MPAA Fights Film Swapping Suits & Software
MPAA fights film swapping with suits and software, a battle waged on multiple fronts. From the historical role of the MPAA in film distribution to the modern-day strategies for combatting piracy, this deep dive examines the complex relationship between the organization, the burgeoning film-swapping communities, and the crucial role of specialized software. We’ll explore the various methods of film swapping, their economic impact, and the legal arguments on both sides of this digital frontier.
This analysis delves into the intricate interplay of the MPAA’s legal actions, the arguments for and against film swapping, and the innovative software tools employed by both sides. We will also examine the potential long-term effects of film swapping on the movie-making process, the viewer experience, and the overall financial health of the film industry. Finally, we’ll explore alternative distribution models and potential solutions to the ongoing conflict.
MPAA’s Approach to Film Distribution
The Motion Picture Association of America (MPAA) plays a crucial role in the film industry, impacting everything from the content of movies to their distribution. Understanding its historical and contemporary strategies is vital to comprehending the modern film landscape. From its early days as a self-regulatory body, the MPAA has evolved into a significant force shaping the industry’s approach to copyright protection and market access.The MPAA’s influence extends across various aspects of film distribution, including combating piracy, managing the transition to digital platforms, and maintaining relationships with studios and distributors.
This evolving role has created a complex dynamic between the MPAA’s objectives and the changing demands of the entertainment industry.
Historical Overview of the MPAA’s Role
The MPAA’s initial focus was on establishing industry standards and self-regulation, primarily concerning film content. Over time, its purview expanded to encompass the protection of intellectual property rights, including the fight against film piracy. The organization’s historical involvement in film distribution is rooted in efforts to combat illegal distribution methods, initially through the use of print and visual aids, to communicate the consequences of copyright infringement.
This involved educational campaigns and legal action against those who violated copyright laws. These initiatives evolved with changing technology, from physical distribution to digital platforms.
Current Strategies for Managing Film Piracy and Distribution
The MPAA employs various strategies to counter film piracy, including technological solutions, legal actions, and industry collaborations. These methods often involve partnerships with online service providers to remove pirated content and promote legitimate distribution channels. The organization works to educate the public about the negative consequences of piracy and the importance of supporting the film industry through legal channels.
This includes utilizing legal frameworks and working with technology companies to limit access to pirated content.
MPAA’s Stance on Digital Distribution and Streaming
The MPAA’s stance on digital distribution and streaming is multifaceted. While acknowledging the inevitability of digital platforms, the organization has sought to ensure that these platforms respect copyright protections and provide a sustainable revenue model for filmmakers and studios. This involves advocating for fair compensation for content used on streaming services and negotiating licensing agreements. The MPAA recognizes the need to adapt to digital trends, but emphasizes the need for clear and enforceable copyright protections in this new environment.
Their response has involved ongoing negotiations and agreements with streaming services to ensure fair compensation for content rights.
MPAA’s Relationship with Studios and Distributors
The MPAA maintains close relationships with film studios and distributors, acting as a liaison and advocate for their interests. The organization provides resources, information, and support to studios, helping them navigate the complexities of film distribution. This includes collaboration on legal strategies, and providing market insights to studios. The MPAA serves as a valuable resource for the industry, helping studios and distributors understand and navigate legal issues and evolving distribution strategies.
Comparison of Past and Present Approaches to Film Distribution
| Aspect | Past Approach | Present Approach |
|---|---|---|
| Content Regulation | Primarily focused on establishing ratings and standards for film content. | Focuses on content regulation while also addressing digital distribution and piracy. |
| Piracy Combat | Relied on print and visual aids, legal actions, and industry partnerships to combat illegal distribution. | Employs technological solutions, legal actions, industry collaborations, and public education campaigns. |
| Digital Distribution | Initial resistance to digital distribution, with a focus on physical formats. | Adapting to digital platforms, advocating for fair compensation and copyright protection. |
| Studio Relations | Providing resources and support to studios, primarily focusing on traditional distribution channels. | Maintaining close relationships, providing resources and support across traditional and digital distribution models. |
The Impact of Film Swapping: Mpaa Fights Film Swapping With Suits And Software
Film swapping, the practice of sharing and exchanging films outside of traditional distribution channels, has become increasingly prevalent. This phenomenon has far-reaching implications for the film industry, impacting everything from box office revenue to production schedules. Understanding these effects is crucial for anyone involved in the film ecosystem.Film swapping encompasses a diverse array of methods, from physical exchanges of DVDs and Blu-rays to online platforms dedicated to sharing digital copies.
This decentralized approach has created a dynamic and evolving landscape that challenges traditional business models.
Methods of Film Swapping
Film swapping utilizes various methods, each with its own unique characteristics. Physical exchanges, often through peer-to-peer networks or dedicated forums, involve the trading of physical media. Digital distribution methods, leveraging file-sharing networks or dedicated platforms, facilitate the exchange of digital copies. The rise of peer-to-peer networks and online file-sharing platforms has made the exchange of digital copies of films readily available, which has had a profound effect on the film industry’s business models.
The MPAA’s fight against film swapping, using legal suits and sophisticated software, is a fascinating example of modern copyright battles. Think about how technology is changing everything, like how Mount St. Helens, a telemetric volcano, allows scientists to monitor its activity remotely mount st helens a telemetric volcano. It’s a similar concept, except instead of magma, it’s digital files, and instead of seismographs, it’s sophisticated algorithms designed to track and stop unauthorized sharing.
The MPAA’s approach highlights the ongoing struggle to balance technological advancement with intellectual property protection in the digital age.
Scale and Reach of Film Swapping Communities
The scale and reach of film swapping communities are significant. Dedicated online forums, social media groups, and file-sharing networks host a vast number of users, demonstrating a substantial audience. The ease of access and the broad availability of film swapping resources contribute to its widespread appeal. Quantifying the exact size of these communities is challenging due to the decentralized nature of the phenomenon and the difficulty in tracking user participation across various platforms.
However, the sheer number of users involved suggests a significant impact on the film industry.
The MPAA’s battle against film swapping, employing legal teams and sophisticated software, highlights the complex interplay between copyright protection and consumer access. This ongoing struggle raises important questions about the ethics of such aggressive measures, prompting deeper examination by industry analysts like those at ethics and industry analysts. Ultimately, the MPAA’s approach continues to be a key point of contention in the digital age of film distribution.
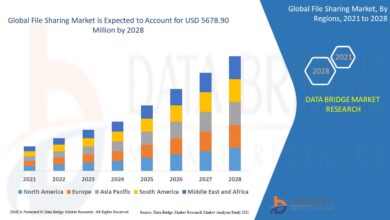
Economic Impact on the Film Industry
Film swapping presents a complex economic impact on the film industry. The unauthorized distribution of copyrighted material directly impacts revenue streams for studios and distributors. The piracy aspect of film swapping is a concern for the financial viability of the industry. However, the phenomenon also potentially fosters a wider appreciation for films, bringing them to audiences who might not otherwise have access.
The debate over the economic impact of film swapping continues to be a central point of discussion in the film industry.
Impact on Box Office Revenue
The relationship between film swapping and box office revenue is a subject of ongoing discussion and analysis. While there is no definitive data linking film swapping to a direct and quantifiable decline in box office revenue, it’s widely believed that unauthorized distribution can potentially deter individuals from purchasing tickets. The exact correlation between film swapping and box office numbers is still under research and investigation.
Consequences on Production and Release Schedules
Film swapping can influence movie production and release schedules. The potential for unauthorized distribution raises concerns for studios, which may adjust their release strategies to mitigate the impact of such practices. This can involve adjusting release windows, focusing on exclusive streaming releases, or incorporating more sophisticated security measures.
Film Swapping Platforms
| Platform Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Peer-to-Peer Networks | These networks facilitate the exchange of files, including films, between users directly. |
| Dedicated File-Sharing Platforms | Specialized platforms offer a structured environment for the sharing and exchange of digital files. |
| Online Forums and Communities | These platforms often serve as hubs for discussions and exchanges related to film swapping. |
The Role of Software in Film Swapping
Film swapping, the process of transferring copyrighted films, has been dramatically influenced by advancements in software technology. This evolution has profoundly altered the methods and possibilities of unauthorized distribution, raising crucial questions about copyright infringement and the effectiveness of existing legal frameworks. From basic file sharing tools to sophisticated encryption bypassers, the software landscape surrounding film swapping has become increasingly complex.The rise of digital distribution has fundamentally changed the nature of film swapping.
Software plays a pivotal role in enabling the creation, sharing, and decryption of digital copies of films, making the process more accessible and efficient. This has fostered a new level of challenge for copyright holders in protecting their intellectual property.
Software Tools Used for Film Swapping
Various software tools facilitate film swapping, each with unique functionalities. These tools often include file-sharing programs, video conversion utilities, and specialized decryption software. The rise of peer-to-peer (P2P) networks has significantly increased the accessibility of such tools, allowing for wider distribution of copyrighted material. These tools are used for file transfer, encoding/decoding, and potentially even bypassing encryption schemes.
Features and Functionalities of Film Swapping Software
Film swapping software often boasts advanced features designed for efficient file transfer and manipulation. These features typically include file compression, encryption, and decryption capabilities. Some applications also provide tools for converting various video formats to facilitate compatibility across different devices. Additionally, certain software might incorporate obfuscation techniques to mask the original file and potentially evade detection.
Security and Privacy Implications
The use of film swapping software raises significant security and privacy concerns. The unauthorized distribution of copyrighted material often carries legal repercussions. Furthermore, users may inadvertently expose their personal information during file sharing, posing privacy risks. The software itself may contain vulnerabilities, making systems susceptible to hacking or malware. The anonymity afforded by certain file-sharing platforms can embolden illicit activities.
Comparison of Film Swapping Software Tools
Different film swapping software tools offer varying levels of functionality and security. Some are open-source, allowing users to scrutinize the code, while others are proprietary, potentially concealing vulnerabilities. The ease of use and availability of support also vary significantly. Factors such as file transfer speed, compatibility, and the presence of anti-piracy features should be considered when evaluating different tools.
The ease of access and use of software also play a role in the extent of its use in film swapping.
Software Advancements and Effectiveness of Film Swapping
Software advancements continuously influence the effectiveness of film swapping. The development of faster processors and more efficient algorithms enhances file transfer speed, making film swapping easier and more readily available. Simultaneously, advancements in encryption and decryption techniques are also constantly being developed, creating a perpetual cat-and-mouse game between copyright holders and those engaging in film swapping.
Evolution of Film Swapping Software
| Era | Software Characteristics | Impact on Film Swapping |
|---|---|---|
| Early 2000s | Limited file-sharing capabilities, basic encryption | Facilitated early forms of film swapping, limited scale |
| Mid-2000s | Rise of P2P networks, improved file compression | Increased accessibility, higher transfer speeds |
| Present | Sophisticated encryption bypassers, obfuscation techniques | Heightened sophistication, increased challenges for copyright protection |
The Conflict Between MPAA and Film Swapping

The Motion Picture Association of America (MPAA) has long been a powerful force in the film industry, safeguarding its interests and the rights of studios. A significant aspect of their role involves protecting the distribution channels and intellectual property surrounding film releases. This conflict with film swapping communities highlights the tension between preserving copyright and enabling accessibility.The MPAA’s efforts to combat film swapping are multifaceted, involving legal actions and strategies aimed at deterring unauthorized distribution of copyrighted material.
The fight reflects the fundamental differences in perspectives on intellectual property rights and the evolving nature of media consumption.
The MPAA’s ongoing battle against film swapping, using legal action and software, feels a bit outdated. Meanwhile, anti-spam technology like sender id antispam tech making strides is showing real promise in protecting online communication. This new technology, much like the MPAA’s methods, aims to limit illicit activity, though in a different digital space. Ultimately, the MPAA’s fight seems like a slow-moving train in a fast-changing digital landscape.
MPAA’s Legal Actions Against Film Swapping
The MPAA employs a range of legal tactics to address film swapping. These actions aim to deter the sharing and distribution of copyrighted films without authorization. These methods often involve lawsuits against individuals and groups involved in film swapping networks, seeking injunctions and financial penalties. These legal battles are crucial in establishing precedents and sending a strong message about the importance of copyright protection.
MPAA’s Arguments Against Film Swapping
The MPAA argues that film swapping constitutes a significant infringement of copyright. They emphasize that the unauthorized distribution of films deprives filmmakers, studios, and other stakeholders of rightful compensation for their work. They claim that this practice undermines the economic viability of the film industry, impacting investment and production of new content. This economic argument is a cornerstone of their legal position.
Furthermore, the MPAA highlights the potential for substantial financial losses for studios due to lost revenue from film piracy.
Arguments in Favor of Film Swapping, Mpaa fights film swapping with suits and software
Arguments in favor of film swapping often center on accessibility and democratization of film. Proponents argue that film swapping provides a means for individuals to access films that might otherwise be unavailable or prohibitively expensive. This accessibility, however, frequently clashes with the MPAA’s position on copyright. Further, some argue that film swapping is a form of cultural exchange, enabling the sharing of diverse cinematic experiences.
Examples of Legal Battles Between the MPAA and Film Swapping Communities
Numerous legal battles have unfolded between the MPAA and film swapping communities. These cases often involve individuals and groups accused of facilitating or participating in film swapping networks. The outcomes of these cases have significantly shaped the legal landscape surrounding film distribution. Examples include lawsuits against file-sharing networks and individuals operating peer-to-peer file-sharing systems. The consequences in these legal battles demonstrate the MPAA’s resolve to protect copyright.
Comparison of MPAA’s Methods and Film Swapping Communities’ Methods
The MPAA employs legal and technological measures to combat film swapping. They utilize copyright infringement lawsuits, takedown notices, and the implementation of technological protection measures to restrict unauthorized access. In contrast, film swapping communities often rely on peer-to-peer networks, encryption techniques, and anonymization tools to circumvent these measures. This highlights a significant difference in strategies and resources employed by both sides.
Table of Legal Precedents in Film Swapping Cases
| Case | Key Legal Precedent | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| MGM v. Grokster | Established the principle of “inducing” copyright infringement. | Court found that companies that distribute technology with the primary purpose of enabling copyright infringement can be held liable. |
| A&M Records v. Napster | Reinforced the importance of copyright protection in the digital age. | Court ruled against Napster for facilitating copyright infringement. |
| Universal City Studios v. Reimerdes | Further clarified the liability of those who provide technology for copyright infringement. | Court held that providing tools with the purpose of facilitating copyright infringement can result in liability. |
Alternatives and Solutions
The ongoing conflict between the MPAA and film-swapping communities highlights a critical need for alternative distribution models that respect intellectual property rights while also ensuring wider access to cinematic works. Traditional methods of distribution are facing challenges in the digital age, necessitating a re-evaluation of the entire process. This section explores various alternatives, successful examples, and potential solutions.This exploration delves into the potential of alternative distribution models, examining their efficacy in balancing copyright concerns with audience access.
Innovative solutions and the role of technology in this transformation will be discussed, including creative approaches to resolve the ongoing film distribution and swapping conflict.
Alternative Film Distribution Models
Traditional theatrical releases, while still prevalent, are facing competition from various emerging models. Streaming services, pay-per-view platforms, and independent film festivals are gaining popularity. These alternative models offer unique advantages, but also pose new challenges in terms of copyright protection and revenue streams.
Examples of Successful Alternative Distribution Models
Several independent film distributors and festivals have found success through innovative approaches. Platforms like Vimeo and YouTube have enabled independent filmmakers to reach wider audiences without relying on traditional distribution channels. Documentaries and short films, often overlooked in traditional distribution models, find their niche on these platforms. This has fostered a thriving independent film scene and demonstrated the potential of alternative models.
Potential Solutions for Balancing Copyright Concerns with Access
Addressing the conflict requires a multifaceted approach. One potential solution is to establish clear licensing agreements that allow for controlled access to films while safeguarding copyright holders’ interests. Furthermore, the development of secure digital distribution platforms can mitigate piracy and ensure that creators receive fair compensation. This could involve blockchain technology to trace the origin and ownership of content, providing a transparent and tamper-proof system.
The Role of Technology in Finding Solutions for Film Distribution
Technology plays a crucial role in the evolution of film distribution. Advanced encryption techniques can protect digital content, while watermarking technologies can help track and identify unauthorized distribution. Furthermore, the development of streaming platforms that offer high-quality content through secure channels can offer a viable alternative to piracy.
Creative Solutions to the Film Distribution and Swapping Conflict
Encouraging legitimate streaming services and promoting access to content through established platforms could reduce the incentive for film swapping. Furthermore, developing educational campaigns that highlight the economic impact of piracy on the film industry and the importance of copyright protection can foster a greater understanding and respect for intellectual property rights. Offering tiered access models, where viewers pay for access to specific content or genres, is another creative approach.
Table of Alternative Film Distribution Models
| Distribution Model | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Theatrical Release | Traditional release in cinemas | High-quality viewing experience, large audience reach | High production costs, limited accessibility |
| Streaming Services | Online platforms for video content | Wider accessibility, lower cost for viewers | Potential for piracy, lower revenue for creators |
| Pay-Per-View | Viewers pay for individual films or events | Direct revenue to creators, potentially higher returns | Limited accessibility, requires user commitment |
| Independent Film Festivals | Showcasing independent films | Opportunity for exposure, builds community | Limited audience reach, uncertain revenue stream |
| Digital Licensing Platforms | Controlled access through digital licenses | Fair compensation to creators, reduced piracy | Requires a robust licensing system, complexity for implementation |
Impact on the Film Industry

Film swapping, the practice of distributing films through methods other than traditional channels, presents a complex and multifaceted challenge to the established film industry. Its impact reverberates through every stage of production, distribution, and consumption, forcing a reevaluation of existing business models and strategies. The implications extend beyond piracy concerns, impacting revenue streams, creative processes, and the overall viewing experience.
Impact on the Overall Film Industry
Film swapping, while potentially democratizing access to films, significantly disrupts the established revenue streams of the film industry. Traditional distribution models, relying on licensing agreements and theatrical releases, are challenged by the ease of access provided by file-sharing platforms. This shift in access patterns can lead to a decline in revenue for studios, distributors, and exhibitors.
Long-Term Effects on the Movie-Making Process
The potential for reduced revenue from film swapping raises concerns about the long-term sustainability of film production. Studios might be less inclined to invest in high-budget productions if the return on investment is uncertain. This could lead to a decrease in the quality and variety of films produced, as studios focus on lower-risk, potentially less ambitious projects. Independent filmmakers may face an even steeper uphill battle, with limited resources and fewer opportunities for wider distribution.
Influence on the Movie-Watching Experience
While film swapping potentially increases access to a wider range of films, it can also lead to a decline in the quality of the viewing experience. The lack of control over the quality of the copied content can result in poor picture and sound quality. The absence of proper licensing agreements might lead to missing special features or subtitles.
The experience may also be negatively impacted by the lack of an engaging cinematic environment, such as a well-maintained theater.
Impact on Movie Revenue and Profits
The direct consequence of film swapping is a significant reduction in revenue for all stakeholders in the film industry. Studios lose revenue from licensing and distribution agreements, distributors lose from theatrical screenings and retail sales, and exhibitors lose from ticket sales. The loss of revenue can result in the cancellation of projects, layoffs, and a decline in overall industry investment.
For example, the widespread availability of pirated content has a direct correlation with declining revenue for major studios.
Potential Effects on the Film Production Industry
The changing landscape of film distribution, driven by film swapping, requires studios to adapt their production strategies. There might be a shift towards producing films with a lower reliance on traditional theatrical releases and a greater emphasis on digital distribution strategies. Studios may need to explore new revenue models, such as subscription services or pay-per-view options, to compensate for lost revenue.
This also creates opportunities for independent filmmakers, who may find new avenues for distribution and audience engagement.
Comparative Analysis of Impacts
| Sector | Impact of Film Swapping |
|---|---|
| Film Studios | Reduced revenue from licensing and distribution; potential for reduced investment in high-budget films; need to explore new revenue models. |
| Distributors | Loss of revenue from theatrical screenings and retail sales; need to adapt to changing distribution models. |
| Exhibitors | Loss of revenue from ticket sales; need to adapt to changing audience preferences and find new revenue streams. |
| Independent Filmmakers | Potential for wider audience reach but face challenges in securing distribution and gaining recognition; need to find innovative distribution strategies. |
| Consumers | Wider access to films; potential for lower-quality viewing experiences; concerns regarding copyright infringement. |
Final Conclusion
The MPAA’s fight against film swapping, fueled by powerful legal suits and sophisticated software, highlights the clash between traditional distribution models and the evolving digital landscape. This conflict underscores the ongoing debate surrounding copyright, access to media, and the evolving role of technology in the film industry. While the MPAA strives to protect its members’ interests, the desire for readily accessible films persists.
The future of film distribution remains uncertain, demanding innovative solutions to balance copyright concerns with the public’s desire for accessible content.