a lot of speculation. While that tech giant’s focus is on this massive merger, it’s interesting to see how other companies like Toshiba are innovating in the PDA space. Toshiba’s push into VoIP and text-to-speech technology in their new PDAs, as detailed in this article toshiba pushes voip and text to speech in new pdas , might offer a glimpse into future mobile functionalities.
Perhaps these advancements could even influence the outcome of the Microsoft-Google situation, and potentially pave the way for similar innovations within Microsoft’s own product lines.
Potential Benefits and Drawbacks for Both Companies
A merger of this scale would have profound implications for both Microsoft and Google. For Microsoft, the acquisition could lead to a significant expansion of its core businesses, but it also presents considerable challenges. Integration complexities and potential antitrust issues would need careful consideration. For Google, the uncertainty of a new corporate structure and potential disruption to its current strategies could cause concerns.
The potential for a loss of autonomy and influence under a new leadership could be a major deterrent.
Comparison Table of Potential Advantages and Disadvantages
| Factor | Microsoft | |
|---|---|---|
| Potential Advantages | Increased market share, access to cutting-edge technology, enhanced cloud computing capabilities, strengthened search dominance. | Potential for improved product development and market expansion. |
| Potential Disadvantages | Integration complexities, potential antitrust issues, loss of Google’s innovative independence. | Loss of autonomy and control, potential disruption to current strategies, challenges in integrating into a new corporate structure. |
Potential Impact on the Tech Industry
A Microsoft-Google acquisition would be a seismic event in the tech world, reshaping the competitive landscape and potentially altering the future of technology for consumers and businesses alike. The combined resources, expertise, and market reach of these titans would undoubtedly create a formidable entity, prompting significant shifts in how we interact with technology.
Potential Effects on Competition, Microsoft eyes google for acquisition
The acquisition would dramatically alter the tech industry’s competitive balance. Microsoft and Google, already dominant players in their respective sectors, would become a near-monopoly in certain areas. This consolidation could lead to reduced innovation as the merged entity focuses on optimizing existing products and services rather than venturing into entirely new fields. Smaller companies might face an uphill battle to compete, potentially leading to a decrease in the diversity of offerings and services available to consumers.
The combined entity could leverage its significant market share to push out smaller rivals, stifling competition and potentially creating a less dynamic and innovative tech environment.
Impact on Innovation
The acquisition’s effect on innovation is complex and multifaceted. While the combined resources could theoretically fund groundbreaking research and development, the potential for bureaucratic hurdles and internal conflicts could also hinder progress. The elimination of competing product lines and strategies could lead to a homogenization of offerings, diminishing the variety of solutions and perspectives that drive innovation. The current rivalry between Google and Microsoft fuels innovation, driving both companies to constantly push the boundaries of their respective fields.
The loss of this competitive dynamic could lead to a decline in innovation. Historical precedents demonstrate that market consolidation can lead to stagnation, as companies focus on maintaining existing market share rather than seeking new opportunities.
Impact on User Experiences
User experiences are likely to be impacted in various ways. The combined company could potentially create more seamless and integrated services across platforms, but this integration might come at the cost of user choice and customization. Users could find themselves with fewer options to choose from and might be faced with a less personalized experience, as the merged entity prioritizes its own internal strategies over individual user needs.
Potential Outcomes and Effects on Tech Sectors
| Tech Sector | Potential Outcomes | Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Search Engines | Domination of search market with potentially less diverse results, less choice for users. | Reduced competition, possible stagnation in search algorithm innovation. |
| Cloud Computing | Significant increase in market share, potential for enhanced cloud services. | Increased pricing power, potentially higher barriers to entry for smaller cloud providers. |
| Operating Systems | Stronger position in the OS market, potential for more integrated user experience across platforms. | Less flexibility and choice for consumers, potentially higher costs. |
| Mobile Devices | Influence over mobile operating systems and apps, potentially leading to a less diverse ecosystem. | Reduced choice for users, possible shift in focus from innovation to controlling market share. |
| Artificial Intelligence | Increased investment in AI research, potential for accelerated development of AI technologies. | Potential for biased AI systems due to consolidated control, limited access to diverse perspectives. |
Regulatory and Legal Considerations
A Microsoft-Google acquisition presents a formidable challenge to regulatory bodies worldwide. The sheer size and market dominance of both companies raise significant concerns about potential anti-competitive practices and stifled innovation. Navigating this complex legal landscape will require careful consideration of antitrust laws, precedent-setting cases, and the potential long-term impact on the tech industry.The regulatory review process for such a large merger is likely to be extensive and thorough.
Independent investigations will likely scrutinize various aspects of the proposed acquisition, from market share analysis to potential competitive harms. This detailed examination aims to ensure that the combined entity does not significantly reduce competition, hindering innovation and ultimately harming consumers.
Potential Regulatory Hurdles
The combination of Microsoft and Google would likely face considerable regulatory hurdles. Both companies hold substantial market share in key technological sectors, raising concerns about the creation of a near-monopoly in certain areas. The potential for anti-competitive behavior, such as limiting choice or increasing prices, requires careful examination by regulatory bodies.
Relevant Antitrust Laws and Regulations
Several antitrust laws and regulations globally could apply to a Microsoft-Google acquisition. These include national laws like the U.S. Clayton Act and the Sherman Act, and international agreements, such as the EU’s antitrust regulations. These laws prohibit mergers that may substantially lessen competition in a relevant market. The specific laws that would be applied will vary depending on the jurisdiction, and the relevant markets must be clearly defined and analyzed.
Past Similar Large-Scale Tech Acquisitions and Regulatory Outcomes
The history of large-scale tech acquisitions offers valuable insights into potential regulatory outcomes. For example, the proposed merger of AT&T and T-Mobile was blocked by the FCC and the Department of Justice. Similarly, the EU has historically challenged and blocked acquisitions deemed to stifle competition. These past cases illustrate the complexities and potential legal challenges of such transactions.
Potential Legal and Regulatory Implications
| Aspect | Potential Implications |
|---|---|
| Market Dominance | Significant concern about the combined entity’s ability to control and manipulate markets, potentially leading to decreased innovation and higher prices. |
| Antitrust violations | Possible penalties or restrictions on the combined entity’s operations to ensure competitive practices are maintained. |
| Consumer harm | Reduced choice, higher prices, and stifled innovation are potential negative outcomes for consumers. |
| Global reach | Multiple jurisdictions may be involved in the regulatory review process, leading to potential delays and complexities. |
These are just some of the potential implications of such a large-scale acquisition. The actual outcomes will depend on the specifics of the transaction, the findings of regulatory investigations, and the evolving interpretation of antitrust laws. A comprehensive legal and regulatory analysis will be critical for determining the viability and long-term sustainability of the proposed merger.
Market Reaction and Public Opinion
A potential Microsoft acquisition of Google would undoubtedly send ripples through the tech market and public consciousness. The sheer scale of the two companies, their dominance in various sectors, and the implications for competition and innovation would generate significant interest and diverse opinions. Public perception will likely hinge on how the deal is presented and perceived to affect consumers and the broader tech ecosystem.
Potential Market Reactions
The market reaction to a potential Microsoft-Google merger would likely be multifaceted and nuanced. Initial reactions might involve a surge in market volatility, as investors grapple with the implications for stock prices, market share, and future competition. Speculation about the deal’s potential benefits and drawbacks would dominate financial news cycles. Long-term, the market’s response would depend heavily on how the merged entity operates and whether it fosters innovation or stifles competition.
Investor Sentiment Analysis
Investor sentiment would be a crucial factor in the market reaction. Positive investor sentiment might emerge if the merger promises significant synergies, cost reductions, or enhanced market share. Conversely, negative sentiment could arise from concerns about reduced competition, potential price increases for consumers, and anti-trust concerns. Analysts would closely scrutinize the potential impact on various sectors, such as cloud computing, search, advertising, and artificial intelligence.
Microsoft’s rumored interest in acquiring Google is definitely a big deal, sparking plenty of speculation. Meanwhile, Broadcom is making waves in the tech world with its new all-in-one Wi-Fi chip, potentially disrupting the market. This development, however, doesn’t seem to significantly alter the larger picture of Microsoft’s potential Google acquisition, leaving many analysts still pondering the strategic implications for the tech industry.
The analysis would often be based on historical data of similar mergers, regulatory scrutiny, and industry forecasts.
Public Opinion on Past Tech Mergers
Public reaction to past major tech mergers provides some context. The public often expresses concern about the potential for reduced competition and higher prices. For example, the reactions to the AT&T-T-Mobile merger and the various proposed mergers in the tech sector (which have been halted or altered) demonstrate the sensitivity around such deals. Reactions are often influenced by the perceived impact on consumers, access to technology, and innovation.
Historical examples of public outcry, such as those related to antitrust concerns and potential market dominance, would be examined to understand potential responses to a Microsoft-Google merger.
Structuring a Summary of Investor and Public Opinion
A structured summary of investor and public opinions on a potential acquisition should incorporate various aspects. A bulleted list can effectively capture the key points. A useful method is to categorize the opinions based on different perspectives.
- Investor Concerns: Potential for reduced competition, increased pricing, and diminished innovation. These concerns would likely be based on financial projections and analysis of market trends.
- Investor Optimism: Potential for significant synergies, cost savings, and expansion into new markets. This would likely be supported by detailed financial modeling and market research.
- Consumer Concerns: Potential for reduced choice, higher prices, and negative impacts on the user experience. These concerns would often center on the specific impact on everyday products and services.
- Consumer Optimism: Potential for improved products and services, increased innovation, and expanded access to technology. These perspectives would be based on expectations of the merged entity’s capabilities.
- Regulatory Concerns: Antitrust scrutiny and potential legal challenges. This is a key element of the public reaction and would be based on the legal precedents and regulatory frameworks governing mergers and acquisitions.
Technological Integration Challenges
A Microsoft-Google merger, while potentially lucrative, presents significant technological integration hurdles. The sheer size and diversity of the two companies’ platforms – from operating systems and search engines to cloud services and hardware – create a complex tapestry of potential conflicts and incompatibilities. Successfully merging these vast ecosystems requires meticulous planning and execution, navigating a minefield of overlapping technologies and user expectations.The challenge extends beyond mere technical integration.
A successful acquisition hinges on maintaining the functionality and value of both existing platforms while simultaneously exploring synergistic opportunities. This requires a profound understanding of each company’s strengths, weaknesses, and user bases. The successful examples of past large tech integrations are few and far between, highlighting the immense complexities involved.
Potential Issues with Overlapping Products and Services
The overlap between Microsoft’s Office suite and Google Workspace, or between their respective cloud computing offerings, poses significant challenges. Competition between similar products, potentially leading to product cannibalization, requires careful strategic planning. Decisions on which products to retain, enhance, or discontinue will be crucial. For instance, a company might choose to combine the strengths of both platforms, such as incorporating Google’s AI capabilities into Microsoft Office or integrating Microsoft’s enterprise security into Google Workspace.
Microsoft’s rumored interest in acquiring Google is sparking a lot of debate, and it inevitably brings up the thorny issue of indemnification, especially given the complexities of open-source software like Linux. This potential acquisition raises questions about how such a massive merger would handle intellectual property and potential liabilities. For a deeper dive into the intricate world of indemnification clauses and the ongoing challenges in the Linux ecosystem, check out this insightful piece on indemnification and Linux insanity.
Ultimately, the whole acquisition scenario is a complex dance of legal maneuvering and technological integration, and the long-term implications for both companies and the tech industry at large remain to be seen.
This integration must be approached strategically, avoiding the elimination of successful products and services.
Challenges in Integrating Software and Hardware
Integrating software and hardware presents a formidable challenge. The different programming languages, operating systems, and hardware architectures employed by both companies introduce considerable technical hurdles. Consider the compatibility issues between Microsoft’s Windows operating system and Google’s Android mobile operating system. Bridging the gap between these diverse technologies demands substantial investment in research and development. Potential solutions include employing a common software foundation, standardizing APIs, and developing a hybrid approach that leverages the best of both platforms.
An example of such integration could be developing a unified platform for cloud storage, accessing both Microsoft OneDrive and Google Drive with a single interface.
Complexity of Merging Two Large and Diverse Technology Platforms
The sheer size and complexity of Microsoft and Google’s technological infrastructures present a formidable challenge. Each company has a vast network of interconnected systems, applications, and services. Integrating these disparate components requires careful planning and a deep understanding of each platform’s intricacies. Failure to account for the intricate relationships between various components could lead to unforeseen disruptions and inconsistencies.
A meticulous mapping of dependencies and interoperability across both platforms is essential. For instance, a crucial aspect would be understanding how the merged entity will manage the enormous data repositories of both companies. The risk of data loss or incompatibility issues is substantial.
Alternatives to Acquisition
A potential Microsoft acquisition of Google, while strategically alluring, presents significant hurdles. Beyond the complex regulatory landscape and potential antitrust concerns, the sheer scale and interwoven ecosystems of these tech giants pose considerable integration challenges. Therefore, exploring alternative strategies to bolster Microsoft’s competitive position becomes crucial.Exploring strategic alternatives allows Microsoft to leverage its strengths without the considerable risks and uncertainties associated with a large-scale acquisition.
These alternatives can be more agile and adaptable to evolving market dynamics, offering a nuanced approach to maintaining and enhancing market leadership.
Potential Strategic Partnerships
Microsoft can strengthen its position by focusing on strategic partnerships that complement its existing capabilities and allow for mutual benefit. This approach fosters collaboration without the complexities of merging two large, established entities.
- Exclusive Licensing Agreements: Microsoft could secure exclusive licensing agreements for Google’s innovative technologies, such as AI models or specific cloud services, to enhance its own product offerings without the need for a full-scale acquisition. This could include access to specific datasets, APIs, or algorithms. For example, a recent partnership between companies in different sectors demonstrated the success of leveraging expertise through exclusive agreements.
- Joint Ventures: Creating a joint venture in a specific technological area allows for shared resources and risk, allowing each company to leverage the strengths of the other without the complete integration required in an acquisition. This strategy can be focused on emerging technologies, expanding into new markets, or addressing a particular market need. Consider the success of joint ventures in the automotive industry, which combine the expertise of different companies to develop innovative technologies.
- Research and Development Collaborations: Collaborating on research and development projects allows for the exchange of ideas and resources, which can lead to breakthroughs that benefit both companies. This collaborative model can be particularly effective in areas like AI, cloud computing, or cybersecurity. Examples exist in the academic sphere, where research partnerships often produce advancements in specific fields.
Illustrative Partnership Models
A visual representation of potential partnership models, illustrating the differing levels of integration and shared resources, is presented below.
| Partnership Model | Description | Level of Integration | Shared Resources |
|---|---|---|---|
| Exclusive Licensing | One company licenses technology to another. | Low | Specific technology, potentially data. |
| Joint Venture | Two companies create a new entity to pursue a specific goal. | Medium | Resources, personnel, and specific expertise. |
| Research & Development Collaboration | Companies work together on research projects. | Low-Medium | Knowledge, expertise, and resources. |
“Strategic partnerships, when properly structured, can yield significant benefits without the substantial risks and uncertainties associated with acquisitions.”
End of Discussion
The potential acquisition of Google by Microsoft is a complex issue with far-reaching implications. While the motivations for such a move are compelling, the challenges are substantial, from integrating two massive platforms to navigating the regulatory landscape. This analysis has explored the potential benefits and drawbacks, and Artikeld the crucial factors that could determine the ultimate outcome. The future of the tech industry hinges on a multitude of factors, and this potential merger is a pivotal point.