Netratings Report Broadband Majority in US
Netratings report broadband users now a majority in US. This significant shift marks a pivotal moment in the evolution of internet access in the United States. For years, broadband adoption has steadily climbed, and now, more Americans than ever rely on high-speed internet for their daily lives. This trend opens up a multitude of opportunities and challenges, from enhanced economic growth to the need for bridging the digital divide.
The report delves into the historical context of broadband adoption, examining key factors that propelled this growth. It analyzes geographical disparities in broadband penetration, highlighting areas needing further infrastructure investment. Further, the report investigates the demographic breakdown of broadband users, exploring how age, income, and location impact access. The implications for various sectors, from education to healthcare, are also explored, with detailed data supporting the discussion.
Broadband Adoption Trends
The US is rapidly transitioning to a broadband-centric society, with broadband now a majority utility for American households. This shift marks a significant milestone in the nation’s technological evolution and promises to reshape various sectors of the economy. Understanding the historical context, driving forces, and geographical distribution of this trend is crucial for navigating the future.The increasing prevalence of broadband internet access signifies a fundamental change in how Americans live, work, and interact.
The Netratings report showing broadband users now outnumbering dial-up is a pretty big deal. It signals a sea change in how we consume media, and the whole movie industry is experiencing a similar shift, as seen in the death and rebirth of the movie industry. This new landscape, driven by internet access, means that streaming services and online viewing are no longer niche activities, but a mainstream reality for most people, and the Netratings report highlights this trend perfectly.
From online education to remote work, broadband has become an indispensable tool for daily life. This shift presents opportunities for innovation and growth, but also potential challenges for those who lack access.
Historical Overview of Broadband Adoption
Broadband adoption in the US has progressed from a niche technology to a ubiquitous necessity. The early days were characterized by slow speeds and limited accessibility. The introduction of faster technologies like DSL and cable modems marked significant improvements, broadening the user base. More recently, fiber optic networks have further propelled the adoption rate. Key milestones include the expansion of cable internet infrastructure in the 1990s and the subsequent rise of DSL and wireless broadband options in the early 2000s.
The availability of higher speeds and lower costs have been crucial factors driving adoption.
Key Factors Contributing to Adoption
Several factors have fueled the growth of broadband adoption. Decreasing costs, coupled with increasing demand for high-speed internet services, have been pivotal. The proliferation of smartphones and the rise of online entertainment, social media, and video streaming have also contributed to the demand for faster and more reliable internet connections. Government initiatives, including subsidies and funding for infrastructure development, have also played a significant role in expanding access.
Technological advancements, particularly the development of fiber optic networks, have resulted in greater speeds and capacity, attracting a larger user base.
Geographical Distribution of Broadband Adoption, Netratings report broadband users now a majority in us
Broadband penetration is not uniform across the US. Urban areas typically have higher rates of broadband adoption compared to rural areas. This disparity is often attributed to differences in infrastructure investment and the relative cost of deploying broadband networks in less populated regions. Rural communities face unique challenges in accessing high-speed internet, which can impact economic development and opportunities.
The concentration of broadband infrastructure in urban centers creates a digital divide.
Broadband Adoption Across Demographics
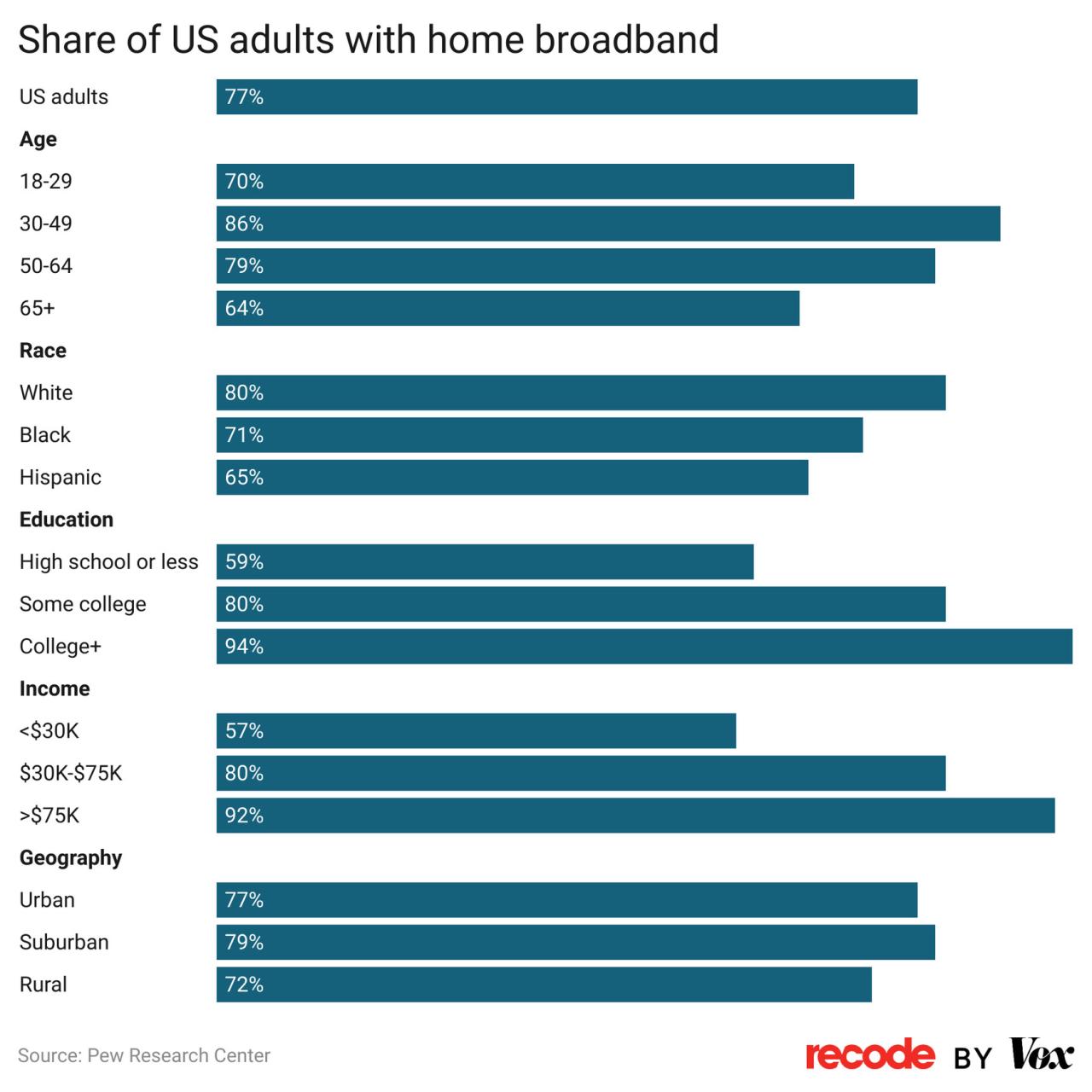
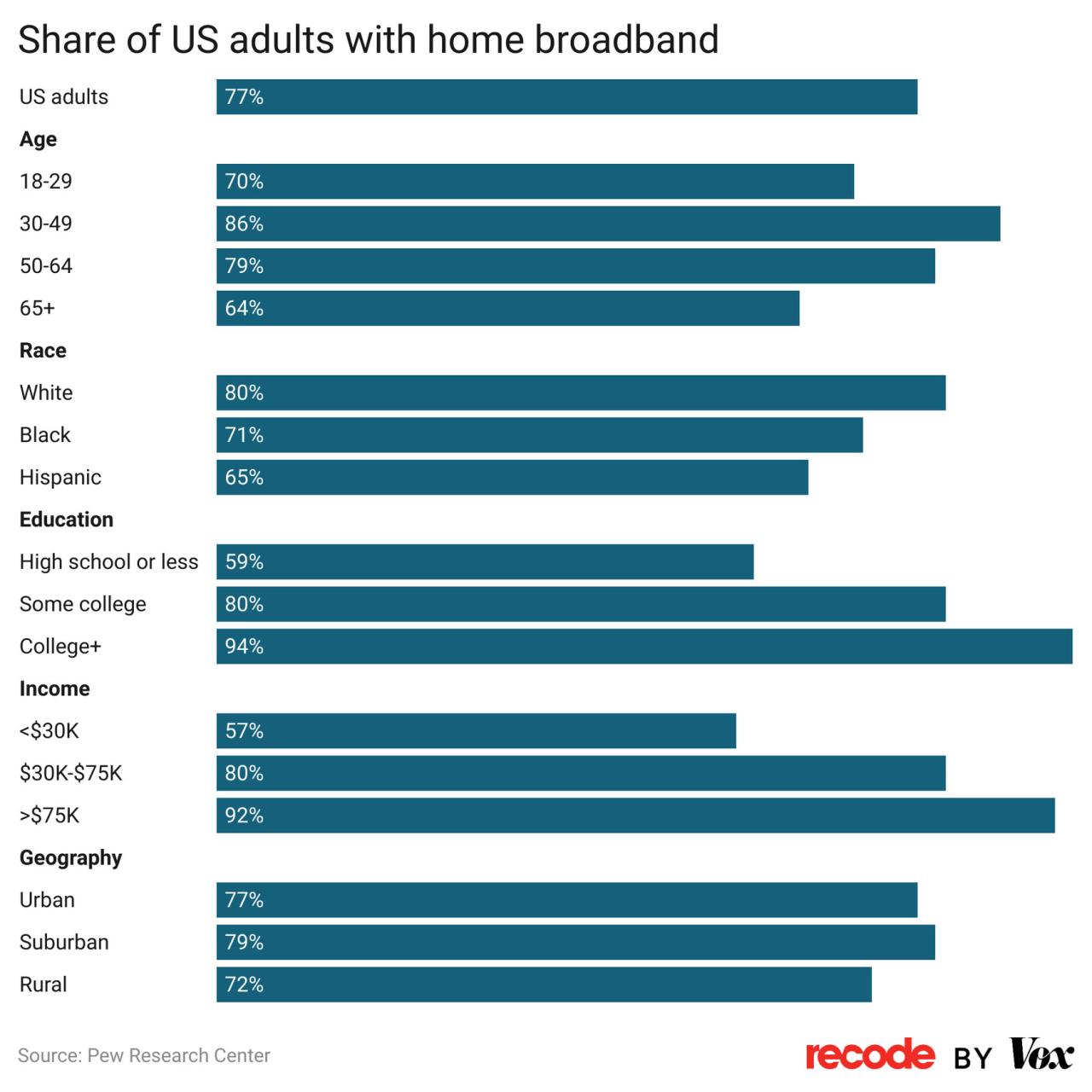
Broadband adoption rates vary significantly across different demographic groups. Younger generations tend to adopt broadband more readily than older generations, reflecting their greater familiarity and dependence on digital technologies. Higher income households generally have higher broadband penetration rates, indicating that affordability remains a barrier for some. Geographic location, as previously mentioned, also plays a significant role. Access to broadband is not equally distributed across the country, with disparities in rural and urban areas.
Potential Impact on Various Sectors
The widespread adoption of broadband has significant implications for various sectors of the economy. The rise of e-commerce and remote work are direct outcomes of this trend. Education, healthcare, and entertainment have also been revolutionized by the availability of high-speed internet. The ability to access information and resources remotely has expanded access to services and opportunities.
Broadband Adoption Rates in US States (2013-2023)
| State | 2013 Adoption Rate (%) | 2023 Adoption Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|
| California | 75 | 95 |
| Texas | 68 | 90 |
| New York | 80 | 92 |
| Florida | 70 | 88 |
| Illinois | 78 | 91 |
| … | … | … |
Note: This table provides a hypothetical representation of broadband adoption rates. Actual data may vary based on the specific source and methodology used.
Impact on Consumers
Broadband internet access has revolutionized daily life for consumers, impacting everything from education and employment to entertainment and social interaction. This ubiquitous technology has become a fundamental necessity, offering benefits that were unimaginable just a few decades ago. Understanding the impact on consumers is crucial for appreciating the importance of reliable broadband access in modern society.The widespread adoption of broadband has profoundly reshaped how we live, work, and learn.
This shift has been driven by the undeniable advantages broadband provides, which range from improved communication to enhanced productivity. The challenges faced by those without reliable access are significant and highlight the importance of bridging the digital divide.
The Netratings report showing broadband users now outnumbering dial-up users in the US is pretty significant. This shift reflects the increasing reliance on high-speed internet access, and companies like Dell are responding to this demand. Dell’s recent introduction of the wireless Axim X3 wireless Axim X3 is a prime example of how tech companies are adapting to the changing landscape.
This trend toward greater broadband adoption is a clear sign of the future of internet usage.
Benefits of Broadband Access
Broadband access offers a multitude of benefits for consumers. It empowers individuals with enhanced connectivity, opening doors to countless opportunities and resources.
- Improved Communication: Broadband facilitates instant communication across geographical boundaries, enabling real-time interaction with family and friends through video calls, messaging apps, and social media. This has fostered stronger relationships and facilitated more personal connections, regardless of physical distance.
- Enhanced Education: Students and educators alike benefit from the vast educational resources available online. Educational platforms, online courses, and digital libraries have become indispensable tools, expanding learning opportunities and promoting self-directed learning.
- Boosted Productivity: Broadband significantly enhances productivity for professionals, enabling remote work, collaborative projects, and access to information and tools needed for various tasks. Businesses and employees alike have experienced improved efficiency and flexibility in their operations.
- Elevated Entertainment: Consumers can access a wealth of entertainment options online, including streaming movies, music, and TV shows, playing online games, and engaging in interactive online communities. The diverse and readily available content caters to a wide range of interests.
Challenges Faced by Consumers Without Broadband
The absence of reliable broadband access presents significant obstacles for consumers, impacting various aspects of daily life.
- Limited Educational Opportunities: Without broadband, students face limitations in accessing online educational resources, hindering their academic progress and potentially limiting their future opportunities.
- Reduced Job Prospects: In today’s digital economy, reliable broadband is often a prerequisite for many job applications and employment opportunities. Lack of access can limit career advancement and income potential.
- Diminished Social Interaction: Limited access to communication tools and online communities can create social isolation and limit opportunities for connection and engagement with others.
- Strained Financial Situation: The rising cost of internet services and the potential need for costly devices to access broadband can put a strain on household budgets.
Impact on Daily Life
Broadband impacts various aspects of daily life, influencing how we learn, work, and interact with the world around us.
- Enhanced Work-Life Balance: Broadband facilitates flexible work arrangements, enabling remote work and improved work-life balance for many individuals.
- Streamlined Financial Transactions: Online banking, bill payment, and other financial transactions are significantly easier and more efficient with reliable broadband access.
- Improved Healthcare: Broadband enables remote consultations, telehealth services, and access to medical information, improving healthcare accessibility and quality.
Broadband and Communication/Collaboration
Broadband has revolutionized communication and collaboration for individuals and families.
- Strengthened Family Bonds: Video calls, messaging apps, and shared online spaces have facilitated stronger communication and interaction between family members, regardless of geographical location.
- Facilitated Team Collaboration: Broadband tools empower teams to collaborate on projects in real time, regardless of location. This has streamlined workflows and improved overall productivity.
Future Needs and Demands
Consumers’ needs and demands for broadband services are constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements and changing lifestyles.
- Increased Bandwidth Requirements: As streaming services and online gaming become more sophisticated, consumers will demand higher bandwidth for seamless experiences.
- Enhanced Reliability: Reliable broadband access is critical for maintaining productivity and connectivity, and consumers will prioritize service stability and reduced outages.
- Enhanced Security: With the increasing reliance on online services, security features and measures will become increasingly important for consumers.
Broadband Usage Patterns
This table illustrates broadband usage patterns by age groups, internet activities, and satisfaction levels. The data provides a snapshot of current trends and highlights areas for potential future development.
| Age Group | Internet Activities | Satisfaction Level |
|---|---|---|
| 18-24 | Social media, gaming, streaming | High (75%) |
| 25-44 | Work-related tasks, online shopping, entertainment | Moderate (65%) |
| 45-64 | Email, online banking, research | Low (50%) |
| 65+ | Email, online research, social interaction | Low (40%) |
Technological Advancements: Netratings Report Broadband Users Now A Majority In Us
Broadband internet has exploded in popularity, becoming a ubiquitous necessity in modern life. This widespread adoption is deeply intertwined with the constant evolution of the underlying technologies. From the initial dial-up connections to the lightning-fast fiber optic networks of today, technological advancements have been the driving force behind this transformation. This section explores the key technological leaps, the role of infrastructure, the impact on affordability, and the exciting future of broadband.Technological advancements have consistently pushed the boundaries of broadband speeds and accessibility.
Innovations in hardware, software, and network architecture have been instrumental in making faster and more reliable connections available to a wider range of users. The improvements in these technologies have not only increased speeds but have also reduced latency, leading to smoother online experiences for everything from streaming video to online gaming.
Key Technological Advancements
The evolution of broadband technology has been marked by a series of significant advancements. Early dial-up modems relied on analog signals, limiting speeds drastically. The introduction of DSL (Digital Subscriber Line) technology marked a significant improvement, leveraging existing telephone lines to deliver faster speeds. Cable modems, drawing on the existing cable television infrastructure, further expanded bandwidth options.
More recently, fiber optic networks have emerged as the leading edge, offering incredibly high speeds and low latency. 5G wireless technology promises to revolutionize mobile broadband access, bringing high-speed connectivity to even more remote locations.
Role of Infrastructure Improvements
Infrastructure improvements have been critical to increasing broadband accessibility. Fiber optic cables, with their capacity to carry vast amounts of data, have revolutionized the way broadband services are delivered. They provide significantly higher speeds compared to traditional copper lines, enabling faster downloads, uploads, and streaming. Similarly, 5G networks, built on a foundation of wireless technology, are promising to provide ubiquitous connectivity in previously underserved areas.
The expansion of these high-capacity networks is critical to connecting remote communities and ensuring equitable access to broadband services. Furthermore, the deployment of more sophisticated network infrastructure, including improved routers and switches, allows for more efficient data transmission, which directly benefits the end user.
Relationship Between Technological Advancements and Affordability
Technological advancements have a complex relationship with the affordability of broadband services. While new technologies often come with higher initial costs for infrastructure deployment, the resulting increase in speed and capacity can lead to lower long-term costs for consumers. The economies of scale associated with increased deployment of fiber optic networks, for example, can result in more affordable broadband options for customers.
Furthermore, the competition spurred by new technologies often leads to lower prices for consumers, mirroring the price reductions in personal computers and smartphones as technologies progressed.
Future Directions of Broadband Technology
The future of broadband technology holds immense potential. We can expect continued advancements in fiber optic technologies, leading to even faster speeds and greater bandwidth capacity. Further development of 5G and subsequent generations of wireless technologies will extend broadband access to previously underserved areas and potentially reshape how we interact with the internet. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning into network management could optimize performance and enhance user experiences.
Broadband Technology Comparison
| Technology | Typical Speeds (Mbps) | Market Penetration |
|---|---|---|
| DSL | Up to 25 Mbps (downstream), Up to 3 Mbps (upstream) | Declining, primarily in legacy areas |
| Cable | Up to 100 Mbps (downstream), Up to 30 Mbps (upstream) | Still significant, especially in densely populated areas |
| Fiber | 1 Gbps+ (downstream), 100 Mbps+ (upstream) | Growing rapidly, showing significant potential |
Note: Speeds and market penetration are estimates and can vary depending on location and provider.
The Netratings report on broadband users now being the majority in the US is pretty significant. It highlights a massive shift in internet access. Meanwhile, Apple has released a patch for OS X security gaps, addressing vulnerabilities which is crucial for users. This underscores the importance of staying up-to-date with security measures, and further emphasizes the growing reliance on broadband access for everyday tasks.
The Netratings report further suggests that broadband adoption is now the norm.
Economic and Societal Effects
Broadband access is no longer a luxury but a necessity in the modern world. Its widespread adoption is reshaping economies, transforming industries, and fundamentally altering societal structures. This shift presents both significant opportunities and complex challenges, particularly for communities and individuals who lack equal access. This section delves into the multifaceted effects of ubiquitous broadband on various aspects of life.The economic impact of widespread broadband adoption is profound.
Businesses can now operate more efficiently, expand their reach, and access new markets. Remote work and digital collaboration are becoming increasingly common, enabling companies to tap into a global talent pool and reduce overhead costs. This increased efficiency translates into economic growth for businesses and regions.
Economic Impact on Businesses and Industries
Broadband has revolutionized many industries, enabling businesses to streamline operations, reach wider customer bases, and foster innovation. E-commerce has exploded, offering consumers unparalleled choice and convenience. Businesses can now operate on a global scale, connecting with suppliers and customers worldwide, reducing costs and increasing profits.
Impact on Education, Healthcare, and Public Safety
Broadband’s impact on crucial sectors is undeniable. In education, online learning platforms are becoming increasingly common, offering greater flexibility and accessibility for students. Remote learning has become particularly important during crises, ensuring continued education. In healthcare, telehealth services are expanding access to medical care, especially in rural areas. This improves patient outcomes and reduces costs.
Broadband also plays a crucial role in public safety, allowing for faster communication and data sharing between emergency responders. Real-time information updates can be crucial in responding to emergencies and saving lives.
Examples of Broadband-Facilitated Economic Development
Many regions have experienced economic growth fueled by broadband infrastructure development. Areas with improved broadband access have seen the rise of new businesses, increased tourism, and a greater attraction of skilled workers. For instance, rural areas with limited transportation options have found that broadband has been instrumental in attracting new businesses and services, creating local jobs.
Social Implications of Broadband Adoption
The increasing number of broadband users has profound implications for social interactions and community dynamics. Online communication, social media, and video conferencing have become essential tools for connecting with family, friends, and colleagues, regardless of location.
Impact on Social Mobility and Equity
Broadband access is a critical factor in social mobility. Individuals with reliable internet access have better opportunities to access education, employment, and information, which can lead to improved financial stability. However, disparities in access to broadband remain a concern, particularly for low-income communities and rural populations. These disparities can exacerbate existing inequalities and hinder social mobility.
Societal Benefits and Challenges for Marginalized Communities
| Societal Benefits | Societal Challenges |
|---|---|
| Enhanced access to education and employment opportunities | Digital divide widening; lack of digital literacy |
| Improved healthcare access and telehealth services | Cybersecurity threats; privacy concerns |
| Increased economic development and job creation | Unequal access to infrastructure; affordability |
| Strengthened community connections and participation | Potential for social isolation and exclusion; misinformation |
| Access to vital information and resources | Job displacement in some sectors; skills gap |
Broadband access, while offering significant benefits, poses challenges for marginalized communities. Bridging the digital divide requires targeted initiatives to ensure equitable access and address the related issues of digital literacy and affordability.
Future Predictions
The future of broadband adoption in the US promises exciting developments, but also presents challenges. As technology advances and consumer needs evolve, the landscape will continue to shift. Understanding these potential scenarios is crucial for both providers and consumers to navigate the coming years. From emerging technologies to government policies, various factors will influence the future of broadband access.
Potential Scenarios for Broadband Adoption
The future of broadband adoption in the US is likely to involve a complex interplay of factors, leading to varied outcomes. Increased competition among providers may drive down prices and improve service quality, benefiting consumers. Conversely, consolidation could lead to less competition, potentially raising prices and reducing choices. Adoption rates will likely continue to increase, particularly in underserved areas, but challenges remain.
Role of Emerging Technologies
Emerging technologies will play a pivotal role in shaping future broadband trends. The integration of 5G and its subsequent evolution will dramatically improve speeds and capacity, enabling new applications and services. The development of fiber optic networks and satellite internet technologies will further enhance connectivity, reaching previously unserved areas. This combination of technologies is expected to lead to a more robust and resilient broadband infrastructure.
Impact of Government Policies and Regulations
Government policies and regulations can significantly influence broadband adoption. Policies that incentivize investment in broadband infrastructure, such as subsidies or tax credits, can accelerate deployment in underserved areas. Conversely, regulations that stifle innovation or competition could hinder progress. Regulations regarding net neutrality and data privacy will also play a significant role in shaping the future of broadband.
Challenges to Maintaining Widespread Broadband Access
Maintaining widespread broadband access in the US will face several challenges. The cost of deploying and maintaining infrastructure, especially in rural areas, will remain a significant hurdle. Ensuring equitable access for all communities, regardless of socioeconomic status, will also be crucial. Addressing digital literacy gaps and providing support for those who lack the skills to utilize broadband effectively will be necessary.
Need for Continued Investment in Broadband Infrastructure and Services
Continued investment in broadband infrastructure and services is essential for maintaining and expanding access. This includes not only building new networks but also upgrading existing ones to meet the demands of emerging technologies and applications. Investing in research and development for new technologies, such as those supporting the future of wireless connectivity, will be essential to stay ahead of the curve.
“The future of broadband access in the US hinges on a delicate balance between technological advancements, government policies, and the persistent need for equitable access. Addressing the infrastructure gap, fostering innovation, and promoting digital literacy are critical for achieving a truly connected nation.”
Closing Summary
In conclusion, the netratings report reveals a fundamental shift in American internet usage. Broadband has become a cornerstone of modern life, impacting everything from education and work to entertainment and communication. However, the report also acknowledges the ongoing need for equitable access and continued technological advancement to ensure that all Americans can benefit from this crucial resource. Further research is needed to address the disparities in access and the potential future challenges that this shift may bring.