Microsoft Warns Excel Users of Zero-Day Attacks
Microsoft warns excel users of zero day attacks – Microsoft warns Excel users of zero-day attacks, highlighting a critical security vulnerability. This urgent warning emphasizes the importance of immediate action to protect against these sophisticated attacks, which could potentially compromise sensitive data and systems. Understanding the nature of these zero-day exploits and Microsoft’s response is crucial for safeguarding your data and systems.
The vulnerability stems from a newly discovered zero-day exploit within Microsoft Excel. This exploit allows attackers to execute malicious code without the user’s knowledge, making it a significant threat to individuals and organizations alike. The nature of the exploit and its potential impact demand immediate attention.
Background on Excel Vulnerabilities
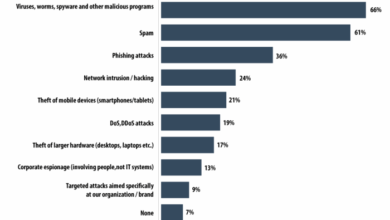
Microsoft Excel, a ubiquitous tool for data analysis and manipulation, has unfortunately been a target for security vulnerabilities throughout its history. These vulnerabilities, often exploited by malicious actors, highlight the critical need for continuous security updates and user awareness. Understanding the evolution of these attacks and the types of vulnerabilities they exploit is crucial for mitigating risks.Excel’s evolving role in modern business and personal computing has increased its susceptibility to sophisticated attack vectors.
Attackers leverage the wide use of Excel spreadsheets to craft malicious documents that, when opened, execute malicious code, potentially compromising entire systems. This trend underscores the need for robust security measures both on the application side and the user end.
Historical Overview of Excel Vulnerabilities
Excel, like many software applications, has a history of vulnerabilities. Early vulnerabilities often stemmed from simple programming errors or weaknesses in handling specific file formats. As technology advanced, attackers began developing more sophisticated techniques, exploiting features like macros and the handling of embedded objects.
Evolution of Attack Methods
The methods used to exploit Excel vulnerabilities have evolved significantly over time. Early attacks focused on exploiting buffer overflows and other common software vulnerabilities. However, more recent attacks often leverage social engineering tactics to trick users into opening malicious documents. This shift has highlighted the critical role of user education and awareness in preventing these attacks.
Examples of Past Vulnerabilities and Their Impact
Numerous past vulnerabilities have demonstrated the potential impact of Excel-based attacks. For instance, vulnerabilities related to macro execution have allowed attackers to steal sensitive data, install malware, or disrupt business operations. The impact of these attacks can range from minor data breaches to significant financial losses and operational disruptions. One noteworthy example involves the widespread use of malicious macros disguised as legitimate spreadsheets, leading to significant data loss in various organizations.
Comparison of Excel Vulnerabilities Over Time
| Year | Vulnerability Type | Attack Method | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Early 2000s | Buffer Overflows | Exploiting memory management flaws | Data corruption, system crashes, potential code execution |
| Mid-2000s | Macro-based exploits | Malicious macros disguised as legitimate documents | Data theft, malware installation, system compromise |
| 2010s-Present | Social Engineering | Tricking users into opening malicious documents via email or other means | Data theft, ransomware attacks, operational disruption |
| 2010s-Present | Zero-day exploits | Exploiting vulnerabilities unknown to the vendor | High impact, potentially bypassing security defenses |
Understanding the “Zero-Day” Attack
Zero-day exploits represent a significant threat in the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity. These attacks exploit vulnerabilities in software that are unknown to the vendor, meaning no patch exists to mitigate them. This lack of prior knowledge makes them particularly dangerous, allowing attackers to leverage the vulnerability before developers have had a chance to identify and fix it. Understanding how zero-day attacks work is crucial for organizations to bolster their defenses.Zero-day exploits are attacks that leverage vulnerabilities in software before the software vendor is aware of the flaw.
This lack of awareness creates a critical window of opportunity for malicious actors. The swiftness with which attackers can exploit these vulnerabilities often leaves organizations scrambling to implement countermeasures. The consequences can range from data breaches and financial losses to severe reputational damage.
The Nature of Zero-Day Exploits
Zero-day exploits are fundamentally attacks that capitalize on unknown software flaws. The “zero-day” moniker refers to the fact that the vulnerability is completely new and unpatched. This characteristic makes them extremely challenging to defend against, as no pre-emptive measures have been taken. The attacker’s knowledge of the vulnerability often allows them to target specific individuals or organizations.
Significance in the Context of Software Vulnerabilities
Zero-day attacks hold a unique position in the realm of software vulnerabilities. Their unprecedented nature poses a significant threat to the security of software systems. The lack of existing patches leaves organizations exposed to immediate exploitation. This is often exacerbated by the rapid spread of malware, which can propagate and infect multiple systems before defenses can be deployed.
A successful zero-day attack can cause widespread damage.
Challenges in Mitigating Zero-Day Threats
Mitigation strategies for zero-day threats face considerable challenges. The very nature of the vulnerability – its unknown nature – hinders preventative measures. Organizations must rely on robust security measures like intrusion detection systems, firewalls, and strong access controls to identify and block malicious activity. Furthermore, continuous monitoring of network activity and the prompt implementation of security updates are crucial.
These measures are often insufficient to fully address the evolving nature of zero-day attacks.
Methods Attackers Employ to Exploit Zero-Day Vulnerabilities
Attackers employ a variety of techniques to exploit zero-day vulnerabilities. Social engineering tactics, such as phishing emails, are often used to trick individuals into downloading malicious software. Advanced persistent threats (APTs) often use highly sophisticated techniques to infiltrate systems, exploiting zero-day vulnerabilities to maintain long-term access. Moreover, attackers may use publicly available tools to identify and exploit zero-day vulnerabilities.
Common Zero-Day Attack Vectors
The table below illustrates common avenues attackers use to exploit zero-day vulnerabilities. Understanding these vectors allows organizations to prioritize security measures and fortify their defenses.
| Attack Vector | Description |
|---|---|
| Malicious Documents (e.g., Microsoft Office files) | Infected documents can exploit zero-day vulnerabilities to execute malicious code upon opening. |
| Compromised Websites | Attackers may compromise legitimate websites to host malicious code that exploits zero-day vulnerabilities in browsers or other software. |
| Exploit Kits | These kits contain pre-built exploits for various zero-day vulnerabilities, allowing attackers to quickly deploy attacks. |
| Vulnerable Third-Party Libraries | If a software application utilizes vulnerable third-party libraries, it becomes a potential entry point for attackers to exploit zero-day vulnerabilities. |
Microsoft’s Warning and Response

Microsoft’s recent warning about a zero-day attack targeting Excel underscores the ever-present threat of sophisticated cyberattacks. This proactive measure highlights the importance of vigilance and timely updates in maintaining a secure digital environment. Understanding Microsoft’s response provides crucial insights into how organizations and individuals can protect themselves from such vulnerabilities.Microsoft’s official statement acknowledged the existence of a zero-day exploit targeting vulnerabilities in its Excel software.
This means the exploit leverages a previously unknown flaw, enabling attackers to potentially gain unauthorized access to systems. The statement emphasizes the urgency of addressing this threat.
Microsoft’s warning about zero-day attacks targeting Excel users is definitely concerning. While these security threats are a serious issue, it’s also cool to see companies like Atari actively engaging with their community. They’re calling gamers to beta test their new TimeShift platform, atari calls gamers to beta test timeshift , which is a fascinating development. Ultimately, though, we need to remember that robust security measures are crucial in today’s digital landscape, especially considering the prevalence of these zero-day exploits.
Microsoft’s Official Statement
Microsoft’s official statement detailed the nature of the vulnerability, emphasizing its potential for significant impact. The statement provided a clear description of the affected software versions and the potential consequences of exploitation. This transparency is crucial in enabling users to understand the threat and take necessary precautions.
Key Security Measures
Microsoft Artikeld several critical security measures to mitigate the risk. These measures include prompt installation of available security updates, emphasizing the importance of keeping software patched and current. This is a fundamental aspect of cyber defense.
Urgency and Importance of the Warning
The warning is crucial due to the zero-day nature of the attack. Zero-day exploits represent a severe threat as they take advantage of vulnerabilities before patches are available. The urgency stems from the potential for immediate exploitation, and Microsoft’s swift action demonstrates its commitment to protecting its users. This proactive approach is critical in the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity threats.
Steps Recommended by Microsoft for Users
Microsoft’s recommendations are straightforward and crucial for user protection. Users are advised to install the latest security updates immediately. The updates contain crucial fixes to address the vulnerabilities. Furthermore, Microsoft recommends regular security audits and monitoring to proactively identify and address potential threats.
Summary of Key Takeaways
| Category | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| Vulnerability Type | Zero-day exploit targeting Excel |
| Impact | Potential for unauthorized access |
| Urgency | Immediate installation of updates is critical |
| Mitigation | Keeping software updated, performing security audits |
| Microsoft’s Response | Proactive and transparent statement |
Impact and Consequences of the Attack
A zero-day exploit targeting Microsoft Excel, if successful, can have devastating consequences for individuals and organizations. The potential for widespread disruption and financial loss is significant, requiring a proactive and informed response. The attack vector’s stealthy nature underscores the critical importance of robust security measures.The impact of a successful zero-day attack goes far beyond simple data loss. It can cripple operations, damage reputations, and lead to substantial financial penalties.
Understanding the potential ramifications is crucial for developing effective mitigation strategies.
Potential Impact on Individuals
Individuals using compromised Excel files could unwittingly become victims of malicious activity. This includes the potential for financial fraud, identity theft, or the installation of malware on their systems. The consequences for individuals range from minor inconveniences to significant financial losses. The subtle nature of the attack makes it crucial for individuals to maintain vigilance and utilize up-to-date security measures.
Potential Impact on Organizations
For organizations, the consequences are even more severe. A successful attack can lead to the theft of sensitive data, disruption of business operations, and significant financial losses. The reputational damage from a data breach can be long-lasting, impacting customer trust and investor confidence.
Financial Consequences
Financial losses can be substantial. Organizations may face regulatory fines, legal costs, and compensation claims from affected individuals. The cost of recovery, including data restoration, system remediation, and incident response, can be astronomical. Furthermore, lost productivity due to downtime can add to the financial burden.
Reputational Consequences
A data breach can irreparably damage an organization’s reputation. Loss of customer trust, negative media coverage, and diminished investor confidence are potential outcomes. The damage to a company’s brand and image can be long-lasting and difficult to repair.
Microsoft’s recent warning about zero-day attacks targeting Excel users is a serious concern. While Microsoft is proactively addressing these vulnerabilities, it’s worth noting that the company also recently sealed a deal with Citrix for terminal server integration. This deal, microsoft citrix seal terminal server deal , might offer some crucial protections against these very same types of attacks in the long run, but users still need to take necessary precautions to protect their systems.
This highlights the ongoing need for vigilance in the face of evolving cyber threats.
Data Breaches and System Compromises
A successful zero-day attack can lead to various data breaches and system compromises. This includes the theft of confidential customer information, intellectual property, financial records, and trade secrets. System compromise can lead to unauthorized access to sensitive data and the potential for malicious modification or deletion of crucial data.
Potential Damage Scenarios
| Scenario | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Data Theft | Sensitive data, such as customer records, financial information, or intellectual property, is stolen. | Financial losses, reputational damage, legal liabilities. |
| System Disruption | Malicious code disrupts critical business operations, leading to downtime and loss of productivity. | Significant financial losses, potential customer dissatisfaction, operational delays. |
| Malware Infection | Malicious code is installed on systems, potentially leading to further compromises. | Data breaches, system instability, potential for ransomware attacks. |
| Ransomware Attack | Criminals encrypt data and demand a ransom for its release. | Financial losses, data loss, reputational damage, operational disruption. |
Prevention and Mitigation Strategies
The recent Excel zero-day vulnerability highlights the critical need for proactive security measures in today’s digital landscape. Ignoring these vulnerabilities leaves organizations and individuals exposed to significant risks, including data breaches, financial losses, and reputational damage. Proactive steps are essential to mitigate the impact of such attacks.Robust preventative measures, encompassing software updates, security awareness training, and a strong security posture, are crucial to safeguard against future attacks.
Implementing these strategies can significantly reduce the likelihood of exploitation and the associated consequences.
Best Practices for Preventing Similar Attacks
Proactive measures are vital to prevent future attacks. Implementing security best practices, including strong passwords, multi-factor authentication, and regular security audits, helps protect against exploitation. These practices form a crucial part of a layered security approach.
- Employing strong passwords and multi-factor authentication is paramount. Complex passwords, combined with multi-factor authentication (MFA), add an extra layer of security, making it more difficult for attackers to gain unauthorized access. Using a password manager can assist in creating and storing strong, unique passwords for various accounts.
- Regular security audits and penetration testing are essential to identify potential vulnerabilities in systems and applications. These audits help uncover weaknesses that attackers could exploit, enabling timely remediation and strengthening the overall security posture.
- Restricting access privileges to only necessary resources is critical. This minimizes the potential damage if a security breach occurs, limiting the scope of the compromise.
Importance of Software Updates and Security Patches
Regularly updating software and applying security patches is a cornerstone of robust cybersecurity. These updates often address critical vulnerabilities that attackers exploit. Ignoring these updates leaves systems susceptible to attacks.
- Automated update mechanisms should be configured to ensure timely installation of critical security patches. This minimizes manual intervention and ensures that systems remain up-to-date.
- Regularly check for and install available updates. A proactive approach to software updates minimizes the attack surface.
- Develop a clear update schedule and procedures to ensure consistent and timely implementation. This ensures the organization’s systems remain protected.
Role of Security Awareness Training
Security awareness training plays a crucial role in educating users about potential threats and how to identify and report suspicious activities. A well-trained workforce is a significant line of defense against cyberattacks.
- Train employees on recognizing phishing emails, suspicious links, and social engineering tactics. This empowers them to identify and avoid potential threats.
- Regularly update training materials to reflect evolving threats and attack methods. Staying current is crucial for effective security awareness training.
- Promote a culture of security awareness throughout the organization. Encouraging proactive security practices from all levels strengthens the overall security posture.
Need for Robust Security Measures
Robust security measures are essential for organizations and individuals to protect themselves from potential cyberattacks. A layered approach, combining various security controls, provides a stronger defense.
- Implement firewalls and intrusion detection systems to monitor and block malicious traffic. These systems act as a first line of defense against unauthorized access attempts.
- Employ endpoint security solutions to protect individual devices from threats. These solutions can detect and block malicious software, safeguarding the organization’s network from infected devices.
- Implement data loss prevention (DLP) solutions to prevent sensitive data from leaving the organization’s control. These solutions help prevent data breaches.
Preventive Measures and Their Effectiveness
The table below Artikels preventive measures and their effectiveness in mitigating the risk of similar attacks.
| Preventive Measure | Effectiveness |
|---|---|
| Strong passwords and MFA | High – Significantly increases the difficulty for attackers to gain unauthorized access. |
| Regular security audits and penetration testing | High – Identifies vulnerabilities before attackers exploit them. |
| Software updates and security patches | High – Addresses known vulnerabilities, reducing the attack surface. |
| Security awareness training | Medium to High – Educates users about threats and how to avoid them. Effectiveness depends on the quality of training. |
| Robust security measures (firewalls, endpoint security, DLP) | High – Provides a layered defense against various attack vectors. |
Comparison with Other Software Vulnerabilities: Microsoft Warns Excel Users Of Zero Day Attacks
Software vulnerabilities are unfortunately a persistent threat across the digital landscape. The recent zero-day attack targeting Excel highlights the ongoing need for vigilance and robust security measures. Understanding how this vulnerability compares to others provides valuable context and helps prioritize defensive strategies.Comparing the Excel vulnerability to other software vulnerabilities reveals both common threads and distinct characteristics. While many vulnerabilities share a similar goal – exploiting weaknesses to gain unauthorized access – the specific methods and targets vary significantly.
This comparison sheds light on the unique nature of the Excel threat, which is a crucial aspect in formulating effective countermeasures.
Common Characteristics of Software Vulnerabilities
Exploits often target predictable human behaviors, such as clicking on suspicious links or opening malicious attachments. The attack vector, the point of entry into a system, is often the critical element. The common thread is the exploitation of flaws in the software’s design or implementation, which can be leveraged by attackers. Furthermore, successful attacks often rely on a combination of factors, including the attacker’s skills, the target’s security posture, and the exploit’s sophistication.
Differences in Vulnerability Types
While the Excel vulnerability leverages a specific file format and macro-related functionality, other vulnerabilities may target different software components or operating systems. For instance, vulnerabilities in web browsers might exploit weaknesses in rendering HTML or JavaScript code. The attack surface – the potential entry points for an attacker – varies considerably between applications, making it difficult to apply a one-size-fits-all security solution.
Examples of Comparable Vulnerabilities
The Log4j vulnerability of 2021 exemplifies a widely impactful vulnerability that affected a vast range of applications. This attack exploited a flaw in the Log4j logging library, allowing remote code execution. Similarly, vulnerabilities in widely used cryptographic libraries can lead to breaches of sensitive data. The attack vector in such instances often involves carefully crafted inputs that exploit weaknesses in the libraries’ design or implementation.
Severity Comparison Table
| Vulnerability | Severity Rating (Hypothetical) | Impact | Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Excel Zero-Day | Critical | Potential for widespread data breaches, system compromise, and financial losses. | Urgent patching, security awareness training, and enhanced security protocols. |
| Log4j | Critical | Extensive compromise of applications using the Log4j library, potentially affecting millions of systems globally. | Immediate updates, thorough security assessments, and robust logging. |
| Heartbleed | Critical | Compromise of sensitive data and encryption keys, leading to potential identity theft and financial fraud. | System upgrades, security audits, and security updates. |
Note: The severity ratings are hypothetical and represent a simplified comparison. Actual severity assessments often involve complex calculations and expert evaluations.
Future Trends and Predictions
The landscape of software vulnerabilities is constantly evolving, and Excel, as a ubiquitous tool, is not immune. Understanding potential future threats is crucial for proactive security measures. Emerging trends in software attacks, coupled with the increasing sophistication of cybercriminals, necessitate a forward-thinking approach to security.
Microsoft’s warning about zero-day attacks targeting Excel users is frustratingly familiar. It’s the new year, but unfortunately, the same old story continues – cyber threats persist, and users need to remain vigilant. This pattern of vulnerabilities, and the constant need for software updates, is a common theme, as discussed in more detail in my recent post about the new year same old story.
So, buckle up, folks, because the ongoing struggle against zero-day attacks like these is likely to remain a top priority for the foreseeable future.
Potential Future Threats in Excel, Microsoft warns excel users of zero day attacks
The rise of artificial intelligence (AI) presents a significant threat vector. AI-powered tools can automate the creation of malicious macros and spreadsheets, potentially making attacks more sophisticated and difficult to detect. Furthermore, the increasing reliance on cloud-based services for data storage and processing introduces new avenues for attack. Compromising cloud accounts containing Excel files can expose sensitive data to attackers.
Emerging Trends in Software Attacks
A notable trend is the increasing use of polymorphic malware. This malware can adapt its code to evade traditional detection methods. This necessitates the development of advanced threat detection techniques that can identify subtle changes in malware behavior. Social engineering tactics, often used in conjunction with malicious software, remain a significant concern. Sophisticated phishing campaigns tailored to exploit specific vulnerabilities in software applications, including Excel, are expected to persist.
Impact on Security Measures
The emergence of these trends necessitates a multi-layered security approach. This includes enhanced security protocols for cloud storage, rigorous code analysis for detecting malicious macros, and user education to identify and avoid social engineering attempts. The focus should be on developing proactive measures that anticipate and mitigate the impact of evolving attack methods.
Potential Scenarios and Predictions
One potential scenario involves a sophisticated AI-powered tool that creates highly targeted phishing campaigns, disguising malicious Excel files as legitimate spreadsheets. This targeted approach could bypass traditional security measures. Another scenario involves a vulnerability in a widely used cloud storage service allowing access to sensitive Excel files, leading to large-scale data breaches.
Future Development of Attacks (Table)
| Year | Attack Type | Method | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2024-2025 | AI-powered Macro Attacks | Automated generation of sophisticated malicious macros. | Increased difficulty in detection and mitigation. |
| 2025-2027 | Cloud-based Data Breaches | Exploiting vulnerabilities in cloud services to access sensitive Excel files. | Large-scale data breaches and reputational damage. |
| 2027-2029 | Polymorphic Malware Attacks | Adaptive malware that evades traditional detection methods. | Increased reliance on advanced threat detection. |
| 2029-2031 | Hyper-Targeted Social Engineering | Highly personalized phishing campaigns leveraging AI. | Increased sophistication in social engineering attacks. |
User Recommendations and Actions

Protecting yourself from zero-day attacks requires proactive measures. Excel users need to understand the potential risks and take immediate steps to mitigate them. This section provides practical advice and a step-by-step guide to securing your data and systems.Staying vigilant and informed is paramount in the face of evolving cyber threats. Taking proactive steps to safeguard your Excel environment is crucial.
Immediate Actions Upon Receiving a Warning
Upon receiving a warning about a zero-day attack targeting Excel, the first priority is to understand the nature of the threat. Microsoft provides detailed information about the vulnerabilities, allowing users to grasp the scope and severity of the attack. This understanding is essential to implementing the necessary security measures.
Verifying Microsoft Updates
Authenticating Microsoft updates is vital to prevent malicious software from masquerading as legitimate updates. Users should only download updates from official Microsoft channels. These channels have built-in security measures to prevent fraudulent downloads.
- Check the Microsoft Update Catalog: Navigate to the official Microsoft Update Catalog. This catalog provides detailed information about available updates, including crucial security patches. Look for updates specifically addressing the vulnerabilities mentioned in the warning.
- Verify the Update’s Digital Signature: Microsoft uses digital signatures to authenticate updates. Verify the digital signature to ensure the update hasn’t been tampered with.
Tools like the Windows Update process typically handle this verification automatically.
Updating Excel
Updating software is a critical security measure. Outdated applications often contain known vulnerabilities, making them easy targets for attacks. Following these steps ensures your Excel installation is secure.
- Check for Updates: Open Microsoft Excel and check for updates. The application itself often has a built-in mechanism to detect and install available updates.
- Download and Install Updates: If updates are available, download and install them immediately. The installation process may require restarting the application or the computer. Follow the on-screen instructions carefully.
- Verify Installation: After installation, verify that the update has been successfully applied. Check the application version to confirm the update was installed correctly.
Recommended User Actions
Implementing these measures will enhance your security posture against zero-day attacks and other potential threats.
- Enable Automatic Updates: Configure your system to automatically download and install updates. This proactive approach ensures that your software is always up-to-date.
- Use Strong Passwords: Employ strong, unique passwords for all accounts. Avoid using easily guessed passwords. A combination of upper and lower case letters, numbers, and symbols creates a strong password.
- Install Anti-virus Software: Implement reputable anti-virus software to protect against various threats.
- Be Cautious with Email Attachments: Exercise caution when opening email attachments, especially from unknown senders. Avoid downloading files from untrusted sources.
- Review Software Security Settings: Regularly review and adjust software security settings to ensure optimal protection.
Concluding Remarks
In conclusion, Microsoft’s warning underscores the ongoing threat landscape and the importance of proactive security measures. Users must prioritize updates and security awareness to mitigate potential risks. This incident serves as a stark reminder that vigilance and proactive measures are vital in safeguarding against evolving cyber threats. Stay informed and protect your systems.