Microsoft Planning to Push Patches Harder
Microsoft planning to push patches harder is a significant shift in their approach to software security. This increased frequency is driven by a rise in cyber threats and vulnerabilities targeting Microsoft products. Expect more frequent releases of security updates, potentially impacting user experience, and demanding adaptation from users and IT professionals alike. The article explores the reasons behind this change, potential impacts, and strategies for managing the increased patching load.
The current patching cadence of Microsoft products will be examined, along with the different types of patches and their potential effects. We’ll look at how Microsoft’s approach compares to competitors and delve into the resources they use for development and deployment. The increasing frequency of patches will be analyzed, considering the evolving attack surface and the influence of emerging technologies.
A critical evaluation of the potential benefits and drawbacks will be presented, along with strategies for users to effectively manage patch installations and deployments. Ultimately, the future implications for software development, user-vendor relationships, and the IT support industry will be considered.
Microsoft’s Patching Strategy

Microsoft’s commitment to maintaining the security and stability of its products is reflected in its proactive patching strategy. This approach involves a complex interplay of development, testing, and deployment processes, impacting both user experience and the overall security posture of the ecosystem. The frequency and types of patches released are crucial factors in determining the effectiveness of this strategy.Microsoft employs a dynamic patching cadence, adjusting its release schedules based on the severity and prevalence of vulnerabilities discovered.
This adaptive strategy aims to mitigate risks while minimizing disruptions to users. Different types of patches cater to various needs, ranging from critical security fixes to incremental feature enhancements.
Microsoft’s plans to push out patches more aggressively are likely a response to the changing tech landscape. The increasing complexity of systems, coupled with the limitations of Moore’s Law, means that security vulnerabilities are more likely to emerge and need patching. This shift in strategy directly relates to the broader discussion around “life after Moore’s Law beyond silicon” life after moores law beyond silicon , forcing companies to adapt to new paradigms of hardware and software development, which in turn impacts their patch release cycles.
Ultimately, this means users can expect a more active and perhaps more frequent patching schedule from Microsoft.
Patching Cadence and Types
Microsoft releases patches for its software products with varying frequencies, depending on the nature of the update. Security patches are typically released more frequently than feature updates, reflecting the urgent need to address vulnerabilities. The specific release cycles are determined by Microsoft’s internal processes and prioritization of reported security issues.
- Security patches are prioritized to address vulnerabilities and protect against exploits. These updates often address critical flaws that could potentially compromise system security, requiring prompt deployment to prevent potential breaches.
- Feature patches introduce new functionalities and improvements to the software. These updates may involve new features, performance enhancements, or bug fixes. They are often released less frequently than security patches, as they undergo rigorous testing to ensure stability and compatibility with existing systems.
- Driver updates address specific hardware components. These patches are released to enhance compatibility, performance, and stability of the software with specific hardware. Drivers are crucial for smooth operation of the devices and the operating system.
Comparison to Competitors
Microsoft’s patching strategy differs from those of competitors like Apple and Google. Apple, known for its integrated ecosystem, tends to release fewer but more comprehensive updates. Google, with its vast range of products, adopts a more frequent patch release cycle, often addressing various aspects of its platform simultaneously.
Significant Patching Events
Numerous instances of significant patching events have shaped Microsoft’s approach. The NotPetya ransomware attack, for example, highlighted the critical need for rapid and comprehensive security patching. This event underscored the potential devastation of unchecked vulnerabilities and the importance of proactive security measures. Other instances of major patching efforts were driven by similar high-profile security breaches or critical flaws discovered in widely used software.
Microsoft’s plans to push out patches more aggressively could be influenced by the predicted IT spending growth direction. Recent forecasts, like those detailed in it spending growth direction predicted , suggest a potential surge in tech investments. This might mean more people and businesses will be relying on Microsoft’s systems, and therefore a higher need for security updates, making their patch pushing strategy even more crucial.
Impact on User Experience
The increasing frequency of patches, while beneficial for security, can sometimes negatively affect user experience. Frequent updates can lead to disruptions during work, and may require users to allocate time for installation and potentially resolve compatibility issues. Microsoft addresses these concerns through streamlined update processes, testing, and user feedback mechanisms.
Resources for Patch Development and Deployment
Microsoft leverages a vast network of engineers, testers, and security researchers to develop and deploy patches. Dedicated teams focus on specific aspects of the patching process, ensuring the reliability and security of updates. Comprehensive testing procedures are crucial to verify the effectiveness and stability of patches before release. Microsoft also utilizes various tools and platforms to automate patch deployment and track their impact on the user base.
Their development process often involves continuous improvement based on feedback and lessons learned from previous patching events.
Reasons for Increased Patching Frequency
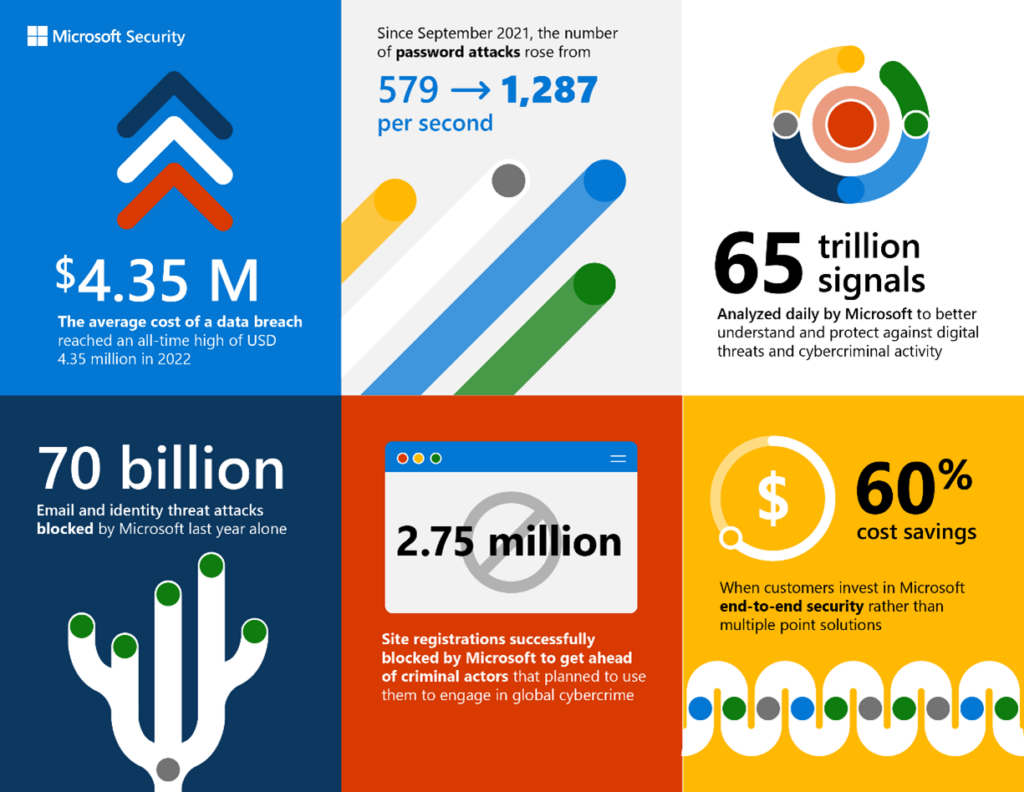
Microsoft’s commitment to security necessitates a more frequent patching cadence. The ever-evolving threat landscape, coupled with the increasing complexity of software, demands a proactive approach to vulnerability mitigation. This proactive approach aims to reduce the risk of successful cyberattacks and protect users from potentially damaging exploits. The need for rapid patching is a direct response to the ever-present and evolving nature of cyber threats.The digital landscape is rife with vulnerabilities, making constant vigilance and proactive patching crucial.
Microsoft’s increased patching frequency is a reflection of this reality. Organizations must understand the reasons behind this shift to better prepare for and respond to emerging threats.
Rising Cyber Threats and Vulnerabilities
The frequency of sophisticated cyberattacks targeting Microsoft products is on the rise. Malicious actors are constantly developing new methods to exploit vulnerabilities, demanding a more agile patching strategy. These attacks are no longer confined to specific industries or geographic locations; they are global in scope and impact. The motivation behind these attacks ranges from financial gain to political disruption.
Evolving Attack Surface for Microsoft Software
Microsoft software, with its vast user base and extensive functionalities, presents a substantial attack surface. The growing integration of various technologies, including cloud services and mobile platforms, further expands this attack surface, making it a prime target for attackers. This increased complexity necessitates a higher degree of scrutiny and a more rapid response in terms of security updates.
Successful Exploits and Targeted Vulnerabilities
Numerous successful exploits have highlighted the critical need for timely patching. Examples include exploits targeting vulnerabilities in remote code execution, memory corruption, and cryptographic libraries. These exploits often leverage publicly disclosed vulnerabilities or zero-day exploits, which require immediate patching to prevent exploitation. For instance, the WannaCry ransomware attack exploited a vulnerability in the SMB protocol, highlighting the impact of neglecting timely security updates.
Impact of Emerging Technologies on Patching
Emerging technologies like Artificial Intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT) further complicate the patching landscape. AI-powered tools are enabling attackers to develop more sophisticated exploits, demanding quicker response times. The interconnected nature of IoT devices introduces a new dimension to the attack surface, requiring a proactive approach to patching across multiple systems. The rapid development cycles of AI and IoT software necessitate faster patching to mitigate risks associated with newly discovered vulnerabilities.
Historical Analysis of Patch Release Frequency
Historically, patch release frequency has increased significantly. The rapid pace of innovation in software and the complexity of modern systems have contributed to this trend. Early versions of Microsoft software saw fewer, more spaced-out releases. However, as the threat landscape evolved, and with the advent of advanced attacks, the need for quicker, more frequent patches became apparent.
The rise of zero-day vulnerabilities and the need to address newly discovered exploits further contributed to the change.
Factors Contributing to Increased Patching Frequency
| Factor | Description | Impact | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Increased Sophistication of Attacks | Cybercriminals are developing more complex and sophisticated attacks, targeting vulnerabilities in software. | Requires faster identification and patching of vulnerabilities to prevent successful exploitation. | Exploits targeting critical infrastructure systems. |
| Expansion of Attack Surface | The increasing integration of various technologies and software components creates a larger attack surface, increasing the potential entry points for attackers. | Leads to a higher volume of potential vulnerabilities that need to be addressed. | Integration of IoT devices into home networks. |
| Emergence of Zero-Day Exploits | Zero-day exploits exploit vulnerabilities unknown to the software vendor, requiring immediate patching. | Creates a critical need for a rapid response and proactive vulnerability management. | Exploiting a newly discovered vulnerability in a widely used operating system. |
| Faster Software Development Cycles | Software development cycles are becoming shorter, leading to more frequent releases and new vulnerabilities being discovered faster. | Requires a faster patching cadence to keep pace with the software development life cycle. | Regular updates and patches for applications and operating systems. |
Potential Impacts of Increased Patching
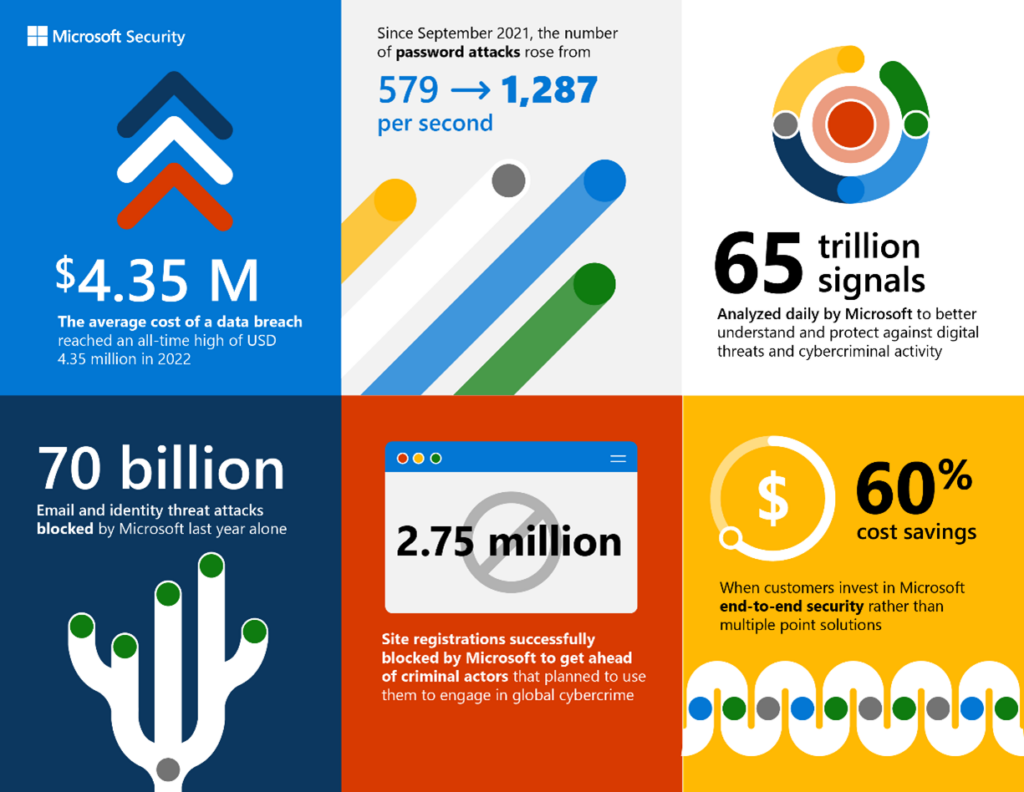
Microsoft’s decision to accelerate its patching cadence reflects a proactive approach to security, aiming to address vulnerabilities faster and mitigate risks. This increased frequency, however, introduces potential trade-offs that demand careful consideration. The impacts extend beyond just security, affecting user experience, support infrastructure, and different user groups in distinct ways.
Positive Effects on Security, Microsoft planning to push patches harder
Increased patching frequency directly translates to quicker mitigation of security vulnerabilities. This proactive approach reduces the window of opportunity for attackers to exploit weaknesses, leading to a lower risk of successful breaches. A recent example of a rapidly patched vulnerability demonstrates how prompt action can prevent widespread compromise. By patching sooner, Microsoft minimizes the potential for malicious actors to leverage exploits, bolstering the overall security posture of its software ecosystem.
Negative Impacts on User Experience
Frequent patching can lead to a higher volume of system updates, potentially disrupting user experience. This could manifest as system instability, performance degradation, or unexpected software conflicts. Users might encounter issues like application crashes, slower boot times, or problems with existing hardware configurations. The frequency of these updates could also overwhelm some users, particularly those with limited technical expertise.
Impact on Microsoft’s Support Resources and Infrastructure
The increased patching frequency necessitates substantial investment in support resources. Microsoft must scale its support teams to handle a larger volume of inquiries related to update issues. This involves training support staff, improving documentation, and developing robust troubleshooting guides. Infrastructure needs also increase to accommodate the higher volume of update deployments and support requests. A significant increase in help desk tickets could occur if users experience compatibility problems.
Impact on Different User Groups
The impact of increased patching differs across user groups. Enterprise users, with their complex systems and extensive dependencies, might experience more significant disruptions due to the cascading effects of updates on their critical infrastructure. Home users, on the other hand, might encounter more minor inconveniences, such as application compatibility issues. The varying degrees of complexity in the environments of these groups dictate the nature of the impact.
Trade-offs Between Security and User Experience
| Benefit | Drawback | Mitigation Strategy ||—|—|—|| Enhanced security posture, reduced risk of exploits | Potential system instability, performance degradation | Thorough testing of updates, clear communication to users regarding anticipated issues, provision of detailed troubleshooting guides, and phased rollout strategies for updates || Quicker vulnerability remediation | Increased user support burden | Increased support staff, robust online support forums, proactive communication with users regarding update schedules || Early identification of vulnerabilities | Potential compatibility issues between applications and updated systems | Compatibility testing, pre-release testing phases, clear documentation on potential compatibility issues || Improved protection against attacks | Increased complexity in managing updates | Automation of update deployment processes, detailed user guides, and support for user questions |
Methods for Handling Increased Patching
Microsoft’s commitment to a more frequent patching schedule necessitates a robust approach to managing these updates. This shift demands a comprehensive strategy for users and businesses to effectively integrate these patches into their existing workflows, minimizing disruption and maximizing security. A well-defined process is crucial for successful implementation and widespread adoption.Effective patch management is paramount for maintaining system stability and security.
A tailored process that balances speed with thoroughness ensures users and businesses can adapt to the increased patching frequency without compromising system integrity.
User Patch Management Process
A clear and user-friendly process for handling patch installations is essential. Users need a straightforward way to identify, download, and apply patches without significant technical hurdles.
Microsoft’s plan to push out patches more aggressively is a smart move, especially considering the current cybersecurity landscape. A critical part of this is recognizing the urgent need to address the nation’s telecom infrastructure issues, like those discussed in the insightful article “time to clean up the nations telecom mess” here. Ultimately, a robust patching strategy, combined with a modern, secure telecom system, is key to a stronger digital future for everyone.
- Automated Patch Notifications: Users should receive clear and concise notifications about available patches, ideally through a dedicated notification system integrated into the operating system or application. This system should provide details on the patch’s purpose, impact, and potential compatibility issues. Examples include email alerts or in-app prompts.
- Phased Patch Deployment: Allowing users to select a preferred deployment schedule for patches ensures a smoother transition. This could be immediate, or on a user-defined interval, such as the end of the day or on a weekend.
- Clear Patch Descriptions: Detailed descriptions of each patch should be readily available to users. This should include a clear explanation of the vulnerability addressed, the patch’s functionality, and any potential compatibility issues.
- Simplified Installation Guidance: Provide clear and concise installation instructions for patches, with visuals or step-by-step guides where applicable. The process should be as intuitive as possible to minimize user errors.
Automated Patch Deployment for Businesses
Businesses require automated systems to efficiently deploy patches across their networks. This automated approach reduces manual intervention and minimizes downtime.
- Centralized Patch Management Systems: Employing a centralized patch management system enables businesses to deploy patches uniformly across their entire network. This allows for coordinated and consistent updates.
- Scheduling and Prioritization: Establish a clear schedule for patch deployments, prioritizing critical security patches to minimize disruptions to business operations. This could involve scheduling deployments during off-peak hours or using specific patch deployment windows.
- Testing Environments: Implement a testing environment where patches can be thoroughly evaluated before deployment to the production network. This will ensure compatibility and stability before applying updates to live systems. A test environment could involve using a subset of production servers or dedicated virtual machines.
- Rollback Mechanisms: Implement a rollback mechanism to revert to a previous stable state if issues arise after a patch deployment. This contingency plan is vital to minimize the impact of unexpected issues.
Patch Release Communication Strategies
Effective communication regarding patch releases is crucial for ensuring smooth deployment and minimizing user confusion.
- Phased Rollouts: Employing phased rollouts allows for targeted testing and minimizes potential issues. This could involve deploying to a select group of users or servers before a wider release.
- Dedicated Patch Release Forums/Channels: Establish dedicated forums or channels for users to ask questions and report issues after a patch release. This provides a centralized point of contact and facilitates rapid issue resolution.
- Patch Summary Emails/Web Pages: Prepare summary emails or dedicated web pages to inform users about the patch release, including the purpose, impacted components, and any potential effects. These resources should be readily accessible to all users.
Patch Release and Deployment Flowchart
A flowchart would visually depict the patch release and deployment process. It would illustrate the stages from initial identification of vulnerabilities to final deployment. This flowchart would show the steps for validation, testing, communication, and deployment. It would be a valuable tool for both users and administrators.[A flowchart would be displayed here. It would include steps such as vulnerability identification, patch development, testing, communication, deployment, and post-deployment monitoring.]
Patch Testing Best Practices
Testing patches thoroughly before deployment is critical to avoid issues after widespread application.
- Thorough Regression Testing: Comprehensive testing should include various scenarios and configurations to ensure compatibility across all potential use cases. Regression tests ensure that the patch does not introduce new bugs or break existing functionality.
- Security Audits: Security audits of patched systems should be performed to validate the effectiveness of the patch and ensure that it does not introduce new security vulnerabilities.
- Performance Benchmarks: Performance benchmarks should be taken to determine if the patch impacts system performance negatively. Testing on different hardware configurations and workloads is important.
Strategies for Dealing with Post-Deployment Issues
Having a proactive strategy to address issues that may arise after patch deployment is crucial.
- Dedicated Support Channels: Establish dedicated support channels for users to report issues promptly. This could include a dedicated help desk or a community forum.
- Monitoring Systems: Employ monitoring systems to track system performance and stability after the patch release. This allows for early detection of any performance degradation or other issues.
- Rollback Procedures: Have clear and well-documented rollback procedures ready in case of issues that necessitate reverting to a previous state.
Future Implications of the Trend: Microsoft Planning To Push Patches Harder
Microsoft’s increased patching frequency signifies a shift in the software lifecycle. This proactive approach, while beneficial in addressing security vulnerabilities, presents a cascade of potential implications across various sectors. The speed and scale of these changes demand a deeper understanding of the future ramifications for developers, users, and the broader IT landscape.
Potential Long-Term Effects on Software Development
The accelerated patching pace will likely lead to a greater emphasis on robust, automated testing procedures. Developers will need to incorporate more stringent quality assurance measures into their workflows, increasing the time and resources devoted to testing. This heightened focus on prevention, alongside the need for quicker response times, will inevitably drive innovation in development methodologies and tools.
Furthermore, the need to anticipate and prepare for potential vulnerabilities in future software versions will be paramount.
Influence on the Relationship Between Software Vendors and Users
The evolving relationship between software vendors and users will be characterized by a greater reliance on ongoing support and updates. Users will expect more frequent, reliable patches, and vendors will need to demonstrate their commitment to security and maintainability. Transparency regarding vulnerabilities and the patching process will be crucial for building and sustaining trust.
Implications for the IT Support Industry
The IT support industry will face significant adjustments as the frequency of patching increases. Support teams will need to be prepared for higher volumes of support requests and a more complex environment. This requires specialized training, improved infrastructure, and potentially the adoption of new tools to manage and deploy patches effectively.
Potential Impacts on the Cybersecurity Landscape
The increased patching frequency could potentially lead to a reduction in successful exploits. By swiftly addressing vulnerabilities, Microsoft aims to mitigate the impact of security breaches. However, the rapid pace of patching could also drive cybercriminals to adapt and develop new attack vectors more quickly. This creates a dynamic and ongoing arms race between security professionals and malicious actors.
Emerging Challenges Related to Increased Patching Pace
One significant challenge will be managing the complexity of deploying patches across diverse environments and user bases. Compatibility issues, conflicts with existing software, and user resistance to updates will require careful consideration and effective communication strategies. Furthermore, the sheer volume of patches could overwhelm systems, leading to issues with deployment efficiency and potentially introducing new vulnerabilities during the patch process.
Potential Future Scenarios
| Scenario | Description | Potential Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Increased User Frustration | Frequent and disruptive updates lead to user dissatisfaction and decreased productivity. | Reduced user adoption, decreased software satisfaction ratings, and potential loss of market share. |
| Enhanced Cybersecurity Posture | Rapid patching mitigates vulnerabilities effectively, leading to a stronger overall cybersecurity posture. | Reduced attack surface, decreased security breaches, and improved user trust. |
| Increased Complexity in IT Support | Managing the increased volume of patches and associated support requests strains IT support teams. | Higher workload for support staff, potential for errors in patch deployments, and increased costs for support services. |
| Cybercriminals Adapt Quickly | Rapid patching incentivizes cybercriminals to develop new attack vectors and exploit vulnerabilities more quickly. | Heightened threat landscape, increased sophistication of attacks, and greater need for advanced security solutions. |
Final Wrap-Up
Microsoft’s decision to prioritize security through more frequent patches raises significant implications for both users and the technology landscape. The increased patching frequency is a direct response to the escalating threat landscape. Balancing security needs with user experience will be crucial. Adapting to this new patching regime will demand proactive strategies from both individual users and enterprise IT departments.
The future implications of this trend, including potential shifts in software development and user expectations, are significant and warrant careful consideration.