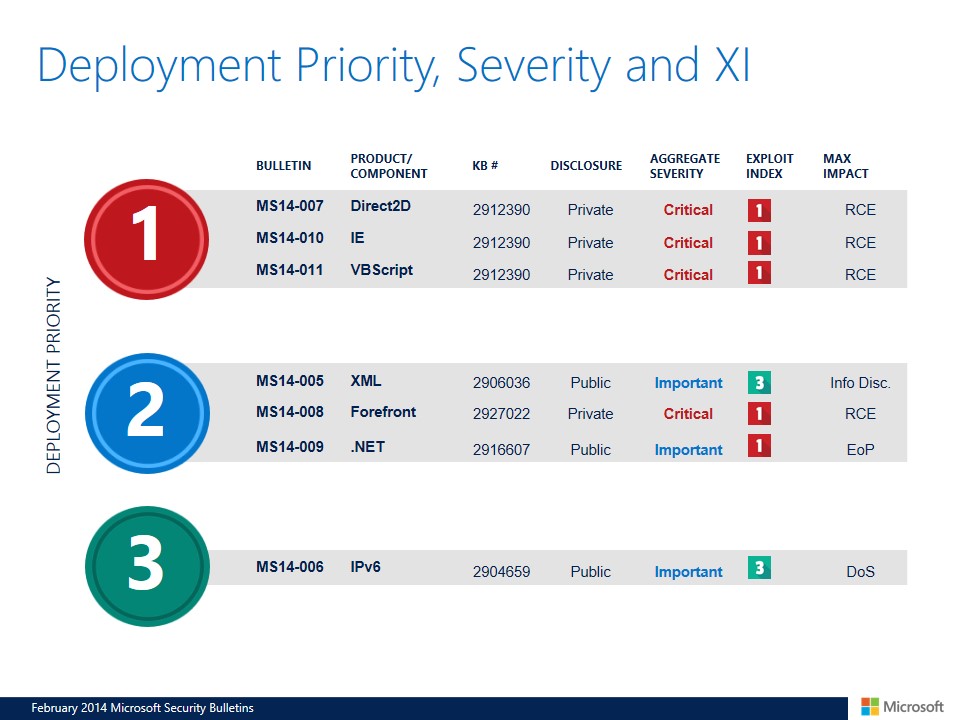
Microsoft Releases Monthly Patches, Delays Explorer Fix
Microsoft releases monthly patches delays explorer fix – Microsoft releases monthly patches, delays Explorer fix sets the stage for a detailed look at the complexities behind software updates. We’ll explore the typical Microsoft patch release schedule, examining security, feature, and driver updates. Delays in fixing Explorer issues are also scrutinized, considering the reasons behind them, their impact on user experience, and potential mitigation strategies. The consequences of these delays, both in terms of reputation and financial implications, are also assessed, offering a comprehensive analysis of this often-overlooked aspect of software development.
The monthly patch release cycle is a critical part of maintaining software security and functionality. Different types of patches—security, feature, and driver—have varying release frequencies. The delay in fixing Explorer issues, a core component of the Windows experience, highlights the intricate challenges involved in software development. This delay can lead to frustrating user experiences and decreased productivity. The potential security risks and financial repercussions of these delays are substantial, and need to be carefully considered.
Microsoft Patch Release Cycle
Microsoft’s monthly patch releases are a crucial part of maintaining the security and functionality of its software products. These updates address vulnerabilities, enhance features, and improve overall system performance. Understanding the release cycle provides insight into the timing and types of updates users can expect.
Typical Monthly Patch Release Schedule
Microsoft follows a predictable, though not always precisely fixed, schedule for its monthly updates. Generally, a new set of patches is released on the second Tuesday of each month. This timing allows software vendors and IT administrators time to prepare for the deployments. However, there are often exceptions due to holidays or unforeseen circumstances. The schedule is documented and communicated publicly, but can vary in some cases.
Types of Patches and Their Purposes
Microsoft releases various types of patches to address different needs. These patches serve different purposes and are released with varying frequency.
Security Patches
Security patches are the most crucial type. They are released monthly to address vulnerabilities in the software that could potentially be exploited by malicious actors. These vulnerabilities, if left unpatched, could expose systems to security risks, data breaches, or other malicious activity. For instance, a recent security patch addressed a critical vulnerability in the Windows kernel, which could have allowed remote attackers to take control of vulnerable systems.
Feature Patches
Feature patches, also known as functionality updates, are released less frequently, often quarterly. These patches introduce new features, enhance existing functionalities, or improve the overall user experience. For example, a recent feature update for Microsoft Office added the ability to collaborate on documents in real-time. Such updates enhance productivity and efficiency for users.
Driver Patches, Microsoft releases monthly patches delays explorer fix
Driver patches are released as needed to address issues or update device drivers. They are not released on a fixed schedule. The frequency of driver updates depends on the reported issues or the need for compatibility with new hardware. For example, if a new graphics card is released, the associated driver would need an update to ensure proper functioning.
Patch Release Frequency Comparison
Explorer Fix Delay
The recent delays in patching Explorer-related issues highlight a complex interplay of factors in software development. Addressing bugs in a critical system like Windows Explorer, which touches upon countless other applications and user interactions, demands meticulous planning and execution. This delay, while frustrating for users, underscores the intricate nature of software maintenance and the need for thorough testing and validation.Delays in addressing Explorer issues stem from a confluence of factors, ranging from the complexity of the codebase to the necessity for comprehensive testing across various hardware and software configurations.
The interplay between these factors influences the release schedule and often necessitates adjustments to accommodate unexpected challenges.
Potential Reasons for Delays
The intricate nature of Explorer’s codebase, its vast integration with other system components, and the diverse range of hardware configurations users employ all contribute to the challenges in timely bug fixes. Debugging and resolving issues in a system as deeply embedded as Explorer requires significant effort and meticulous testing across a wide spectrum of scenarios.
Factors Contributing to Timing of Fixes
A multitude of factors influence the scheduling of Explorer bug fixes. These include the severity of the issue, the availability of resources for testing and development, and the prioritization of critical bugs within the broader Microsoft patch release cycle. The need for comprehensive testing across various operating systems, hardware configurations, and applications significantly impacts the timeline for bug fixes.
Complexity of Fixing Explorer Issues
Fixing Explorer issues is complex due to its critical role in the operating system. Modifications to Explorer can potentially impact the stability and functionality of other applications and system components. This necessitates rigorous testing and validation to prevent unintended consequences. For instance, a fix for a display bug in Explorer might inadvertently introduce a compatibility problem with a specific graphics driver, requiring additional debugging time.
Impact on User Experience and Productivity
Delayed Explorer fixes can significantly impact user experience and productivity. Issues like slow performance, erratic behavior, or display glitches can lead to frustration and reduced efficiency. The impact is amplified when Explorer issues impede access to essential files or applications. For example, if Explorer stops responding or crashes, users lose access to their documents, making it difficult to complete tasks.
This, in turn, leads to lost productivity and potentially missed deadlines.
Impact Assessment

Delayed Microsoft patch releases, particularly those impacting critical systems like the Explorer, can have far-reaching consequences. These delays create vulnerabilities that attackers can exploit, leading to potential reputational damage and financial losses for the company and its users. Understanding the potential risks associated with these delays is crucial for proactive mitigation strategies.
Potential Reputational Damage
Microsoft’s reputation hinges on its commitment to security and user trust. Delays in patching critical vulnerabilities can erode this trust. Negative publicity generated by security breaches stemming from unpatched systems can significantly damage their brand image. Past examples of major security breaches demonstrate the long-lasting impact negative publicity can have on a company’s perceived reliability and trustworthiness.
For instance, a major data breach following a delay in patching a known vulnerability could lead to a significant drop in user confidence and market share.
Security Risks Associated with Delayed Explorer Fixes
Delayed Explorer fixes introduce substantial security risks. The Explorer, as a crucial component of the Windows operating system, is frequently targeted by malicious actors seeking access to sensitive data or system control. Unpatched vulnerabilities in the Explorer can allow attackers to gain unauthorized access to user systems, potentially leading to data theft, system compromise, or the deployment of malware.
This risk is particularly high for users who heavily rely on Explorer for data management and access.
Financial Implications of Delayed Fixes
Delayed patch releases can lead to substantial financial repercussions for Microsoft. The cost of addressing security breaches, paying out fines for data breaches, and the loss of user trust can translate into significant financial losses. The following table Artikels the potential financial implications of delayed fixes across different delay periods. It is important to note that these figures are estimates and the actual impact can vary based on the specific vulnerabilities and the scale of the breach.
User Perspective
Microsoft’s commitment to security updates is crucial, but delays in patching Explorer can significantly impact the user experience. These delays, while often necessary for thorough testing and resolution, can lead to frustrating issues and reduced productivity. Understanding the user’s perspective is essential for gauging the impact of these release cycles.
Impact on User Experience
Delayed Explorer fixes can create a ripple effect, affecting various aspects of the user experience. Users rely on the Explorer to navigate their files and applications efficiently. When these functions are compromised by bugs or vulnerabilities, their workflow becomes disrupted.
Common User Frustrations
Users often encounter several frustrating situations due to Explorer issues. Common complaints include:
- Inconsistent File Operations: Files might disappear, become corrupted, or fail to open correctly. This can lead to data loss or severe disruptions in work processes, especially for users with extensive file management needs.
- Slow Performance and Functionality: Explorer’s sluggish performance or unexpected crashes can slow down overall system responsiveness, making users wait longer to complete tasks.
- Security Risks: Unpatched vulnerabilities in Explorer can expose users to potential security breaches. These risks can range from minor inconveniences to major data compromises, depending on the severity of the issue and how it’s exploited.
- Compatibility Issues: Explorer updates can sometimes introduce incompatibility issues with other software applications or devices. This can lead to issues with file sharing, printing, or accessing specific files.
Effect on User Productivity and Workflow
Explorer’s role in user workflow is undeniable. The Explorer’s stability and responsiveness directly impact a user’s ability to perform tasks efficiently. Delays in patching create a domino effect, disrupting productivity and potentially leading to wasted time and frustration. For example, a crucial document may be inaccessible due to an Explorer bug, or a critical workflow step may be interrupted by a malfunctioning Explorer feature.
This disruption in workflow can range from minor inconveniences to significant delays in project completion.
User Reactions to Delayed Patch Releases
User reactions to delayed patch releases vary. Some users may tolerate the inconvenience, while others express frustration and concern. Users with specific needs, such as large-scale file transfers or complex workflows, are disproportionately affected by these delays. Some might resort to workarounds, while others might look for alternative solutions. The degree of frustration is also dependent on the severity and frequency of the Explorer issues.
Potential Mitigation Strategies
Addressing delays in Microsoft patch releases and Explorer fixes requires a multifaceted approach. Proactive measures, robust bug tracking processes, and improved communication channels are crucial to minimizing future disruptions and ensuring a smoother user experience. The goal is to anticipate potential problems, streamline the resolution process, and keep users informed throughout the entire patch deployment lifecycle.
Microsoft’s recent delay in releasing monthly patches to fix Explorer issues is a bit frustrating, isn’t it? While we’re waiting for those crucial fixes, it makes me think about broader privacy concerns, like those surrounding RFID tags. The increasing use of RFID tags raises questions about the collection and potential misuse of personal data. For a deeper dive into this topic, check out this informative piece on rfid tags and the question of personal privacy.
Hopefully, Microsoft will prioritize the Explorer patch soon, so we can get back to our daily tasks without these annoying glitches!
Proactive Measures to Prevent Future Delays
Implementing preventative measures is essential for reducing the likelihood of future delays. These strategies focus on identifying potential bottlenecks and proactively addressing them before they escalate into significant issues. A critical element is anticipating potential dependencies and conflicts in the software development pipeline.
- Comprehensive Testing Regimes: Establishing rigorous and thorough testing procedures for each component of the patch is vital. This includes simulating various scenarios, considering diverse hardware configurations, and incorporating user feedback to ensure compatibility and stability. For example, extensive beta testing programs can help identify and address issues early on, reducing the risk of widespread problems after a patch is released.
- Resource Allocation & Planning: Adequate staffing and allocation of resources to development and testing teams are crucial. This includes assigning dedicated personnel to each task to ensure timely completion and avoiding bottlenecks. By proactively allocating resources, Microsoft can ensure that crucial development tasks, like the Explorer fix, receive the necessary attention to avoid delays.
- Predictive Modeling & Risk Assessment: Employing data analysis and predictive modeling to forecast potential challenges and resource requirements can be extremely helpful. This can allow the team to anticipate potential roadblocks and plan for them in advance, preventing delays. For instance, analyzing historical data on bug reporting and fix times can help predict resource needs for upcoming patch cycles.
Best Practices for Effective Bug Tracking and Resolution
Efficient bug tracking and resolution is essential to minimize delays. A well-defined process, including clear documentation and communication, helps streamline the entire process.
Microsoft’s latest monthly patches, while addressing crucial issues, have unfortunately delayed a fix for the Explorer bug. This is a bit frustrating, especially considering the ongoing shift in how we compress files, with the potential end of zip compression as we know it looming on the horizon. the end of zip compression as we know it might not directly impact the Explorer issue, but it certainly underscores the evolving landscape of file management.
Hopefully, Microsoft can expedite the Explorer fix soon, keeping us from having to constantly adjust to the changes.
- Standardized Bug Reporting Templates: Implementing standardized templates for bug reporting ensures consistency and clarity. This includes standardized fields for bug descriptions, steps to reproduce, expected behavior, and actual behavior. This allows developers to quickly understand and address the issue.
- Prioritization of Bugs Based on Severity and Impact: Prioritizing bug fixes based on their severity and potential impact on users is vital. This ensures that critical issues are addressed promptly, preventing significant disruptions. For example, security vulnerabilities or bugs affecting the core functionality of Explorer should be prioritized over minor graphical glitches.
- Collaborative Development Environments: Encouraging collaboration between development and testing teams through shared platforms and communication channels is essential. This facilitates rapid issue identification and resolution, reducing the time required for fixes. Real-time collaboration tools and platforms can be employed to ensure efficient communication.
Strategies to Improve Communication with Users About Patch Delays
Transparent communication with users is essential to manage expectations and maintain trust. Proactive communication can mitigate negative impact during delays.
- Early Communication & Regular Updates: Providing clear and timely updates to users about patch delays is crucial. This includes outlining the reasons for the delay, the expected timeframe for resolution, and the impact on their experience. This builds trust and confidence with users.
- User Feedback Mechanisms: Implementing user feedback mechanisms, such as surveys, forums, or dedicated channels for reporting issues, is essential. This provides valuable insights into the user experience and helps identify emerging problems. This allows Microsoft to tailor their communication to address user concerns.
- Dedicated Support Channels: Providing dedicated support channels, such as phone lines or online chat, allows users to ask questions and get assistance related to the delay. This approach fosters trust and empowers users to understand the situation.
Methods for Prioritizing Explorer Fixes Within the Development Pipeline
Prioritization is key to ensuring critical fixes are addressed promptly. A clear method for evaluating fixes ensures that Explorer’s stability and functionality are maintained.
- Impact Assessment Matrix: Developing an impact assessment matrix to categorize Explorer fixes based on their potential impact on user experience and system stability is essential. This allows for a structured approach to prioritization. This matrix should categorize fixes based on factors like the number of users affected, the severity of the issue, and the potential for system instability.
- Stakeholder Input: Incorporating input from various stakeholders, including developers, testers, and product managers, is crucial. This ensures that all perspectives are considered when prioritizing fixes. For example, product managers can provide insight into the impact on user workflows, while developers can provide technical details on the complexity of the fix.
- Metric-Based Prioritization: Establishing clear metrics to track the frequency, severity, and impact of Explorer issues is essential. This provides a data-driven approach to prioritizing fixes, ensuring that the most significant problems are addressed first. Metrics could include the number of reported issues, the time to resolution, and the number of users affected.
Technical Analysis
Microsoft’s Explorer patches, crucial for maintaining system stability and user experience, present unique technical challenges. The intricate nature of the Explorer component, interacting with a multitude of system processes and user-driven actions, necessitates meticulous analysis and testing before deployment. Addressing bugs in this component often involves tracing complex interactions and understanding the specific conditions triggering the issue.
Technical Challenges in Addressing Explorer Bugs
Debugging Explorer-related issues often involves dissecting complex interactions between the Explorer shell, file systems, and user-initiated actions. The sheer volume of potential interactions, combined with the dynamic nature of file system changes and user input, creates a multifaceted debugging process. Isolating the root cause of an issue can be time-consuming, requiring careful examination of system logs, application traces, and user reports.
Furthermore, the wide range of hardware and software configurations used by Microsoft users contributes to the complexity of issue reproduction and resolution.
Importance of Thorough Testing for Explorer Patches
Thorough testing is paramount for Explorer patches to ensure compatibility and stability across a broad spectrum of hardware and software configurations. Incomplete testing can lead to unexpected issues, including application crashes, performance degradation, and security vulnerabilities, potentially affecting millions of users. Comprehensive testing protocols must account for diverse user scenarios, hardware variations, and software configurations. The potential for user-triggered conflicts with existing applications and services highlights the necessity of extensive testing.
Testing Procedures for Explorer Patches to Ensure Compatibility
Rigorous testing procedures are implemented to verify the compatibility and stability of Explorer patches. This includes automated regression testing, designed to identify any regressions in existing functionalities. The process often involves running patches on various test environments, simulating diverse hardware and software configurations. Manual testing is crucial, involving expert testers replicating user scenarios and reporting potential issues.
Specific testing criteria should include compatibility with older and newer versions of Windows, various hardware configurations, and different applications, ensuring seamless integration.
Technical Factors Affecting Patch Deployment
Several technical factors influence the successful deployment of Explorer patches. These factors include the complexity of the Explorer component itself, the potential for compatibility issues with other applications and drivers, and the need to balance patch rollout speed with the risk of introducing new issues. Patch size can also be a significant factor, impacting deployment time and user experience during the update process.
- Patch Size and Deployment Time: Larger patches often require more time for deployment, potentially impacting user productivity and potentially introducing latency or stability issues during the process. Microsoft must carefully consider the balance between rapid deployment and thorough testing, especially when dealing with significant patch sizes. For example, if a patch is too large, users may experience prolonged download times, increasing the likelihood of interruptions during critical tasks.
- Compatibility with Other Applications and Drivers: Explorer interacts with a vast array of applications and drivers. Testing must ensure that the patch does not introduce conflicts or disrupt existing functionality. For instance, a poorly tested patch could cause problems with specific applications, leading to unexpected errors or crashes.
- Balancing Patch Rollout Speed with Risk: The faster a patch is rolled out, the greater the potential risk of introducing unexpected issues. A careful balance is required between rapid deployment and thorough testing to minimize disruption to users while ensuring stability.
Specific Technical Factors Affecting Patch Deployment
Deployment considerations encompass network infrastructure limitations, user hardware capabilities, and the need to manage diverse user scenarios. Maintaining compatibility across various versions of Windows, while simultaneously mitigating the risk of conflicts with other software, necessitates sophisticated planning. Careful consideration of the potential impact on various hardware configurations and software dependencies is vital.
Alternative Solutions
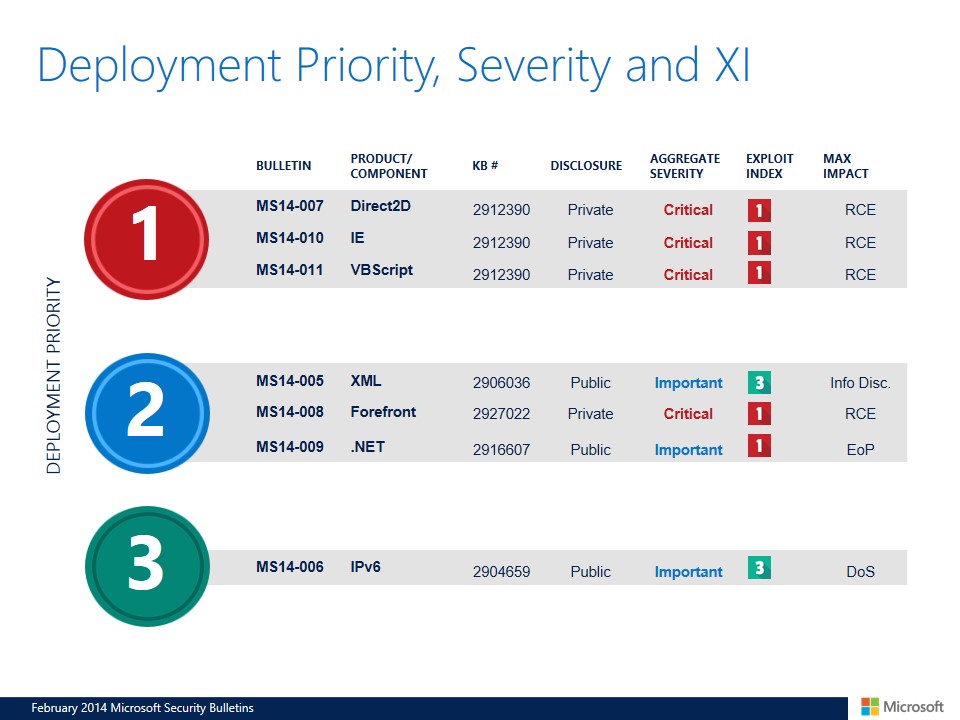
Microsoft’s recent patch release delays, particularly concerning Explorer issues, necessitate alternative solutions for users. These solutions are crucial for minimizing disruptions while waiting for official fixes. Addressing these problems proactively ensures a smoother user experience during this transitional period.Users may experience various symptoms related to Explorer functionality, including slow performance, unexpected crashes, or incompatibility with specific applications. Implementing temporary workarounds can effectively alleviate these issues, allowing users to continue working productively despite the delay in official patches.
Workarounds for Common Explorer Problems
Temporary fixes can mitigate the impact of delayed patches. These solutions are not a replacement for the permanent fixes but offer practical approaches to address immediate issues.
- Disabling Unnecessary Extensions: Certain browser extensions can interfere with Explorer’s functionality, leading to performance problems or instability. Temporarily disabling these extensions might resolve the issue. For example, if a particular add-on is known to conflict with Explorer’s rendering engine, temporarily disabling it might restore proper functionality.
- Updating Drivers: Outdated or incompatible drivers can cause various issues, including Explorer malfunctions. Ensuring drivers are up-to-date can prevent unexpected behavior. This step is crucial for maintaining stable system performance, as outdated drivers might lead to conflicts with Explorer’s underlying components.
- Using Compatibility Mode: If Explorer exhibits issues with specific websites or applications, enabling compatibility mode for the affected programs can sometimes restore functionality. For instance, forcing a program to run in an older version of Windows can ensure compatibility with the Explorer version in use. This technique may temporarily resolve the problem until a patch is available.
- Clearing Browser Cache and Cookies: Accumulated temporary files can sometimes disrupt Explorer’s operations. Clearing the browser’s cache and cookies can free up resources and improve performance. This approach can be particularly useful for users experiencing slow loading times or unexpected behavior. Regularly clearing the cache and cookies can resolve minor performance issues caused by outdated or corrupted data.
Minimizing Impact of Delayed Patches
Strategies for minimizing the impact of delayed patches are vital for maintaining productivity. By implementing these measures, users can mitigate the negative effects while awaiting official fixes.
Microsoft’s delayed monthly patches for Explorer are definitely a concern, highlighting vulnerabilities that could be exploited. This isn’t an isolated incident, as recent reports from Symantec reveal a disturbing trend of more sophisticated attacks. For example, Symantec’s analysis indicates a rising number of blended attacks, combining various techniques to bypass security measures. This underscores the need for proactive security measures, and highlights the urgency in addressing the Explorer fix.
In short, these delayed patches are a critical issue, and ongoing research like Symantec’s work ( symantec more computer attacks use blended tactics ) are crucial for staying ahead of these evolving threats.
- Prioritizing Essential Tasks: Focus on completing crucial tasks first to minimize disruption from potential Explorer issues. This approach ensures essential work is done even with temporary performance limitations. For instance, completing urgent projects or handling critical emails can be prioritized over less time-sensitive activities.
- Scheduling Maintenance Tasks: Scheduling tasks like driver updates or cache cleaning for off-peak hours can minimize disruption during crucial work periods. Scheduling these tasks ensures they are completed without impacting ongoing operations, preventing unnecessary delays. This proactive measure reduces the potential impact of temporary issues.
- Utilizing System Restore Points: Creating frequent restore points can enable quick recovery in case of unexpected issues. Using restore points offers a backup solution, allowing users to revert to a stable state if a temporary workaround doesn’t resolve the problem. This approach ensures that users can easily recover from unexpected problems.
Community Support Options
Community support plays a crucial role in resolving issues arising from delayed patches. Utilizing these resources can offer solutions and insights into troubleshooting issues.
- Microsoft Forums and Communities: Microsoft’s official forums and communities are valuable resources for seeking support and solutions. These platforms allow users to connect with others experiencing similar problems and potentially find solutions from other users or support staff. Users can ask questions, share their experiences, and seek guidance.
- Dedicated Support Groups: Online groups dedicated to specific applications or software versions can provide insights and workarounds. These forums can offer a wealth of experience-based solutions. These groups can offer a more targeted and focused approach to problem-solving.
Historical Context: Microsoft Releases Monthly Patches Delays Explorer Fix
Microsoft’s patch release cycle, while aiming for stability and security, has faced occasional delays. Understanding the history of these delays provides valuable context for assessing the current situation and anticipating future challenges. Analyzing past instances reveals patterns and potential factors contributing to these delays, which ultimately impacts user experience and trust in the software.
Previous Instances of Patch Delays
Microsoft has experienced various patch release delays across its product lines. These delays have affected operating systems like Windows, productivity suites like Office, and other applications. Specific examples include instances where security patches were delayed due to unforeseen issues in testing or unforeseen vulnerabilities discovered in the software.
Reasons Behind Delays
Several factors contribute to patch release delays. These include:
- Complexity of the Software: Modern software is incredibly complex, with millions of lines of code and intricate dependencies. Identifying and fixing vulnerabilities within this complex ecosystem can be a time-consuming process, particularly for critical updates. The sheer scale and interconnectedness of the software introduce delays in identifying and addressing vulnerabilities.
- Unforeseen Vulnerabilities: Discovering critical vulnerabilities in the software during the testing phase can necessitate significant rework and adjustments to the patch. A major vulnerability discovered after a patch is already under development can cause a delay in release, as Microsoft needs to ensure the patch is comprehensive and thoroughly addresses the new vulnerability.
- Testing and Verification Procedures: Rigorous testing is crucial for ensuring the stability and security of patches. Extensive testing across diverse hardware and software configurations can take significant time. The goal is to prevent regressions, ensure the patch doesn’t introduce new issues, and validate its effectiveness in different environments. This is particularly important for critical updates that affect the core functionality of the software.
- Resource Constraints: Microsoft, like any software company, faces limitations in terms of resources, including personnel, infrastructure, and time. Delays can occur if the development team is stretched thin or if essential resources are unavailable for the specific project. The ability to manage resources and prioritize tasks effectively is essential in maintaining the integrity of the patch release cycle.
Impact on User Satisfaction
Delays in patch releases can negatively impact user satisfaction. Users rely on timely security updates to protect their systems from malware and vulnerabilities. The perceived lack of proactive security measures can erode trust in the software. Users may also experience disruptions in their workflow due to incompatibility issues or other unexpected problems caused by the delays.
- Security Concerns: Delayed patches leave systems vulnerable to potential attacks. Users are at greater risk of exploitation while waiting for security updates.
- Disruptions to Workflows: Patches can introduce compatibility issues, impacting productivity and workflow. This is particularly concerning for businesses that depend on the stability of the software.
- Decreased Trust: Consistent delays in patch releases can erode user trust and confidence in the product’s reliability. The perceived vulnerability can discourage users from continuing to use the software.
Patterns and Trends in the Release Cycle
Analyzing past instances of delays helps identify patterns and trends. This can include identifying specific stages in the release cycle that are most susceptible to delays, or potential correlation between release frequency and the likelihood of encountering unforeseen issues. The aim is to predict and mitigate delays effectively.
- Release Frequency Correlation: Analyzing the frequency of releases and the occurrences of delays can help determine if there’s a correlation between the two.
- Issue Types Correlation: Delays can be correlated with the types of issues encountered. For instance, complex vulnerabilities or those requiring extensive rework might be more likely to cause delays.
Closing Notes
In conclusion, Microsoft’s patch release schedule, while seemingly routine, presents complex challenges in balancing security, feature updates, and timely bug fixes. Delays in addressing Explorer issues, particularly, underscore the intricate interplay between technical complexities, user expectations, and the overall impact on the software ecosystem. Proactive measures to prevent future delays, improved communication with users, and prioritized bug tracking are crucial to ensuring a smooth user experience.
Ultimately, maintaining a responsive and reliable patch release cycle is essential for both Microsoft and its users.