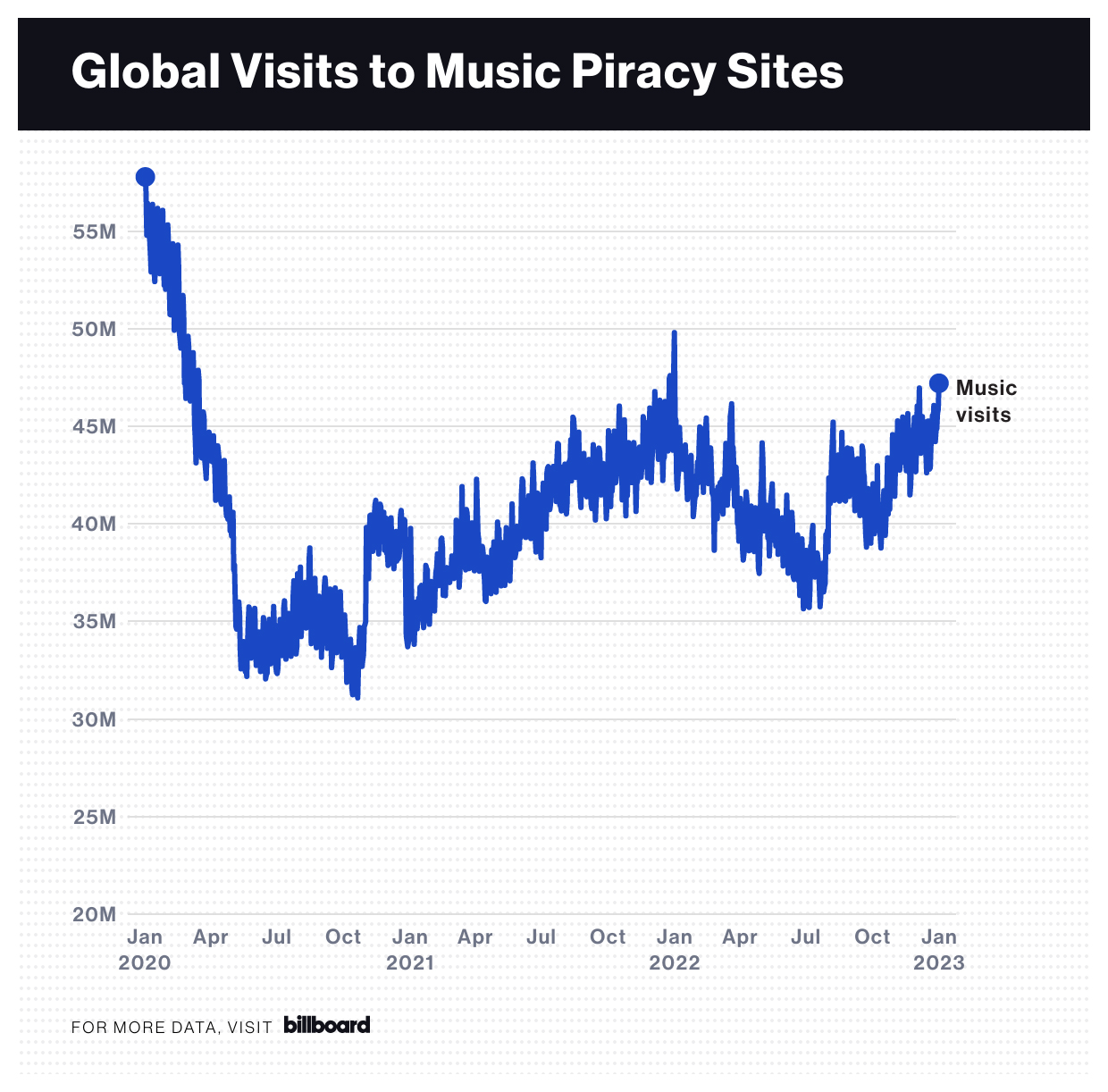
Music Sales Strong Despite Digital Piracy
Music sales strong despite digital piracy, a surprising trend that challenges conventional wisdom. The music industry, navigating the ever-shifting landscape of technology and consumer behavior, has found surprising resilience. While digital piracy has undeniably impacted revenue streams, the rise of streaming services and evolving consumer preferences have created new avenues for growth. This in-depth exploration examines the factors behind this phenomenon, analyzing historical trends, the impact of piracy, the role of streaming, countermeasures, and future projections.
This analysis will delve into the complexities of the music industry’s evolution, examining the historical shift from physical media to digital downloads and finally to streaming services. We’ll examine how these transitions have affected artists’ earnings and the industry’s overall revenue. Furthermore, we’ll scrutinize the strategies employed by the industry to combat piracy and how consumer preferences have influenced these strategies.
Music Industry Trends
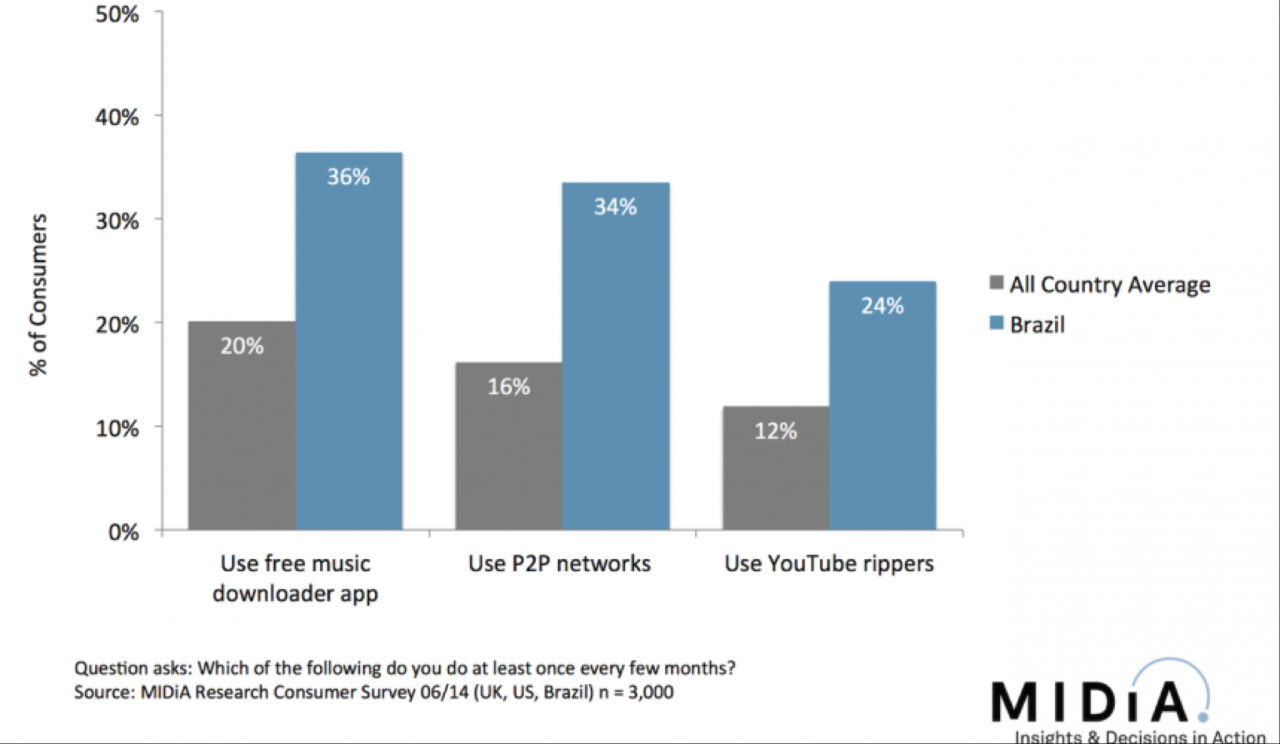
The music industry has undergone a dramatic transformation over the past few decades, shifting from primarily physical formats to a complex landscape of digital consumption. This evolution has been driven by technological advancements, changing consumer habits, and economic forces, ultimately impacting how artists are discovered, music is distributed, and revenue is generated. Understanding these trends is crucial for anyone involved in the industry, from artists and labels to streaming services and music retailers.The transition from vinyl records and cassette tapes to CDs and then digital downloads has been accompanied by significant shifts in listener behavior.
This evolution highlights the dynamic relationship between technology and artistic expression, forcing the music industry to adapt and innovate to maintain relevance and profitability.
Historical Overview of Music Sales Trends
The music industry’s history is marked by a progression from physical sales to digital consumption. Initially, physical formats like vinyl records and albums dominated, with significant revenue generated from record stores and retailers. The introduction of compact discs (CDs) in the 1980s dramatically reshaped the landscape, offering higher sound quality and more convenient storage. This transition, however, also faced the challenge of piracy, which began to significantly impact sales.
Evolution of Music Consumption Habits
Consumer behavior has evolved considerably. Initially, music consumption was largely centered around physical purchases. Listeners would buy albums based on artist reputation and popularity, or influenced by radio play. The advent of digital downloads, followed by streaming services, shifted consumer behavior towards on-demand access and personalized playlists. The convenience and accessibility of streaming services have significantly impacted the frequency and nature of music listening.
The “album” concept, once central to music consumption, has become less relevant, with listeners opting for individual tracks or curated playlists.
Comparison of Revenue Streams Across Eras
The music industry’s revenue streams have been significantly impacted by the shift from physical formats to digital platforms. The decline of physical sales has been countered by the rise of digital downloads and streaming services. Early revenue streams relied heavily on record sales, whereas the digital era saw a diversification of revenue sources, including downloads, subscriptions, and advertising.
The transition to a subscription-based model has altered the relationship between artists, labels, and consumers.
Key Factors Influencing Music Sales
Technological advancements and economic conditions are major factors influencing music sales. The development of digital recording and distribution technologies, such as MP3 compression and online streaming platforms, have fundamentally changed how music is accessed and consumed. Economic downturns, as well as global events, can impact consumer spending habits, influencing the demand for music and the success of new releases.
Evolution of Music Sales Revenue Streams (Past 20 Years)
| Year | Physical Sales | Digital Downloads | Streaming |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2003 | High | Low | Non-existent |
| 2008 | Decreasing | Increasing | Emerging |
| 2013 | Low | Low | Increasing |
| 2018 | Very Low | Negligible | High |
| 2023 | Negligible | Negligible | Dominant |
This table illustrates the dramatic shift in music revenue streams over the past two decades, highlighting the decline of physical sales and the rise of streaming as the dominant revenue source. The transition was not linear; periods of fluctuation and overlap existed. This data reflects the evolving landscape of music consumption and the industry’s adaptation to new technologies.
Digital Piracy’s Impact
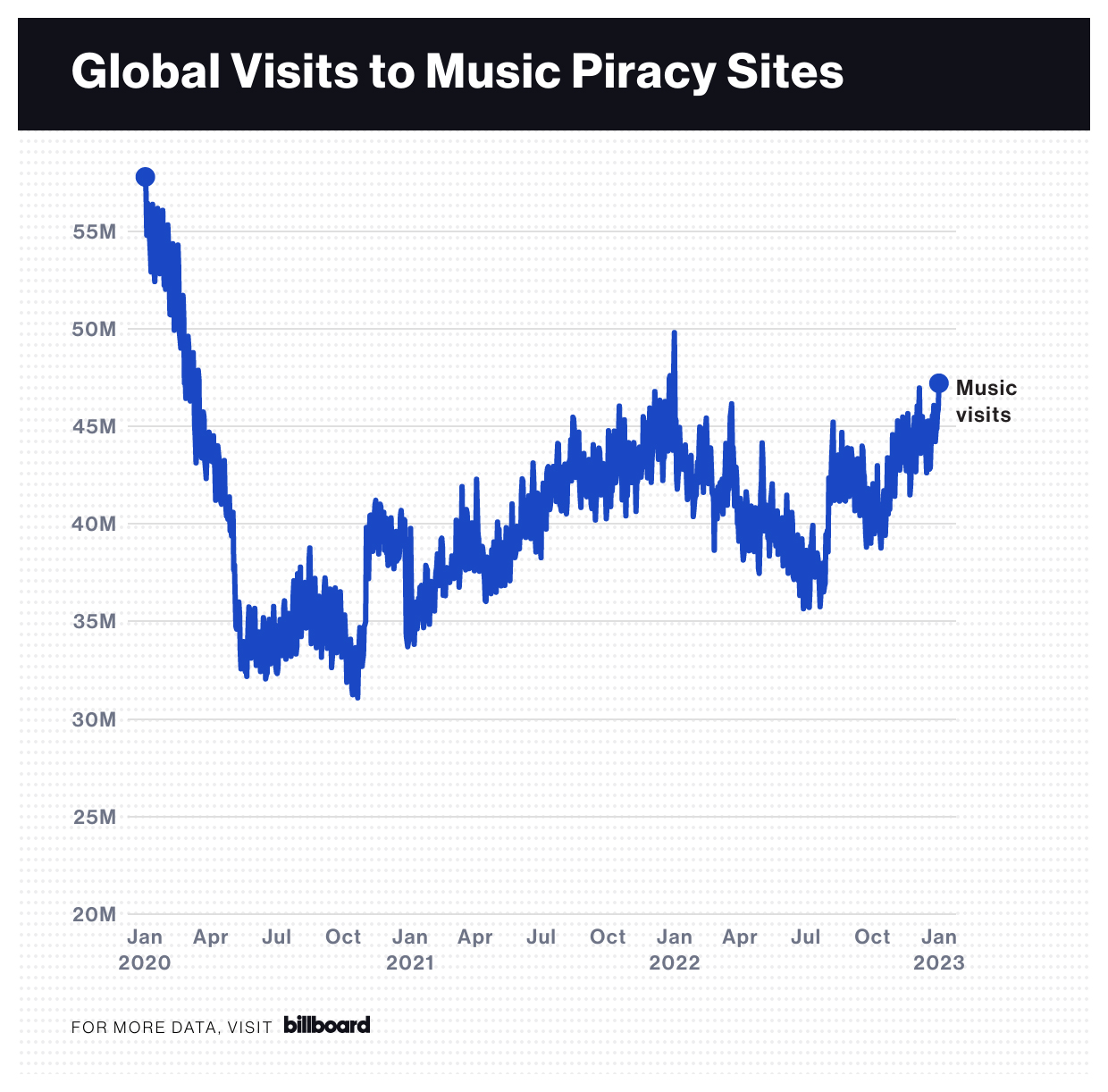
Digital piracy, the unauthorized reproduction and distribution of copyrighted material, presents a significant challenge to the music industry. While the industry has adapted to the digital age, the enduring threat of piracy continues to impact revenue streams, artist earnings, and the overall health of the music ecosystem. This article delves into the methods of digital piracy, its detrimental effects, and its impact across different genres.Digital piracy is a pervasive issue affecting the music industry in numerous ways.
The ease with which copyrighted material can be copied and shared online has fueled the problem. From peer-to-peer file-sharing networks to torrent websites and unauthorized streaming platforms, various avenues facilitate piracy. This widespread accessibility makes it challenging for artists and labels to effectively combat the issue.
Methods of Digital Piracy
Digital piracy employs a variety of methods to circumvent copyright protections. These methods are often sophisticated and constantly evolve, making it difficult for enforcement agencies to keep pace. A primary method involves the use of peer-to-peer (P2P) file-sharing networks. These networks allow users to directly download files from other users, bypassing official distribution channels. Torrent websites also play a significant role in facilitating piracy, providing centralized repositories of copyrighted material for download.
Moreover, unauthorized streaming platforms, often mimicking legitimate services, offer copyrighted music without proper licensing, contributing to the spread of piracy.
Challenges to Music Sales
Digital piracy poses substantial challenges to music sales. The availability of pirated copies diminishes the demand for legally purchased music. Consumers tempted by free downloads may opt for illegal copies instead of purchasing albums or individual tracks. This reduces revenue for artists, labels, and music streaming services, impacting their ability to invest in new music creation and promotion.
Impact on Artists’ Earnings
Piracy directly impacts artists’ earnings by reducing the number of legal sales and streams. Artists depend on royalties and revenue generated from music sales and streaming to sustain their careers. Significant losses due to piracy mean less income for recording and production costs, music videos, and promotional activities. This ultimately affects their ability to create and release new music, further hindering their artistic growth.
Impact on Music Industry Revenue
The music industry suffers substantial revenue losses due to piracy. This impacts record labels, distributors, and music streaming services. Reduced revenue hampers their ability to invest in new talent, production, and marketing. Consequently, the entire music ecosystem is affected, potentially impacting jobs and hindering innovation.
Impact on Different Genres
The impact of piracy varies across different music genres. Genres with a larger fan base and greater accessibility online, like pop or hip-hop, often experience a higher degree of piracy. However, genres with a more niche audience, such as classical or jazz, are also not immune to piracy, although the scale of impact may be lower. The varying degrees of impact reflect the popularity and accessibility of specific genres.
Estimated Losses Due to Digital Piracy
| Genre | Estimated Loss (USD Millions) | Impact Description | Source/Note |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pop | 150-200 | High popularity and accessibility contribute to significant piracy. | Industry estimates |
| Hip-Hop | 120-150 | Large fan base and extensive online presence make it vulnerable. | Industry estimates |
| Rock | 80-100 | Significant fan base but less accessibility compared to pop and hip-hop. | Industry estimates |
| Classical | 20-30 | Niche audience, but online piracy still exists. | Industry estimates |
Streaming’s Role
Streaming services have dramatically reshaped the music industry, altering how artists release and distribute their work, and how listeners consume it. This shift has created both opportunities and challenges, significantly impacting music sales and the overall compensation models for artists. The rise of these platforms necessitates a nuanced understanding of their influence on the traditional music ecosystem, including the often-complex relationship between streaming and digital piracy.The advent of streaming services like Spotify, Apple Music, and Amazon Music has dramatically altered the music consumption landscape.
Listeners now have access to vast libraries of music on demand, fostering a shift away from physical albums and individual song downloads. This shift has profoundly impacted how artists are compensated and how the music industry operates as a whole. Understanding this impact is crucial to comprehending the evolving dynamics of the music industry.
Music sales are surprisingly robust, even with rampant digital piracy. It seems the enduring appeal of music, combined with the innovative use of technology like streaming services, is driving this trend. Perhaps this resilience can be mirrored in education, where handheld learning tools are becoming increasingly sophisticated, offering personalized learning experiences. Check out this insightful piece on education and technology the future of handheld learning for a deeper dive into how technology is shaping the future of learning.
This suggests that despite the ease of sharing digital content, the demand for quality, legal products remains high in the music industry.
Impact on Music Sales
Streaming platforms have demonstrably impacted music sales, but not necessarily in a straightforward manner. While the traditional model of album sales has diminished, streaming services have created new revenue streams for artists. The sheer volume of listeners exposed to music through streaming has increased the potential for discoverability and, consequently, increased sales of physical merchandise, merchandise in digital stores, and concert tickets.
These secondary revenue streams have become increasingly important for artists in the current environment.
Artist Compensation Models
Streaming services utilize various compensation models, significantly impacting how artists are paid. These models often involve a complex interplay of factors such as the number of streams, the popularity of the artist, and the specific platform’s policies.
- Variable Royalties: Many streaming services utilize variable royalty models. This means that artists’ earnings are dependent on the number of streams their music receives. The rate per stream varies considerably, with factors such as the artist’s popularity, the genre, and the platform itself playing a significant role in determining the rate. Higher popularity often translates to higher royalties, but the precise formula is typically not disclosed to maintain competitive positioning.
- Fixed-Rate Models: In some cases, particularly for emerging artists, fixed-rate models are used. This means that the artist receives a predetermined amount for each stream, which can be more predictable than variable royalty structures. However, these models often come with fewer financial incentives than variable models.
- Collective Licensing: Collective licensing is a common practice, where organizations such as PROs (Performing Rights Organizations) act as intermediaries between artists and streaming services. This model ensures fair compensation to songwriters, composers, and artists, distributing payments based on usage data. This mechanism ensures a wider distribution of income across creators involved in a particular song or album.
Relationship Between Streaming and Digital Piracy, Music sales strong despite digital piracy
Streaming services are not immune to the challenges posed by digital piracy. The availability of music on streaming platforms can paradoxically create a market where illegal downloads are easier to access. The ease of access to music on legal platforms, coupled with the persistent appeal of free downloads, contributes to the continued existence of digital piracy. However, streaming’s sheer size and user base can also serve as a deterrent to piracy, as a significant portion of music consumers opt for legal streaming services over illegal downloads.
Strategies to Combat Piracy
Streaming services employ various strategies to combat piracy. These strategies are often multifaceted and may include technical solutions, legal actions, and educational campaigns.
- Technical Measures: Implementing robust DRM (Digital Rights Management) and anti-piracy technologies can help to reduce the appeal of illegal downloads. These technologies aim to prevent unauthorized copying and distribution of music content.
- Legal Actions: Taking legal action against individuals and organizations engaged in piracy can be an effective deterrent. This often involves pursuing legal channels to hold infringers accountable.
- Educational Campaigns: Promoting awareness about the importance of copyright and the availability of legal streaming services can help to shift consumer behavior. Educational initiatives often target young people and individuals who are less aware of the consequences of copyright infringement.
Comparison of Artist Compensation Models
| Streaming Platform | Compensation Model | Royalty Structure | Artist Support Programs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spotify | Variable | Per stream, dependent on artist popularity | Artist development and promotion initiatives |
| Apple Music | Variable | Per stream, dependent on artist popularity | Music promotion tools and marketing assistance |
| Amazon Music | Variable | Per stream, dependent on artist popularity | Artist development resources and promotion opportunities |
| Tidal | Variable, with higher tier options | Per stream, with potential higher rates for premium users | Focus on high-quality audio and artist support |
Countermeasures Against Piracy
The music industry, while thriving in many areas, continues to grapple with the persistent challenge of digital piracy. While streaming services have undeniably revolutionized the landscape, illegal downloads and unauthorized sharing still represent a significant revenue loss for artists and labels. This necessitates a multifaceted approach to combat piracy, combining legal action with technological advancements.The fight against piracy isn’t simply about catching offenders; it’s about creating a system where the incentives for legal consumption outweigh those for illegal activity.
This requires a proactive and evolving strategy that adapts to the changing tactics of pirates and the ever-evolving digital landscape.
Music sales are surprisingly robust despite the prevalence of digital piracy. It seems the industry is finding new ways to thrive. This is further highlighted by Apple’s recent updates to the iMac and iPod, touting the continued success of iTunes, demonstrating a strong belief in the value of legally purchased music. apple updates imac and ipod touts itunes success.
Ultimately, the continued strength in music sales, even in the face of piracy, points to the enduring appeal of music and the power of legitimate platforms to thrive in a digital age.
Legal Measures to Combat Piracy
Copyright protection and enforcement are crucial elements in the fight against digital piracy. Robust copyright laws, coupled with aggressive enforcement, provide a legal framework for holding individuals and organizations accountable for infringing on artists’ rights. This involves pursuing legal action against those who facilitate or profit from piracy, from online platforms to individuals who download or share copyrighted material.
Technological Measures to Combat Piracy
Technological solutions play a vital role in preventing and deterring piracy. These methods focus on making it more difficult and less appealing for users to access pirated content. Digital rights management (DRM) technologies, watermarking, and content authentication are critical tools in this arsenal.
Effectiveness of Anti-Piracy Strategies
The effectiveness of different anti-piracy strategies varies significantly. Some strategies, like DRM, are relatively effective at preventing the initial distribution of pirated content, while others, such as copyright enforcement, focus on punishing the perpetrators after the fact. The success of any strategy often hinges on factors like the technological capabilities of the platforms and the level of cooperation from both industry stakeholders and legal authorities.
Examples of Successful Anti-Piracy Initiatives
Several notable initiatives have demonstrated the effectiveness of targeted strategies. For instance, the music industry’s proactive efforts to partner with ISPs to block access to pirate websites have significantly reduced the availability of illegal downloads. Further, the use of watermarking technology to identify pirated content has helped in tracking and prosecuting offenders.
Table of Legal and Technological Measures
| Category | Measure | Description | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|---|
| Legal Measures | Copyright Enforcement | Legal action against individuals and organizations facilitating or profiting from piracy. | Variable, depends on jurisdiction and enforcement capability. |
| International Cooperation | Collaboration between different countries to address cross-border piracy. | Often effective in reducing piracy in certain regions. | |
| Technological Measures | Digital Rights Management (DRM) | Technical measures to control access and distribution of copyrighted material. | Relatively effective in preventing initial distribution. |
| Watermarking | Embedding unique identifiers into digital content to identify pirated copies. | Helpful in tracking and prosecuting offenders. | |
| Content Authentication | Verifying the legitimacy of digital content to ensure authenticity. | Promising in the fight against counterfeiting and piracy. |
Consumer Behavior: Music Sales Strong Despite Digital Piracy
Music consumption is no longer a passive activity; it’s a dynamic reflection of evolving tastes and technological advancements. Understanding consumer behavior in the music industry is crucial for artists, labels, and streaming services to adapt and thrive. Consumers are increasingly empowered by choice and accessibility, demanding personalized experiences and value for their investment. This necessitates a deep dive into the factors shaping their purchasing decisions and the ever-shifting landscape of music consumption.
Factors Influencing Purchasing Decisions
Consumer decisions in the music industry are shaped by a complex interplay of factors. Price sensitivity, brand loyalty, perceived quality, and the availability of alternative options all play significant roles. Furthermore, social influences, such as recommendations from friends and family, and exposure to trending artists or genres, can significantly impact purchase decisions.
Music sales are surprisingly robust, even with rampant digital piracy. It seems the industry is finding new ways to adapt, perhaps mirroring the ongoing battle of wifi standards competing for market dominance, like the latest 6 and 7. This competition, much like the struggle against piracy, highlights how the industry needs to constantly innovate to stay ahead of the curve, ultimately ensuring music sales continue to thrive despite the challenges.
wifi standards compete for market dominance. Ultimately, the music industry’s resilience in the face of piracy speaks volumes about its adaptability and ability to innovate.
Changing Consumer Preferences for Music Consumption
Consumer preferences for music consumption are rapidly evolving. The rise of on-demand streaming services has altered how people discover, listen to, and engage with music. The convenience and affordability of streaming have redefined the value proposition for consumers, leading to a decline in physical media purchases. Simultaneously, the desire for curated playlists and personalized recommendations has become paramount.
Demographic Differences in Purchasing Habits
Different demographics exhibit distinct purchasing habits. Younger generations, often more comfortable with digital platforms, are more likely to embrace streaming services and digital downloads. Older generations, while increasingly adapting to new technologies, might retain preferences for physical formats or traditional radio listening.
Impact of Streaming Services on Consumer Behavior
Streaming services have fundamentally altered consumer behavior by offering a vast library of music at a low cost. This accessibility has fostered increased experimentation with different genres and artists, leading to broader musical tastes. The ability to discover new music through curated playlists and recommendations further enhances this experience. Furthermore, the ease of access to music has fostered a culture of on-demand listening, shifting consumer expectations around music availability and consumption.
Purchasing Habits by Age Group
Understanding how different age groups consume music is vital for targeted marketing strategies. The table below provides a general overview of purchasing habits and preferred music consumption methods across different age groups.
| Age Group | Preferred Consumption Method | Purchasing Habits | Impact of Streaming |
|---|---|---|---|
| 18-24 | Streaming Services (e.g., Spotify, Apple Music), Digital Downloads | Highly reliant on streaming services for convenience and cost-effectiveness. Often seek personalized recommendations and curated playlists. | Streaming has become the primary mode of consumption. Digital downloads remain a secondary source. |
| 25-34 | Streaming Services, Digital Downloads, Occasional Physical Purchases | A mix of streaming and digital downloads, but some may still retain interest in physical albums or singles. | Streaming has significantly impacted their listening habits. Physical purchases remain a niche interest. |
| 35-54 | Streaming Services, Radio, Physical Purchases (less frequent) | Transitioning to streaming services, but retain some loyalty to traditional radio or physical formats. May still purchase albums for nostalgic value. | Streaming adoption is growing, but physical formats remain relevant. |
| 55+ | Radio, Streaming Services (increasingly), Physical Purchases (occasional) | The most likely to use traditional radio and physical media. Streaming adoption is slower, but growing. | Streaming adoption is gradual but increasing among this demographic. |
The Future of Music Sales
The music industry, forever evolving, faces a fascinating future. While the current digital landscape shows robust sales, the underlying trends suggest a continued shift towards innovative consumption models. This shift will be significantly influenced by emerging technologies, AI’s growing role, and the necessity for artists to adapt to the dynamic environment. The path ahead is not just about selling music; it’s about creating engaging experiences and monetizing them in novel ways.
Projected Music Sales Trends
The future of music sales is a blend of established and emerging trends. Streaming will remain a dominant force, likely consolidating its position with further integration of features like personalized playlists and interactive experiences. The rise of subscription services, and potentially, tiered access levels based on features and content availability, will further shape the market. Downloadable albums and singles are unlikely to disappear entirely, but their market share will likely continue to diminish.
This is already evident in the gradual shift towards streaming as the primary mode of music consumption.
Impact of Emerging Technologies
Emerging technologies will fundamentally alter how music is consumed and experienced. Virtual and augmented reality (VR/AR) experiences will likely play an increasingly important role, allowing users to interact with music in immersive ways. For example, envision a concert experience where fans can be transported to a virtual venue, interact with the artist in real time, and even receive personalized concert merchandise delivered virtually.
Interactive music applications, incorporating AR elements into everyday life, can further personalize the listening experience.
Role of Artificial Intelligence
AI’s impact on the music industry is multifaceted. AI-powered tools are already assisting artists with music creation, from composing to mixing and mastering. Personalized recommendations, powered by AI, will further enhance user experience on streaming platforms. AI-generated music, while raising ethical concerns, might also open up new avenues for creativity and artist collaborations, allowing for the creation of unique sonic landscapes.
The music industry is moving towards an era where AI tools are used not just to enhance production but to generate new sounds and ideas.
Artist Adaptation
Artists must adapt to this evolving landscape to remain relevant. This includes diversifying revenue streams beyond traditional album sales and concert tickets. Creating engaging online content, establishing a strong social media presence, and building direct relationships with fans will become increasingly important. Artists who embrace new technologies and understand the importance of digital engagement will be best positioned for success.
This involves actively engaging with their fan base online, fostering a sense of community, and using emerging technologies to build a unique brand identity.
Music Industry in 2040 Scenario
| Feature | Description ||——————-|——————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————-|| Revenue Streams | Subscription services (tiered access) dominate, accounting for 60% of revenue.
Live, interactive VR/AR concerts, personalized merchandise sales, and licensing for AI-generated music represent substantial secondary revenue streams. || Piracy Rates | Significantly lower than current levels, due to sophisticated anti-piracy measures and the integration of DRM technologies into all music delivery channels. However, the prevalence of grey market sales through peer-to-peer platforms remains a concern.
|| Consumer Habits | Personalized, interactive music experiences are the norm. VR/AR concerts are common, with fan interaction and personalized experiences paramount. Direct artist engagement and community building are crucial for consumer loyalty. |
Conclusive Thoughts
In conclusion, the music industry’s resilience in the face of digital piracy is a testament to its adaptability. While piracy remains a challenge, the emergence of streaming services has presented a significant opportunity for growth and diversification. The future of music sales will likely continue to be shaped by evolving consumer preferences, technological advancements, and the ongoing battle against piracy.
Artists and industry players will need to adapt and innovate to navigate this dynamic environment successfully.